Buzz on Bees. Snack suggestions
|
|
|
- Laura Reeves
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 REAP Lessons Buzz on Bees Lesson Overview Buzz on Bees introduces pollinators and pollination to students. It connects food production to pollination and helps students understand how the process works. They will learn about the importance of pollinators, specifically bees, and how they collect nectar and make honey. Objectives Students will learn 1. What role pollinators play in growing food and the process of pollination (WI Standards for Agriculture, Food and Natural Resources PS3.a.3.m and PS3.a.4.m; Next Generation Science Standards 2-LS2-2) 2. How bees simultaneously pollinate and make honey Lesson Introduction Using the PowerPoint slides on pages 8-13, show students the images of pollinators and pollinated items and ask them to silently think about how they might be related. Once everyone has had time to think, go through the images. Identify what insects and plant products they see, then ask why they think they go together - students will understand that pollinators all participate in pollinating very diverse plants. Then, continue to name different fruits and vegetables that rely on pollinators to become food. After making the connection that plant products rely on pollination, begin activities that explain the actual process. Activities -Act out why bees pollinate play -Flowers and Pollinators Art/Game -Buzz on Bees powerpoint + facts -Read a book -Buzz on Bees Rap -Pollinating Teamwork Activity -Bee Theater and Flower Anatomy Snack suggestions If possible, serve a local seasonal snack. - crackers with honey (try to bring multiple kinds of honey) - yogurt mixed with honey - fruit or veggie with honey drizzled on top - popcorn with honey drizzled on top - honey taste-test Book suggestions -The Beeman by Laurie Krebs. This book tells the story of a beekeeper and is a good way to talk about apiaries. It also contains informational glossary that talks about how bees communicate, how hives are structured, and the roles of different bees. -The Magic School Bus: Inside a Beehive. This book is informative and mainly focuses on the structure of a beehive. Conclusion By the end of this lesson, students should understand the importance of pollinators in our food system. They will know how and why bees make honey and how the process of pollination works. Students will also understand how much of our food depends on pollination and why we should care about pollinator health. page 1
2 REAP Lessons -Buzz on Bees Buzz on Bees - Lesson Planning Keep in mind that these lessons are best formatted to a 45 minute time slot. The approximate activity time can be adjusted to your preferences. It is suggested that you choose one introduction option to pair with a few activities. Happy planning! snack Materials Checklist Introduction Activity 1 Activity 2 Activity 3 Conclusion Notes page 2
3 REAP Lessons - Buzz on Bees Buzz on Bees - Introduction Using the PowerPoint slides on pages 8-13, show students the images of pollinators and pollinated items and ask them to silently think about how they might be related. Once everyone has had time to think, go through the images. Identify what insects and plant products they see, then ask why they think they go together - students will understand that pollinators all participate in pollinating very diverse plants. Then, continue to name different fruits and vegetables that rely on pollinators to become food. After making the connection that plant products rely on pollination, begin activities that explain the actual process. Pollination - The process by which the pollen is transferred from the male part of the plant (anther) to the female part of the plant (stigma) where it can be fertilized and reproduction can take place. Or, the process by which insects/other pollinators help plants to make seeds. Pollinator - Animals of all types (insects, bats, birds, etc) that visit flowers and take away their pollen and deposit it into other flowers; the animals that carry out the process of pollination Buzz on Bees - Activities Why Bees Pollinate Play (gr 1-5) Assign roles to students by giving them nametags and having them hold images to represent their character. Narrate the following scene: Bees start making honey, which is their food, by visiting flowers. They collect a sugary juice called nectar from the blossom by sucking it out with their tongues. They store it in what s called their honey stomach, which is different from their food stomach. When they have a full load, they fly back to the hive. There, they pass it on through their mouths to other worker bees who chew it for about half an hour. It s passed from bee to bee, until it gradually turns into honey. Then the bees store it in honeycomb cells, which are like tiny jars made of wax. The honey is still a bit wet, so they fan it with their wings to make it dry out and become more sticky. When it s ready, they seal the cell with a wax lid to keep it clean. Supplies -nametags / images Time - 10 to 15 minutes So that s how bees make honey. They don t make very much of it, though. It takes at least eight bees all their life to make one single teaspoonful. Fortunately for us, they usually make more than they need, so we can have some, too. page 3
4 REAP Lessons - Buzz on Bees Buzz on Bees - Activities Flowers and Pollinators Art/Game (gr 3-5) Stage 1: Drawing Divide the class in two and supply everyone with a piece of paper and markers. One half is the pollinator group, the other is the flower group. Each student draws either a pollinator (bee, butterfly, beetle, bird, etc.) or a flower on their paper, depending on their group. Optionally, students can cut out their drawing and tape it to their shirt. Once the drawing is finished, put two pieces of doubled up masking tape in the center of each flower, so that there s a sticky side pointing out. Stage 2: Pollinating Give each flower student five pieces of pollen/pompoms and instruct them to spread out across the classroom and stand still. The pollinator students will walk from flower to flower. When a pollinator comes to a flower, if the pollinator has already collected pollen, they stick it to one of the pieces of masking tape and get a new piece of pollen from that flower, then keep walking. If they have no pollen yet, the flower gives them one of their pieces and the pollinator keeps walking. When a flower has two pieces of pollen stuck to it, they sit down and become a fruit. Game ends when all flowers are seated. Supplies -One piece of blank paper per student -Safety scissors (optional) -Markers, crayons, etc. -Masking tape - Pollen pom poms Time - Stage 1: 10 to 20 minutes Stage 2: 5-10 minutes Buzz on Bees Powerpoint + Facts (Gr k-5) This slide show helps students identify different pollinators and learn about what crops are pollinated by them. It includes facts (in the notes) so that students can learn how often bees visit flowers, how far they travel to them, how many flowers it takes to fill up their nectar stomach, and how many bees are needed to make a jar of honey. This visual aid can help in the introduction, or it can be its own activity where the focus is on the facts. Supplies -Buzz on Bees powerpoint Time -5 to 10 minutes Reading A Book (gr k-5) Reading a book can be a great way to reinforce this lesson. The Beeman is a story about a beekeeper that includes an informational glossary at the end. Be sure to ask guiding questions to ensure that students understand the story and what being a beekeeper entails. Supplies -The Beeman book Time - 5-1o minutes page 4
