MICROSCOPY AND CELLS BIO 171 WEEK 3
|
|
|
- Candice Stokes
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MICROSCOPY AND CELLS BIO 171 WEEK 3
2 MICROSCOPY THE COMPOUND LIGHT MICROSCOPE System of lenses arranged to produce an enlarged, focusable image of a specimen.
3 MICROSCOPY THE MICROSCOPE Illuminating System Light source Condenser lens Condenser lens Light source
4 MICROSCOPY THE MICROSCOPE Ocular lenses Imaging System Objective lenses Ocular lenses Body tube Objective lens Body tube
5 MICROSCOPY THE MICROSCOPE Other parts Stage Stage clips Arm Base Course adjustment knob Fine adjustment knob Arm Stage Base
6 Course Adjustment Knob Stage Fine Adjustment Knob
7 MICROSCOPY RULES AND USE Always carry upright with one hand under the base and the other around the arm. Only clean lenses with lens paper Always start on low-power objective. If shifting to a higher power objective, rotate carefully. Always use fine adjustment knob when using a higher power objective
8 USING A COMPOUND LIGHT MICROSCOPE 1) Ensure that lowest-power objective is in place. 2) Place specimen on the stage. 3) Adjust slide so that the area of interest is in view. 4) Use the course adjustment knob to focus on the specimen. 5) Slowly rotate the high-power objective into place, making sure that the lens does not touch the slide. 6) Use the FINE ADJUSTMENT KNOB ONLY to further refine your focus.
9 ACTIVITIES - MICROSCOPY 3.1 Using a compound microscope 3.2 Magnification 3.3 Field of view 3.4 Depth of field 3.5 Preparing a Wet Mount
10 CELL THEORY All living organisms are composed of cells The cell is the basic unit of life Cells arise from pre-existing cells Cells contain hereditary information which is passed from cell to cell during cell division Scientific Theory: Explanation of some aspect of the natural world that has been substantiated through repeated experiments or testing. Examples: Atomic theory, Germ theory, Theory of Evolution, Theory of Homeostasis, Theory of Gravity, Theory of Molecular Bonds
11 INTRO CYTOLOGY REVIEW Prokaryotes
12 INTRO CYTOLOGY REVIEW PROKARYOTES Prokaryote = before nucleus No nucleus or membrane-bound organelles Regions of concentrated DNA Nucleoid Ribosomes particles involved in protein synthesis Flagella used for movement Pili attach to surfaces or exchange genetic material
13 ENDOSYMBIOTIC THEORY Prokaryotic organism is engulfed or parasitizes early eukaryote Mitochondria consume oxygen to extract energy (ATP) from glucose, produce carbon dioxide and water. Chloroplasts consume water and carbon dioxide; capture energy from light, transforms light energy into chemical energy (glucose) and releases oxygen. Both mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA.
14 INTRO CYTOLOGY REVIEW EUKARYOTES See Table 4.1 for differences between cell types
15 PLANT CELLS Elodea slide Onion
16 ACTIVITIES Chapter 3 - Microscopy 3.1 Using a compound microscope 3.2 Determining magnification 3.3 Alternate Procedure Field of view 3.4 Determine depth of field 3.5 Prepare wet mount of pond water 3.6 Look through dissecting scope Chapter 4 The Cell 4.1 Cyanobacteria (Merismopedia, Nostoc, and Oscillatoria) 4.2 Yogurt 4.3 Elodea Prepared slides 4.5 Stained Onion Cells Stain with Iodine (IKI) 4.7 Examine amyloplasts (in potato) 4.9 Examine amoeba 4.10 Examine Paramecium 4.11 Examine Spirogyra 4.12 Examine Unknown/Pond Water
17 CYANOBACTERIA Sometimes called blue-green algae Large prokaryotes with chlorophyll and other pigments for photosynthesis Surrounded by mucilaginous sheath Contributed to early oxygenation of ancient earth s atmosphere
18 BACTERIA Yogurt Lactobacillus Gram positive bacteria Converts lactose into lactic acid (milk yogurt) How does the size of Lactobacillus compare to the Cyanobacteria?
