LEARNING/TEACHING ACTIVITIES LEARNING/TEACHING RESOURCES 1 2
|
|
|
- Garry McCoy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2
3 For use with Biology Secondary Form Two Biology : Term One SUB- Introduction define the term transport. list substances transported in. link surface area to volume ratio of organisms to the transport system of the organisms. explain the necessity of transport in. Defining the term transport Listing substances transported in organisms Relating surface area to volume ratio of organisms to transport systems Large small cubes surface area to volume ratio of different cubes pages pages 3 WEEK 3 Structure of root root hairs draw the structure of the root root hair. relate the structure of the root hair to the functions. Discussing the structure of root root hairs Drawing the root root hair Relating the structure to the functions Chart of root root hairs pages 4 pages 3 4 Structure of root root hairs (practical lesson) observe prepared slides of roots root hairs. compare monocotyledonous dicotyledonous root sections. observe charts drawings of root sections. Observing comparing prepared slides of monocotyledonous dicotyledonous roots root hairs under a microscope Observing charts drawing of root section Microscopes Prepared slides of root sections root hairs Charts on root sections of monocotyledonous dicotyledonous roots pages 4 pages 3 WEEK Xylem vessels relate the structure of the xylem vessel to its function. Discussion on structure of the xylem vessel its function Photographs of xylem vessels Chart on xylem vessels pages 8 9 pages 3 6
4 For use with WEEK SUB- Tracheid elements Absorption of water mineral salts relate the structure of the tracheid elements to their functions. distinguish between xylem vessels tracheid elements. describe water salt uptake by roots from the soil. physiological processes involved in uptake of water mineral salts. Relate the structure of tracheids to their functions Distinguish between vessels tracheids Discussion on the structure of tracheid elements Explaining water absorption mineral salt uptake by roots in Discussion of water absorption uptake of mineral salts in Photographs of tracheids elements Chart on tracheids elements Chart on roots, root hairs sections of roots Photographs of roots root hairs pages 8 9 pages 3 pages 5 pages 3 Biology Form Term WEEK 3 Internal tissues of the stem Role of the leaf in transpiration draw the monocotyledonous dicotyledonous stem sections. relate the structure of xylem to its role in transpiration. draw the structure of leaf relate its parts to their functions. Discussion on the structure of xylem to its functions Drawing the stem sections Discussion on parts of a leaf how they relate to their functions Photographs of monocotyledonous dicotyledonous stem sections showing the xylem Chart on the stem sections Chart on the section of a leaf pages 6 7 pages 3 page 7 pages 3 7
5 For use with WEEK 3 SUB- Transport of water mineral salts in (practical lesson) demonstrate the movement of water in. observe prepared leaf sections to identify vascular tissues. Carrying out an experiment to demonstrate the movement of water in Observing prepared leaf section under a light microscope Identifying vascular tissues in leaves Coloured water Beaker Plant with flowers having white petals Clock Prepared leaf sections Microscopes page 4 pages 3 Biology Form Term Continuous assessment test By the end of the test, the learner should have answered all the questions asked. Learner to answer the given questions Teacher to supervise test Question paper Marking scheme WEEK 4 Movement of water in discuss the forces involved in movement of water in such as transpiration pull, cohesion adhesion capillarity root pressures. demonstrate the forces involved in movement of water in. Describing the forces involved in movement of water in Discussion on forces involved in movement of water in Carrying out experiments to show the forces involved Tubes of different diameters Beaker containing coloured water Fresh plant stump with fluid oozing pages pages 3 Factors affecting the rate of transpiration explain various factors affecting the rate for transpiration. Explaining various factors affecting the rate of transpiration Plant seedlings with few roots others with many roots pages 8 pages 3 8
6 For use with SUB- Rate of water loss in draw a potometer. describe the procedure of using a potometer to investigate the rate of water loss in. Discussion on how to use a potometer in investigating the rate of water loss Drawing a potometer Investigating water loss in using a potometer a potometer Improvised potometer Cobalt chloride paper Pins Clips pages 5 6 pages 8 Biology Form Term WEEK 6 WEEK 5 Importance of transpiration The phloem The phloem Function of phloem discuss the importance of transpiration in. draw the phloem relate its structure to its function. list down materials translocated in the phloem. draw the structure of the phloem. relate parts of the phloem to their functions. discuss the function of the phloem. list down materials translocated the sites of storage in the phloem. Discussion on the significance of transpiration in Drawing the phloem discussing the functions in relation to structure Listing down the materials translocated in Drawing the phloem Discussion on the function of the parts of the phloem Discussion on the functions of the phloem Listing down materials translocated storage sites in the phloem Wilted potted Potted growing normally Chart on the structure of the phloem Photographs of phloem Charts or drawings of the phloem structure Chart on structure of the phloem page pages 3 pages 4 pages 3 page pages 3 pages 4 pages 3 9
7 For use with WEEK 8 WEEK 7 WEEK 6 Continuous assessment test SUB- Function of the phloem (practical lesson) Introduction unicellular organisms Open circulatory system Closed circulatory system Topics covered so far set up an experiment to investigate translocation of food substances in a dicotyledonous plant. describe transport of substances in unicellular organisms. explain the necessity of an elaborate transport system in most. discuss the open circulating system. draw the open circulatory system of an insect. define closed transport system. distinguish between closed open circulatory system. answer all the given questions in the test. 30 Setting up an experiment to investigate translocation Discussion on the results of experiment Explaining transport in unicellular organisms Explaining the need of an elaborate transport system in most Discussing the open circulatory system of an insect Drawing labelling the open circulatory system Defining closed circulatory system Distinguishing it from open circulatory system Learner to answer questions Teacher to supervise the test Young plant Sharp knife Saplings Chart on amoeba showing movement of gases in out by diffusion the circulatory system of a coackroach Chart on closed circulatory system differences between open closed circulatory system Question paper Marking scheme page 4 pages 3 page pages 4 5 pages 4 pages 4 5 pages 3 pages 4 5 Biology Form Term
8 For use with WEEK 8 SUB- Double circulatory system draw the double circulatory system in mammals. dissect a rabbit observe its transport system. Discussing the double circulatory system Observing the transport system of a rabbit Drawing the double circulatory system of a mammal the circulatory system of a mammal Dissected rabbit displaying the circulatory system pages 4, 4 44 pages 4 5 Biology Form Term The mammalian heart draw the mammalian heart. relate the structure of the heart to its functions. Drawing the mammalian heart relating its structure to its function Discussing the structure of the mammalian heart the structure of the mammalian heart Model of heart pages 4 5 pages 4 5 WEEK 0 WEEK 9 Blood flow in the circulatory system of mammals Blood vessels Disease defects of the circulatory system trace the path taken by blood from the heart to the body parts back to the heart. explain the structure of arteries, veins capillaries. relate the structure of the arteries, veins capillaries to their functions. name the common diseases of circulatory system such as thrombosis, varicose veins arteriosclerosis. suggest methods of control/ prevention for the diseases. Discussing the blood flow in mammals Tracing the path taken by blood from the heart to all body parts back to the heart Explaining relating the structure to their functions Drawing the arteries, veins capillaries Making models of blood vessels Name the diseases of the circulatory system Suggest methods of control/prevention the path of blood flow in the circulatory system of a mammal Charts showing arteries, veins capillaries Models of blood vessels Different colours of plasticine Resource person such as a school nurse Photographs of people suffering from diseases of the circulatory system pages 5 6 pages 4 5 pages 9 3 pages 4 5 pages 3 33 pages 4 5 3
