HOW TO RECOGNIZE AN INSECT?
|
|
|
- Ashlie Jones
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
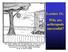
1 HOW TO RECOGNIZE AN INSECT? EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVES AND CONTENT In this activity, students use their observational skills to discover the characteristics of insects. ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE Matter: Organization of living things: classification of life forms (animals); anatomy of animals (parts) Techniques and instrumentation: Use of simple observational instruments Appropriate language: Terminology related to an understanding of living things Tables Drawings, sketches SUGGESTED MATERIALS Scientific equipment: Prepared insect slides Mounted insect specimens Binocular magnifiers Magnifying glasses Microscopes Small terrariums Images of insects and other arthropods Perishable scientific materials: Live or frozen insects Other living or frozen arthropods Household materials: Empty pill bottles with lids Note: It is recommended to leave specimens that will be placed on slides in the freezer for several days to make them easier to cut. CONTEXT: SITUATIONAL PROBLEM OR RESEARCH QUESTION Bzzz bzzz You can t get to sleep because a mosquito is in your room buzzing around your ears. Ah bugs! They re everywhere. But do you really know them? Are all little creatures insects? How can you find out what characterizes real insects so you can recognize them easily? ÉCLAIRS DE SCIENCES GUIDE 1
2 SUGGESTED PREPARATORY ACTIVITIES (INTRODUCTION) The teacher begins a discussion on insects, asking the students to create a list of the characteristics that distinguish them from other animal groups. The students could also name insects they know and check whether they conform to the listed criteria. If it s the right season, the students could be asked to collect a few specimens and bring them to school to examine them. Insects can also be purchased from certain pet stores specializing in exotic animals. The teacher then has the students observe the anatomical differences between several species. INITIAL IDEAS AND HYPOTHESES Here are a few examples of hypotheses the students might formulate based on their initial ideas: Example 1 I predict that insects always have six legs, while other bugs have more. I predict this because ants, which are insects, have six legs, and spiders, which are not insects, have eight. Example 2 I predict that different insects have differently shaped legs. I predict this because I once watched crickets jump and I noticed that they have large hind legs, while mosquitoes have very small legs. Example 3 I predict that the shape of an insect s mouth depends on what it eats. I predict this because I have seen butterflies unroll their proboscis to drink nectar from flowers. Example 4 I predict that I can group insects into families just by observing their common characteristics (stripes, number of wings and wing shape, etc.) I predict this because some insects look very similar to each other, while others are very different. WORK PLAN AND EXPERIMENTATION Here are a few examples of experiments the students can carry out to verify their hypotheses: Example A The students compare the anatomy of insects to that of other bugs (arthropods) using complete specimens (dead or living). They determine the characteristics of each specimen: number of legs, body divisions, number of wings, presence of antennae, soft or hard body, etc. They record their observations and try to classify the arthropods into different groups according to their common characteristics RECORD ALL YOUR IDEAS AND OBSERVATIONS IN YOUR EXPERIMENT WORKBOOK. 2 ÉCLAIRS DE SCIENCES GUIDE
3 Example B The students use a microscope or binocular magnifiers to observe and compare the form of the legs of several insects on pre-mounted slides. They sketch each type of leg. Note: The students could also decide to observe the shape of the antennae or wings. Example C The students select live insects from terrariums to observe their mouthparts. A few dead specimens can be observed more closely with a magnifying glass or binocular magnifier. The students draw the different mouthparts and try to associate them to the foods the insects eat. To validate their discoveries, they can complement their experience with documentary research. Example D The students select several pre-identified insects and observe them closely under a magnifying glass. They decide on which classification criteria they want to use: number of wings, presence of hard wings, shape of legs, etc. They check identification guides to determine which orders the selected insects belong to and compare their own classification to that of the reference books. DISCUSSION: SUGGESTED INTEGRATION ACTIVITIES (CONSOLIDATION) The teacher has the students report on their observations. Together, they verify and correct the initial list of insect characteristics. The teacher presents images of insects and other arthropods to make sure the students can properly differentiate them. One of the images can be used to identify the different parts of an insect (head, thorax, abdomen, antennae, compound eyes, mouthparts, etc.). SUGGESTED ACTIVITIES FOR APPLYING KNOWLEDGE (APPLICATION) The teacher suggests that the students do supplementary research on one of the insect species or families studied. They find information on the insect s anatomy, range, adaptation, food, reproduction and behavior and present their research in the form of a poster to be hung in the school s hallways. The activity could conclude with a video on the lifecycle of butterflies. EXPERIMENTAL FACTORS To ensure scientific rigor, the students should evaluate the experimental factors that might influence the experimental results. Variety of species Quality of specimens Type of observation instruments Differences among individuals of the same species ÉCLAIRS DE SCIENCES GUIDE 3
4 SCIENTIFIC CONCEPTUAL CONTENT Arthropods The class Insecta is part of the phylum Arthropoda, or arthropods. These animals have an external skeleton (exoskeleton) and jointed limbs. The other classes of arthropods are diplopods (millipedes), chilopods (centipedes), arachnids (spiders and scorpions), and crustaceans (crabs, lobsters, etc.). Characteristics of insects Insects can be distinguished from other arthropods by their body divided into three parts (head, thorax abdomen), the presence of antennae, six legs, and one or two pairs of wings (not always present). Insects are the largest class of animals, accounting for over 75% of all animal species (12 to 15 million species). Only one million of these species have been inventoried and identified. Insects are divided into about 30 different orders, the largest of which is Coleoptera, or beetles, accounting for 40% of all insects. Head The heads of insects have two large compound eyes or one to three simple eyes called ocelli. Compound eyes are made up of many facets (up to 30,000 in certain dragonflies) and allow insects to perceive colors and detect motion. Ocelli only detect light. Some insects, such as bees, can perceive ultraviolet wavelengths. Insects have a pair of antennae with a multitude of shapes. These antennae of often have small hairs called sensilla, which are connected to the central nervous system. Sensilla allow insects to touch, taste and feel. Finally, the head contains the mouth, which is in fact several appendages collectively called the mouthparts. Mouthparts The mouthparts are insects utensils. Many insects use their mandibles to chew their food: praying mantises use them to cut up their prey, caterpillars to masticate plants, and ants to grind up seeds. Other insects consume liquids and have straw-like mouthparts adapted to their needs. Butterflies have a proboscis, a tube through which they suck up nectar from flowers; mosquitoes have a stylet to pierce the skin and aspirate blood, while true bugs have a rostrum to suck the sap of plants and other liquids. Thorax The thorax is where insects six legs and wings are attached. The thorax is divided into three segments, each of which hosts a pair of legs. Legs Insects have six legs that, depending on the species, are used to walk, jump, cling or even skate on water. Equipped with suction cups and tiny claws, the feet of flies allow them to defy gravity and walk on ceilings. The legs of grasshoppers and fleas allow them to jump. Backswimmers use their legs to swim, while water striders use them to glide over the water. The auditory organs of crickets and grasshoppers are located in their legs. Many species of caterpillar have false legs they use to cling to plants. 4 ÉCLAIRS DE SCIENCES GUIDE