19 ELODEA Look for chloroplasts, nucleus, cell wall, central vacuole.
20 ONION CELLS Stain with IKI (Iodine) Compare stained VS unstained onion cells
21 AMYLOPLASTS Plastids that store starch Stain potato with iodine
22 SPIROGYRA Filamentous green alga Named for spiral arrangement of chloroplasts.
23 ACTIVITIES Chapter 3 - Microscopy 3.1 Using a compound microscope 3.2 Determining magnification 3.3 Alternate Procedure Field of view 3.4 Determine depth of field 3.5 Prepare wet mount of pond water 3.6 Look through dissecting scope Chapter 4 The Cell 4.1 Cyanobacteria (Merismopedia, Nostoc, and Oscillatoria) 4.2 Yogurt 4.3 Elodea Prepared slides 4.5 Stained Onion Cells Stain with Iodine (IKI) 4.7 Examine amyloplasts (in potato) 4.9 Examine amoeba (prepared slide) 4.10 Examine Paramecium (prepared slide) 4.11 Examine Spirogyra 4.12 Examine Unknown/Pond Water Answer questions in lab manual Dispose of pipettes in BIOWASTE Dispose of used slides in can on desk
Microscope History Robert Hooke
 1 Microscope History Robert Hooke First described cells in 1665. He viewed thin slices of cork and compared the boxy partitions he observed to the cells (small rooms) in a monastery. (1635 1702) 2 Microscope
1 Microscope History Robert Hooke First described cells in 1665. He viewed thin slices of cork and compared the boxy partitions he observed to the cells (small rooms) in a monastery. (1635 1702) 2 Microscope
CELL LAB OBJECTIVES INTRODUCTION: CELL UNIT. After completing this lab you should be able to:
 AP BIOLOGY CELL UNIT ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR CELL LAB OBJECTIVES After completing this lab you should be able to: 1. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, 2. Prepare wet mount slides
AP BIOLOGY CELL UNIT ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR CELL LAB OBJECTIVES After completing this lab you should be able to: 1. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, 2. Prepare wet mount slides
Chapter 7 Cell Structure
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure Mr. C. Biology 1 07 Cell Structure Chapter 7 Cell Structure All living things are made of cells. Cells are made up of 3 main parts, Cell Membrane A skin that controls what enters
Chapter 7 Cell Structure Mr. C. Biology 1 07 Cell Structure Chapter 7 Cell Structure All living things are made of cells. Cells are made up of 3 main parts, Cell Membrane A skin that controls what enters
DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST Topic 3- Cells and Transport
 Topic 3- Cells and Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma membranes D) All cells can
Topic 3- Cells and Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma membranes D) All cells can
Animal Cell Organelles. Plant Cell. Organelle. Cell Wall. Chloroplasts. Vacuole
 Cell Biology Higher Electron vs Light Microscope Light use light and lenses to magnify specimen Electron use a beam of electrons to form an image Electron higher magnification and higher resolution Electron
Cell Biology Higher Electron vs Light Microscope Light use light and lenses to magnify specimen Electron use a beam of electrons to form an image Electron higher magnification and higher resolution Electron
Foundation Cell Biology
 Foundation Cell Biology Electron vs Light Microscope Light use light and lenses to magnify specimen Electron use a beam of electrons to form an image Electron higher magnification and higher resolution
Foundation Cell Biology Electron vs Light Microscope Light use light and lenses to magnify specimen Electron use a beam of electrons to form an image Electron higher magnification and higher resolution
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Lab Activity
 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Lab Activity Name: Blk: INTRODUCTION Prokaryotic Cells Cells (the smallest individual units of life) are divided into two basic categories: prokaryotic cells, and eukaryotic
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Lab Activity Name: Blk: INTRODUCTION Prokaryotic Cells Cells (the smallest individual units of life) are divided into two basic categories: prokaryotic cells, and eukaryotic
Organelles & Cells Student Edition. A. chromosome B. gene C. mitochondrion D. vacuole
 Name: Date: 1. Which structure is outside the nucleus of a cell and contains DNA? A. chromosome B. gene C. mitochondrion D. vacuole 2. A potato core was placed in a beaker of water as shown in the figure
Name: Date: 1. Which structure is outside the nucleus of a cell and contains DNA? A. chromosome B. gene C. mitochondrion D. vacuole 2. A potato core was placed in a beaker of water as shown in the figure
Page 1. Name: UNIT: PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND RESPIRATION TOPIC: PHOTOSYNTHESIS
 Name: 4667-1 - Page 1 UNIT: PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND RESPIRATION TOPIC: PHOTOSYNTHESIS 1) The diagram below illustrates the movement of materials involved in a process that is vital for the energy needs of organisms.
Name: 4667-1 - Page 1 UNIT: PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND RESPIRATION TOPIC: PHOTOSYNTHESIS 1) The diagram below illustrates the movement of materials involved in a process that is vital for the energy needs of organisms.
Bio10 Practice Lab Exam 1
 Bio10 Practice Lab Exam 1 Instructions: Answer the following questions using the concepts pertaining to laboratory exercises. This information is in your textbook, lab manual, or instructor provided handouts.
Bio10 Practice Lab Exam 1 Instructions: Answer the following questions using the concepts pertaining to laboratory exercises. This information is in your textbook, lab manual, or instructor provided handouts.
Lab 1: Using the Microscope & Cell Biology
 Name Lab 1: Using the Microscope & Cell Biology The anatomy of the compound microscope Review or learn the following parts of the compound microscope and their functions. Eyepieces Objectives Arm Stage
Name Lab 1: Using the Microscope & Cell Biology The anatomy of the compound microscope Review or learn the following parts of the compound microscope and their functions. Eyepieces Objectives Arm Stage
Structure and Function of Plant and Animal Cells
 Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 8 Structure and Function of Plant and Animal Cells WORKBOOK Name: 8.1 A Closer Look pp. 158-164 Read pp. 158-159 Before the invention of microscope technology,
Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 8 Structure and Function of Plant and Animal Cells WORKBOOK Name: 8.1 A Closer Look pp. 158-164 Read pp. 158-159 Before the invention of microscope technology,
CHAPTER 7.1 OUTLINE SHEET
 CHAPTER 7.1 OUTLINE SHEET A. Development of Cell Theory 1. Identifying Cells a. Anton van Leeuwenhoek b. Robert Hooke 2. Development of Cell Theory a. Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow 1. Schleiden 2. Schwann
CHAPTER 7.1 OUTLINE SHEET A. Development of Cell Theory 1. Identifying Cells a. Anton van Leeuwenhoek b. Robert Hooke 2. Development of Cell Theory a. Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow 1. Schleiden 2. Schwann
The diagram below represents levels of organization within a cell of a multicellular organism.
 STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
Unit 1 Cell Biology Topic 1: Cell Structure
 Unit 1 Cell Biology Topic 1: Cell Structure Lesson 1.1.1 I will know I am successful if I can: 1. Label all parts of plant and animal cells and state their functions 2. State the differences between plant
Unit 1 Cell Biology Topic 1: Cell Structure Lesson 1.1.1 I will know I am successful if I can: 1. Label all parts of plant and animal cells and state their functions 2. State the differences between plant
Cell Review. 1. The diagram below represents levels of organization in living things.