9 For use with WEEK WEEK SUB- The structure functions of the blood The structure functions of the blood Blood grouping blood transfusion Blood grouping blood transfusion list the components of blood. state the functions of each of the blood components. explain how oxygen carbon dioxide are transported in the blood. describe the mechanisms of blood clotting its importance. describe the human blood group system. state the importance of blood groups in blood transfusion. discuss the rhesus factor. state the role of the rhesus factor in blood transfusion. Listing components of blood Relating blood components to their functions Modelling red blood cells (RBC) Explaining how oxygen carbon dioxide are transported in blood Describing the blood clotting mechanism its importance Describing blood groups Stating the importance of human blood groups in blood transfusion Playing cards/ bottle tops in pairs Discussing the rhesus factor its role in blood transfusion Resource person, such as school nurse Model RBC using plasticine School nurse blood clotting mechanism Personnel such as school nurse blood groups possible transfusions Prepared cards/ bottle tops School nurse Blood transfusion personnel pages pages 4 5 pages pages 4 5 pages pages 4 5 pages pages 4 5 Biology Form Term 3 4 The structure of the heart (practical lesson) examine the external internal structure of a cow s heart. investigate pulse rate at the wrist. Examining a mammalian heart structure identifying various parts Working in pairs to examine pulse rate before after vigorous activities Fresh heart of a mammal such as a cow Dissecting kit H lens Stop watch pages pages 4 5 3
10 For use with SUB- Immune responses define immunity. describe immune responses. differentiate between natural artificial immunity. Defining immunity Describing immune responses Distinguishing between natural artificial immunity types of immunity pages 39 4 pages 4 5 Biology Form Term WEEK Vaccination describe importance of vaccination against diseases, such as tuberculosis, poliomyelitis, measles, diphtheria, whooping cough. Defining vaccination Describing the importance of vaccination Drawing the vaccination timetable vaccination timetable Personnel from post natal clinic pages 40 4 pages 4 5 Allergic reactions define allergic reactions explain their causes. carry out an experiment to demonstrate the unidirectional flow of blood in the cutaneous veins of the forearm. Defining allergic reactions explaining their causes Carrying out an experiment to demonstrate the unidirectional flow of blood along the veins School nurse Rubber bs Bages or hkerchiefs pages 4 4, 45 pages 4 5 WEEK 3 Revision/ End of term examination 33
11 For use with Biology Secondary Form Two Biology : Term Two SUB- Definition importance of gaseous exchange define gaseous exchange. explain the importance of gaseous organisms. Defining gaseous exchange Discussion on the importance of gaseous exchange Chart on the importance gaseous organisms page 48 pages 6 33 WEEK exchange in stomata draw label open closed stomata. explain stomatal gaseous exchange. Describing the parts of the stomata Drawing labeling of open closed stoma Discussion on stomatal gaseous exchange open closed stomata pages pages 6 33 Stomata (practical lesson) investigate the presence of stomata on leaves. investigate the shape of guard cells the distribution of stomata on leaves. Investigating presence of stomata on leaves in groups Investigating the shape of guard cells Discussion on the distribution of stomata on leaves of various Water in a beaker Leaves of various Means of heating Clear nail varnish Light microscope Cover slip Forceps Microscope slide Leaves of various page 54 pages 6 33 WEEK Mechanism of opening closing stomata describe photosynthetic/glucose accumulation theory of opening closing of stomata. Discussion on photosynthetic theory of opening closing of stomata open closed stomata pages pages
12 For use with WEEK SUB- Mechanism of opening closing of stomata Internal structure of stems leaves (practical lesson) describe inter-conversion of starch glucose ion accumulation theories. investigate the internal structure of stems leaf stalk in aerial aquatic. investigate tissue distribution in aerial leaves stem. Discussion on interconversion of starch glucose ion accumulation theories Investigation of the structure of stems leaf stalks in aerial aquatic open closed of stomata Microscope Prepared permanent slides of aerial leaves stems Water lily leaf stalk Bougainvillea twig Beaker containing water Scalpel page 50 pages 6 33 page 55 pages 6 33 Biology Form Term Cuticular lenticular gaseous exchange describe cuticular lenticular gaseous exchange. Discussion on lenticular gaseous exchange Discussion on cuticular gaseous exchange internal leaf structure lenticels page 5 pages 6 33 WEEK 3 exchange through the roots describe how gaseous exchange takes place through the epidermis of the roots. Discussion on gaseous exchange through the roots Photograph of pneumatophores breathing roots pages 5 54 pages 6 33 exchange structures examine various types of gaseous exchange structure relate them to their functions. Examining types of gaseous exchange structures in different organisms Tadpoles Insect (alive) Fish Frog Earthworm page 57 35
13 For use with SUB- exchange surfaces exchange in amoeba state the characteristics of gaseous exchange surfaces in different organisms. describe the mechanism of gaseous amoeba. Discussion on characteristics of gaseous exchange surfaces Discussion on mechanism of gaseous amoeba diagrams of different gaseous exchange surfaces such as insects, fish, frog earthworms diagram on gaseous amoeba pages Biology Form Term WEEK 4 Continuous assessment test answer all the questions asked in the test. Learner to write down the answers Teacher to supervise test Question paper Marking scheme 3 4 exchange in insect examine the gaseous exchange structures of a grasshopper or a locust. draw the gaseous exchange structure of an insect. Examining gaseous exchange structures in insects Discussion of findings Drawing the structure of a gaseous exchange system in an insect Chart on tracheal system in insects Live grasshopper Dissecting board Pins H lens Dissecting kit Chloroform Cotton wool page 58 WEEK 5 exchange in bony fish draw label the structure of gaseous bony fish. relate the gills to their function. Discussion on gills of a bony fish Drawing labelling the gill chamber gills of bony fish Discussion on functions of parts of the gills diagrams of gill chamber gills of a bony fish pages
14 For use with WEEK 6 WEEK 5 SUB- Mechanism of gaseous exchange in bony fish exchange in bony fish (practical lesson) exchange in frogs exchange in human beings exchange in human beings describe the mechanism of gaseous bony fish. examine the location number of gills in gill chambers of bony fish. examine, draw label the gill of a bony fish. describe gaseous a frog through its gills, skin mouth lungs. draw label the structures involved in gaseous human beings. examine a dissected mammal to locate the gaseous exchange structures. describe the mechanism of breathing in human beings. Discussion on mechanism of gaseous bony fish Examining, drawing labelling isolated gills in bony fish Discussion on gaseous a frog Discussion on structures of gaseous human beings Drawing of structures involved in gaseous humans Identifying the structures of gaseous a dissected rabbit (mammal) Discussion on mechanism of breathing in human beings diagram of gill chamber of bony fish Tilapia fish H lenses Gills of a bony fish Dissecting kit Pins Dissecting board position of mouth cavity, lungs nostrils in a frog the respiratory system in human beings the lungs rib cage in human beings Dissected rabbit displaying gaseous exchange system pages 60 6 page 69 pages 6 6 pages page 64 Biology Form Term 37
15 For use with WEEK 8 WEEK SUB- Breathing mechanism in human beings exchange in human beings Continuous assessment test exchange in mammals (practical lesson) describe how gaseous exchange occurs in the alveoli. explain how human lungs are adapted to their functions. answer all the questions asked in the test. demonstrate the breathing mechanism of the lungs diaphragm in a model thoracic cavity. demonstrate the breathing movement of ribs muscles by using a model. Discussion on gaseous exchange at the alveoli Discussion on the adaptations of lungs in humans examination of mammalian lung Learners to write down the answers to the questions Teacher to supervise the students Carrying out demonstration of breathing mechanism in human beings using a model exchange of gases in alveoli of human beings Lungs from a mammal e.g. goat Question papers Marking scheme A bell jar Two balloons Rubber stopper with a hole Y-shaped glass tube Rubber sheet String Petroleum jelly page 66 page 66 page 7 Biology Form Term 38
16 For use with SUB- Factors affecting the rate of breathing explain the factors which control the rate of breathing in human beings. Discussion on factors affecting the rate of breathing in human beings Chart with table showing factors affecting breathing pages Biology Form Term WEEK 0 WEEK Respiration Respiration Respiratory diseases exchange in (practical lesson) Introduction Tissue respiration Anaerobic respiration state causes, symptoms prevention measures of respiratory diseases. demonstrate the effect of exercise on the rate of breathing. define respiration. state the significance of respiration. draw label mitochondria. describe anaerobic respiration in. Discussion on causes, symptoms prevention measures of respiratory diseases Carrying out experiment to show the effect of exercise on rate of breathing Discussion on definition significance of respiration Drawing labelling mitochondria Discussion on anaerobic respiration in Chart on respiratory diseases Chair Stopwatch Skipping rope diagram of mitochondria Chart on mitochondria page 7 page 74 page 74 pages pages pages