5 REAP Lessons - Buzz on Bees Buzz on Bees - Activities Buzz on Bees Rap (gr 3-5) This activity connects information learned about the importance of pollinators to our food system to language arts through the development of a rap, poem, mini-play, or song about pollinators! Students will enjoy coming up with rhymes and other stories with their classmates about our friends the bees. Separate students into groups of 3-5. Instruct that they will be creating raps, songs, mini plays, chants, or songs about bees. Encourage them to feature at least 1 fact from the list below. Encourage creativity by brainstorming rhyming words with common pollinator terms such as bee, nectar, pollen, and fruit. Have them work as a team to develop the songs and write them down. Also encourage students to make motions to go along with their rap. Supplies -Worksheet with directions and facts -pencils Time - 15 to 20 minutes Once everyone is amply prepared, have groups come up and share their rap in front of the class. While students do not have to present, create a supportive environment for them to share. For those that do present, acknowledge how brave they are! It can be hard to get up in front of the class, so try to have students practice public speaking in this informal way. Remind them to use louder voices and have groups rehearse before presenting. Notes: Teachers can use this lesson to emphasize collaborative group work concepts such as cooperation and active listening. This activity is best used after completing the Buzz on Bees lesson with your class. Teachers can further tailor the lesson by connecting it to other language arts subjects being studied at the time (e.g. poetry, plays, rhyming, rhythm, fiction, non-fiction, illustrated stories, etc.). Facts to incorporate into raps: Bees, birds, bats, and butterflies are all pollinators. Pollinators help keep us healthy by pollinating important plants that create fruits that we love to eat. Bees make honey out of nectar from flowers. Bees pollinate so many fruits that we love such as asparagus, cantaloupes, cucumbers, pumpkins, blueberries, watermelons, almonds, apples, cranberries, cherries, and cocoa (that is used to make chocolate)! We can take care of bees by planting many different colors of flowers that bloom at different times of the year so that they can eat nectar all season long. page 5
6 REAP Lessons - Buzz on Bees Buzz on Bees - Activities Pollinating Teamwork Activity (JB s Flower Cups) (gr 3-5) Preparation: REAP office has cups for this activity. To make your own, print out, draw, or cut felt pieces to make images of different flowers that become edible fruits. Glue these to paper cups. On the bottom, write what edible fruit (apple, squash, corn, strawberry, etc.) the flower will turn into. Supplies - Eight to ten cups representing different flowers. - Pollen pompoms (number of pieces = (number of students) x (four or five) ) Calculate your pollen numbers. Four or five pieces of pollen per student is generally a good number for an average size class. The amount of pollen required to pollinate a flower (x) should be a little less than the number of pieces each flower would get if the pollen is evenly divided amongst them (ed). I.e. x < ed; ed = [number of students] x [pollen per student] / [number of flowers] If you have fifteen students, give each five pieces of pollen, and hide ten cups, then: ed = 15 x 5 / 10 = 7.5. So tell students each flower needs 6 pieces (a little under 7.5) to be pollinated. Time - ~10 minutes Directions: Place the cups around the lesson area (classroom, garden, etc.). Depending on the students age, make them somewhat tricky to find. Tell the students that they are now a hive of bees, working together to gather nectar and pollinate flowers. Around the room are cups that represent different flowers. Each flower needs x pieces of pollen to be pollinated and become a fruit. Each bee will start the game with y pieces (four or five is often good), and walk around, distributing pollen to the flowers. Don t take pollen out of the flower cups! You can only put in the pollen pieces you get at the start of the game. If we want to get the most fruits possible, we need to make sure all the flowers get a medium amount of pollen, instead of some flowers getting a whole lot and some getting none at all. Now, can bees talk? (no). But do you think that bees communicate? (yes). Bees communicate by moving their bodies, for example doing a waggle dance. If you find a flower, you can let the other bees know by your buzzing, and by dancing. Once you have no more pollen left, come back to the hive (the carpet or other designated area) and sit down. After the students finish pollinating flowers, collect all the cups and find out which were pollinated! Going one by one, check what fruit the flower will become by reading the bottom of the cup ( this flower, if pollinated, will grow into a! ), then count out the pieces of pollen it has to find out if there will be fruit. Counting together as a group can be fun and heighten the anticipation. page 6
7 REAP Lessons - Buzz on Bees Buzz on Bees - Activities Bee Theater and Flower Anatomy (gr k-5) Objective: Internalize how pollination happens through creative play and visual aids. Directions: Note: Depending on age of the students, adjust the amount of new vocabulary and complexity of pollination that you introduce. Introduce pollination to your students. You might ask for a show of hands on who likes different fruits that are insect-pollinated, then announce that without bees and other pollinators, we couldn t eat these fruits. But how does pollination actually happen? Draw a flower on whiteboard, or show one of the 3D flowers. A flower has three important parts for pollination: the stamens (male, consisting of anther and filament) the pistil (female, consisting of stigma and style), and the ovary, which becomes a fruit if the flower is pollinated. The stamen makes pollen. The pistil needs pollen. When pollen lands on top of the pistil (on the stigma), the pollen creates a pollen tube to burrow down the pistil (through the style) and to the ovary, which can now start becoming a fruit. If the pollen came from the same flower, it s called self-pollination. If the wind or an animal carried it from a different flower, it s called cross-pollination. Many flowers attract pollinators like bees by producing a sweet nectar for them to eat. If using a white board, draw a second flower and a bee, and draw out this process as you describe it. If using props, get them out here and recruit three student volunteers to act out a bee collecting and depositing pollen, and drinking nectar from each of the two flowers. The bee gets the bee scarf and the proboscis. The flowers get a 3D flower each with pollen pompoms attached. The bee will go to the first flower, mime drinking nectar, collect the pollen and put it in the leg baskets on scarf. Then the bee goes to the second flower, mimes drinking nectar, spills a bit of the pollen from the baskets onto the pistil (you may want to be the wind, and assist with the spilling to make sure it goes on the correct flower part) and collects the rest of the pollen, then flies away. The spilled pollen travels down the 3D flower s hollow style, then the petals and flower parts are tucked into the hollow ovary, filling it out to make a fruit. Sources: Supplies - EITHER a whiteboard and markers, - OR Bee Theater props: Two 3D flowers/fruits (convertible) Bee scarf with leg baskets for pollen. Pollen pieces (pompoms) Drinking straw proboscis Time minutes page 7
8 page 8
9 page 9
10 How many miles do bees fly to get to flowers? (up to 5 miles) / How many trips do bees make to flowers in a day? (10) / How many flowers does it take to fill a bee s nectar sac? ( flowers) page 10
11 page 11
12 page 12
13 How many bees does it take to fill a honey jar? (22,000) page 13
14 REAP Lessons Spanish Pollination Vocabulary pollination self-pollination cross-pollination pollinate pollinated pollinator(s) pollen nectar stamen(s) anther(s) filament(s) pistil stigma style pollen tube ovary ovule flower fruit (n.f.) polinización (n.f.) autopolinización (n.f.) polinización cruzada (v.) polinizar (participle) polinizado/a(s) (n.f.) polinizadora(s) (n.m.) polen (n.m.) néctar (n.m.) estambre(s) (n.f.) antera(s) (n.m.) filamento(s) (n.m.) pistilo (n.m.) estigma (n.m.) estilo (n.m.) tubo de polen / tubo polínico (n.m.) ovario (n.m.) óvulo (n.f.) flor (n.f.) fruta bee butterfly beetle insect bat bird (n.f.) abeja (n.f.) mariposa (n.m.) escarabajo (n.m.) insecto (n.m.) murciélago (n.m.) pájaro page 14
Lesson Adapted from Food, Land, People
 Theme: Spring in the Garden Grade Level: K- 5 th Time Required: 45 minutes Number of Students: 15-25 Buzzy Buzzy Bee! Lesson Adapted from Food, Land, People Description Students learn about pollination
Theme: Spring in the Garden Grade Level: K- 5 th Time Required: 45 minutes Number of Students: 15-25 Buzzy Buzzy Bee! Lesson Adapted from Food, Land, People Description Students learn about pollination
How Does Pollination Work?