 Cell Review 1. The diagram below represents levels of organization in living things. Which term would best represent X? 1) human 2) tissue 3) stomach 4) chloroplast 2. Which statement is not a part of
Cell Review 1. The diagram below represents levels of organization in living things. Which term would best represent X? 1) human 2) tissue 3) stomach 4) chloroplast 2. Which statement is not a part of
Vocab Check. How many words were familiar to you? Botany Pre-Test
 Vocab Check How many words were familiar to you? Botany Pre-Test Homework Chapter 4 Section 1 in textbook Read and complete questions on socrative.com same room number/set up PELOQUINSCIENCE Learning Targets
Vocab Check How many words were familiar to you? Botany Pre-Test Homework Chapter 4 Section 1 in textbook Read and complete questions on socrative.com same room number/set up PELOQUINSCIENCE Learning Targets
Introduction to Cells. Intro to Cells. Scientists who contributed to cell theory. Cell Theory. There are 2 types of cells: All Cells:
 Intro to Cells Key Concept: Cells are the basic unit of life. Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: 1 Animal Cell
Intro to Cells Key Concept: Cells are the basic unit of life. Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: 1 Animal Cell
Microscopy and the Diversity of Microorganisms
 Microscopy and the Diversity of Microorganisms Today we will learn how to use one of the most important tools a biologist has, the microscope. We will use the microscope to study organisms throughout the
Microscopy and the Diversity of Microorganisms Today we will learn how to use one of the most important tools a biologist has, the microscope. We will use the microscope to study organisms throughout the
Cells Cytology = the study of cells. Nonliving Levels. Organization Levels of Life. Living Levels 11/14/13. More Living Levels
 Cells Cytology = the study of cells What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5. ORGANIZED 6. RESPOND to environment
Cells Cytology = the study of cells What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5. ORGANIZED 6. RESPOND to environment
INTRODUCTION prokaryotic eukaryotic pigments
 INTRODUCTION This exercise is intended for you to get familiar and comfortable with using a microscope as well as identifying common microbial groups. Thus, we will observe representatives of all microbes
INTRODUCTION This exercise is intended for you to get familiar and comfortable with using a microscope as well as identifying common microbial groups. Thus, we will observe representatives of all microbes
Topic 3: Cells Ch. 6. Microscopes pp Microscopes. Microscopes. Microscopes. Microscopes
 Topic 3: Cells Ch. 6 -All life is composed of cells and all cells have a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA. pp.105-107 - The development of the microscope was the key to understanding that all living
Topic 3: Cells Ch. 6 -All life is composed of cells and all cells have a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA. pp.105-107 - The development of the microscope was the key to understanding that all living
Biology Homework Chapter 5: The Cell Pages Answer the questions with complete thoughts!
 Name Biology Homework Chapter 5: The Cell Pages 115-133 Answer the questions with complete thoughts! Per. * Sections 5.1 through 5.3: Cells Are the Units of Life: Read pages 115 to 122 PART A: Define the
Name Biology Homework Chapter 5: The Cell Pages 115-133 Answer the questions with complete thoughts! Per. * Sections 5.1 through 5.3: Cells Are the Units of Life: Read pages 115 to 122 PART A: Define the
CELL PRACTICE TEST
 Name: Date: 1. As a human red blood cell matures, it loses its nucleus. As a result of this loss, a mature red blood cell lacks the ability to (1) take in material from the blood (2) release hormones to
Name: Date: 1. As a human red blood cell matures, it loses its nucleus. As a result of this loss, a mature red blood cell lacks the ability to (1) take in material from the blood (2) release hormones to
Chapter 10 The cell is the basic unit of life.
 Chapter 10 The cell is the basic unit of life. Using a Microscope - Worksheet (diagram and functions of a microscope) - Lab (p. 394-395) What you are viewing under a microscope (P.393) - Magnified image
Chapter 10 The cell is the basic unit of life. Using a Microscope - Worksheet (diagram and functions of a microscope) - Lab (p. 394-395) What you are viewing under a microscope (P.393) - Magnified image
13. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 Name 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and
Name 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and
Biology Lab Practical Review Biology 1110 Instructor: Kate Blinka
 Biology Lab Practical Review Biology 1110 Instructor: Kate Blinka 1. Know and be able to label the parts of a microscope. Including: Eyepiece, arm, base, optical lens, stage, iris diaphram, coarse focus,
Biology Lab Practical Review Biology 1110 Instructor: Kate Blinka 1. Know and be able to label the parts of a microscope. Including: Eyepiece, arm, base, optical lens, stage, iris diaphram, coarse focus,
3.2 Cell Organelles. KEY CONCEPT Eukaryotic cells share many similarities.
 KEY CONCEPT Eukaryotic cells share many similarities. ! Cells have an internal structure. ! Cells have an internal structure. The cytoskeleton has many functions. ! Cells have an internal structure. The
KEY CONCEPT Eukaryotic cells share many similarities. ! Cells have an internal structure. ! Cells have an internal structure. The cytoskeleton has many functions. ! Cells have an internal structure. The
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 1 2 Number
Basic Structure of a Cell Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 1 2 Number
Biology. Introduction to Cells. Sunday, November 8, 15
 Biology Introduction to Cells Cell Theory Biology is the study of life. Ideas about cells are built on the cell theory which states: 1. All living things are made of cells and their products. 2. The cell
Biology Introduction to Cells Cell Theory Biology is the study of life. Ideas about cells are built on the cell theory which states: 1. All living things are made of cells and their products. 2. The cell
Cells. A. The iodine diffused into the bag. B. The starch was changed to sugar.