17 For use with SUB- Biology Form Term WEEK WEEK 0 Respiration Respiration Respiration Respiration (practical lesson) Economic importance of anaerobic respiration Aerobic respiration identify the gas given off when food is burnt. investigate the gas produced during fermentation. explain the economic importance of anaerobic respiration. explain aerobic respiration. compare energy production in aerobic anaerobic respiration. Carrying out experiments to investigate the gas produced when food is burnt Discussion on economic importance of anaerobic respiration Explaining aerobic respiration Discussion on energy formation in aerobic anaerobic respiration Retort st Maize flour Test-tubes Source of heat Boiling tubes Delivery tube Rubber stopper Lime water Clump Chart on economic importance of anaerobic respiration Chart on energy formation energy output in aerobic respiration pages 80 8 pages page 77 pages pages pages
18 For use with WEEK Respiration Respiration SUB- Tissue respiration (practical lesson) Tissue respiration (practical lesson) investigate the production of heat by germinating seeds. demonstrate that respiration takes place in. show aerobic respiration in. show that aerobic respiration takes place in. Carrying out the various experiments in groups Carrying out the experiments Discussion on the results observed Two vacuum flasks Two thermometers Beans cotton wool Sterilizer such as formalin Bell jar Soda lime Two conical flasks Black cloth Lime water Potted plant Delivery tube Filter pump Corks Petroleum jelly Grasshopper Two pieces of muslin cloth or wire net Bicarbonate indicator Two conical flasks Measuring cylinder Two rubber bungs Two labels Bell jar Two conical flasks Lime water Delivery tubes Soda lime Rat Filter pump Petroleum jelly pages 8 8 pages pages pages Biology Form Term WEEK 3 Revision end of term examination 4
19 For use with Biology Secondary Form Two Biology : Term Three SUB- Definition of terms define the terms stated. distinguish between excretion egestion. explain the necessity of excretion in. Defining excretion, egestion secretion Distinguishing between excretion egestion Explaining the necessity of excretion in major terms their definitions page 86 WEEK WEEK in in in describe the methods of excretion in. list down useful harmful excretory products in. describe the uses of excretory products in. draw an amoeba. describe excretion in fresh water amoeba. Describing the methods of excretion in Listing excretory products in Describing the uses of excretory products in Drawing of amoeba Describing the excretion of water nitrogenous wastes in amoeba excretory products in method of excretion in the excretory products, sources their economic importance in an amoeba in stages of excreting water other wastes pages page 87 page 88 4
20 For use with SUB- in explain the need for complex organs for excretion. list down organs involved in excretion in. list down waste products released by various organs. Explaining the need for complex excretory organs Listing the excretory organs substances released the specialized organs the main excretory products page 88 Biology Form Term 3 WEEK The human kidney examine the kidney of a mammal. draw the external structure of a kidney. make a vertical section through the kidney. identify the internal parts of the kidney. Examining the kidney Making a vertical section identifying the parts of the kidney Drawing the internal structure of the kidney Kidney of a mammal Sharp knife section of a kidney pages 9, 05 Functions of the nephron draw label the parts of the nephron. relate its structure to its role in urine formation. Drawing labelling the nephron Discussion on the structure of the nephron in relation to its function the structure of the nephron pages 9 94 WEEK 3 Neuro-endocrine system describe the role of various hormones in urine formation. Describing the role of insulin, ADH aldosterone in urine formation Diagram of nephron showing the movement of sodium ions water pages
21 For use with SUB- Biology Form Term 3 WEEK 3 Neuro-endocrine system describe the components role of the neuro-endocrine systems. distinguish between internal external environments. general working of the homeostatic mechanism. Describing the components role of the neuro-endocrine system Distinguishing between internal external environment Explaining the general working of the homeostatic mechanism Flow chart showing the homeostatic mechanism; positive negative feedback pages Continuous assessment test answer all the questions asked in the test. Learner to answer all the questions Teacher to prepare give the test Question papers Marking schemes WEEK 4 Osmoregulation describe the role of the kidney in osmoregulation. explain the role of hypothalamus in osmoregulation. Describing the role of the kidney in osmoregulation Describing the role of the hypothalamus in osmoregulation Flow chart showing the homeostatic mechanism in regulating osmotic pressure by the kidney pages Diabetes insipidus other common kidney diseases describe the causes symptoms of diabetes insipidus other common kidney diseases. state possible control/ prevention methods of diabetes insipidus. Describing the causes, symptoms, prevention control of diabetes insipidus other diseases associated with the kidney the diseases, causes, symptoms control/prevention methods pages 96,
22 For use with SUB- in draw label parts of the skin. relate the parts of skin to their functions. Discussion on the parts of the skin their functions Drawing labelling parts of the skin relating parts to their functions Chart or photograph of the section of the skin pages Biology Form Term 3 WEEK 5 The role of skin in describe the role of the skin in osmoregulation thermoregulation. Describing the role of the skin in osmoregulation thermoregulation diagram of the skin pages Thermoregulation in human beings describe behavioral physiological means of thermoregulation in. Describing the behavioural physiological means of thermoregulation Photographs of warmly dressed people during cold weather Photograph of people with light clothing during hot weather pages WEEK 6 Heat loss heat gain Surface area to volume ratio in relation to thermoregulation describe the various methods of heat loss gain in mammals. relate the body size of mammals to heat loss heat gain. Discussion on methods of heat loss gain in mammals Discussion on relationship of body size in mammals to heat loss gain Resource person e.g. physics teacher to describe methods of heat loss heat gain Pictures of large mammals small mammals page 99 page 99 45
23 For use with WEEK 8 WEEK 7 WEEK SUB- Role of the liver in Functions of the liver Diseases of the liver Continuous assessment test. in (practical lessson) draw the liver describe its role in. describe other functions of the liver. describe the symptoms possible control of diabetes mellitus other diseases of the liver. answer all the questions asked in the test. describe the role of catalase enzyme in breaking down hydrogen peroxide. use liver kidney to investigate the reaction. 46 Describing the liver its role in Drawing labelling the liver associated parts Describing other functions of the liver Describing the symptoms control of diabetes mellitus other liver diseases Learner to answer the questions Teacher to supervise students Carrying out the experiment to investigate the effect of catalase enzyme on hydrogen peroxide Discussion on results obtained in the experiment the external structure of liver in relation to gut, gall bladder blood vessels functions of the liver diseases of the liver, causes control/ treatment Question paper Marking scheme Hydrogen peroxide Beakers (two) Measuring cylinder Piece of liver kidney Splint Ruler pages 0 04 pages pages pages Biology Form Term 3
24 For use with WEEK 9 SUB- Role of the liver in regulation of blood glucose Regulation of blood sugar describe the role of the liver in blood sugar control. describe the role of insulin hormone. draw describe a flow chart showing the regulation of blood sugar. Describing the role of the liver in blood sugar control using insulin hormone Describing the feed back mechanism of blood sugar control steps in controlling blood sugar levels Flow chart showing regulation of blood sugar page 97 page 98 Biology Form Term 3 WEEK 0 Temperature regulation in other Continuous assessment test describe temperature regulation in other. answer the questions asked in the test. Describing temperature regulation in other Learner to answer questions in the test Teacher to supervise students as they do the test Photographs of bird, reptiles camels showing behaviour of temperature regulation Question paper Marking scheme page 00 WEEK Revision exchange in relate parts of the lung to their functions. draw label the parts of the lungs. Describing the parts of the lung relating the parts to their functions. Drawing labelling the parts of the lungs the parts of the lungs pages 63 64, 66 47
25 For use with SUB- Biology Form Term 3 WEEK Revision exchange in describe the functions of lungs as discussed during gaseous exchange. Reviewing gaseous exchange functions of lungs Reading notes on gaseous exchange Notes on gaseous exchange Charts showing lungs pages WEEK 4 Revision exchange in (practical lesson) identify a mammal s lungs. observe describe the structure of lungs in relation to functions. Identifying fresh lungs of a mammal Observing describing the structure of a mammal s lungs in relation to their functions Fresh lungs of a cow Livestock officer pages WEEK 3 Revision/ End of year examination 48
GASEOUS EXCHANGE. (a) Identify the organ and the parts labelled M, N, and P. (b) How the structures are labelled P adapted to their function?
 NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE 1. 1992 Q11 P1 GASEOUS EXCHANGE The diagram below represents an organ from a bony fish. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow 2. 1994 Q14 P1 (a) Identify
NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE 1. 1992 Q11 P1 GASEOUS EXCHANGE The diagram below represents an organ from a bony fish. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow 2. 1994 Q14 P1 (a) Identify
INSTRUCTIONS Attempt all the questions in section A and B and one C in the spaces provided ANSWERS TO SECTION A FOR OFFICIAL USE ONLY
 GHS EOT I S. 3 BIOLOGY 553/1 (THEORY) APRIL 2018 TIME: 2 HOURS NAME:.CLASS/NO.. INSTRUCTIONS Attempt all the questions in section A and B and one C in the spaces provided ANSWERS TO SECTION A 1 7 13 19
GHS EOT I S. 3 BIOLOGY 553/1 (THEORY) APRIL 2018 TIME: 2 HOURS NAME:.CLASS/NO.. INSTRUCTIONS Attempt all the questions in section A and B and one C in the spaces provided ANSWERS TO SECTION A 1 7 13 19
Nerve cells have many branches that help them send signals throughout the body.
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of atoms or cells. You might even say you are made of organs, like skin and a heart. These answers are all correct. Each focuses on a different
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of atoms or cells. You might even say you are made of organs, like skin and a heart. These answers are all correct. Each focuses on a different
B4 Organising animals and plants. Student Book answers. B4.1 The blood. Question Answer Marks Guidance
 B4. The blood Any three from: 3 transport of blood cells, transport of dissolved gases, transport of food, transport of hormones, removal of waste products, defence against infection, preventing blood
B4. The blood Any three from: 3 transport of blood cells, transport of dissolved gases, transport of food, transport of hormones, removal of waste products, defence against infection, preventing blood
Guided teaching hours: 9 hours
 Organising animals and plants Chapter overview Guided teaching hours: 9 hours In this chapter, students will learn about the organisation of animals and plants. They should be able to recognise the components
Organising animals and plants Chapter overview Guided teaching hours: 9 hours In this chapter, students will learn about the organisation of animals and plants. They should be able to recognise the components
TWGHs Chen Zao Men College S3 Biology Teaching Schedule ( )
 TWGHs Chen Zao Men College S3 Biology Teaching Schedule (2015-2016) Date Period Topics Practical / Activities 2/9 4/9 1 Laboratory safety Note taking skills 7/9 20/10 11 Ch 1 Molecules of life Chemicals
TWGHs Chen Zao Men College S3 Biology Teaching Schedule (2015-2016) Date Period Topics Practical / Activities 2/9 4/9 1 Laboratory safety Note taking skills 7/9 20/10 11 Ch 1 Molecules of life Chemicals
Biology 2 Chapter 21 Review
 Biology 2 Chapter 21 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is not a tissue system of vascular plants? a. vascular
Biology 2 Chapter 21 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is not a tissue system of vascular plants? a. vascular
Endocrine Physiology. Introduction to Endocrine Principles
 Endocrine Physiology Introduction to Endocrine Principles There are TWO major groups of hormones Peptide and protein hormones Amine hormones Peptide and protein hormones act through cell membrane receptors
Endocrine Physiology Introduction to Endocrine Principles There are TWO major groups of hormones Peptide and protein hormones Amine hormones Peptide and protein hormones act through cell membrane receptors
Life Science. Structure of a plant; Plants are living organisms just like. animals and humans. Like all living. things they need key things to live;
 6.6.3 Life Science Structure of a plant; Plants are living organisms just like animals and humans. Like all living things they need key things to live; water, sunlight, oxygen and food. Plants are different
6.6.3 Life Science Structure of a plant; Plants are living organisms just like animals and humans. Like all living things they need key things to live; water, sunlight, oxygen and food. Plants are different
Chapter 6: LIST OF PRACTICALS AND APPARATUS:
 Chapter 6: LIST OF PRACTICALS AND APPARATUS: PRACTICALS IX-X Chapter 1: Introduction to Biology 1. Study of different types of bacteria with the help of prepared slides and of Amoeba, Paramecium, Volvox
Chapter 6: LIST OF PRACTICALS AND APPARATUS: PRACTICALS IX-X Chapter 1: Introduction to Biology 1. Study of different types of bacteria with the help of prepared slides and of Amoeba, Paramecium, Volvox
The Science Department Academic Year Year 10 Biology Curriculum Overview
 The Science Department Academic Year 2012-2013 Year 10 Biology Curriculum Overview Subject: Biology Term 1 Year Level: 10 Week Starting date Unit Learning Outcomes In this unit we will. Curriculum links
The Science Department Academic Year 2012-2013 Year 10 Biology Curriculum Overview Subject: Biology Term 1 Year Level: 10 Week Starting date Unit Learning Outcomes In this unit we will. Curriculum links
Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology
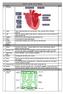 Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant
 Name: Date: Period: CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant Plants are incredible organisms! They can make all their own food from the simple inputs of: Sunlight air (carbon dioxide) water minerals
Name: Date: Period: CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant Plants are incredible organisms! They can make all their own food from the simple inputs of: Sunlight air (carbon dioxide) water minerals
2 sentences. Why your first answer was wrong Why your new answer is correct
 2 sentences Why your first answer was wrong Why your new answer is correct Which biochemical process is outlined in the diagram? A. Anaerobic Respiration B. Aerobic Respiration C. Photosynthesis D. Transpiration
2 sentences Why your first answer was wrong Why your new answer is correct Which biochemical process is outlined in the diagram? A. Anaerobic Respiration B. Aerobic Respiration C. Photosynthesis D. Transpiration
Transportation in Plants
 Transportation in Plants Bell Ringer - 5 Min Why do you need transportation in living organisms? Explain your answer with a suitable example. Water movement through plants How does water move through a
Transportation in Plants Bell Ringer - 5 Min Why do you need transportation in living organisms? Explain your answer with a suitable example. Water movement through plants How does water move through a
Name..Index Number. Candidate s Signature: School... Write your name and index Number in the spaces provided above
 Name..Index Number. Candidate s Signature: School... 231/1 BIOLOGY FORM 4 PAPER 1 TIME:2Hours Instructions to Candidates Write your name and index Number in the spaces provided above Sign and write date
Name..Index Number. Candidate s Signature: School... 231/1 BIOLOGY FORM 4 PAPER 1 TIME:2Hours Instructions to Candidates Write your name and index Number in the spaces provided above Sign and write date
2018 Version. Photosynthesis Junior Science
 2018 Version Photosynthesis Junior Science 1 Plants fill the role of Producers in a community Plants are special because they have leaves and are able to produce their own food by the process of photosynthesis
2018 Version Photosynthesis Junior Science 1 Plants fill the role of Producers in a community Plants are special because they have leaves and are able to produce their own food by the process of photosynthesis
Transport, Storage and Gas Exchange in Flowering Plants
 Sixth Year Biology Transport, Storage and Gas Exchange in Flowering Plants Miss Rochford In this topic: Uptake and transport of: Water and minerals Carbon dioxide Gas exchange Transport of photosynthesis
Sixth Year Biology Transport, Storage and Gas Exchange in Flowering Plants Miss Rochford In this topic: Uptake and transport of: Water and minerals Carbon dioxide Gas exchange Transport of photosynthesis
Year 8: Living World- Functioning Organisms
 Year 8: Living World- Functioning Organisms Revise assumed knowledge: ST3-10LW describes how structural features and other adaptations of living things help them to survive in their environment Check Date
Year 8: Living World- Functioning Organisms Revise assumed knowledge: ST3-10LW describes how structural features and other adaptations of living things help them to survive in their environment Check Date
Plant and animal cells (eukaryotic cells) have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material enclosed in a nucleus.
 4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
Chapter C3: Multicellular Organisms Plants
 Chapter C3: Multicellular Organisms Plants Multicellular Organisms Multicellular organisms have specialized cells of many different types that allow them to grow to a larger size than single-celled organisms.
Chapter C3: Multicellular Organisms Plants Multicellular Organisms Multicellular organisms have specialized cells of many different types that allow them to grow to a larger size than single-celled organisms.