5 Wings Most insects have one or two pairs of wings. Lice, fleas and silverfish are apterous, or wingless. Flies have one pair of wings and a pair of halteres (atrophied wings) that help stabilize them in flight. Beetles have two types of wings: membranous wings for flying and hardened forewings, or elytra, which are used as armor and protect their bodies at rest. Butterfly wings are surely the most remarkable. They are covered with rows of small colorful scales. Abdomen Insect abdomens contain several vital organs such as the heart, the viscera and the reproductive system. They also contain spiracles, tiny openings through which air enters the animal s respiratory system. CULTURAL REFERENCES Person Passionate about insects since he was a boy, Georges Brossard (born in 1940) started a career as a notary before he became an entomologist. He has travelled the world for many years searching for insects. In 1990, he founded the Montréal Insectarium, to which he bequeathed 250,000 specimens of his collection. Evolution Insects have been on Earth for about 350 million years. In comparison, human beings (Homo sapiens) is a very young species. We have only existed for about 200,000 years. Detrimental or beneficial? Insects have a vital function in nature. Both predator and prey, they help keep ecosystems in balance. Insects pollinate plants, produce honey, wax and silk, decompose and reuse waste, and control parasites and other pests. On the other hand, some insects are vectors of diseases such as the plague and malaria, and they can destroy crops. However, insects can be used as biological pest control agents. For instance, in farming and forestry, natural predators of pests can be introduced to keep pesticide use to a minimum (e.g., ladybugs eat aphids in fields and greenhouses). FOR MORE CULTURAL REFERENCES, VISIT THE ÉCLAIRS DE SCIENCES WEBSITE: ÉCLAIRS DE SCIENCES GUIDE 5
6 REFERENCES Borror, Donald J. and Richard E. White. Le guide des insectes du Québec et de l Amérique du Nord. Les guides Peterson collection. Boucherville: Éditions Broquet, Dubuc, Yves. Les insectes du Québec, guide d identification. Saint-Constant: Éditions Broquet, Elzinga, Richard J. Fundamentals of Entomology. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall, Hickman, Pamela. Découvrons les insectes. Activités nature collection. Waterloo: Éditions Michel Quintin, Lajoie, Monique and Alain Foisy. Les insectes, 200 questions et réponses. Québec: Les publications du Québec, Mound, Laurence. Le peuple des insectes. Les yeux de la découverte collection. Paris: Éditions Gallimard, Insectarium de Montréal. La toile des insectes du Québec. In Ville de Montréal: Insectarium de Montréal. [Website, 2003] www2.ville.montreal.qc.ca/insectarium/toile/toile.htm. Consulted November 26, Conception Montréal Science Centre A project of Produced by Major financial partners 6 ÉCLAIRS DE SCIENCES GUIDE
7 process of active discovery general learning process in science and technology (in elementary school) Planning and carrying out Context related to everyday life Outcome Initial ideas and hypothesis Situation problem or Discovery question or Need to be fulfilled Question related to the operation of an object (how does it work?) My initial ideas: I share my own ideas. My hypothesis: I predict that... I think that because I imagine my prototype. I think it works like this My equipment: I observe and handle the equipment. How could this equipment be useful to me? I choose my equipment and my materials. Carrying out my process: What will the steps be? What precautions should I take? My actions: I carry out the steps of my protocol. I note or draw what I observe, what I do and what I discover. My results: What is my answer to the problem, question or need? My outcome: Do my results confirm my hypothesis or not? Are my results similar to those of the other teams? Can the other teams' results help me to find answers to my problem, my question or my initial need? What could I communicate concerning my discoveries? New question? What I learned: What do I retain from this activity? What could I communicate concerning my results or my discoveries? 2011 /REV0202EN
*Add to Science Notebook Name 1
 *Add to Science Notebook Name 1 Arthropods, Ch. 13, pg. 374-382 Characteristics of Arthropods *Arthropods are the largest group of animals. *Arthropods have jointed and include,,, and. *Arthropod appendages
*Add to Science Notebook Name 1 Arthropods, Ch. 13, pg. 374-382 Characteristics of Arthropods *Arthropods are the largest group of animals. *Arthropods have jointed and include,,, and. *Arthropod appendages
Arthropods. Ch. 13, pg
 Arthropods Ch. 13, pg. 374-382 382 Arthropods Insects Arachnids Centipedes and Millipedes Crustaceans Characteristics of Arthropods Arthropods have jointed appendages and include legs, antennae, claws,
Arthropods Ch. 13, pg. 374-382 382 Arthropods Insects Arachnids Centipedes and Millipedes Crustaceans Characteristics of Arthropods Arthropods have jointed appendages and include legs, antennae, claws,
World of Insects. Characteristics, Orders, and Collecting
 World of Insects Characteristics, Orders, and Collecting What You Should Know About Insects Taxonomy Kingdom Animalia Phylum Arthropoda Class - Insecta Insects Are Arthropods Insects are the largest group
World of Insects Characteristics, Orders, and Collecting What You Should Know About Insects Taxonomy Kingdom Animalia Phylum Arthropoda Class - Insecta Insects Are Arthropods Insects are the largest group
EXTERNAL ANATOMY OF INSECTS
 External Anatomy of Insects 1 The insect s exoskeleton is made up of a series of plates EXTERNAL ANATOMY OF INSECTS These plates make up the insect s exoskeleton. These plates are connected by joints or
External Anatomy of Insects 1 The insect s exoskeleton is made up of a series of plates EXTERNAL ANATOMY OF INSECTS These plates make up the insect s exoskeleton. These plates are connected by joints or
Arthropoda ARTHRO JOINTED PODA FEET
 Arthropoda ARTHRO JOINTED PODA FEET The arthropods are a group of animals which has attained the greatest biological success largest number of species and individuals and occupy the greatest number of
Arthropoda ARTHRO JOINTED PODA FEET The arthropods are a group of animals which has attained the greatest biological success largest number of species and individuals and occupy the greatest number of
Biology: Get out your packet from yesterday! If you would like to use gloves on Mon and Tues for Dissection PLEASE BRING THEM!!!
 Biology: Get out your packet from yesterday! Today: 5/15/2014 Learning Objectives: *Discuss answers from yesterday Describe the characteristics of animals that belong to the Phylum Arthropoda *Arthropod
Biology: Get out your packet from yesterday! Today: 5/15/2014 Learning Objectives: *Discuss answers from yesterday Describe the characteristics of animals that belong to the Phylum Arthropoda *Arthropod
Who Eats What? Mouthparts and Meals
 Who Eats What? Mouthparts and Meals Essential Question: What do insects eat? Background Information The ecological roles that animals play in their ecosystems or habitats are, for the most part, determined
Who Eats What? Mouthparts and Meals Essential Question: What do insects eat? Background Information The ecological roles that animals play in their ecosystems or habitats are, for the most part, determined
INVERTEBRATES. The Earth and Living Things. Carme Font Casanovas 1
 INVERTEBRATES Living Things. Carme Font Casanovas 1 How many animals can you see? ant rose coral snake anemone fish grass bee Living Things. Carme Font Casanovas 2 Invertebrates There are animals without
INVERTEBRATES Living Things. Carme Font Casanovas 1 How many animals can you see? ant rose coral snake anemone fish grass bee Living Things. Carme Font Casanovas 2 Invertebrates There are animals without
Station 1. Note: There are no samples at this station. 1. True or False: Odonata use their superior flying abilities as a defense.