 Name: Date: 1. A student filled a bag of dialysis tubing with a milky-white starch solution and placed the bag in a beaker of iodine-water as shown in the diagram. An hour later, the student observed that
Name: Date: 1. A student filled a bag of dialysis tubing with a milky-white starch solution and placed the bag in a beaker of iodine-water as shown in the diagram. An hour later, the student observed that
Student Exploration: Cell Types
 3. Name: Date: Student Exploration: Cell Types Vocabulary: ATP, bacteria, carbon dioxide (CO 2), cell, cellular respiration, compound light microscope, eukaryote, multicellular, muscle cell, neuron, organelle,
3. Name: Date: Student Exploration: Cell Types Vocabulary: ATP, bacteria, carbon dioxide (CO 2), cell, cellular respiration, compound light microscope, eukaryote, multicellular, muscle cell, neuron, organelle,
Cell organelles. Cell Wall
 Cell organelles Cell Wall Plant cells have an outermost structure called a cell wall. A cell wall is a rigid structure that gives support to a cell. Plants and algae have cell walls made of a complex sugar.
Cell organelles Cell Wall Plant cells have an outermost structure called a cell wall. A cell wall is a rigid structure that gives support to a cell. Plants and algae have cell walls made of a complex sugar.
Cells and Microscopes Biology Concepts of Biology 2.1
 Cells and Microscopes Biology 100 - Concepts of Biology 2.1 Name Instructor Lab Section Objectives: To gain an understanding of how to: Correctly use the compound light microscope Differentiate between
Cells and Microscopes Biology 100 - Concepts of Biology 2.1 Name Instructor Lab Section Objectives: To gain an understanding of how to: Correctly use the compound light microscope Differentiate between
Complete the table by stating the function associated with each organelle. contains the genetic material.... lysosome ribosome... Table 6.
 1 (a) Table 6.1 gives the functions of certain organelles in a eukaryotic cell. Complete the table by stating the function associated with each organelle. The first row has been completed for you. Organelle
1 (a) Table 6.1 gives the functions of certain organelles in a eukaryotic cell. Complete the table by stating the function associated with each organelle. The first row has been completed for you. Organelle
Student Exploration: Cell Types
 Name: Period: Student Exploration: Cell Types Vocabulary: ATP, bacteria, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), cell, cellular respiration, compound light microscope, eukaryote, multicellular, muscle cell, neuron, organelle,
Name: Period: Student Exploration: Cell Types Vocabulary: ATP, bacteria, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), cell, cellular respiration, compound light microscope, eukaryote, multicellular, muscle cell, neuron, organelle,
Investigating Cells Lab. 1. What major differences do you expect to see between bacterial cells and plant/animal
 Investigating Cells Lab Name 7 th Grade PSI Questions: o How do you use a microscope? o What do bacterial cells look like? o Are there any visible differences between plant cells and animal cells? o What
Investigating Cells Lab Name 7 th Grade PSI Questions: o How do you use a microscope? o What do bacterial cells look like? o Are there any visible differences between plant cells and animal cells? o What
2nd Quarter Lab Assessment Review Packet
 Name Date Period Labs to be Assessed: 2nd Quarter Lab Assessment Review Packet Lab #8 - Using Measuring Tools Lab #9 - Introduction to the Compound Microscope Lab #10 - Using The Compound Microscope Lab
Name Date Period Labs to be Assessed: 2nd Quarter Lab Assessment Review Packet Lab #8 - Using Measuring Tools Lab #9 - Introduction to the Compound Microscope Lab #10 - Using The Compound Microscope Lab
7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
 1 of 49 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic
1 of 49 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic
LAB EXERCISE: Microscopy and the Cell
 LAB EXERCISE: Microscopy and the Cell Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab topic, you should be able to: 1. Identify the parts of compound and stereoscopic microscopes and be proficient in their
LAB EXERCISE: Microscopy and the Cell Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab topic, you should be able to: 1. Identify the parts of compound and stereoscopic microscopes and be proficient in their
The Basic Unit of Life Lab (Adapted from lab of same name) State Standard
 NAME: DATE: PERIOD: The Basic Unit of Life Lab (Adapted from lab of same name) State Standard 12.11.04 In this investigation, you will review the history of the microscope, practice the techniques for
NAME: DATE: PERIOD: The Basic Unit of Life Lab (Adapted from lab of same name) State Standard 12.11.04 In this investigation, you will review the history of the microscope, practice the techniques for
Explain your answer:
 Biology Midterm Exam Review Introduction to Biology and the Scientific Method Name: Date: Hour: 1. Biology is the study of: 2. A living thing is called a(n): 3. All organisms are composed of: 4. The smallest
Biology Midterm Exam Review Introduction to Biology and the Scientific Method Name: Date: Hour: 1. Biology is the study of: 2. A living thing is called a(n): 3. All organisms are composed of: 4. The smallest
Microscopes. October 28, 2014
 Microscopes Magnification Power You multiply the ocular lens magnification by the magnification of the objective lens you are using. Ocular lens is 10X Low Power is 4X Total magnification 10 X 4 = 40X
Microscopes Magnification Power You multiply the ocular lens magnification by the magnification of the objective lens you are using. Ocular lens is 10X Low Power is 4X Total magnification 10 X 4 = 40X
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell What jobs do cells have to do for an organism to live Gas exchange CO 2 & O 2 Eat (take in & digest food) Make energy ATP Build
Cell Structure and Function Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell What jobs do cells have to do for an organism to live Gas exchange CO 2 & O 2 Eat (take in & digest food) Make energy ATP Build
2.1 CELL STRUCTURE. The cell is the smallest unit of living organisms that shows the characteristics of life.
 2.1.1 Microscopy The cell is the smallest unit of living organisms that shows the characteristics of life. A general introduction to the microscope. The light microscope All cells are microscopic which
2.1.1 Microscopy The cell is the smallest unit of living organisms that shows the characteristics of life. A general introduction to the microscope. The light microscope All cells are microscopic which
Cell Structure: What cells are made of. Can you pick out the cells from this picture?