 How Does Pollination Work? What is pollination? What is pollination? Pollination the transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower Fertilization occurs when the male
How Does Pollination Work? What is pollination? What is pollination? Pollination the transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower Fertilization occurs when the male
Parts of a Flower. A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society Learning Through Gardening Program
 Parts of a Flower A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society Learning Through Gardening Program OVERVIEW: Students create a flower with craft materials in order to learn the parts of flowers and
Parts of a Flower A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society Learning Through Gardening Program OVERVIEW: Students create a flower with craft materials in order to learn the parts of flowers and
Pollination A Sticky Situation! A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society s Learning Through Gardening program
 Pollination A Sticky Situation! A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society s Learning Through Gardening program OVERVIEW: Pollination is a sticky situation. In this active lesson, students learn
Pollination A Sticky Situation! A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society s Learning Through Gardening program OVERVIEW: Pollination is a sticky situation. In this active lesson, students learn
Community Involvement in Research Monitoring Pollinator Populations using Public Participation in Scientific Research
 Overview Community Involvement in Research Monitoring Pollinator Populations using Public Participation in Scientific Research Public Participation in Scientific Research (PPSR) is a concept adopted by
Overview Community Involvement in Research Monitoring Pollinator Populations using Public Participation in Scientific Research Public Participation in Scientific Research (PPSR) is a concept adopted by
The Basics: Grade Level 5 th - 8th. Subject Areas Life sciences. Duration 95 minutes. Number of Docents Needed 2. Wetland Stewards Program Lesson 8 1
 Grade Level 5 th - 8th The Basics: POLLINATORS AND WILDFLOWERS Summary Students will understand that plants depend on pollinators to reproduce and maintain their populations. They learn about wetland plant
Grade Level 5 th - 8th The Basics: POLLINATORS AND WILDFLOWERS Summary Students will understand that plants depend on pollinators to reproduce and maintain their populations. They learn about wetland plant
Pollinator Adaptations
 Adapted from: Life Lab Garden Pollinators unit Pollinator Adaptations Overview: Students will learn about pollinators and their adaptations, and match flowers to the kinds of pollinators they attract.
Adapted from: Life Lab Garden Pollinators unit Pollinator Adaptations Overview: Students will learn about pollinators and their adaptations, and match flowers to the kinds of pollinators they attract.
BEE BODIES HONEY BEE ANATOMY. Essential Question: MATERIALS. Chart Paper Markers Journals, Paper, or Digital Notebooks
 BEE BODIES HONEY BEE ANATOMY LEARNING OBJECTIVES Essential Question: HOW DOES A HONEY BEE S STRUCTURE SUPPORT ITS FUNCTION IN THE ECOSYSTEM? n n n Distinguish between the structural and behavioral adaptations
BEE BODIES HONEY BEE ANATOMY LEARNING OBJECTIVES Essential Question: HOW DOES A HONEY BEE S STRUCTURE SUPPORT ITS FUNCTION IN THE ECOSYSTEM? n n n Distinguish between the structural and behavioral adaptations
Elementary Science: Pollination
 Elementary Science: Pollination A collection of hands-on lessons and activities for the elementary classroom that explore the process and importance of pollination and pollinators. Table of Contents A
Elementary Science: Pollination A collection of hands-on lessons and activities for the elementary classroom that explore the process and importance of pollination and pollinators. Table of Contents A
POST-TRIP LESSON: PLANT PARTS BINGO
 POST-TRIP LESSON: PLANT PARTS BINGO Overview: Students play a game to reinforce vocabulary and concepts learned in the Plant Parts, Seed to Harvest, and Pollination modules during the field trip. Sauvie
POST-TRIP LESSON: PLANT PARTS BINGO Overview: Students play a game to reinforce vocabulary and concepts learned in the Plant Parts, Seed to Harvest, and Pollination modules during the field trip. Sauvie
o Can you find any nectar? Brood? Honey? o Can you find any drones and drone cells? o Can you find the queen bee?
 o Can you find any nectar? Brood? Honey? o Can you find any drones and drone cells? o Can you find the queen bee? *NOTE: The queen in Observation Hive #1 has a yellow mark on her. Put the wooden panels
o Can you find any nectar? Brood? Honey? o Can you find any drones and drone cells? o Can you find the queen bee? *NOTE: The queen in Observation Hive #1 has a yellow mark on her. Put the wooden panels
Module 6: Interdependence and Garden Life
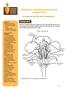 Module 6: Interdependence and Garden Life Pollination and the Next Generation Objectives Students will be able to: list the parts to a flower; show how to pollinate flowers explain the best pollination
Module 6: Interdependence and Garden Life Pollination and the Next Generation Objectives Students will be able to: list the parts to a flower; show how to pollinate flowers explain the best pollination
Next Generation Science Standards
 Flower Functions Students learn the basic structure of a plant and how each part works together as a system to obtain essential resources needed for the plant s survival. Grade Level: 1st Phenomena: How
Flower Functions Students learn the basic structure of a plant and how each part works together as a system to obtain essential resources needed for the plant s survival. Grade Level: 1st Phenomena: How
Plant Lifecycle 3 rd 5 th Grade
 Key Understandings Students will understand that each plant has a lifecycle and the plant lifecycle is a continual process A lifecycle is a continuous cycle that contains: birth, growth, reproduction,
Key Understandings Students will understand that each plant has a lifecycle and the plant lifecycle is a continual process A lifecycle is a continuous cycle that contains: birth, growth, reproduction,
Big Green Lessons. Key Understandings. Standards Alignment. Plant Lifecycle: 3 rd -5 th Grade
 Big Green Lessons Plant Lifecycle: 3 rd -5 th Grade Key Understandings Standards Alignment In this lesson, students will understand that each plant has a lifecycle and the plant lifecycle is a continual
Big Green Lessons Plant Lifecycle: 3 rd -5 th Grade Key Understandings Standards Alignment In this lesson, students will understand that each plant has a lifecycle and the plant lifecycle is a continual
Lesson: The Buzz on Bees
 Lesson: The Buzz on Bees Environmental Literacy Question: How have humans affected the Chesapeake Bay and its watershed? Topic/Essential Questions: How do the structures of plants help them survive in
Lesson: The Buzz on Bees Environmental Literacy Question: How have humans affected the Chesapeake Bay and its watershed? Topic/Essential Questions: How do the structures of plants help them survive in
U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service. Attracting Pollinators to Your Garden
 U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Attracting Pollinators to Your Garden Why are Pollinators Important? Pollinators are nearly as important as sunlight, soil and water to the reproductive success of over 75%
U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Attracting Pollinators to Your Garden Why are Pollinators Important? Pollinators are nearly as important as sunlight, soil and water to the reproductive success of over 75%
Lesson: Honeybees and Trees
 Camp Woodlands/Kindergarten Environmental Literacy Revised 2016 Lesson: Honeybees and Trees Topic/Essential Question: How do honeybees and trees help each other? Unit: Why Are Trees Terrific? Kindergarten
Camp Woodlands/Kindergarten Environmental Literacy Revised 2016 Lesson: Honeybees and Trees Topic/Essential Question: How do honeybees and trees help each other? Unit: Why Are Trees Terrific? Kindergarten
Insect Investigations
 Investigative Questions What are some adaptations that insects have that help them to feed on different foods and from different parts of plants, especially flowers? Goal: Students explore the ways that
Investigative Questions What are some adaptations that insects have that help them to feed on different foods and from different parts of plants, especially flowers? Goal: Students explore the ways that
Flower Power!! Background knowledge material and dissection directions.