 Station 1 Note: There are no samples at this station. 1. True or False: Odonata use their superior flying abilities as a defense. 2. What do Orthopterans use for defense? A. Stink glands B. Eye spots C.
Station 1 Note: There are no samples at this station. 1. True or False: Odonata use their superior flying abilities as a defense. 2. What do Orthopterans use for defense? A. Stink glands B. Eye spots C.
Blank paper & clip boards or nature journals Pencils Bug jars/bug boxes & Insect ID sheets/field guides
 LESSON: Catch and Release Insects GRADE: 5 th TIME: 45 min. SUMMARY: A field leader uses introduce students to the definition of insects and different insect groups. Afterwards, students work in groups
LESSON: Catch and Release Insects GRADE: 5 th TIME: 45 min. SUMMARY: A field leader uses introduce students to the definition of insects and different insect groups. Afterwards, students work in groups
Activity: Build a Bug
 Activity: Build a Bug Grade Level: 3 rd -5 th grade Time required: 20 minutes for preparation; 1 hour for activity Subjects covered: Life sciences, Adaptations, and Insects Skills covered: Observation,
Activity: Build a Bug Grade Level: 3 rd -5 th grade Time required: 20 minutes for preparation; 1 hour for activity Subjects covered: Life sciences, Adaptations, and Insects Skills covered: Observation,
LEARN 10 Insect Orders of the Wenatchee Watershed
 LEARN 10 Insect Orders of the Wenatchee Watershed Text and photos by Susan Ballinger. Photos of specimens from the collection of Dr. Robert Gillespie, Wenatchee Valley College Order Odonata dragonflies
LEARN 10 Insect Orders of the Wenatchee Watershed Text and photos by Susan Ballinger. Photos of specimens from the collection of Dr. Robert Gillespie, Wenatchee Valley College Order Odonata dragonflies
Pages in the Montana Master Gardener Handbook
 Insect Identification Pages 309-326 in the Montana Master Gardener Handbook Integrated Pest Management Integrated Pest Management is an effective and environmentally sensitive approach to pest management
Insect Identification Pages 309-326 in the Montana Master Gardener Handbook Integrated Pest Management Integrated Pest Management is an effective and environmentally sensitive approach to pest management
Entomology Review or What s that Bug? Lady Beetle larvae
 Entomology Review or What s that Bug? Lady Beetle larvae pillbugs (crustaceans) spiders, ticks, and Not all bugs are insects. snails (molluscs) spiders (arachnids) centipedes (chilopods) mites (arachnids)
Entomology Review or What s that Bug? Lady Beetle larvae pillbugs (crustaceans) spiders, ticks, and Not all bugs are insects. snails (molluscs) spiders (arachnids) centipedes (chilopods) mites (arachnids)
Season: Spring, summer Grade: Cycle 2, years 1 and 2 (3rd and 4th year) Duration: 60 minutes. Introduction: Guiding Questions:
 Introduction: Insects have existed for millions of years! In fact, the first insects are dated to about 400 million years ago, and they were the first group to develop flight. Since they have been around
Introduction: Insects have existed for millions of years! In fact, the first insects are dated to about 400 million years ago, and they were the first group to develop flight. Since they have been around
Basics of Entomology. Brandi Ashley
 Basics of Entomology Brandi Ashley Entomology Entomology is the study of insects There are more than 100,000 different of species of insects in North America. In the typical yard there can be a 1,000+
Basics of Entomology Brandi Ashley Entomology Entomology is the study of insects There are more than 100,000 different of species of insects in North America. In the typical yard there can be a 1,000+
Beneficial Aspects. Extent and Economic Importance. Entomology For Master Gardeners
 Entomology For Master Gardeners Molly Greenwood Spring 2017 Extent and Economic Importance Major form of higher life Attack all stages of all species Damage equals harvest Beneficial aspects Beneficial
Entomology For Master Gardeners Molly Greenwood Spring 2017 Extent and Economic Importance Major form of higher life Attack all stages of all species Damage equals harvest Beneficial aspects Beneficial
University of Kentucky Department of Entomology Insects in the Classroom: Lesson Plan No. 105
 University of Kentucky Department of Entomology Insects in the Classroom: Lesson Plan No. 105 BENEFICIAL BUG SCAVENGER HUNT Prepared by Blake Newton, Extension Specialist Developed from an activity designed
University of Kentucky Department of Entomology Insects in the Classroom: Lesson Plan No. 105 BENEFICIAL BUG SCAVENGER HUNT Prepared by Blake Newton, Extension Specialist Developed from an activity designed
 www.ugaextension.com 1 General Entomology Susan Ellis, www.insectimages.org Prepared from information written by Dr. Kris Braman, Dr. Beverly Sparks, Dr. David Adams Learning objectives Basic classification
www.ugaextension.com 1 General Entomology Susan Ellis, www.insectimages.org Prepared from information written by Dr. Kris Braman, Dr. Beverly Sparks, Dr. David Adams Learning objectives Basic classification
BEE BODIES HONEY BEE ANATOMY. Essential Question: MATERIALS. Chart Paper Markers Journals, Paper, or Digital Notebooks
 BEE BODIES HONEY BEE ANATOMY LEARNING OBJECTIVES Essential Question: HOW DOES A HONEY BEE S STRUCTURE SUPPORT ITS FUNCTION IN THE ECOSYSTEM? n n n Distinguish between the structural and behavioral adaptations
BEE BODIES HONEY BEE ANATOMY LEARNING OBJECTIVES Essential Question: HOW DOES A HONEY BEE S STRUCTURE SUPPORT ITS FUNCTION IN THE ECOSYSTEM? n n n Distinguish between the structural and behavioral adaptations
BUTTERFLY SCIENCE. 9 Science Activities for PreK, K & EarthsBirthday.org
 BUTTERFLY SCIENCE 9 Science Activities for PreK, K & 1-3 1 800 698 4438 EarthsBirthday.org CONTENTS Butterfly Life Cycle Song 4 Changing Butterfly Dance 5 What Is a Caterpillar? 6 Caterpillar & Pupa Timelines
BUTTERFLY SCIENCE 9 Science Activities for PreK, K & 1-3 1 800 698 4438 EarthsBirthday.org CONTENTS Butterfly Life Cycle Song 4 Changing Butterfly Dance 5 What Is a Caterpillar? 6 Caterpillar & Pupa Timelines
What Bugs you? An Educator s Guide to the Program
 What Bugs you? An Educator s Guide to the Program GRADES: 3-6 PROGRAM DESCRIPTION: This program explores one of the largest groups of arthropods, the insects. At the completion of this program students
What Bugs you? An Educator s Guide to the Program GRADES: 3-6 PROGRAM DESCRIPTION: This program explores one of the largest groups of arthropods, the insects. At the completion of this program students
Lecture 11: Why are arthropods successful?