 Cell Structure: What cells are made of Can you pick out the cells from this picture? Review of the cell theory Microscope was developed 1610. Anton van Leeuwenhoek saw living things in pond water. 1677
Cell Structure: What cells are made of Can you pick out the cells from this picture? Review of the cell theory Microscope was developed 1610. Anton van Leeuwenhoek saw living things in pond water. 1677
The Cell. The basic unit of all living things
 The Cell The basic unit of all living things 1 Robert Hooke was the first to name the cell (1665) 2 The Cell Theory The cell is the unit of Structure of all living things. The cell is the unit of Function
The Cell The basic unit of all living things 1 Robert Hooke was the first to name the cell (1665) 2 The Cell Theory The cell is the unit of Structure of all living things. The cell is the unit of Function
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below which represents a typical green plant cell and on your knowledge of biology.
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below which represents a typical green plant cell and on your knowledge of biology. 5. Which letter corresponds to that of the endoplasmic reticulum?
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below which represents a typical green plant cell and on your knowledge of biology. 5. Which letter corresponds to that of the endoplasmic reticulum?
II. Eukaryotic Cell Structure A. Boundaries 1. plasma membrane a. serves as a boundary b/w the cell and its environment b. controls movement of
 I. History of the cell theory A. Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1600s) - dutch lens maker could see things with his lenses that were invisible to the naked eye - developed the simple microscope B. Robert Hooke
I. History of the cell theory A. Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1600s) - dutch lens maker could see things with his lenses that were invisible to the naked eye - developed the simple microscope B. Robert Hooke
Microscope Lab Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
 Name: Date: Period: Microscope Lab Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Objectives: 1. Explain the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and distinguish each type under the microscope. 2. Compare animal
Name: Date: Period: Microscope Lab Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Objectives: 1. Explain the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and distinguish each type under the microscope. 2. Compare animal
Biology First Nine Weeks Review
 Name Date Test Date: November 12, 2009 Biology First Nine Weeks Review Modified True/False Directions: Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or fals If false, change the identified word to
Name Date Test Date: November 12, 2009 Biology First Nine Weeks Review Modified True/False Directions: Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or fals If false, change the identified word to
Van Leeuwenhoek. 1 st crude microscope made by the Dutchman
 The Cell History of Cells In 1665, English scientist Robert Hooke used the first compound light microscope to see plant tissues He viewed several thin slices of cork He called the small chambers within
The Cell History of Cells In 1665, English scientist Robert Hooke used the first compound light microscope to see plant tissues He viewed several thin slices of cork He called the small chambers within
Biology I. Chapter 7
 Biology I Chapter 7 Interest Grabber NOTEBOOK #1 Are All Cells Alike? All living things are made up of cells. Some organisms are composed of only one cell. Other organisms are made up of many cells. 1.
Biology I Chapter 7 Interest Grabber NOTEBOOK #1 Are All Cells Alike? All living things are made up of cells. Some organisms are composed of only one cell. Other organisms are made up of many cells. 1.
Some history. Now, we know that Robert Hooke was not looking at living cells, but the remains of dead cell walls.
 The Life of a Cell Some history In 1665, Robert Hooke examined the bark of an oak tree under an early microscope. He thought he was looking at something similar to the small rooms of dormitories and prisons;
The Life of a Cell Some history In 1665, Robert Hooke examined the bark of an oak tree under an early microscope. He thought he was looking at something similar to the small rooms of dormitories and prisons;
BIO.A.1 Basic Biological Principles
 BIO.A.1 Basic Biological Principles Bio.A.1.1 - Explain the characteristics common to all organisms Bio.A.1.2 Describe relationships between the structure & function at biological levels of organization
BIO.A.1 Basic Biological Principles Bio.A.1.1 - Explain the characteristics common to all organisms Bio.A.1.2 Describe relationships between the structure & function at biological levels of organization
BIO 2 GO! 3216a The Cell Organelles and Nucleus Function
 BIO 2 GO! 3216a The Cell Organelles and Nucleus Function The cell is the smallest unit of life. Each living cell has a nucleus which functions to control the actions of the rest of the cell. Upon successful
BIO 2 GO! 3216a The Cell Organelles and Nucleus Function The cell is the smallest unit of life. Each living cell has a nucleus which functions to control the actions of the rest of the cell. Upon successful
Ch 7: Cell Structure and Functions. AP Biology
 Ch 7: Cell Structure and Functions AP Biology The Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of cells. 2. New cells come from existing cells. 3. Cells are the basic units of structure and function of living
Ch 7: Cell Structure and Functions AP Biology The Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of cells. 2. New cells come from existing cells. 3. Cells are the basic units of structure and function of living
It took more than years for scientists to develop that would allow them to really study.