 Flower Power!! Background knowledge material and dissection directions. 96 Plant Dissection 3.2 Plants Essential Question: Why do plants have flowers? Questions: As you read the lab background, complete
Flower Power!! Background knowledge material and dissection directions. 96 Plant Dissection 3.2 Plants Essential Question: Why do plants have flowers? Questions: As you read the lab background, complete
Curriculum links. Learning objective. Introduction
 pring Pollination Curriculum links cience Unit 2B Plants and animals in the local environment Unit 5B Life cycles Unit 6A Interdependence and adaptation Geography Unit 8 Improving the environment Art and
pring Pollination Curriculum links cience Unit 2B Plants and animals in the local environment Unit 5B Life cycles Unit 6A Interdependence and adaptation Geography Unit 8 Improving the environment Art and
BEES AND FORESTS. Activity 1 After the clip. 1. On which coast of Tasmania north, east or west does the annual Leatherwood flowering take place?
 BEES AND FORESTS Activity 1 After the clip 1. On which coast of Tasmania north, east or west does the annual Leatherwood flowering take place? 2. Julian Wolfhagen is the president of which association
BEES AND FORESTS Activity 1 After the clip 1. On which coast of Tasmania north, east or west does the annual Leatherwood flowering take place? 2. Julian Wolfhagen is the president of which association
Pollinator Slide Show Notes DIRECTIONS IN ALL CAPS 1
 Pollinator Slide Show Notes DIRECTIONS IN ALL CAPS 1 THIS PRESENTATION IS INTENDED TO BE USED IN SECTIONS TO SUPPORT TEACHING ON THE TOPICS PRESENTED. ANY OF THE SLIDES CAN BE USED AS HANDOUTS. YOU CAN
Pollinator Slide Show Notes DIRECTIONS IN ALL CAPS 1 THIS PRESENTATION IS INTENDED TO BE USED IN SECTIONS TO SUPPORT TEACHING ON THE TOPICS PRESENTED. ANY OF THE SLIDES CAN BE USED AS HANDOUTS. YOU CAN
2nd Grade. Slide 1 / 106. Slide 2 / 106. Slide 3 / 106. Plants. Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106 2nd Grade Plants 2015-11-24 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 106 Click on the topic to go to that section What are plants? Photosynthesis Pollination Dispersal Slide
Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106 2nd Grade Plants 2015-11-24 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 106 Click on the topic to go to that section What are plants? Photosynthesis Pollination Dispersal Slide
The Importance of Bees
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: The Importance of Bees Imagine a world without bees. Some might rejoice at the thought of never being stung by one of those little yellow buzzers, and others might miss the
Name: Class Period: Due Date: The Importance of Bees Imagine a world without bees. Some might rejoice at the thought of never being stung by one of those little yellow buzzers, and others might miss the
Learning about bees - Maths Questions
 Learning about bees - Maths Questions Preparation: Before beginning this activity, cut out each of the hexagons in the Learning about bees - maths questions resource. You may consider pre-assigning the
Learning about bees - Maths Questions Preparation: Before beginning this activity, cut out each of the hexagons in the Learning about bees - maths questions resource. You may consider pre-assigning the
Activity: Honey Bee Adaptation Grade Level: Major Emphasis: Major Curriculum Area: Related Curriculum Areas: Program Indicator: Student Outcomes:
 Activity: Honey Bee Adaptation Grade Level: Grade 5 Major Emphasis: Invertebrates and Their Environments Major Curriculum Area: Science Related Curriculum Areas: Refer to Outdoor Education Curriculum Matrix
Activity: Honey Bee Adaptation Grade Level: Grade 5 Major Emphasis: Invertebrates and Their Environments Major Curriculum Area: Science Related Curriculum Areas: Refer to Outdoor Education Curriculum Matrix
Lesson Six: The Role of Humans and Animals in Pollination
 Lesson Six: The Role of Humans and Animals in Pollination Grade Level: 2nd Grade Objective: The purpose of this lesson is to help students understand the important role that humans and animals play in
Lesson Six: The Role of Humans and Animals in Pollination Grade Level: 2nd Grade Objective: The purpose of this lesson is to help students understand the important role that humans and animals play in
2nd Grade. Plants.
 1 2nd Grade Plants 2015 11 24 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Click on the topic to go to that section What are plants? Photosynthesis Pollination Dispersal 3 Lab: What do plants need? What do plants
1 2nd Grade Plants 2015 11 24 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Click on the topic to go to that section What are plants? Photosynthesis Pollination Dispersal 3 Lab: What do plants need? What do plants
Lesson: Honeybees and Trees
 Lesson: Honeybees and Trees Topic/Essential Question: How do honeybees and trees help each other? Unit: Why Are Trees Terrific? Kindergarten Environmental Literacy Content Standards: NGSS K-LS1-1. Use
Lesson: Honeybees and Trees Topic/Essential Question: How do honeybees and trees help each other? Unit: Why Are Trees Terrific? Kindergarten Environmental Literacy Content Standards: NGSS K-LS1-1. Use
Botany Basics Kitchen Botany Facilitator Guide
 Botany Basics Kitchen Botany Facilitator Guide Big Picture Concept: Plant parts have different functions and provide us with much of the food we eat. Program Description: What do plant parts and their
Botany Basics Kitchen Botany Facilitator Guide Big Picture Concept: Plant parts have different functions and provide us with much of the food we eat. Program Description: What do plant parts and their
Lesson Adaptation Activity: Developing and Using Models
 Lesson Adaptation Activity: Developing and Using Models Related MA STE Framework Standard: 2-LS2-2. Develop a simple model that mimics the function of an animal in dispersing seeds or pollinating plants.*
Lesson Adaptation Activity: Developing and Using Models Related MA STE Framework Standard: 2-LS2-2. Develop a simple model that mimics the function of an animal in dispersing seeds or pollinating plants.*
Ch. 4- Plants. STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION And Taxonomy
 Ch. 4- Plants STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION And Taxonomy Plants belong to the kingdom: Plantae PLANTS AND PLANT REPRODUCTION STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION And Classification Two types of seed plants are gymnosperms
Ch. 4- Plants STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION And Taxonomy Plants belong to the kingdom: Plantae PLANTS AND PLANT REPRODUCTION STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION And Classification Two types of seed plants are gymnosperms
Bees. Garden Classroom. 90 minutes. Grade 6 4/10. ESY Berkeley Teaching Staff Edible Schoolyard Project Berkeley, CA. Bees Safety Pollinators Honey
 LESSON: 4/10 SIXTH GRADE GARDEN ROTATION STANDARDS ALIGNED: YES Bees PLACE OF LEARNING: Garden Classroom DURATION: 90 minutes GRADE LEVEL: Grade 6 CONTRIBUTOR ESY Berkeley Teaching Staff Edible Schoolyard
LESSON: 4/10 SIXTH GRADE GARDEN ROTATION STANDARDS ALIGNED: YES Bees PLACE OF LEARNING: Garden Classroom DURATION: 90 minutes GRADE LEVEL: Grade 6 CONTRIBUTOR ESY Berkeley Teaching Staff Edible Schoolyard
Part 2: Adaptations and Reproduction
 Part 2: Adaptations and Reproduction Review: Plants need 6 things to grow 1. Air (Carbon Dioxide) 2. Water 3. Light 4. Nutrients 5. Proper Temperature 6. Space Adaptations Adaptations are characteristics
Part 2: Adaptations and Reproduction Review: Plants need 6 things to grow 1. Air (Carbon Dioxide) 2. Water 3. Light 4. Nutrients 5. Proper Temperature 6. Space Adaptations Adaptations are characteristics
Dedicated to bees, and My dad who loved reading to the kids on his lap, My children who spent plenty of time on his lap and mine, And Melvin, who
 Dedicated to bees, and My dad who loved reading to the kids on his lap, My children who spent plenty of time on his lap and mine, And Melvin, who thinks all laps belong to him. Published by Melvin TC PO
Dedicated to bees, and My dad who loved reading to the kids on his lap, My children who spent plenty of time on his lap and mine, And Melvin, who thinks all laps belong to him. Published by Melvin TC PO
Pea Patch Pollination Game
 Pea Patch Pollination Game Classroom Activity: 5-8 Time: One 45-60-minute class period Overview: In this activity, students play a simulation game modeling changes in a plant population (a Pea Patch) caused
Pea Patch Pollination Game Classroom Activity: 5-8 Time: One 45-60-minute class period Overview: In this activity, students play a simulation game modeling changes in a plant population (a Pea Patch) caused
Click Teacher Guide: May/June 2018
 Flower Power Flowers are more than meet the eye and nose! Students learn all about and how they are pollinated to make seeds that grow into new young plants. CONVERSATION QUESTION How do plants use? TEACHING
Flower Power Flowers are more than meet the eye and nose! Students learn all about and how they are pollinated to make seeds that grow into new young plants. CONVERSATION QUESTION How do plants use? TEACHING
Objective Students will construct bee puppets and use them to act out some behaviors.