 Lecture 11: Why are arthropods successful? Goals: 1. Define success 2. Compare insects to other living organisms, understand what insect adaptations have contributed to their success 3. Relate methods
Lecture 11: Why are arthropods successful? Goals: 1. Define success 2. Compare insects to other living organisms, understand what insect adaptations have contributed to their success 3. Relate methods
ARTHROPOD ADVENTURE ASSIGNMENT FOR GROUP LEADER A FEW WEEKS PRIOR TO TRIP:
 ARTHROPOD ADVENTURE ACTIVITY: After a brief review of arthropods...including anatomy, types of arthropods, and types of metamorphosis, the group takes a short walk in the desert discovering arthropods
ARTHROPOD ADVENTURE ACTIVITY: After a brief review of arthropods...including anatomy, types of arthropods, and types of metamorphosis, the group takes a short walk in the desert discovering arthropods
28 3 Insects Slide 1 of 44
 1 of 44 Class Insecta contains more species than any other group of animals. 2 of 44 What Is an Insect? What Is an Insect? Insects have a body divided into three parts head, thorax, and abdomen. Three
1 of 44 Class Insecta contains more species than any other group of animals. 2 of 44 What Is an Insect? What Is an Insect? Insects have a body divided into three parts head, thorax, and abdomen. Three
Name Class Date. Matching On the lines provided, write the letter of the description that best matches each term on the left. 1.
 Chapter 28 Arthropods and Echinoderms Chapter Vocabulary Review Matching On the lines provided, write the letter of the description that best matches each term on the left. 1. thorax a. shedding of the
Chapter 28 Arthropods and Echinoderms Chapter Vocabulary Review Matching On the lines provided, write the letter of the description that best matches each term on the left. 1. thorax a. shedding of the
Activity: Honey Bee Adaptation Grade Level: Major Emphasis: Major Curriculum Area: Related Curriculum Areas: Program Indicator: Student Outcomes:
 Activity: Honey Bee Adaptation Grade Level: Grade 5 Major Emphasis: Invertebrates and Their Environments Major Curriculum Area: Science Related Curriculum Areas: Refer to Outdoor Education Curriculum Matrix
Activity: Honey Bee Adaptation Grade Level: Grade 5 Major Emphasis: Invertebrates and Their Environments Major Curriculum Area: Science Related Curriculum Areas: Refer to Outdoor Education Curriculum Matrix
WHAT DO FOSSILS TELL US?
 ACTIVITY 4 WHAT DO FOSSILS TELL US? EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVES AND CONTENT In this activity, students develop their observational skills and are initiated into the understanding and analysis of the traces left
ACTIVITY 4 WHAT DO FOSSILS TELL US? EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVES AND CONTENT In this activity, students develop their observational skills and are initiated into the understanding and analysis of the traces left
Lesson Plan: Vectors and Venn Diagrams
 Prep Time: Minimal Lesson Plan: Vectors and Venn Diagrams Age Level: Can be modified for any grade Materials Needed: Blank Venn diagrams can be printed for students to complete (included in this document),
Prep Time: Minimal Lesson Plan: Vectors and Venn Diagrams Age Level: Can be modified for any grade Materials Needed: Blank Venn diagrams can be printed for students to complete (included in this document),
Welcome to the 4H Entomology Project!
 Welcome to the 4H Entomology Project! If you re interested in wildlife ---the outdoors? Have you ever thought of insects and their relatives? They are found almost everywhere in the world and occupy many
Welcome to the 4H Entomology Project! If you re interested in wildlife ---the outdoors? Have you ever thought of insects and their relatives? They are found almost everywhere in the world and occupy many
Unit 12 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 12 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 12 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Mollusks. Use Target Reading Skills. b. invertebrate c. segmented body d. unsegmented body
 Name Date Class Mollusks This section descnbes the features of mollusks aud identifies three mapr groups of mollusks. Use Target Reading Skills As vou read, compare and contrast the three groups of mollusks
Name Date Class Mollusks This section descnbes the features of mollusks aud identifies three mapr groups of mollusks. Use Target Reading Skills As vou read, compare and contrast the three groups of mollusks
Entomology. Janet Spencer Extension Agent, ANR Isle of Wight County
 Entomology Janet Spencer Extension Agent, ANR Isle of Wight County Entomology The study of insects Dominant groups of animals on earth today Life on earth: Modern humans=200,000 years Insects=350 million
Entomology Janet Spencer Extension Agent, ANR Isle of Wight County Entomology The study of insects Dominant groups of animals on earth today Life on earth: Modern humans=200,000 years Insects=350 million
Objectives. Teaching Basic Entomology. My questions for you. Anatomy of an insect 2/27/15
 Objectives GARDEN INSECT PESTS: HOW STUDENTS CAN ENGAGE IN INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT Introduction to entomology Provide examples of activities and exercises you can use in the classroom (k-8) Common insects
Objectives GARDEN INSECT PESTS: HOW STUDENTS CAN ENGAGE IN INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT Introduction to entomology Provide examples of activities and exercises you can use in the classroom (k-8) Common insects
Bosque Leaf Hunt Relay
 20. Bosque Leaf Hunt Relay 284 This activity was adapted from the activity Leaf Hunt Relay from Project Learning Tree and the Insect Variation developed by Bob Cain, Forest Entomologist for New Mexico
20. Bosque Leaf Hunt Relay 284 This activity was adapted from the activity Leaf Hunt Relay from Project Learning Tree and the Insect Variation developed by Bob Cain, Forest Entomologist for New Mexico
GENERAL TOPIC SPECIFIC TOPIC
 SUBJECT: TEACHER: DATE: GRADE: DURATION: GENERAL TOPIC: SPECIFIC TOPIC: Integrated Science Mr. S. Campbell 7 2 wks Grouping Grouping- Plants And Animals Grouping- Plants And Animals Students will be able
SUBJECT: TEACHER: DATE: GRADE: DURATION: GENERAL TOPIC: SPECIFIC TOPIC: Integrated Science Mr. S. Campbell 7 2 wks Grouping Grouping- Plants And Animals Grouping- Plants And Animals Students will be able
3rd GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS UDI 2.- FAUNIA. ANIMALS- INVERTEBRATES (8)
 INVERTEBRATES 3rd GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS UDI 2.- FAUNIA. ANIMALS- INVERTEBRATES (8) Invertebrates do not have a backbone. There are many different types of invertebrate animals. Some live on land and some
INVERTEBRATES 3rd GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS UDI 2.- FAUNIA. ANIMALS- INVERTEBRATES (8) Invertebrates do not have a backbone. There are many different types of invertebrate animals. Some live on land and some
WHERE DOES THE SUN GO WHEN IT SETS?