 CELLS NOTES All living things are made of! THE DISCOVERY OF CELLS The Scientist Who? When? What was discovered? Robert Hooke Anton van Leeuwenhoek Looked through a very simple at a thin slice of and saw
CELLS NOTES All living things are made of! THE DISCOVERY OF CELLS The Scientist Who? When? What was discovered? Robert Hooke Anton van Leeuwenhoek Looked through a very simple at a thin slice of and saw
7 Characteristics of Life
 7 Characteristics of Life 1. Interdependence 2. Metabolism 3. Homeostasis 4. Cellular Structure and Function 5. Reproduction 6. Heredity 7. Evolution The Cell Theory All living things are composed of one
7 Characteristics of Life 1. Interdependence 2. Metabolism 3. Homeostasis 4. Cellular Structure and Function 5. Reproduction 6. Heredity 7. Evolution The Cell Theory All living things are composed of one
Cell Organelles. 2. Cells are the basic unit of organization in an organism Cells tissues organ organ system organism
 Cell Organelles What are some of the differences you see between these two cells? A. Cell Theory 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of organization in an organism
Cell Organelles What are some of the differences you see between these two cells? A. Cell Theory 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of organization in an organism
Cell Energetics. How plants make food and everyone makes energy!
 Cell Energetics How plants make food and everyone makes energy! Carbon Cycle Where did the mitochondria and chloroplast come from? Endosymbiotic Theory Endosymbiotic theory = a theory that some of the
Cell Energetics How plants make food and everyone makes energy! Carbon Cycle Where did the mitochondria and chloroplast come from? Endosymbiotic Theory Endosymbiotic theory = a theory that some of the
Biology 160 Cell Lab. Name Lab Section: 1:00pm 3:00 pm. Student Learning Outcomes:
 Biology 160 Cell Lab Name Lab Section: 1:00pm 3:00 pm Student Learning Outcomes: Upon completion of today s lab you will be able to do the following: Properly use a compound light microscope Discuss the
Biology 160 Cell Lab Name Lab Section: 1:00pm 3:00 pm Student Learning Outcomes: Upon completion of today s lab you will be able to do the following: Properly use a compound light microscope Discuss the
Parts of the Cell book pgs
 Parts of the Cell book pgs. 12-18 Animal Cell Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Go to Section: Eukaryotic Cell: Organelles & Functions 1. Cell Membrane (Nickname: skin ) Function: A protective layer that covers
Parts of the Cell book pgs. 12-18 Animal Cell Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Go to Section: Eukaryotic Cell: Organelles & Functions 1. Cell Membrane (Nickname: skin ) Function: A protective layer that covers
Cellular Transportation & Respiration
 Cellular Transportation & Respiration Passive Transport A cell membrane is semiperamble, which means that it allows only certain substances to enter or leave a cell. Passive transport is the movement of
Cellular Transportation & Respiration Passive Transport A cell membrane is semiperamble, which means that it allows only certain substances to enter or leave a cell. Passive transport is the movement of
Unit 3: Cells. Objective: To be able to compare and contrast the differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells.
 Unit 3: Cells Objective: To be able to compare and contrast the differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells. The Cell Theory All living things are composed of cells (unicellular or multicellular).
Unit 3: Cells Objective: To be able to compare and contrast the differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells. The Cell Theory All living things are composed of cells (unicellular or multicellular).
CELL THEORY, STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
 CELL THEORY, STRUCTURE & FUNCTION History of Cells Robert Hooke (1665) observed cork under a microscope Thought they looked like the rooms monks lived in called cells. History of Cells Antony Van Leeuwenhoek
CELL THEORY, STRUCTURE & FUNCTION History of Cells Robert Hooke (1665) observed cork under a microscope Thought they looked like the rooms monks lived in called cells. History of Cells Antony Van Leeuwenhoek
 http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html 4A: Students will compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Robert Hooke (1665) Used a compound microscope to look at thin slices of cork (oak
http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html 4A: Students will compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Robert Hooke (1665) Used a compound microscope to look at thin slices of cork (oak
How do cell structures enable a cell to carry out basic life processes? Eukaryotic cells can be divided into two parts:
 Essential Question How do cell structures enable a cell to carry out basic life processes? Cell Organization Eukaryotic cells can be divided into two parts: 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm-the portion of the cell
Essential Question How do cell structures enable a cell to carry out basic life processes? Cell Organization Eukaryotic cells can be divided into two parts: 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm-the portion of the cell
Warm-Up. Answer the following questions in a complete sentence and explain why each answer is correct.
 Warm-Up Answer the following questions in a complete sentence and explain why each answer is correct. Unlike a eukaryotic cell, a prokaryotic does not have A. DNA. B. a cell membrane. C. cytoplasm. D.
Warm-Up Answer the following questions in a complete sentence and explain why each answer is correct. Unlike a eukaryotic cell, a prokaryotic does not have A. DNA. B. a cell membrane. C. cytoplasm. D.
7-1 Life Is Cellular. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 7-1 Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell What is the cell theory? The Discovery of the Cell The cell theory states: All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure
7-1 Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell What is the cell theory? The Discovery of the Cell The cell theory states: All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure
Day 1. What You ll Learn. 1. Organisms are living things. 2. All organisms are made of one or more cells.
 What You ll Learn Day 1 1. Organisms are living things. 2. All organisms are made of one or more cells. 3. There are two main types of cells: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic A cell is the basic unit and structure
What You ll Learn Day 1 1. Organisms are living things. 2. All organisms are made of one or more cells. 3. There are two main types of cells: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic A cell is the basic unit and structure
Chapter: Life's Structure and Classification
 Table of Contents Chapter: Life's Structure and Classification Section 1: Living Things 1- What is an organism? Any living thing is called an organism. Organisms vary in size: 1)one-celled or unicellular
Table of Contents Chapter: Life's Structure and Classification Section 1: Living Things 1- What is an organism? Any living thing is called an organism. Organisms vary in size: 1)one-celled or unicellular
Investigation: What Are the Different Types of Cells?