 Bee Dance Objective Students will construct bee puppets and use them to act out some behaviors. Background Honeybees are social insects. They depend on one another for survival. Bees live in groups called
Bee Dance Objective Students will construct bee puppets and use them to act out some behaviors. Background Honeybees are social insects. They depend on one another for survival. Bees live in groups called
Honey Bees: A Pollination Simulation
 Honey Bees: A Pollination Simulation Grade Level(s) 3-5 Estimated Time 2 hours Purpose Students will identify the parts of a honey bee, the stages of its life cycle, and its role in pollination. Materials
Honey Bees: A Pollination Simulation Grade Level(s) 3-5 Estimated Time 2 hours Purpose Students will identify the parts of a honey bee, the stages of its life cycle, and its role in pollination. Materials
SAMPLE PAGE. Flowers Express Lapbook. Any Age. A Journey Through Learning
 A J T L Any Age Flowers Express Lapbook Mini Lapbook, Study Guides, Activities, and Coloring Sheets A Journey Through Learning www.ajourneythroughlearning.com Copyright 2013 A Journey Through Learning
A J T L Any Age Flowers Express Lapbook Mini Lapbook, Study Guides, Activities, and Coloring Sheets A Journey Through Learning www.ajourneythroughlearning.com Copyright 2013 A Journey Through Learning
FLOWERS AND POLLINATION. This activity introduces the relationship between flower structures and pollination.
 FLOWERS AND POLLINATION This activity introduces the relationship between flower structures and pollination. Objectives for Exam #1 1. Identify flower structures and match those structures to specific
FLOWERS AND POLLINATION This activity introduces the relationship between flower structures and pollination. Objectives for Exam #1 1. Identify flower structures and match those structures to specific
The grade 5 English science unit, Plants, meets the academic content standards set in the Korean curriculum, which state students should:
 This unit deals with the structures and functions of plant organs including roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. Students learn that a plant is sustained by the systematic functioning of all its organs.
This unit deals with the structures and functions of plant organs including roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. Students learn that a plant is sustained by the systematic functioning of all its organs.
Educator s Guide. Wisconsin Ag in the Classroom Wisconsin Farm Bureau Foundation P.O. Box 5550 Madison, WI
 Educator s Guide The Wisconsin Farm Bureau Foundation and Ag in the Classroom Program presents a companion lesson and activity booklet for the 2015 Book of the Year. Order forms can be found at www.wisagclassroom.org.
Educator s Guide The Wisconsin Farm Bureau Foundation and Ag in the Classroom Program presents a companion lesson and activity booklet for the 2015 Book of the Year. Order forms can be found at www.wisagclassroom.org.
Lesson: The Buzz on Bees
 Lesson: The Buzz on Bees Environmental Literacy Question: How have humans affected the Chesapeake Bay and its watershed? Topic/Essential Questions: How do the structures of plants help them survive in
Lesson: The Buzz on Bees Environmental Literacy Question: How have humans affected the Chesapeake Bay and its watershed? Topic/Essential Questions: How do the structures of plants help them survive in
Day of Science and Service May 8, 2014
 Day of Science and Service May 8, 2014 On May 8, 2014, be a scientist for the day! Create a buzz. Get outside, record your observations, share your pictures and tell us what s happening in your community.
Day of Science and Service May 8, 2014 On May 8, 2014, be a scientist for the day! Create a buzz. Get outside, record your observations, share your pictures and tell us what s happening in your community.
BOTANY, PLANT PHYSIOLOGY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 6: PLANT PARTS AND FUNCTIONS Part 4 - Flowers and Fruit
 BOTANY, PLANT PHYSIOLOGY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 6: PLANT PARTS AND FUNCTIONS Part 4 - Flowers and Fruit Script to Narrate the PowerPoint, 06PowerPointFlowers and Fruit.ppt It is not permitted to export
BOTANY, PLANT PHYSIOLOGY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 6: PLANT PARTS AND FUNCTIONS Part 4 - Flowers and Fruit Script to Narrate the PowerPoint, 06PowerPointFlowers and Fruit.ppt It is not permitted to export
Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan
 Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan Lesson Name Presenter(s) The Water Cycle UC Berkeley PhD students Grade Level 1 Standards Connection(s) Earth Sciences, physics sciences CA Science Content
Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan Lesson Name Presenter(s) The Water Cycle UC Berkeley PhD students Grade Level 1 Standards Connection(s) Earth Sciences, physics sciences CA Science Content
Grade Level Suggestion: Grades 4 th to 8 th. Time Frame: minutes.