 ACTIVITY 6 WHERE DOES THE SUN GO WHEN IT SETS? EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVES AND CONTENT The goal of the activity is for students to understand the alternation of day and night and the apparent movement of the
ACTIVITY 6 WHERE DOES THE SUN GO WHEN IT SETS? EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVES AND CONTENT The goal of the activity is for students to understand the alternation of day and night and the apparent movement of the
Incredible Invertebrates
 Invertebrates activity one: lesson plan Incredible Invertebrates Invertebrates are, by far, the most successful creatures in animal kingdom. You can find them on land, in the air, and in the water, dominating
Invertebrates activity one: lesson plan Incredible Invertebrates Invertebrates are, by far, the most successful creatures in animal kingdom. You can find them on land, in the air, and in the water, dominating
Garden Insects of Central WA
 Garden Insects of Central WA Ø Ruth Hardison Ø Mike Bush Ø Master Gardener Training- January 27, 2016 Photo courtesy- Susan Spain, Yakima Co. Master Gardener A Little Taxonomy Kingdom = Animal Phylum =
Garden Insects of Central WA Ø Ruth Hardison Ø Mike Bush Ø Master Gardener Training- January 27, 2016 Photo courtesy- Susan Spain, Yakima Co. Master Gardener A Little Taxonomy Kingdom = Animal Phylum =
Learning about bees - Maths Questions
 Learning about bees - Maths Questions Preparation: Before beginning this activity, cut out each of the hexagons in the Learning about bees - maths questions resource. You may consider pre-assigning the
Learning about bees - Maths Questions Preparation: Before beginning this activity, cut out each of the hexagons in the Learning about bees - maths questions resource. You may consider pre-assigning the
HOW DO YOU BUILD AN ELECTRIC GAME?
 HOW DO YOU BUILD AN ELECTRIC GAME? EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVES AND CONTENT The primary goals of this activity are to teach students about the concept of electrical circuits connected in series and to give them
HOW DO YOU BUILD AN ELECTRIC GAME? EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVES AND CONTENT The primary goals of this activity are to teach students about the concept of electrical circuits connected in series and to give them
Leica EZ4D Scope Training
 Leica EZ4D Scope Training By: Ryan S. Davis Arthropod Diagnostician UPPDL Fine tuning your photographic skills, and taking pictures of what s important Lecture Preparing insects for photographing Ways
Leica EZ4D Scope Training By: Ryan S. Davis Arthropod Diagnostician UPPDL Fine tuning your photographic skills, and taking pictures of what s important Lecture Preparing insects for photographing Ways
Introduction to Insects
 Introduction to Insects PJ Liesch UW-Madison Dept. Entomology! What%are%Insects?%! Spiders%and%other%critters%! Insect%Biology%! Anatomy%! Damage%they%cause%! Growth%and%Development%! Diversity%and%Classification%!
Introduction to Insects PJ Liesch UW-Madison Dept. Entomology! What%are%Insects?%! Spiders%and%other%critters%! Insect%Biology%! Anatomy%! Damage%they%cause%! Growth%and%Development%! Diversity%and%Classification%!
Insect Investigations
 Investigative Questions What are some adaptations that insects have that help them to feed on different foods and from different parts of plants, especially flowers? Goal: Students explore the ways that
Investigative Questions What are some adaptations that insects have that help them to feed on different foods and from different parts of plants, especially flowers? Goal: Students explore the ways that
Characteristics and Classification of Living Organism (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Characteristics and Classification of Living Organism (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Characteristics of Living Organisms o Movement o Respiration o Sensitivity o Growth o Reproduction o Excretion o
Characteristics and Classification of Living Organism (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Characteristics of Living Organisms o Movement o Respiration o Sensitivity o Growth o Reproduction o Excretion o
INSECTS IN AND AROUND YOUR HOME GARDEN. James N. Hogue
 INSECTS IN AND AROUND YOUR HOME GARDEN James N. Hogue Along with bacteria the insects are the most numerous and dominant life forms on Earth. Around 1 million insect species have been described. There
INSECTS IN AND AROUND YOUR HOME GARDEN James N. Hogue Along with bacteria the insects are the most numerous and dominant life forms on Earth. Around 1 million insect species have been described. There
Public Schools of Brookline
 1 st Grade Science & Engineering Overview The Science & Engineering (LEs) outline the content that students will learn and skills (practices) that students will be able to do from prek through Grade 8.
1 st Grade Science & Engineering Overview The Science & Engineering (LEs) outline the content that students will learn and skills (practices) that students will be able to do from prek through Grade 8.
Michigan Farm Bureau Agriscience Lessons -- Connections to Michigan Content Standards
 Michigan Farm Bureau Agriscience Lessons -- Connections to Michigan Content Standards 2nd GRADE LESSON - "Understanding Insects as Friends or Foes" Michigan Farm Bureau Promotion and Education This lesson
Michigan Farm Bureau Agriscience Lessons -- Connections to Michigan Content Standards 2nd GRADE LESSON - "Understanding Insects as Friends or Foes" Michigan Farm Bureau Promotion and Education This lesson
The Importance of Bees
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: The Importance of Bees Imagine a world without bees. Some might rejoice at the thought of never being stung by one of those little yellow buzzers, and others might miss the
Name: Class Period: Due Date: The Importance of Bees Imagine a world without bees. Some might rejoice at the thought of never being stung by one of those little yellow buzzers, and others might miss the
Observing Daphnia. Student Resources 1.4 Observing Daphnia, Pages 1 and Counting Daphnia Populations Inquiry Focus Observe
 Observing Daphnia Observing Daphnia, Page 1 30 minutes Pairs Observe the daphnia in your cup. List two ways you can tell the adults from the babies: 1 Babies are smaller. 2 Babies are brownish. How do
Observing Daphnia Observing Daphnia, Page 1 30 minutes Pairs Observe the daphnia in your cup. List two ways you can tell the adults from the babies: 1 Babies are smaller. 2 Babies are brownish. How do
Insect Success. Insects are one of the most successful groups of living organisms on earth
 Insect Success Insects are one of the most successful groups of living organisms on earth Why Insects are so successful Insects comprise about 95% of all known animal species. Actually it is insects instead
Insect Success Insects are one of the most successful groups of living organisms on earth Why Insects are so successful Insects comprise about 95% of all known animal species. Actually it is insects instead
HOW CAN LIGHT S INTENSITY BE VARIED?
 ACTIVITY 1 HOW CAN LIGHT S INTENSITY BE VARIED? EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVES AND CONTENT In this activity, which covers the concepts of transparency and opacity, students gain a better understanding of how light
ACTIVITY 1 HOW CAN LIGHT S INTENSITY BE VARIED? EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVES AND CONTENT In this activity, which covers the concepts of transparency and opacity, students gain a better understanding of how light
FLOWERS AND POLLINATION. This activity introduces the relationship between flower structures and pollination.