 Name: Date: Investigation: What Are the Different Types of Cells? All living organisms are made of cells. The smallest cells are about 0.001 millimeters in diameter and belong to one of two domains: Bacteria
Name: Date: Investigation: What Are the Different Types of Cells? All living organisms are made of cells. The smallest cells are about 0.001 millimeters in diameter and belong to one of two domains: Bacteria
Biology: Life on Earth
 Teresa Audesirk Gerald Audesirk Bruce E. Byers Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 4 Cell Structure and Function Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall, Inc. Chapter 4 Outline 4.1 What
Teresa Audesirk Gerald Audesirk Bruce E. Byers Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 4 Cell Structure and Function Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall, Inc. Chapter 4 Outline 4.1 What
NCERT solution for Cell - Structure and Functions Science
 NCERT solution for Cell - Structure and Functions Science 1 Question 1 Indicate whether the following statements are True (T) or False (F). (a) Unicellular organisms have one-celled body. (b) Muscle cells
NCERT solution for Cell - Structure and Functions Science 1 Question 1 Indicate whether the following statements are True (T) or False (F). (a) Unicellular organisms have one-celled body. (b) Muscle cells
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell Prokaryotic Cells No nucleus Archaea & Eubacteria One circular chromosome Extremely small Eukaryotic Cells Has a nucleus!!! Membrane-bound organelles Plants, Animals, Fungi, &
Basic Structure of a Cell Prokaryotic Cells No nucleus Archaea & Eubacteria One circular chromosome Extremely small Eukaryotic Cells Has a nucleus!!! Membrane-bound organelles Plants, Animals, Fungi, &
Introduction 1) List the 3 types of cells you will be comparing in today s lesson. a. b. c.
 Name: Date: Period: Cell Structure Internet Lesson Directions: Answer the following question by visiting the web site below. http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cell_structure/cell_structure.htm
Name: Date: Period: Cell Structure Internet Lesson Directions: Answer the following question by visiting the web site below. http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cell_structure/cell_structure.htm
2. Cell surface proteins or receptors, that help cells communicate, are embedded within the cell membrane s phospholipid bilayer.
 UNIT 3 TEST BIOLOGY: 1.1.1, 1.1.2, 1.1.3 Cells, Cell Structures, Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic, Bacteria & Protists, Microscopes, Cell Communication, & Stem Cells True/False Indicate whether the statement
UNIT 3 TEST BIOLOGY: 1.1.1, 1.1.2, 1.1.3 Cells, Cell Structures, Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic, Bacteria & Protists, Microscopes, Cell Communication, & Stem Cells True/False Indicate whether the statement
Cell Structure and Function. Chapter 4
 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Chapter 4: Cell Structure Section 1: The History of Cell Biology Section 2: Introduction to Cells Section 3: Cell Organelles and Features Section 4: Unique Features
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Chapter 4: Cell Structure Section 1: The History of Cell Biology Section 2: Introduction to Cells Section 3: Cell Organelles and Features Section 4: Unique Features
Chapter 7.2. Cell Structure
 Chapter 7.2 Cell Structure Daily Objectives Describe the structure and function of the cell nucleus. Describe the function and structure of membrane bound organelles found within the cell. Describe the
Chapter 7.2 Cell Structure Daily Objectives Describe the structure and function of the cell nucleus. Describe the function and structure of membrane bound organelles found within the cell. Describe the
Cell Organelles. Wednesday, October 22, 14
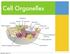 Cell Organelles Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells have a cell membrane It is the layer that surrounds the cell and controls what goes in and out Bacteria (Prokaryotic Cell) Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells
Cell Organelles Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells have a cell membrane It is the layer that surrounds the cell and controls what goes in and out Bacteria (Prokaryotic Cell) Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells
STEMscopedia: PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS
 B.L 14.2 and 14.3 Reflect Take a moment to think about all of the living things on Earth. There is great diversity among organisms, from microscopic bacteria to massive blue whales the largest animals
B.L 14.2 and 14.3 Reflect Take a moment to think about all of the living things on Earth. There is great diversity among organisms, from microscopic bacteria to massive blue whales the largest animals
Biology. Introduction to Cells. Tuesday, February 9, 16
 Biology Introduction to Cells Biology Biology is the study of life. In Biology, we are going to start small (the cell) and end with explaining a larger system (organisms) How small? http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/
Biology Introduction to Cells Biology Biology is the study of life. In Biology, we are going to start small (the cell) and end with explaining a larger system (organisms) How small? http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/
BASIC BIOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES
 BASIC BIOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES A1 A1. Basic Biological Principles 1. Describe the characteristics of life shared by all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms 2. Compare cellular structures and their function
BASIC BIOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES A1 A1. Basic Biological Principles 1. Describe the characteristics of life shared by all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms 2. Compare cellular structures and their function
What is a cell? A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Who discovered cells?
 INTRODUCTION TO THE CELL What is a cell? A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Who discovered cells? Robert Hooke (by looking at a piece of cork under a microscope What is
INTRODUCTION TO THE CELL What is a cell? A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Who discovered cells? Robert Hooke (by looking at a piece of cork under a microscope What is
Endosymbiotic Theory. p
 Endosymbiotic Theory p. 427-428 The Endosymbiotic Theory Review: What is a theory? What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? The endosymbiotic theory is the idea that a long time
Endosymbiotic Theory p. 427-428 The Endosymbiotic Theory Review: What is a theory? What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? The endosymbiotic theory is the idea that a long time