 I Have, Who Has? An Interactive Vocabulary Game Prairie Ecosystem Study Vocabulary Grades 4 th -8th Introduction: Below is a collection of cards that connect to the Prairie Study Vocabulary for 4 th -
I Have, Who Has? An Interactive Vocabulary Game Prairie Ecosystem Study Vocabulary Grades 4 th -8th Introduction: Below is a collection of cards that connect to the Prairie Study Vocabulary for 4 th -
GENERAL CURRICULUM MULTI-SUBJECT SUBTEST
 GENERAL CURRICULUM MULTI-SUBJECT SUBTEST SUPPLEMENTAL SAMPLE OPEN-RESPONSE ITEM WITH SAMPLE RESPONSES AND ANALYSES NOTE: This sample open-response item is provided as a supplement to the Test Information
GENERAL CURRICULUM MULTI-SUBJECT SUBTEST SUPPLEMENTAL SAMPLE OPEN-RESPONSE ITEM WITH SAMPLE RESPONSES AND ANALYSES NOTE: This sample open-response item is provided as a supplement to the Test Information
Self-Guided Tour. Plants and the Plant Life Cycle. K to 2nd Grade
 Time Required: 60 min April to October Topic: Observing plant life cycles in the Garden Materials: For each student: Pencil or crayons Clipboards (recommended) Comparison Worksheet Colored dots (recommended)
Time Required: 60 min April to October Topic: Observing plant life cycles in the Garden Materials: For each student: Pencil or crayons Clipboards (recommended) Comparison Worksheet Colored dots (recommended)
Backward Design Fourth Grade Plant Unit
 Collin Zier Assessment November 2 nd, 2012 Backward Design Fourth Grade Plant Unit Stage One Desired Results Established Goals: Wisconsin s Model Academic Standards for Science 4 th Grade Standard F Life
Collin Zier Assessment November 2 nd, 2012 Backward Design Fourth Grade Plant Unit Stage One Desired Results Established Goals: Wisconsin s Model Academic Standards for Science 4 th Grade Standard F Life
Year 7 Science 7B1: Microscopes, Cells and Plant Reproduction PPA Challenge
 Year 7 Science 7B1: Microscopes, Cells and Plant Reproduction PPA Challenge Name: Form: Task Sheet 1 (Bronze Challenge): What parts does a microscope have? Use the words in the boxes below to label the
Year 7 Science 7B1: Microscopes, Cells and Plant Reproduction PPA Challenge Name: Form: Task Sheet 1 (Bronze Challenge): What parts does a microscope have? Use the words in the boxes below to label the
Lesson Plan: Plant Something Bee Friendly
 Lesson Plan: Plant Something Bee Friendly Elementary Bees (honeybees and solitary bee species) are essential pollinators for much of the world s food including many food and forage crops across British
Lesson Plan: Plant Something Bee Friendly Elementary Bees (honeybees and solitary bee species) are essential pollinators for much of the world s food including many food and forage crops across British
The Life Cycle of a Flowering Plant
 The Life Cycle of a Flowering Plant Focus: Students draw upon their own observations of their plants as well as research and class discussion to explore the life cycle of flowering plants. Specific Curriculum
The Life Cycle of a Flowering Plant Focus: Students draw upon their own observations of their plants as well as research and class discussion to explore the life cycle of flowering plants. Specific Curriculum
TIME: 45 minutes. LESSON: Curious About Clouds GRADE: 1 st SUMMARY:
 LESSON: Curious About Clouds GRADE: 1 st TIME: 45 minutes SUMMARY: Students will make observations about the weather and sky, listen to a story about weather and discuss it. Students will go outside and
LESSON: Curious About Clouds GRADE: 1 st TIME: 45 minutes SUMMARY: Students will make observations about the weather and sky, listen to a story about weather and discuss it. Students will go outside and
Page 1 of 5. New: evidence, measure, nutrients, light, soil, transport, volume, water, warmth, insect, pollen, pollinate, nectar.
 National Curriculum Objectives: (Statutory requirements) a) Identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering : roots, stem/trunk, leaves and flowers b) Explore the requirements of for
National Curriculum Objectives: (Statutory requirements) a) Identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering : roots, stem/trunk, leaves and flowers b) Explore the requirements of for
Structures of Seed Plants
 CHAPTER 12 SECTION 4 Introduction to Plants Structures of Seed Plants BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the functions of roots and stems?
CHAPTER 12 SECTION 4 Introduction to Plants Structures of Seed Plants BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the functions of roots and stems?
Funding for the duplication of this publication is provided by the St. Lucie County Board of County Commissioners.
 This booklet was adapted by Kate O Neill, Program Specialist from Africanized Honey Bees on the Move, University of Arizona. Reviewed by: Anita Neal, St. Lucie County Extension Director 8400 Picos Road,
This booklet was adapted by Kate O Neill, Program Specialist from Africanized Honey Bees on the Move, University of Arizona. Reviewed by: Anita Neal, St. Lucie County Extension Director 8400 Picos Road,
V Q \ = 7]Z 4IVL 126 Unit 5
![V Q \ = 7]Z 4IVL 126 Unit 5 V Q \ = 7]Z 4IVL 126 Unit 5](/thumbs/77/75709676.jpg) 126 Unit 5 Is it cold and windy? Or is it a sunny day? Is it raining cats and dogs? Or can we go out to play? I will learn to talk about seasons and weather plant life environments caring for the earth
126 Unit 5 Is it cold and windy? Or is it a sunny day? Is it raining cats and dogs? Or can we go out to play? I will learn to talk about seasons and weather plant life environments caring for the earth
Chapter 24-Flowering Plant and Animal Coevolution
 Chapter 24-Flowering Plant and Animal Coevolution coevolutionary plant-animal associations alliances that have influenced the evoluton of both partners. These examples show that plants have acquired traits
Chapter 24-Flowering Plant and Animal Coevolution coevolutionary plant-animal associations alliances that have influenced the evoluton of both partners. These examples show that plants have acquired traits
 Honeybees There are more than 22,000 types of bees in the world. Do you know which bees make honey? Without honeybees, you wouldn t have any honey to spread on your toast in the morning. You may have seen
Honeybees There are more than 22,000 types of bees in the world. Do you know which bees make honey? Without honeybees, you wouldn t have any honey to spread on your toast in the morning. You may have seen
Plants can be either herbaceous or woody.
 Plant Structure Plants can be either herbaceous or woody. Herbaceous plants are plants with growth which dies back to the ground each year, in contrast with woody plants Most herbaceous plants have stems
Plant Structure Plants can be either herbaceous or woody. Herbaceous plants are plants with growth which dies back to the ground each year, in contrast with woody plants Most herbaceous plants have stems
Project Essential Questions
 GRADE K Project Overview Eric Carle Inspired Art Project Essential Questions How were you inspired by Eric Carle to create your picture? How did you use Eric Carle s artistic practices to create your living
GRADE K Project Overview Eric Carle Inspired Art Project Essential Questions How were you inspired by Eric Carle to create your picture? How did you use Eric Carle s artistic practices to create your living
Pollination Power Understanding the Role of Pollinators in the Environment and Food Production
 Pollination Power Understanding the Role of Pollinators in the Environment and Food Production Grade Level: 3 Learning Environment: Classroom Outdoor Area (School yard, garden) Prep Time: 20 minutes (print
Pollination Power Understanding the Role of Pollinators in the Environment and Food Production Grade Level: 3 Learning Environment: Classroom Outdoor Area (School yard, garden) Prep Time: 20 minutes (print
Lesson Plan: Plant Something Bee Friendly
 Lesson Plan: Plant Something Bee Friendly Middle School Bees (honeybees and solitary bee species) are essential pollinators for much of the world s food including many food and forage crops across British
Lesson Plan: Plant Something Bee Friendly Middle School Bees (honeybees and solitary bee species) are essential pollinators for much of the world s food including many food and forage crops across British
Name Date Block. Plant Structures
 Name Date Block What are the Functions of Roots, Stems, and Leaves? Plant Structures Each part of a plant plays an important role in its structure and function. Roots, stems, and leaves are just three
Name Date Block What are the Functions of Roots, Stems, and Leaves? Plant Structures Each part of a plant plays an important role in its structure and function. Roots, stems, and leaves are just three
Plant Growth & Reproduction
 Water loss (ml) Water loss (ml) Water loss (ml) Water loss (ml) 4/24/2014 Plant Growth & Reproduction BI 103 Plant-Animal Systems Turn in Homework #1 Lab Wed! (schedule change) 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 no wind
Water loss (ml) Water loss (ml) Water loss (ml) Water loss (ml) 4/24/2014 Plant Growth & Reproduction BI 103 Plant-Animal Systems Turn in Homework #1 Lab Wed! (schedule change) 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 no wind
Blank paper & clip boards or nature journals Pencils Bug jars/bug boxes & Insect ID sheets/field guides
 LESSON: Catch and Release Insects GRADE: 5 th TIME: 45 min. SUMMARY: A field leader uses introduce students to the definition of insects and different insect groups. Afterwards, students work in groups
LESSON: Catch and Release Insects GRADE: 5 th TIME: 45 min. SUMMARY: A field leader uses introduce students to the definition of insects and different insect groups. Afterwards, students work in groups
Pollinator Activity #1: How to Raise a Butterfly
 How to Raise a Butterfly How to Raise a Butterfly A Conversation Where do you most often see butterflies? What are they doing when you see them? Have you ever seen a butterfly in another form? They have
How to Raise a Butterfly How to Raise a Butterfly A Conversation Where do you most often see butterflies? What are they doing when you see them? Have you ever seen a butterfly in another form? They have
Teacher Packs in Experimental Science. Bio Pack 4. Agents of pollination
 Teacher Packs in Experimental Science Bio Pack 4 Agents of pollination Pack contents: A. Teacher s Guide B. Students Guide C. Assessment Student s sheet D. Extensions to experiment E. Useful Links F. Health
Teacher Packs in Experimental Science Bio Pack 4 Agents of pollination Pack contents: A. Teacher s Guide B. Students Guide C. Assessment Student s sheet D. Extensions to experiment E. Useful Links F. Health
Enrichment Lesson 1: Making a Bee line
 Dedicated to Reducing Pesticides Focus Areas: Animal Lifestyles; Science, Physical Education Focus Skills: understanding patterns, conducting an experiment, role playing, cooperating to achieve a goal
Dedicated to Reducing Pesticides Focus Areas: Animal Lifestyles; Science, Physical Education Focus Skills: understanding patterns, conducting an experiment, role playing, cooperating to achieve a goal
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science
 IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Biology 8.2 - Sexual Reproduction in Plants Sexual Reproduction in Plants In a plant, the flower is the sexual organ, and it has both male and females parts.