 FLOWERS AND POLLINATION This activity introduces the relationship between flower structures and pollination. Objectives for Exam #1 1. Identify flower structures and match those structures to specific
FLOWERS AND POLLINATION This activity introduces the relationship between flower structures and pollination. Objectives for Exam #1 1. Identify flower structures and match those structures to specific
Good Bugs & Bad Bugs Student Booklet
 Good Bugs & Bad Bugs Student Booklet Molly Keck Program Specialist Urban IPM 3355 Cherry Ridge, Suite 212 San Antonio, Texas 78230 Phone: 210-467-6575 Email: mekeck@ag.tamu.edu Lesson 1 - Entomology Reading
Good Bugs & Bad Bugs Student Booklet Molly Keck Program Specialist Urban IPM 3355 Cherry Ridge, Suite 212 San Antonio, Texas 78230 Phone: 210-467-6575 Email: mekeck@ag.tamu.edu Lesson 1 - Entomology Reading
Primitively there is a pair of ganglia per body segment but there has been progressive fusion of ganglia both within and between segments.
 Multicellular organisms contain systems of organs that carry out specialised functions that enable them to survive and reproduce examining the specialised cells and tissues involved in structure and function
Multicellular organisms contain systems of organs that carry out specialised functions that enable them to survive and reproduce examining the specialised cells and tissues involved in structure and function
Good Bugs & Bad Bugs
 Good Bugs & Bad Bugs Molly Keck Program Specialist Urban IPM 3355 Cherry Ridge, Suite 212 San Antonio, Texas 78230 Phone: 210-467-6575 Email: mekeck@ag.tamu.edu Preface Insects are a very diverse group
Good Bugs & Bad Bugs Molly Keck Program Specialist Urban IPM 3355 Cherry Ridge, Suite 212 San Antonio, Texas 78230 Phone: 210-467-6575 Email: mekeck@ag.tamu.edu Preface Insects are a very diverse group
Scheme of Examination (B.Sc. (Hons.) Agriculture) ( )
 Scheme of Examination (B.Sc. (Hons.) Agriculture) (2016-2020) 20 Marks (Internal) + 80 marks (External) 20% Internal Examination 20 Marks (Mid term examination/internal assessment) 1). Internal theory
Scheme of Examination (B.Sc. (Hons.) Agriculture) (2016-2020) 20 Marks (Internal) + 80 marks (External) 20% Internal Examination 20 Marks (Mid term examination/internal assessment) 1). Internal theory
Insects. Name. Date Comp Ed, Inc.
 Name Date Copyright@ 2013 Comp Ed, Inc. www.schoolexpress.com All animals with six legs are called insects. Insects were on the Earth millions of years before people. Insects live all over the world. There
Name Date Copyright@ 2013 Comp Ed, Inc. www.schoolexpress.com All animals with six legs are called insects. Insects were on the Earth millions of years before people. Insects live all over the world. There
An Introduction to Bugs. Whitney Cranshaw Colorado State University
 An Introduction to Bugs Whitney Cranshaw Colorado State University An Introduction to Bugs Whitney Cranshaw Colorado State University Arthropod Features Segmented body Exoskeleton Jointed appendages
An Introduction to Bugs Whitney Cranshaw Colorado State University An Introduction to Bugs Whitney Cranshaw Colorado State University Arthropod Features Segmented body Exoskeleton Jointed appendages
USU 4-H Insect Tote. Supplies
 USU 4-H Insect Tote Supplies BIG IDEA: Environments are made up of diverse populations of organisms. UNDERSTANDINGS: Focusing on small organisms, such as insects, help us to see interactions we may not
USU 4-H Insect Tote Supplies BIG IDEA: Environments are made up of diverse populations of organisms. UNDERSTANDINGS: Focusing on small organisms, such as insects, help us to see interactions we may not
GHS BIOLOGY P553/1 April 2010 Time hours S 2 EOT 1. Attempt all the questions in section A and B in the spaces provided
 GHS BIOLOGY P553/1 April 2010 Time 1. 30 hours S 2 EOT 1 INSTRUCTIONS Attempt all the questions in section A and B in the spaces provided Answers to section A 1 7 13 19 25 2 8 14 20 26 3 9 15 21 27 4 10
GHS BIOLOGY P553/1 April 2010 Time 1. 30 hours S 2 EOT 1 INSTRUCTIONS Attempt all the questions in section A and B in the spaces provided Answers to section A 1 7 13 19 25 2 8 14 20 26 3 9 15 21 27 4 10
BIO Lab 17: Classification of Organisms
 Classification of Organisms And God said: Let the earth bring forth the living creature in its kind, Cattle and creeping things, and beasts of the earth, according to their kinds. And it was so done.and
Classification of Organisms And God said: Let the earth bring forth the living creature in its kind, Cattle and creeping things, and beasts of the earth, according to their kinds. And it was so done.and
Warning: Some material in this presentation and related videos may be too graphic for some people. T. Trimpe 2009
 Warning: Some material in this presentation and related videos may be too graphic for some people. T. Trimpe 2009 http://sciencespot.net/ What do they do? Forensic entomologists apply their knowledge of
Warning: Some material in this presentation and related videos may be too graphic for some people. T. Trimpe 2009 http://sciencespot.net/ What do they do? Forensic entomologists apply their knowledge of
Creepy, Crawly Critters
 Creepy, Crawly Critters Objective Students will identify different insects as well as the body parts of insects. Background There are over 1.5 million kinds of insects. They come in all shapes and sizes.
Creepy, Crawly Critters Objective Students will identify different insects as well as the body parts of insects. Background There are over 1.5 million kinds of insects. They come in all shapes and sizes.
Lesson: The Buzz on Bees
 Lesson: The Buzz on Bees Environmental Literacy Question: How have humans affected the Chesapeake Bay and its watershed? Topic/Essential Questions: How do the structures of plants help them survive in
Lesson: The Buzz on Bees Environmental Literacy Question: How have humans affected the Chesapeake Bay and its watershed? Topic/Essential Questions: How do the structures of plants help them survive in
Listening. The Air. Did you know? Did you know?
 Listening 1. Find a place to sit. 2. Close your eyes and listen carefully to all the sounds you can hear. Cup your hands around your ears and turn your head to help you listen in particular directions.
Listening 1. Find a place to sit. 2. Close your eyes and listen carefully to all the sounds you can hear. Cup your hands around your ears and turn your head to help you listen in particular directions.
OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION. Entomology. OSUE Master Gardeners Mahoning County Class of Bill Snyder April 4, 2017
 OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION Entomology OSUE Master Gardeners Mahoning County Class of 2017 Bill Snyder April 4, 2017 MG Note: Entomology: The study of Insects Although the manual chapter is enktled
OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION Entomology OSUE Master Gardeners Mahoning County Class of 2017 Bill Snyder April 4, 2017 MG Note: Entomology: The study of Insects Although the manual chapter is enktled
INSTRUCTIONS TO TEACHERS. Bee Life Grade 2 Science and Technology Unit
 INSTRUCTIONS TO TEACHERS Bee Life Grade 2 Science and Technology Unit ONTARIO TEACHER-FOCUSED TOOLKIT INSTRUCTIONS TO TEACHERS Bee Life Instructions to Teachers This unit is a Science and Technology lesson
INSTRUCTIONS TO TEACHERS Bee Life Grade 2 Science and Technology Unit ONTARIO TEACHER-FOCUSED TOOLKIT INSTRUCTIONS TO TEACHERS Bee Life Instructions to Teachers This unit is a Science and Technology lesson
BOOK 3 OUR PLANET SECTION 2 WORLD OF LIFE
 BOOK 3 OUR PLANET SECTION 2 WORLD OF LIFE ANIMAL AND PLANT CELLS There are two general types of cell - the animal cell and the plant cell. The animal cell is the most basic with the fewest parts. The plant
BOOK 3 OUR PLANET SECTION 2 WORLD OF LIFE ANIMAL AND PLANT CELLS There are two general types of cell - the animal cell and the plant cell. The animal cell is the most basic with the fewest parts. The plant
Pollination A Sticky Situation! A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society s Learning Through Gardening program
 Pollination A Sticky Situation! A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society s Learning Through Gardening program OVERVIEW: Pollination is a sticky situation. In this active lesson, students learn
Pollination A Sticky Situation! A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society s Learning Through Gardening program OVERVIEW: Pollination is a sticky situation. In this active lesson, students learn
The Wonderful World of Insects. James A. Bethke University of California Cooperative Extension Farm Advisor Floriculture and Nursery San Diego County
 The Wonderful World of Insects James A. Bethke University of California Cooperative Extension Farm Advisor Floriculture and Nursery San Diego County Taxonomy The Insects The Orders Part I Taxonomy Scientific
The Wonderful World of Insects James A. Bethke University of California Cooperative Extension Farm Advisor Floriculture and Nursery San Diego County Taxonomy The Insects The Orders Part I Taxonomy Scientific
SOBA Bee School April, 2015
 SOBA Bee School April, 2015 Bee Girl - University of Montana, Missoula - Iridovirus and Microsporidian Linked to CCD - Sonagraphic analysis of hive health - Pesticide effects - Bomb sniffing bees - OLLI
SOBA Bee School April, 2015 Bee Girl - University of Montana, Missoula - Iridovirus and Microsporidian Linked to CCD - Sonagraphic analysis of hive health - Pesticide effects - Bomb sniffing bees - OLLI
Pollinator Activity #1: How to Raise a Butterfly
 How to Raise a Butterfly How to Raise a Butterfly A Conversation Where do you most often see butterflies? What are they doing when you see them? Have you ever seen a butterfly in another form? They have
How to Raise a Butterfly How to Raise a Butterfly A Conversation Where do you most often see butterflies? What are they doing when you see them? Have you ever seen a butterfly in another form? They have
4-H Natural Resources Curriculum How Does The Environment in Kentucky Affect The Insects (and Related Arthropods) That Live There?
 4-H Natural Resources Curriculum How Does The Environment in Kentucky Affect The Insects (and Related Arthropods) That Live There? The goal of this portion of the curriculum is to introduce students to
4-H Natural Resources Curriculum How Does The Environment in Kentucky Affect The Insects (and Related Arthropods) That Live There? The goal of this portion of the curriculum is to introduce students to
2nd Grade. Slide 1 / 106. Slide 2 / 106. Slide 3 / 106. Plants. Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106 2nd Grade Plants 2015-11-24 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 106 Click on the topic to go to that section What are plants? Photosynthesis Pollination Dispersal Slide
Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106 2nd Grade Plants 2015-11-24 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 106 Click on the topic to go to that section What are plants? Photosynthesis Pollination Dispersal Slide
Lesson 3 Classification of Insects
 Lesson 3 Classification of Insects Timeframe 1 Fifty minute class period Target Audience Middle School (6-8) Life Science but easily adapted to Grades 4-12 Materials - Petri Dishes - Magnifying Lenses
Lesson 3 Classification of Insects Timeframe 1 Fifty minute class period Target Audience Middle School (6-8) Life Science but easily adapted to Grades 4-12 Materials - Petri Dishes - Magnifying Lenses
Importance of Taxonomic Collections
 Importance of Taxonomic Collections Document earth s biodiversity Facilitate the process of researching relationships among and within different groups of organisms Study ecological processes using special
Importance of Taxonomic Collections Document earth s biodiversity Facilitate the process of researching relationships among and within different groups of organisms Study ecological processes using special
Food Chains. energy: what is needed to do work or cause change
 Have you ever seen a picture that shows a little fish about to be eaten by a big fish? Sometimes the big fish has an even bigger fish behind it. This is a simple food chain. A food chain is the path of
Have you ever seen a picture that shows a little fish about to be eaten by a big fish? Sometimes the big fish has an even bigger fish behind it. This is a simple food chain. A food chain is the path of
Manitoba Curriculum Framework of Outcomes Grades K-3
 Grades K-3 Reference Specific Learning Outcomes Wetlands Rainforest It is expected that students will: 100-4 observe and identify similarities and differences in the needs of living Organisms, Migration,
Grades K-3 Reference Specific Learning Outcomes Wetlands Rainforest It is expected that students will: 100-4 observe and identify similarities and differences in the needs of living Organisms, Migration,
BIODIVERSITY MONITORING PROJECT QUICK LESSON #3 Insect Monitoring A Classroom Model
 Background BIODIVERSITY MONITORING PROJECT QUICK LESSON #3 Insect Monitoring A Classroom Model National education standards emphasize that science in schools should reflect science as a process, rather
Background BIODIVERSITY MONITORING PROJECT QUICK LESSON #3 Insect Monitoring A Classroom Model National education standards emphasize that science in schools should reflect science as a process, rather
WHY ARE THE PLANETS SOMETIMES NOT VISIBLE FROM EARTH?