Exchanging Materials in Plants
 Exchanging Materials in Plants 1 of 23 Boardworks Ltd 2012 2 of 23 Boardworks Ltd 2012 3 of 23 Boardworks Ltd 2012 All living things need to exchange materials Plants need to obtain certain materials for
Exchanging Materials in Plants 1 of 23 Boardworks Ltd 2012 2 of 23 Boardworks Ltd 2012 3 of 23 Boardworks Ltd 2012 All living things need to exchange materials Plants need to obtain certain materials for
Paget High School. Preparing for A level Biology
 Paget High School Preparing for A level Biology You will need a copy of the Head Start guide above and use it to make notes on the learning outcomes below. Topic areas Learning outcome Describe with the
Paget High School Preparing for A level Biology You will need a copy of the Head Start guide above and use it to make notes on the learning outcomes below. Topic areas Learning outcome Describe with the
Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education (K.C.S.E.)
 Name.. Index No:. 231/1 Candidate s Signature.. BIOLOGY Date: PAPER 1 (THEORY) JULY/AUGUST 2014 TIME: 2 HOURS Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education (K.C.S.E.) 231/1 Biology Paper 1 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
Name.. Index No:. 231/1 Candidate s Signature.. BIOLOGY Date: PAPER 1 (THEORY) JULY/AUGUST 2014 TIME: 2 HOURS Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education (K.C.S.E.) 231/1 Biology Paper 1 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
Introduction to Plant Transport
 Introduction to Plant Transport The algal ancestors of plants were completely immersed in water and dissolved minerals. The adaptation to land involved the differentiation of the plant body into roots,
Introduction to Plant Transport The algal ancestors of plants were completely immersed in water and dissolved minerals. The adaptation to land involved the differentiation of the plant body into roots,
PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY)
 PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY) provides a thorough revision for students taking the GCE O-Level Science (Biology) Examination. Past examination questions have been carefully classified into
PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY) provides a thorough revision for students taking the GCE O-Level Science (Biology) Examination. Past examination questions have been carefully classified into
Topic 2 notes Organisms and energy
 Topic 2 notes Organisms and energy AEROBIC RESPIRATION All cells in the body need energy - this energy is released in a process known as respiration Cells that are more active need more energy - e.g during
Topic 2 notes Organisms and energy AEROBIC RESPIRATION All cells in the body need energy - this energy is released in a process known as respiration Cells that are more active need more energy - e.g during
Unit B: Cells and Systems
 Unit B: Cells and Systems Topic 4: Fluid Movement in Cells The Cell Membrane A cell membrane allows some to enter or leave the cell, while stopping other substances. It is a selectively membrane. (A permeable
Unit B: Cells and Systems Topic 4: Fluid Movement in Cells The Cell Membrane A cell membrane allows some to enter or leave the cell, while stopping other substances. It is a selectively membrane. (A permeable
Stewards Pooi Kei College Secondary 3 Biology Teaching Schedule ( )
 Stewards Pooi Kei College Secondary Biology Teaching Schedule (009-010) Subject Teachers: KSit (Form coordinator), WChiang, SLee /10-day Cycle: Cycles 1 (1/9 11/9) Teaching Topics/Content Ch. 1 Introducing
Stewards Pooi Kei College Secondary Biology Teaching Schedule (009-010) Subject Teachers: KSit (Form coordinator), WChiang, SLee /10-day Cycle: Cycles 1 (1/9 11/9) Teaching Topics/Content Ch. 1 Introducing
Bio Factsheet. Transport in Plants. Number 342
 Number 342 Transport in Plants This Factsheet: Explains why plants need a transport system Describes what plants transport Describes the tissues which carry out transport Outlines the position of the xylem
Number 342 Transport in Plants This Factsheet: Explains why plants need a transport system Describes what plants transport Describes the tissues which carry out transport Outlines the position of the xylem
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN ANIMALS
 GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN ANIMALS The majority of animals need oxygen in order to oxidize the organic materials and produce energy for cellular activities. The oxidation of the food not only yields energy but
GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN ANIMALS The majority of animals need oxygen in order to oxidize the organic materials and produce energy for cellular activities. The oxidation of the food not only yields energy but
Introduction to Plant Transport
 Introduction to Plant Transport The algal ancestors of plants were completely immersed in water and dissolved minerals. The adaptation to land involved the differentiation of the plant body into roots,
Introduction to Plant Transport The algal ancestors of plants were completely immersed in water and dissolved minerals. The adaptation to land involved the differentiation of the plant body into roots,
The three principal organs of seed plants are roots, stems, and leaves.
 23 1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure The three principal organs of seed plants are roots, stems, and leaves. 1 of 34 23 1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure Roots: absorb
23 1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure The three principal organs of seed plants are roots, stems, and leaves. 1 of 34 23 1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure Roots: absorb
Transport in Plants (Ch. 23.5)
 Transport in Plants (Ch. 23.5) Transport in plants H 2 O & minerals transport in xylem Transpiration Adhesion, cohesion & Evaporation Sugars transport in phloem bulk flow Gas exchange photosynthesis CO
Transport in Plants (Ch. 23.5) Transport in plants H 2 O & minerals transport in xylem Transpiration Adhesion, cohesion & Evaporation Sugars transport in phloem bulk flow Gas exchange photosynthesis CO
Recap. Waxy layer which protects the plant & conserves water. Contains chloroplasts: Specialized for light absorption.
 Recap Contains chloroplasts: Specialized for light absorption Waxy layer which protects the plant & conserves water mesophyll Layer contains air spaces: Specialized for gas exchange Vascular Tissue Exchange
Recap Contains chloroplasts: Specialized for light absorption Waxy layer which protects the plant & conserves water mesophyll Layer contains air spaces: Specialized for gas exchange Vascular Tissue Exchange
Internal Adaptations
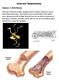 Station 1: Bird Bones Internal Adaptations The bones of birds have hollow openings inside. Therefore, bird bones are less dense than human bones. These hollow spaces cause the bird to have lighter mass,
Station 1: Bird Bones Internal Adaptations The bones of birds have hollow openings inside. Therefore, bird bones are less dense than human bones. These hollow spaces cause the bird to have lighter mass,
Name # Class Date Regents Review: Cells & Cell Transport
 Name # Class Date Regents Review: Cells & Cell Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma
Name # Class Date Regents Review: Cells & Cell Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma
Behavioral and Structural Adaptations PPT Guided Notes
 A Essential Standard 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms accomplish the following life functions through adaptations with particular environments and that these adaptations have evolved to ensure survival
A Essential Standard 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms accomplish the following life functions through adaptations with particular environments and that these adaptations have evolved to ensure survival
Page 1. Name: UNIT: PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND RESPIRATION TOPIC: PHOTOSYNTHESIS
 Name: 4667-1 - Page 1 UNIT: PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND RESPIRATION TOPIC: PHOTOSYNTHESIS 1) The diagram below illustrates the movement of materials involved in a process that is vital for the energy needs of organisms.
Name: 4667-1 - Page 1 UNIT: PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND RESPIRATION TOPIC: PHOTOSYNTHESIS 1) The diagram below illustrates the movement of materials involved in a process that is vital for the energy needs of organisms.
fr>uafcji *> \E % jw r"'''f^,""'i;- ~^H^^
 NAME DATE Carolina Transpiration Kit for AP Biology Imagine that your family has received a bouquet of cut flowers as a gift. You place the flowers in a vase with a small volume of water, and return the
NAME DATE Carolina Transpiration Kit for AP Biology Imagine that your family has received a bouquet of cut flowers as a gift. You place the flowers in a vase with a small volume of water, and return the
LEAF STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
 Name Class Date LEAF STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Plants are incredible organisms! They can make all their own food from the simple inputs of: sunlight carbon dioxide water minerals This biological wizardry is
Name Class Date LEAF STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Plants are incredible organisms! They can make all their own food from the simple inputs of: sunlight carbon dioxide water minerals This biological wizardry is
What factors, including environmental variables, affect the rate of transpiration in plants?