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Biology 8.2 - Sexual Reproduction in Plants Sexual Reproduction in Plants In a plant, the flower is the sexual organ, and it has both male and females parts.
Bees! Communication. Sustainability. Nourishment. Life Skills. Academics. Garden Lesson G6-13
 Garden Lesson G6-13 Bees! Communication Students interpret visual aids, take part in group discussion, make an inference and share it with others. Sustainability Bees are a significant pollinator and are
Garden Lesson G6-13 Bees! Communication Students interpret visual aids, take part in group discussion, make an inference and share it with others. Sustainability Bees are a significant pollinator and are
Creepy, Crawly Critters
 Creepy, Crawly Critters Objective Students will identify different insects as well as the body parts of insects. Background There are over 1.5 million kinds of insects. They come in all shapes and sizes.
Creepy, Crawly Critters Objective Students will identify different insects as well as the body parts of insects. Background There are over 1.5 million kinds of insects. They come in all shapes and sizes.
The Pollinators Journey
 The Pollinators Journey Summary Students perform a short play about threatened migratory pollinators. Grade Level: K-4; 5-8 Time: 2 to 3 class periods (90 minutes or more) Subjects: Science, Language Arts,
The Pollinators Journey Summary Students perform a short play about threatened migratory pollinators. Grade Level: K-4; 5-8 Time: 2 to 3 class periods (90 minutes or more) Subjects: Science, Language Arts,
Arizona Grown Specialty Crop Lesson Plan. LEVEL: Grades K-3
 Arizona Grown Specialty Crop Lesson Plan Apple: Bare to Pick U LEVEL: Grades K-3 SUBJECTS: Language Arts, Science, Social Studies and Art AZ ACADEMIC STANDARDS : R-R3, R-F4, W- R1, ISS-R2, M1-F1, W-F4,
Arizona Grown Specialty Crop Lesson Plan Apple: Bare to Pick U LEVEL: Grades K-3 SUBJECTS: Language Arts, Science, Social Studies and Art AZ ACADEMIC STANDARDS : R-R3, R-F4, W- R1, ISS-R2, M1-F1, W-F4,
2. Assembly 1. Overview 3. Play
 Bee-matching game 2. Assembly You will need a color printer, laminator, scissors, magnets and/or Velcro tape, and hot glue. Additionally, you will need a surface such as a tri-fold board, felt board, etc.
Bee-matching game 2. Assembly You will need a color printer, laminator, scissors, magnets and/or Velcro tape, and hot glue. Additionally, you will need a surface such as a tri-fold board, felt board, etc.
Botany: Plant Dissection Student Advanced Version
 Botany: Plant Dissection Student Advanced Version In this lab, we will learn about the structure and function of plants, and how plants are useful in our everyday lives. Key Concepts: Plants have been
Botany: Plant Dissection Student Advanced Version In this lab, we will learn about the structure and function of plants, and how plants are useful in our everyday lives. Key Concepts: Plants have been
Soil and Erosion. Spring Lesson 5 - Grade 5. Lesson Description. Learning Objectives. Materials and Preparation
 Soil and Erosion Lesson Description In this lesson students learn about erosion. They learn about the four different kinds of erosion and do experiments that demonstrate each kind. They learn how erosion
Soil and Erosion Lesson Description In this lesson students learn about erosion. They learn about the four different kinds of erosion and do experiments that demonstrate each kind. They learn how erosion
Plant and Animal Interactions
 Plant and Animal Interactions 21 LESSON For each student: For each adult: Materials Needed Student Data Sheet: Plant and Animal Interactions pencil clipboard Leader Sheet: Plant and Animal Interactions
Plant and Animal Interactions 21 LESSON For each student: For each adult: Materials Needed Student Data Sheet: Plant and Animal Interactions pencil clipboard Leader Sheet: Plant and Animal Interactions
Lesson 2. Parts of a plant Contains: Worksheet 3.1 Support worksheet 3.1
 Unit 3. Plants Lesson 2. Parts of a plant Contains: Worksheet 3.1 Support worksheet 3.1 WORKSHEET 3.1 1. Read and circle the words that are part of a plant. Draw the plant. This plant has six roots. It
Unit 3. Plants Lesson 2. Parts of a plant Contains: Worksheet 3.1 Support worksheet 3.1 WORKSHEET 3.1 1. Read and circle the words that are part of a plant. Draw the plant. This plant has six roots. It
Fonts and alphabets licensed from
 Fonts and alphabets licensed from www.letteringdelights.com Pumpkins are a great way to teach and reinforce both Language Arts and Science standards. Hands on experiences are some of the best learning
Fonts and alphabets licensed from www.letteringdelights.com Pumpkins are a great way to teach and reinforce both Language Arts and Science standards. Hands on experiences are some of the best learning
Classroom Activities
 Classroom Activities Thanks to: North Carolina Ag in the Classroom Florida Ag in the Classroom Photosynthesis Promenade Greetings from North Carolina Ag in the Classroom! Ag in the Classroom is happy to
Classroom Activities Thanks to: North Carolina Ag in the Classroom Florida Ag in the Classroom Photosynthesis Promenade Greetings from North Carolina Ag in the Classroom! Ag in the Classroom is happy to
Photosynthesis Promenade
 Photosynthesis Promenade Summary: Students simulate the process of photosynthesis through a wholebody demonstration. Objective Students will be able to illustrate how plants use the sun s energy to make
Photosynthesis Promenade Summary: Students simulate the process of photosynthesis through a wholebody demonstration. Objective Students will be able to illustrate how plants use the sun s energy to make
After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: The gametophyte grows as an independent plant.