 ACTIVITY 4 WHY ARE THE PLANETS SOMETIMES NOT VISIBLE FROM EARTH? EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVES AND CONTENT In this activity, students learn about how the planets revolve around the Sun. They also become familiar
ACTIVITY 4 WHY ARE THE PLANETS SOMETIMES NOT VISIBLE FROM EARTH? EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVES AND CONTENT In this activity, students learn about how the planets revolve around the Sun. They also become familiar
Introduction. 1 Background Information...2 Adaptation Scavenger Hunt...3 Science Standards.. 4
 Please arrive 30 minutes before your program. Teachers and chaperones must be present during the staff-facilitated 45-minute program. Introduction. 1 Background Information.....2 Adaptation Scavenger Hunt......3
Please arrive 30 minutes before your program. Teachers and chaperones must be present during the staff-facilitated 45-minute program. Introduction. 1 Background Information.....2 Adaptation Scavenger Hunt......3
Approximate Pacing for First Grade Insects and Plants Unit
 Approximate Pacing for First Grade Insects and Plants Unit p.1 = Part 1 p.2 = Part 2 p.3 = Part 3 The schedule for this unit is almost COMPLETELY dependent on what the living organisms are doing and where
Approximate Pacing for First Grade Insects and Plants Unit p.1 = Part 1 p.2 = Part 2 p.3 = Part 3 The schedule for this unit is almost COMPLETELY dependent on what the living organisms are doing and where
PARATAXONOMIST GUTPELA SAVE TEST PART 1 YOUR NAME:.. 1. Write names of all body parts you know for the following insect drawings: A
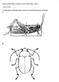 1 PARATAXONOMIST GUTPELA SAVE TEST 2006 - PART 1 YOUR NAME:.. 1. Write names of all body parts you know for the following insect drawings: A B 2 C D 2. These are chewing mouthparts. Name their parts (=
1 PARATAXONOMIST GUTPELA SAVE TEST 2006 - PART 1 YOUR NAME:.. 1. Write names of all body parts you know for the following insect drawings: A B 2 C D 2. These are chewing mouthparts. Name their parts (=
Insect Life Cycle Sort: Complete and Incomplete Metamorphosis
 Insect Life Cycle Sort: Complete and Incomplete Metamorphosis Suggestions for Using This Product BACKGROUND INFORMATION This set was carefully prepared to represent life cycles in a variety of ways. A
Insect Life Cycle Sort: Complete and Incomplete Metamorphosis Suggestions for Using This Product BACKGROUND INFORMATION This set was carefully prepared to represent life cycles in a variety of ways. A
Goldenrod Galls and the Scientific Method
 Goldenrod Galls and the Scientific Method Overview Groups of students are given several goldenrod stems with galls. They are asked to make observations, come up with questions and make hypotheses. They
Goldenrod Galls and the Scientific Method Overview Groups of students are given several goldenrod stems with galls. They are asked to make observations, come up with questions and make hypotheses. They
Honey Bees: A Pollination Simulation
 Honey Bees: A Pollination Simulation Grade Level(s) 3-5 Estimated Time 2 hours Purpose Students will identify the parts of a honey bee, the stages of its life cycle, and its role in pollination. Materials
Honey Bees: A Pollination Simulation Grade Level(s) 3-5 Estimated Time 2 hours Purpose Students will identify the parts of a honey bee, the stages of its life cycle, and its role in pollination. Materials
Plant and Animal Interactions
 Plant and Animal Interactions 21 LESSON For each student: For each adult: Materials Needed Student Data Sheet: Plant and Animal Interactions pencil clipboard Leader Sheet: Plant and Animal Interactions
Plant and Animal Interactions 21 LESSON For each student: For each adult: Materials Needed Student Data Sheet: Plant and Animal Interactions pencil clipboard Leader Sheet: Plant and Animal Interactions
2nd Grade. Plants.
 1 2nd Grade Plants 2015 11 24 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Click on the topic to go to that section What are plants? Photosynthesis Pollination Dispersal 3 Lab: What do plants need? What do plants
1 2nd Grade Plants 2015 11 24 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Click on the topic to go to that section What are plants? Photosynthesis Pollination Dispersal 3 Lab: What do plants need? What do plants
Phylum Arthropoda. Phylum Arthropoda. Arthropods dominate the planet by number of species 7/5/2017. Out of Chaos, Order(s) Lots and lots of relatives
 Out of Chaos, Order(s) 2017 Master Gardener College Erwin Duke Elsner Consumer Horticulture/Small Fruit Extension Educator 520 W. Front Street elsner@anr.msu.edu 231-922-4822 Phylum Arthropoda Insects
Out of Chaos, Order(s) 2017 Master Gardener College Erwin Duke Elsner Consumer Horticulture/Small Fruit Extension Educator 520 W. Front Street elsner@anr.msu.edu 231-922-4822 Phylum Arthropoda Insects
Welcome to the Philadelphia Insectarium and Butterfly Pavilion!
 Welcome to the Philadelphia Insectarium and Butterfly Pavilion! Dear Teachers, We would like to invite you to experience the world of insects and other arthropods! Here at the Insectarium, we want to provide
Welcome to the Philadelphia Insectarium and Butterfly Pavilion! Dear Teachers, We would like to invite you to experience the world of insects and other arthropods! Here at the Insectarium, we want to provide
Life Science 7 th NOTES: Ch Animals Invertebrates
 Life Science 7 th NOTES: Ch 10-11 Animals Invertebrates Write the correct word in the blanks to show directions on an animal body: ** Word Bank (Posterior, Ventral, Dorsal, Anterior) top surface front
Life Science 7 th NOTES: Ch 10-11 Animals Invertebrates Write the correct word in the blanks to show directions on an animal body: ** Word Bank (Posterior, Ventral, Dorsal, Anterior) top surface front
Ecology: The science concerned with the relationships among living things and their environment.
 ECOSYSTEM VOCABULARY IN PACKET Ecology: The science concerned with the relationships among living things and their environment. Ecosystem: A community that includes all the living and nonliving things
ECOSYSTEM VOCABULARY IN PACKET Ecology: The science concerned with the relationships among living things and their environment. Ecosystem: A community that includes all the living and nonliving things
Name Class Date. After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 14 3 Invertebrates SECTION Introduction to Animals BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What structures and systems perform basic life functions
CHAPTER 14 3 Invertebrates SECTION Introduction to Animals BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What structures and systems perform basic life functions
Pollinator Adaptations
 Adapted from: Life Lab Garden Pollinators unit Pollinator Adaptations Overview: Students will learn about pollinators and their adaptations, and match flowers to the kinds of pollinators they attract.
Adapted from: Life Lab Garden Pollinators unit Pollinator Adaptations Overview: Students will learn about pollinators and their adaptations, and match flowers to the kinds of pollinators they attract.
Welcome to the Iowa Certified Nursery Professional Training program Module 7: Introduction to Plant Diseases and Insects.
 Welcome to the Iowa Certified Nursery Professional Training program Module 7: Introduction to Plant Diseases and Insects. 1 After completing this module you should: 1. Understand the causes of abssiotic
Welcome to the Iowa Certified Nursery Professional Training program Module 7: Introduction to Plant Diseases and Insects. 1 After completing this module you should: 1. Understand the causes of abssiotic
Hey There, Stink Bug! Activities
 Hey There, Stink Bug! Activities Butterfly Symmetry Butterflies are symmetrical. The design and colors on each wing are identical. Complete the picture of the butterfly to demonstrate symmetry. Hey There,
Hey There, Stink Bug! Activities Butterfly Symmetry Butterflies are symmetrical. The design and colors on each wing are identical. Complete the picture of the butterfly to demonstrate symmetry. Hey There,
Ode-to-nata (Aeshna canadensis) productions presents
 Ode-to-nata (Aeshna canadensis) productions presents Taxonomy and Anatomy of Apis millefera What s in a (Latin)name? Apis= bee Melli= honey Ferre= to bear honey bearing bee A quick overview of classification.
Ode-to-nata (Aeshna canadensis) productions presents Taxonomy and Anatomy of Apis millefera What s in a (Latin)name? Apis= bee Melli= honey Ferre= to bear honey bearing bee A quick overview of classification.
A. camouflage B. hibernation C. migration D. communication. 8. Beetles, grasshoppers, bees, and ants are all.
 1. A flounder is a type of fish. The flounder can change its color to match the surroundings. If a shark approaches, the flounder lays still, blending into the sandy ocean bottom. This is known as. 2 Which
1. A flounder is a type of fish. The flounder can change its color to match the surroundings. If a shark approaches, the flounder lays still, blending into the sandy ocean bottom. This is known as. 2 Which