 Big Idea 4 Interactions investigation 11 TRANSPIRATION* What factors, including environmental variables, affect the rate of transpiration in plants? BACKGROUND Cells and organisms must exchange matter
Big Idea 4 Interactions investigation 11 TRANSPIRATION* What factors, including environmental variables, affect the rate of transpiration in plants? BACKGROUND Cells and organisms must exchange matter
Investigation 11 Transpiration
 Introduction What factors, including environmental variables, affect the rate of transpiration in plants? Background Cells and organisms must exchange matter with the environment to grow, reproduce, and
Introduction What factors, including environmental variables, affect the rate of transpiration in plants? Background Cells and organisms must exchange matter with the environment to grow, reproduce, and
UNIQUE SCIENCE ACADEMY
 1 (a) UNIQUE SCIENCE ACADEMY Test (Unit 7) Name :... Paper: Biolog y Date :... Code: 5090 Class: CII Time Allowed: 35Minutes Maximum Marks: 25 1 Theory Section: [Total 18 Marks] Translocation and transpiration
1 (a) UNIQUE SCIENCE ACADEMY Test (Unit 7) Name :... Paper: Biolog y Date :... Code: 5090 Class: CII Time Allowed: 35Minutes Maximum Marks: 25 1 Theory Section: [Total 18 Marks] Translocation and transpiration
Name the tube-like tissue found in part C in which water moves. Name the cells which are responsible for controlling the size of the opening at Z
 Past Questions on Plant Structure Note: You need to be able to draw and label all the diagrams in this worksheet for your exam. Name the parts labelled B, C and E. C E Give one main function each for the
Past Questions on Plant Structure Note: You need to be able to draw and label all the diagrams in this worksheet for your exam. Name the parts labelled B, C and E. C E Give one main function each for the
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/01 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 2004 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet Soft
UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/01 Paper 1 Multiple hoice May/June 2004 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet Soft
Organs and leaf structure
 Organs and leaf structure Different types of tissues are arranged together to form organs. Structure: 2 parts (Petiole and Leaf Blade) Thin flat blade, large surface area Leaves contain all 3 types of
Organs and leaf structure Different types of tissues are arranged together to form organs. Structure: 2 parts (Petiole and Leaf Blade) Thin flat blade, large surface area Leaves contain all 3 types of
GRADE 7: Life science 4. UNIT 7L.4 7 hours. Growing plants. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning. Expectations
 GRADE 7: Life science 4 Growing plants UNIT 7L.4 7 hours About this unit This unit is the fourth of six units on life science for Grade 7. This unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of lessons
GRADE 7: Life science 4 Growing plants UNIT 7L.4 7 hours About this unit This unit is the fourth of six units on life science for Grade 7. This unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of lessons
CELL PRACTICE TEST
 Name: Date: 1. As a human red blood cell matures, it loses its nucleus. As a result of this loss, a mature red blood cell lacks the ability to (1) take in material from the blood (2) release hormones to
Name: Date: 1. As a human red blood cell matures, it loses its nucleus. As a result of this loss, a mature red blood cell lacks the ability to (1) take in material from the blood (2) release hormones to
BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (TELANGANA) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH CLASS BIOLOGY MODEL PAPER PAPER - II (ENGLISH VERSION)
 BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (TELANGANA) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH CLASS BIOLOGY MODEL PAPER PAPER - II (ENGLISH VERSION) Time: 2 hrs. 45 mins. PART - A& B Max. Marks: 40 i) In the time duration of
BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (TELANGANA) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - I TENTH CLASS BIOLOGY MODEL PAPER PAPER - II (ENGLISH VERSION) Time: 2 hrs. 45 mins. PART - A& B Max. Marks: 40 i) In the time duration of
Tissues and organs PART 2
 Tissues and organs PART 2 The structure and function of the mesophytic leaf (a plant organ) The mesopyhtic leaf (lives in a moderately moist environment) contains 7 layers of tissue: 1. Upper epidermis
Tissues and organs PART 2 The structure and function of the mesophytic leaf (a plant organ) The mesopyhtic leaf (lives in a moderately moist environment) contains 7 layers of tissue: 1. Upper epidermis
ST. FRANCIS SECONDARY SCHOOL Annual Exam 2017 BIOLOGY
 ST. FRANCIS SECONDARY SCHOOL Annual Exam 2017 BIOLOGY NAME: FORM: TIME: 2 Hours Section A: Section A answer ALL questions. This section carries 50 marks. Section B: Section B answer BOTH questions. This
ST. FRANCIS SECONDARY SCHOOL Annual Exam 2017 BIOLOGY NAME: FORM: TIME: 2 Hours Section A: Section A answer ALL questions. This section carries 50 marks. Section B: Section B answer BOTH questions. This
Chapter 35 Regulation and Transport in Plants
 Chapter 35 Regulation and Remember what plants need Photosynthesis light reactions Calvin cycle light sun H 2 O ground CO 2 air What structures have plants evolved to supply these needs? Interdependent
Chapter 35 Regulation and Remember what plants need Photosynthesis light reactions Calvin cycle light sun H 2 O ground CO 2 air What structures have plants evolved to supply these needs? Interdependent
Grading Scheme 2 nd, Semester Tests 30% Quizzes 15% Labs 10% Assignments 10% Exam 30% Participation 5%
 San Pedro High School San Pedro Town Belize District Telefax: 226-2045 Email Address: esantizo@sphs.edu.bz 4 th Form BIOLOGY YEARLY CURRICULUM Text: BIOLOGY FOR CXC Credit Hours: 5 Teacher: Mr. Erick Santizo
San Pedro High School San Pedro Town Belize District Telefax: 226-2045 Email Address: esantizo@sphs.edu.bz 4 th Form BIOLOGY YEARLY CURRICULUM Text: BIOLOGY FOR CXC Credit Hours: 5 Teacher: Mr. Erick Santizo
AP Biology Chapter 36
 Chapter 36 Chapter 36 Transport in Plants 2006-2007 Transport in plants - Overview H2O & minerals transport in xylem transpiration evaporation, adhesion & cohesion negative pressure Sugars transport in
Chapter 36 Chapter 36 Transport in Plants 2006-2007 Transport in plants - Overview H2O & minerals transport in xylem transpiration evaporation, adhesion & cohesion negative pressure Sugars transport in
Unit 1 Plants - Extra Worksheets
 Unit 1 Plants - Extra Worksheets 1 Complete the sentences using the words in the box. Plants can make their own using light from the. They also need carbon gas and. 2 Label the parts of the diagram to
Unit 1 Plants - Extra Worksheets 1 Complete the sentences using the words in the box. Plants can make their own using light from the. They also need carbon gas and. 2 Label the parts of the diagram to
Main Topic Sub-topics Students should be able to R O G
 Second Year Science Syllabus Biology Revision Check-list Where is your learning at? Green: I know it all. Orange: I have some idea check the answers. Red: I need to start studying this section. Main Topic
Second Year Science Syllabus Biology Revision Check-list Where is your learning at? Green: I know it all. Orange: I have some idea check the answers. Red: I need to start studying this section. Main Topic
active transport active transport support
 1 Which row matches the cell membrane and cell wall of a palisade cell to their functions? cell membrane active transport active transport support support cell wall active transport support active transport
1 Which row matches the cell membrane and cell wall of a palisade cell to their functions? cell membrane active transport active transport support support cell wall active transport support active transport
Chapter 3.2 The organisation of multicellular organisms
 biology sample book.indd 25 28/06/2016 7:49:20 PM TOPIC 3 MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS Chapter 3.2 The organisation of multicellular organisms Understanding Multicellular organisms have a hierarchical structural
biology sample book.indd 25 28/06/2016 7:49:20 PM TOPIC 3 MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS Chapter 3.2 The organisation of multicellular organisms Understanding Multicellular organisms have a hierarchical structural
Lab 3: Transpiration. 1 Purpose. BIO124 Plant Science Lab 3 Transpiration 1
 1 Purpose The goals of this lab are to (1) observe water movement against gravity from stems to leaves of plants and (2) investigate environmental factors that regulate the rate of transpiration. Introduction
1 Purpose The goals of this lab are to (1) observe water movement against gravity from stems to leaves of plants and (2) investigate environmental factors that regulate the rate of transpiration. Introduction
PLANT Labs summary questions (30 pts)
 PLANT Labs summary questions (30 pts) 1. SEEDS--Without this part of the seed, the embryo has no food to grow before photosynthesis. a. seed coat b. embryo c. leaves d. cotyledon e. tap root 2. SEEDS--Which
PLANT Labs summary questions (30 pts) 1. SEEDS--Without this part of the seed, the embryo has no food to grow before photosynthesis. a. seed coat b. embryo c. leaves d. cotyledon e. tap root 2. SEEDS--Which
Nonvascular Plants mosses, liverworts and hornworts are nonvascular plants. These lack vascular tissue which is a system of tubes that transport
 Nonvascular Plants mosses, liverworts and hornworts are nonvascular plants. These lack vascular tissue which is a system of tubes that transport food, water and minerals throughout the plant. Water and
Nonvascular Plants mosses, liverworts and hornworts are nonvascular plants. These lack vascular tissue which is a system of tubes that transport food, water and minerals throughout the plant. Water and
AP Biology Transpiration and Stomata
 AP Biology Transpiration and Stomata Living things must exchange matter with the environment to survive, Example: Gas Exchange in Plants photosynthesis cellular respiration 1. During which hours does a
AP Biology Transpiration and Stomata Living things must exchange matter with the environment to survive, Example: Gas Exchange in Plants photosynthesis cellular respiration 1. During which hours does a
Year 8: Living World- Functioning Organisms.