3.1 Cell Theory. KEY CONCEPT Cells are the Basic unit of life.
 3.1 Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the Basic unit of life. 3.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists and improvements in the microscope. Many scientists contributed to
3.1 Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the Basic unit of life. 3.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists and improvements in the microscope. Many scientists contributed to
Bio-CP Chapter 7 Cell Notes
 Bio-CP Chapter 7 Cell Notes I. Cell = Building block of all living organisms A. Robert Hooke (1665) observed cork under a crude microscope 1. He called the boxes cells because they looked like little rooms
Bio-CP Chapter 7 Cell Notes I. Cell = Building block of all living organisms A. Robert Hooke (1665) observed cork under a crude microscope 1. He called the boxes cells because they looked like little rooms
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 4-1 The History of Cell Biology
 STUDY GUIDE SECTION 4-1 The History of Cell Biology Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. One early piece of evidence supporting the cell theory was the observation
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 4-1 The History of Cell Biology Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. One early piece of evidence supporting the cell theory was the observation
Introduction to Cells- Stations Lab
 Introduction to Cells- Stations Lab Station 1: Microscopes allow scientists to study cells. Microscopes: How do light microscopes differ from electron microscopes? (How does each work? How much can each
Introduction to Cells- Stations Lab Station 1: Microscopes allow scientists to study cells. Microscopes: How do light microscopes differ from electron microscopes? (How does each work? How much can each
Chapter 5: The Fundamental Unit of Life
 Chapter 5: The Fundamental Unit of Life KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept] CONCEPTS RATING Study of historical perceptive related to cell discovery Study of Microscope ** Study
Chapter 5: The Fundamental Unit of Life KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept] CONCEPTS RATING Study of historical perceptive related to cell discovery Study of Microscope ** Study
The Unity of Life. All living things are made up of small individual units called cells.
 The Unity of Life All living things are made up of small individual units called cells. Robert Hooke (1600 s) - examined slices of cork with a magnifying glass and observed box-like structures which he
The Unity of Life All living things are made up of small individual units called cells. Robert Hooke (1600 s) - examined slices of cork with a magnifying glass and observed box-like structures which he
Student Exploration: Cell Types
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Cell Types Vocabulary: ATP, bacteria, carbon dioxide (CO 2), cell, cellular respiration, compound light microscope, eukaryote, multicellular, muscle cell, neuron, organelle,
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Cell Types Vocabulary: ATP, bacteria, carbon dioxide (CO 2), cell, cellular respiration, compound light microscope, eukaryote, multicellular, muscle cell, neuron, organelle,
Discovery of the Cell
 Cell Structure Discovery of the Cell Who discovered cells? 1665 Robert Hooke used a compound microscope to examine a piece of cork (20X magnification) He saw little boxes in the cork and called them cells
Cell Structure Discovery of the Cell Who discovered cells? 1665 Robert Hooke used a compound microscope to examine a piece of cork (20X magnification) He saw little boxes in the cork and called them cells
Overview of Cells. Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Organelles The Endosymbiotic Theory
 Overview of Cells Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Organelles The Endosymbiotic Theory Prokaryotic Cells Archaea Bacteria Come in many different shapes and sizes.5 µm 2 µm, up to 60 µm long Have large
Overview of Cells Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Organelles The Endosymbiotic Theory Prokaryotic Cells Archaea Bacteria Come in many different shapes and sizes.5 µm 2 µm, up to 60 µm long Have large
It helps scientists understand the workings of the human body and of other animals and plants
 Science 8 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 1 Cells Online resources: Click on Chapter 1 at the site below. http://www.nelson.com/bcscienceprobe8/student/weblinks.html Chapter 1.1 1. Organism is another word used
Science 8 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 1 Cells Online resources: Click on Chapter 1 at the site below. http://www.nelson.com/bcscienceprobe8/student/weblinks.html Chapter 1.1 1. Organism is another word used
CELL THEORY & CELL TYPES. Honors Biology, Arizona College Prep, Mrs. Glassmeyer Textbook Reference: 4.1, , The Living World 7 th edition
 CELL THEORY & CELL TYPES Honors Biology, Arizona College Prep, Mrs. Glassmeyer Textbook Reference: 4.1,4.3-4.4, The Living World 7 th edition Learning Goals: Unit Learning Goal: Student will be able to
CELL THEORY & CELL TYPES Honors Biology, Arizona College Prep, Mrs. Glassmeyer Textbook Reference: 4.1,4.3-4.4, The Living World 7 th edition Learning Goals: Unit Learning Goal: Student will be able to
Biology Cell Unit Homework Packet #1
 Name DUE: Biology Cell Unit Homework Packet #1 Hour HW #1 Microscope Questions Exploration Drawing Lab Post-Lab Questions / 5 possible points Homework #1: Microscope Exploration Lab When working with a
Name DUE: Biology Cell Unit Homework Packet #1 Hour HW #1 Microscope Questions Exploration Drawing Lab Post-Lab Questions / 5 possible points Homework #1: Microscope Exploration Lab When working with a
Biol 1409: Study Guide for Exam I. Introduction to Diversity
 Biol 1409: Study Guide for Exam I Introduction to Diversity 1. Define Biosphere and describe where it is found 2. Describe why our planet is so hospitable to life 3. Name and briefly describe the major
Biol 1409: Study Guide for Exam I Introduction to Diversity 1. Define Biosphere and describe where it is found 2. Describe why our planet is so hospitable to life 3. Name and briefly describe the major
Cell Webquest MAKE SURE YOUR COMPUTER SOUNDS ARE OFF BEFORE STARTING!!!
 Name Cell Webquest MAKE SURE YOUR COMPUTER SOUNDS ARE OFF BEFORE STARTING!!! http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cell_structure/cell_st ructure.htm 1. What are the three basic
Name Cell Webquest MAKE SURE YOUR COMPUTER SOUNDS ARE OFF BEFORE STARTING!!! http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cell_structure/cell_st ructure.htm 1. What are the three basic