 CHAPTER 12 SECTION 3 Introduction to Plants Seed Plants 7.2.a, 7.5.f California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How are seed
CHAPTER 12 SECTION 3 Introduction to Plants Seed Plants 7.2.a, 7.5.f California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How are seed
Upskilling community leaders for Australian Pollinator Week
 Upskilling community leaders for Australian Pollinator Week Classroom or other educational activities DISCLAIMER Hello and thank you for being part of this project. This presentation is designed to be
Upskilling community leaders for Australian Pollinator Week Classroom or other educational activities DISCLAIMER Hello and thank you for being part of this project. This presentation is designed to be
UNIT AT A GLANCE. Name: Trinh Le Topic: Plants Grade Level: 2
 UNIT AT A GLANCE Name: Trinh Le Topic: Plants Grade Level: 2 Introducing the Topic: Activity: Lunch Menu Detectives (Students trace ingredients to plants) Importance of Plants: Read Bits That Grow Big,
UNIT AT A GLANCE Name: Trinh Le Topic: Plants Grade Level: 2 Introducing the Topic: Activity: Lunch Menu Detectives (Students trace ingredients to plants) Importance of Plants: Read Bits That Grow Big,
Nonvascular plants Vascular plants Spore Gymnosperm Angiosperm Germinate. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Nonvascular plants Vascular plants Spore Gymnosperm Angiosperm Germinate Tubes for Transport Warm Up 1 Tubes for Transport Nonvascular plants are simple plants that lack vascular tissue, which easily transports
Nonvascular plants Vascular plants Spore Gymnosperm Angiosperm Germinate Tubes for Transport Warm Up 1 Tubes for Transport Nonvascular plants are simple plants that lack vascular tissue, which easily transports
Teacher s Guide. Bees. PA G E S 2 3 Bee Happy Structure and life cycle of bees. 4 5 To Bee or Not to Bee Bees and their look-alikes
 Teacher s Guide Bees Dear Educator, Your students will stay as busy as bees as they buzz through this issue of KIDS DISCOVER. Your young scientists will explore the topics at the right in Bees. This Teacher
Teacher s Guide Bees Dear Educator, Your students will stay as busy as bees as they buzz through this issue of KIDS DISCOVER. Your young scientists will explore the topics at the right in Bees. This Teacher
Transcription of Science Time video Spring and Flowers
 Transcription of Science Time video Spring and Flowers The video for this transcript can be found on the Questacon website at: http://canberra.questacon.edu.au/sciencetime/ Transcription from video: Hi,
Transcription of Science Time video Spring and Flowers The video for this transcript can be found on the Questacon website at: http://canberra.questacon.edu.au/sciencetime/ Transcription from video: Hi,
LASER READER MINI-POSTERS, STUDENT WORKSHEET MASTERS AND ANSWER KEYS
 LASER READER MINI-POSTERS, STUDENT WORKSHEET MASTERS AND ANSWER KEYS Dear Assembly Coordinator and Teachers, The following pages contain mini-posters, student worksheet masters and answer keys. They are
LASER READER MINI-POSTERS, STUDENT WORKSHEET MASTERS AND ANSWER KEYS Dear Assembly Coordinator and Teachers, The following pages contain mini-posters, student worksheet masters and answer keys. They are
UNIT 3. PLANTS. PRIMARY 4/ Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández
 UNIT 3. PLANTS PRIMARY 4/ Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández They help to keep it in place. Roots They take in the water and minerals a plant needs to make its food. They support the leaves.
UNIT 3. PLANTS PRIMARY 4/ Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández They help to keep it in place. Roots They take in the water and minerals a plant needs to make its food. They support the leaves.
This activity will help students to differentiate between living and non-living and to identify characteristics of living things.
 Next Generation Science Standards K-LS1-1 www.maineagintheclassroom.org Exploring Marine Science and Aquaculture Grades K-2 Living vs Non-living Developed by the University of Maine Cooperative Extension
Next Generation Science Standards K-LS1-1 www.maineagintheclassroom.org Exploring Marine Science and Aquaculture Grades K-2 Living vs Non-living Developed by the University of Maine Cooperative Extension
GARGAMEL'S MAGIC SPELL
 GARGAMEL'S MAGIC SPELL - 2014 - Licensed through I.M.P.S (Brussels) - www.smurfs.com. All Rights Reserved. Welcome to the Popcorn ELT Readers series, a graded readers series for low-level learners of English.
GARGAMEL'S MAGIC SPELL - 2014 - Licensed through I.M.P.S (Brussels) - www.smurfs.com. All Rights Reserved. Welcome to the Popcorn ELT Readers series, a graded readers series for low-level learners of English.
PHOTOSYNTHESIS. Can Plants Make Their Own Food? W 671
 W 671 PHOTOSYNTHESIS Can Plants Make Their Own Food? Brigitte Passman, 4-H Youth Development Agent Tipton County Jennifer Richards, Curriculum Specialist, Tennessee 4-H Youth Development Tennessee 4-H
W 671 PHOTOSYNTHESIS Can Plants Make Their Own Food? Brigitte Passman, 4-H Youth Development Agent Tipton County Jennifer Richards, Curriculum Specialist, Tennessee 4-H Youth Development Tennessee 4-H
Anatomy of Flowering Plants
 Dry Lab BIOLOGY Anatomy of Flowering Plants Investigation Manual ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTS Table of Contents 2 Overview 2 Outcomes 2 Time Requirements 3 Background 6 Safety 6 Materials 7 Activity 1 10
Dry Lab BIOLOGY Anatomy of Flowering Plants Investigation Manual ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTS Table of Contents 2 Overview 2 Outcomes 2 Time Requirements 3 Background 6 Safety 6 Materials 7 Activity 1 10
Cell parts. nucleus cytoplasm cell surface membrane. cell wall vacuole chloroplast
 7Ab/12 Cell parts nucleus cytoplasm cell surface membrane cell wall vacuole chloroplast found in plant cells only found in plant cells only found in plant cells only found in animal and plant cells found
7Ab/12 Cell parts nucleus cytoplasm cell surface membrane cell wall vacuole chloroplast found in plant cells only found in plant cells only found in plant cells only found in animal and plant cells found
BUTTERFLY SCIENCE. 9 Science Activities for PreK, K & EarthsBirthday.org
 BUTTERFLY SCIENCE 9 Science Activities for PreK, K & 1-3 1 800 698 4438 EarthsBirthday.org CONTENTS Butterfly Life Cycle Song 4 Changing Butterfly Dance 5 What Is a Caterpillar? 6 Caterpillar & Pupa Timelines
BUTTERFLY SCIENCE 9 Science Activities for PreK, K & 1-3 1 800 698 4438 EarthsBirthday.org CONTENTS Butterfly Life Cycle Song 4 Changing Butterfly Dance 5 What Is a Caterpillar? 6 Caterpillar & Pupa Timelines
Pollination, the Grand Interaction Among Flowers, Bees, Growers and Beekeepers
 Pollination, the Grand Interaction Among Flowers, Bees, Growers and Beekeepers EASTERN KENTUCKY BEEKEEPING SCHOOL PROGRAM, January 20, 2018 Hazard Community and Technical College John A. Skinner University
Pollination, the Grand Interaction Among Flowers, Bees, Growers and Beekeepers EASTERN KENTUCKY BEEKEEPING SCHOOL PROGRAM, January 20, 2018 Hazard Community and Technical College John A. Skinner University