 Year 8: Living World- Functioning Organisms. Revise assumed knowledge: ST3-10LW describes how structural features and other adaptations of living things help them to survive in their environment Check
Year 8: Living World- Functioning Organisms. Revise assumed knowledge: ST3-10LW describes how structural features and other adaptations of living things help them to survive in their environment Check
Maintaining a balance
 Gill Sans Bold Biology HSC Course Stage 6 Maintaining a balance Part 4: Transport in plants IncorporatingOctober2002 AMENDMENTS Gill Sans Bold Contents Introduction...2 Movement of materials in plants...3
Gill Sans Bold Biology HSC Course Stage 6 Maintaining a balance Part 4: Transport in plants IncorporatingOctober2002 AMENDMENTS Gill Sans Bold Contents Introduction...2 Movement of materials in plants...3
Gas Exchange 3/26/12. Biology: life study of. What is Life? Ch. 44 pg Properties of Life Cellular Structure: the unit of life, one or many
 Biology: life study of What is Life? Properties of Life Cellular Structure: the unit of life, one or many Metabolism: photosynthesis, respiration, fermentation, digestion, gas exchange, secretion, excretion,
Biology: life study of What is Life? Properties of Life Cellular Structure: the unit of life, one or many Metabolism: photosynthesis, respiration, fermentation, digestion, gas exchange, secretion, excretion,
Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes
 Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes Life Processes All living things do all seven of the life processes. Things that are not living may do some but do not do all seven of the life processes. These are: Movement
Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes Life Processes All living things do all seven of the life processes. Things that are not living may do some but do not do all seven of the life processes. These are: Movement
adaptation a structure, feature, or behavior that helps an organism survive and/or reproduce (IG)
 FOSS Living Systems Module Glossary 3 rd Edition 2012 adaptation a structure, feature, or behavior that helps an organism survive and/or reproduce (IG) algae a large plantlike group of water organisms
FOSS Living Systems Module Glossary 3 rd Edition 2012 adaptation a structure, feature, or behavior that helps an organism survive and/or reproduce (IG) algae a large plantlike group of water organisms
- know that in multi-cellular organisms cells are massed together to form tissues, and tissues can be massed together to form organs
 Science Age 12-13 (A) BIOLOGY: ORGANISMS, THEIR BEHAVIOUR AND THE ENVIRONMENT 1. Cells and their functions - know that in multi-cellular organisms cells are massed together to form tissues, and tissues
Science Age 12-13 (A) BIOLOGY: ORGANISMS, THEIR BEHAVIOUR AND THE ENVIRONMENT 1. Cells and their functions - know that in multi-cellular organisms cells are massed together to form tissues, and tissues
Slide 1 / Arrange the following in order from least complex to most complex: organ, tissue, cell, organism, organ system.
 Slide 1 / 64 1 Arrange the following in order from least complex to most complex: organ, tissue, cell, organism, organ system. Slide 2 / 64 2 List the four major groups of tissues in animals. Slide 3 /
Slide 1 / 64 1 Arrange the following in order from least complex to most complex: organ, tissue, cell, organism, organ system. Slide 2 / 64 2 List the four major groups of tissues in animals. Slide 3 /
Plant and animal cells (eukaryotic cells) have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material enclosed in a nucleus.
 4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
Chapter. Transport in. Structure of. 1- Epidermis: 2- Cortex: All plants 2- a specialized. In higher moving by. hydra and. with cuticles) 1-2-
 Chapter 2 Transport in living organisms The concept of transport and the need for it: All plants need CO 2, water and mineral salts to perform photosynthesis In primitive plants such as algae these materials
Chapter 2 Transport in living organisms The concept of transport and the need for it: All plants need CO 2, water and mineral salts to perform photosynthesis In primitive plants such as algae these materials
3 Movement of substances in living organisms
 Mark schemes Movement of substances in living organisms Using and interpreting data a) (0 to 0 minutes) () decrease (in CO ) () carbon dioxide used in photosynthesis (0 to 0 minutes) () (steep) rise then
Mark schemes Movement of substances in living organisms Using and interpreting data a) (0 to 0 minutes) () decrease (in CO ) () carbon dioxide used in photosynthesis (0 to 0 minutes) () (steep) rise then
Transport of substances in plants
 Transport of substances in plants We have already looked at why many organisms need transport systems with special reference to surface area and volume. The larger the volume : surface area ratio, the
Transport of substances in plants We have already looked at why many organisms need transport systems with special reference to surface area and volume. The larger the volume : surface area ratio, the
CHAPTER TRANSPORT
 CHAPTER 2 2.4 TRANSPORT Uptake of CO2 FOCUS: Uptake and transport of water and mineral salts Transport of organic substances Physical forces drive the transport of materials in plants over a range of distances
CHAPTER 2 2.4 TRANSPORT Uptake of CO2 FOCUS: Uptake and transport of water and mineral salts Transport of organic substances Physical forces drive the transport of materials in plants over a range of distances
1. Cell Theory Organelle containing the genetic information of the cell.
 GLOSSARY MATCHING GAME The words and definitions are all mixed up. Cut out each word and definition and glue the correct matches into your workbook. Word Definition 1. Cell Theory Organelle containing
GLOSSARY MATCHING GAME The words and definitions are all mixed up. Cut out each word and definition and glue the correct matches into your workbook. Word Definition 1. Cell Theory Organelle containing
Water and Food Transportation
 Water and Food Transportation Sugars in a Plant Sugar Form Location in Plant Organ Function of Sugar form Glucose Leaf Energy (made in photosynthesis summer, used in cellular respiration for growth-spring)
Water and Food Transportation Sugars in a Plant Sugar Form Location in Plant Organ Function of Sugar form Glucose Leaf Energy (made in photosynthesis summer, used in cellular respiration for growth-spring)
Biology 5094 O Level 2013 Answers Scheme
 Biology 5094 O Level 2013 Answers Scheme Paper 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 B C C D D A D C D C 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 C D A A D B C C B D 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 D B A C B B B A B B 31 32 33 34
Biology 5094 O Level 2013 Answers Scheme Paper 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 B C C D D A D C D C 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 C D A A D B C C B D 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 D B A C B B B A B B 31 32 33 34
Key Plant Unit Test Multiple Choice
 Plant Unit Test Multiple Choice For questions 1 25, circle the letter of the best answer from the choices provided. (2 pts each) For questions 1 3, refer to the diagram of the plant cell below: A B C D
Plant Unit Test Multiple Choice For questions 1 25, circle the letter of the best answer from the choices provided. (2 pts each) For questions 1 3, refer to the diagram of the plant cell below: A B C D
PLANT STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Read pages Re-read and then complete the questions below.
 PLANT STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Read pages 600-602. Re-read and then complete the questions below. 1. PLANT TISSUES - plant tissues are made up of 3 basic cell types: Parenchyma, Collenchyma or Sclerenchyma
PLANT STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Read pages 600-602. Re-read and then complete the questions below. 1. PLANT TISSUES - plant tissues are made up of 3 basic cell types: Parenchyma, Collenchyma or Sclerenchyma
Scheme of work Cambridge IGCSE Biology (0610)
 Scheme of work Cambridge IGCSE Biology (0610) Unit 3: Plant nutrition and transport Recommended prior knowledge Students should have a basic knowledge of carbohydrates and proteins and their uses within
Scheme of work Cambridge IGCSE Biology (0610) Unit 3: Plant nutrition and transport Recommended prior knowledge Students should have a basic knowledge of carbohydrates and proteins and their uses within
ARIF ULLAH ITHS
 SUMMARY Feature of xylem and phloem and their role. Distribution of xylem and phloem (vascular bundles) in stem and root of dicotyledonous plants. Transport of water from the root to the atmosphere through
SUMMARY Feature of xylem and phloem and their role. Distribution of xylem and phloem (vascular bundles) in stem and root of dicotyledonous plants. Transport of water from the root to the atmosphere through
Chapter 2 1. Using an annotated diagram, describe the structure of a plant cell. (12 marks)
 Essays Chapter 2 1. Using an annotated diagram, describe the structure of a plant cell. 2. Compare and contrast the structure of prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. 3. Describe the correct procedures
Essays Chapter 2 1. Using an annotated diagram, describe the structure of a plant cell. 2. Compare and contrast the structure of prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. 3. Describe the correct procedures
The table lists some functions of parts of a plant. Match the part of the plant (A, B, C or D) to its function by writing the letters in the table.
 Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows a flowering plant. A Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D. (c) (d) B C D A... B C... D [4] The table lists some functions of parts of a plant. Match
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows a flowering plant. A Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D. (c) (d) B C D A... B C... D [4] The table lists some functions of parts of a plant. Match
OCR Biology Checklist
 Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
OCR Biology Checklist
 Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Gill Sans Bold. Biology Preliminary Course Stage 6. Patterns in nature. Part 5: Obtaining and transporting materials in plants
 Biology Preliminary Course Stage 6 Patterns in nature Part 5: Obtaining and transporting materials in plants IncorporatingOctober2002 AMENDMENTS Contents Introduction... 2 Autotrophic and heterotrophic
Biology Preliminary Course Stage 6 Patterns in nature Part 5: Obtaining and transporting materials in plants IncorporatingOctober2002 AMENDMENTS Contents Introduction... 2 Autotrophic and heterotrophic
NABTEB Past Questions and Answers - Uploaded online
 NATIONAL BUSINESS AND TECHNICAL EXAMINATIONS BOARD PART I INTRODUCTORY BIOLOGY 1. (i) Define the term Osmosis. 2006 MAY/JUNE NBC/NTC EXAMINATIONS 006-1 BIOLOGY (ESSAY) Osmosis is the movement of water
NATIONAL BUSINESS AND TECHNICAL EXAMINATIONS BOARD PART I INTRODUCTORY BIOLOGY 1. (i) Define the term Osmosis. 2006 MAY/JUNE NBC/NTC EXAMINATIONS 006-1 BIOLOGY (ESSAY) Osmosis is the movement of water
6 Plant Nutrition. Question Paper. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Plant Nutrition Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Unit ooklet IGSE iology ambridge International Examinations 6 Plant Nutrition
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Plant Nutrition Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Unit ooklet IGSE iology ambridge International Examinations 6 Plant Nutrition
Laboratory 9: Transpiration
 Laboratory 9: Transpiration YOU MUST KNOW The role of water potential and transpiration in the movement of water from roots to leaves. The effects of various environmental conditions on the rate of transpiration.
Laboratory 9: Transpiration YOU MUST KNOW The role of water potential and transpiration in the movement of water from roots to leaves. The effects of various environmental conditions on the rate of transpiration.
Two major categories. BIOLOGY 189 Fundamentals of Life Sciences. Spring 2004 Plant Structure and Function. Plant Structure and Function
 BIOLOGY 189 Fundamentals of Life Sciences Spring 2004 Plant Structure and Function 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 Examination #1 Class Average: 33/60 for 55% 4 Chapters 31-32 32 2 0 6 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55
BIOLOGY 189 Fundamentals of Life Sciences Spring 2004 Plant Structure and Function 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 Examination #1 Class Average: 33/60 for 55% 4 Chapters 31-32 32 2 0 6 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55
Name Period Date Science 7R - Marking Period 3 Review SCIENTIFIC METHOD 1. What are the steps of the scientific method?
 Name Period Date Science 7R - Marking Period 3 Review SCIENTIFIC METHOD 1. What are the steps of the scientific method? 2. What is meant by State the Problem? 3. What is a hypothesis? 4. In which step
Name Period Date Science 7R - Marking Period 3 Review SCIENTIFIC METHOD 1. What are the steps of the scientific method? 2. What is meant by State the Problem? 3. What is a hypothesis? 4. In which step
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science
 IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Biology 4.2 - Plant Nutrition Photosynthesis You need to know the definition of photosynthesis as: the fundamental process by which plants manufacture carbohydrates
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Biology 4.2 - Plant Nutrition Photosynthesis You need to know the definition of photosynthesis as: the fundamental process by which plants manufacture carbohydrates
DAY 1 Leaf Structure
 DAY 1 Leaf Structure Design a Leaf!! What would be the best structure for a leaf to carry out its major function PHOTOSYNTHESIS!!!??? Place the following in order from the top of the leaf to the bottom.
DAY 1 Leaf Structure Design a Leaf!! What would be the best structure for a leaf to carry out its major function PHOTOSYNTHESIS!!!??? Place the following in order from the top of the leaf to the bottom.
screw clip air bubble Transpiration itself is not measured directly by a potometer....
 1. Transpiration is the loss of water from plants by evaporation. The diagram below shows a potometer, an apparatus used to estimate transpiration rates. water reservoir leafy shoot screw clip air bubble
1. Transpiration is the loss of water from plants by evaporation. The diagram below shows a potometer, an apparatus used to estimate transpiration rates. water reservoir leafy shoot screw clip air bubble
Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true.
 Unit 4 Review Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 1. A stimulus is anything that threatens the
Unit 4 Review Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 1. A stimulus is anything that threatens the
8.L.5.1 Practice Questions
 Name: ate: 1. The diagram below represents a series of events that occur in living cells. Which molecule is indicated by X?. glucose. TP. carbon dioxide. protein 2. The diagram represents one metabolic
Name: ate: 1. The diagram below represents a series of events that occur in living cells. Which molecule is indicated by X?. glucose. TP. carbon dioxide. protein 2. The diagram represents one metabolic
PLANT PHYSIOLOGY B 4 WATER RELATIONS OF PLANTS (10 MARKS) B 5 BIOENERGETICS (12 MARKS) B 6 GROWTH AND GROWTH REGULATORS IN PLANTS
 TOPICS PLANT PHYSIOLOGY B 4 WATER RELATIONS OF PLANTS (10 MARKS) B 5 BIOENERGETICS (12 MARKS) B 6 GROWTH AND GROWTH REGULATORS IN PLANTS (05MARKS) B.4 WATER RELATIONS OF PLANTS (10 marks) IMBIBITION,DIFFUSION,OSMOSIS
TOPICS PLANT PHYSIOLOGY B 4 WATER RELATIONS OF PLANTS (10 MARKS) B 5 BIOENERGETICS (12 MARKS) B 6 GROWTH AND GROWTH REGULATORS IN PLANTS (05MARKS) B.4 WATER RELATIONS OF PLANTS (10 marks) IMBIBITION,DIFFUSION,OSMOSIS
SEKOLAH MENENGAH LAKI-LAKI METHODIST, K.L TEACHING & LESSONS PLAN BIOLOGY FORM SIX SECOND TERM 2017 TOPICS/THEMES LEARNING OUTCOMES TEACHING AIDS
 SEKOLAH MENENGAH LAKI-LAKI METHODIST, K.L TEACHING & LESSONS PLAN BIOLOGY FORM SIX SECOND TERM 017 1 SECOND TERM: PHYSIOLOGY Week days 7 Gas Exchange 1 Candidates should be able to: 1 Jan 6 Jan 7.1 Gaseous
SEKOLAH MENENGAH LAKI-LAKI METHODIST, K.L TEACHING & LESSONS PLAN BIOLOGY FORM SIX SECOND TERM 017 1 SECOND TERM: PHYSIOLOGY Week days 7 Gas Exchange 1 Candidates should be able to: 1 Jan 6 Jan 7.1 Gaseous
Which farm is likely to have been using too much fertiliser on its land? farm C. farm B
 1 What is produced by anaerobic respiration in yeast? lactic acid carbon dioxide 2 What is the word equation for aerobic respiration in plants? carbon dioxide + water glucose + oxygen glucose + carbon
1 What is produced by anaerobic respiration in yeast? lactic acid carbon dioxide 2 What is the word equation for aerobic respiration in plants? carbon dioxide + water glucose + oxygen glucose + carbon
