Performance of Source Nursary of Pollen Parent and Cms Lines of Brassica napus L.
|
|
|
- Kathleen Watson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Performance of Source Nursary of Pollen Parent and Cms Lines of Brassica napus L. S. C. Saha Plant Breeder, Research and Development Farm Supreme Seed Company Ltd., Dhaka, Bangladesh Sabina Yeasmin Department of Agronomy, Bangladesh Agricultural University Mymensingh 2202, Bangladesh A. K. M. Aminul Islam (Corresponding author) Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Agricultural University Gazipur 1706, Bangladesh M. G. Rasul Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Agricultural University Gazipur 1706, Bangladesh M. A. K. Mian Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Agricultural University Gazipur 1706, Bangladesh Received: July 2, 2010 Accepted: September 17, 2010 doi: /jas.v3n2p114 Abstract The study was conducted with the objective to know the performance of floral and yield characteristics of pollen and CMS parent. Significant variation was observed for flowering and yield contributing characteristics among two CMS lines (Z 1 and Z 2 ) and 21 pollen parents. The pollen parent Nap2019 was found as early flowering whereas the parent Nap2013 was the late for first flowering. The highest length of anther was found in Nap9907 and short anther in Nap9905. Slender anther was produced by the genotype Nap2037 and bold anther was produced by the genotype Nap9907. Length of filament was the highest in Nap2012 and the lowest in Nap0130. For yield contributing characteristics, the genotype Nap9906 matured earlier than all other genotypes while the maximum duration took by Nap2013. The longest inflorescence was found in the genotype Nap2001 and the smallest in Nap9906. The highest number of siliqua per plant was counted in Nap2066 and it was the lowest in 114
2 Nap9906. Wide variability in respect of number of seeds per siliqua was exhibited among the genotypes and it was the lowest in Nap9901 and the highest in Nap In case of 1000-seed weight, the genotype Nap2022 produced larger seeds and the genotype Nap9907 produced smaller seeds. The highest seed yield per plant was recorded in the genotype Nap2066 and the lowest in Nap9905. In case of CMSZ 1 and CMSZ 2, 50% plants were flowered within 45 days after sowing. The CMS plant produced small, slender anther with shorter filament compare to pollen parents. The out crossing rate of CMSZ 1 and CMSZ 2 was 40.31% and 47.96%, respectively. Time required for days to 80% maturity of CMSZ 1 and CMSZ 2 were about 106 days. The number of siliqua per plant was found the highest in CMSZ 1 and the lowest in CMSZ 2. The average number of seeds per siliqua and seed yield per plant was recorded the highest in CMSZ 1 and the lowest in CMSZ 2. The pollen parent with desirable performance and CMS parents CMSZ 2 having higher out crossing rate can be used for future Brassica napus hybrid breeding program. Keywords: Rapeseed (Brassica napus L), Pollen parent, CMS line, Floral characteristics, Seed yield 1. Introduction Rapeseed (B. napus L) play a vital role in human diet but the consumption rate of oil in Bangladesh is far below than that of balanced diet (6 g oil per day per capita). The seeds of mustard and rapeseed contain 42% oil and 25% protein (Khaleque, 1985). Recent data indicated that oil crops produces 0.16 million tons of edible oil in every year as against the total requirements of 0.5 million tons for a population of 130 million in Bangladesh (Anon., 1999 and Mondal et al., 2001). The shortage of edible oil has become a chronic problem for the nation. To fulfil the requirement, the country has to import edible oils at the cost of bigger amount of foreign exchange. The share of rapeseed and mustard was tons, which comes to 52 percent of the total edible oil production (Anon., 2007). The yield of rapeseed and mustard is generally low in Bangladesh as compared with the world average. The main problems for this low yield are the use of low yielding local indigenous cultivars, unavailability of locally developed high yielding or hybrid varieties. The present seed yield per hectare of mustard in Bangladesh is far below the level attained in the developed countries of the world (BBS, 2008). Commercial F 1 hybrid cultivars become increasingly important for oilseed crops. For commercial exploitation of hybrid technology in mustard, a cytoplasmic male sterile line (A), a maintainer line (B) and a restorer line (R) are required. Before using in hybrid seed production, these CMS lines and pollen parents need to be evaluated thoroughly for different morphological, floral and agronomic traits. Investigations leading to the development of new CMS (Cytoplasmic Male Sterile) lines and identification of maintainer lines from the germplasm have brightened the prospects of development of commercial hybrids in Brassica (Ogura, 1968). Morph-physiological, floral and yield traits of pollen as well as CMS parent can helps to identify suitable genotypes for commercial hybrids. Extent of outcrossing on a male sterile line is influenced by its floral traits, stigma size, exertion rate, length of filament of the flower in Brassica napus (Barrett and Eckert, 1990; Dudley et al., 2007; Goodwillie et al., 2009). Therefore, the present investigation was undertaken with the objective to evaluate pollen parent and CMS lines for different morphological, floral and agronomic traits. 2. Materials and Methods The research work was conducted at the experimental farm, Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Agricultural University (BSMRAU), Salna, Gazipur, Bangladesh. Among twenty three genotypes, two were CMS (Cytoplasmic Male Sterile) lines (Z1 and Z2: two different cytoplasmic sources) and twenty one male parents or pollen parents (parents from where pollen collected) were used as plant materials. The pollen parent and CMS lines were grown in different row in the experimental field with row spacing of 30 cm between row and plant spacing of 15 cm within the row. The experiment was laid out in a Randomized Complete Block Design (RCBD) with three replications. Fertilizers were applied at the rate of 270, 170, 100, 150, 5 kg/ha of Urea, TSP, MP, Gypsum and Zinc sulphate, respectively. Cowdung was applied at the rate of 10 M ton/ha. Whole amount of cowdung TSP, MP, Gypsum, Zinc sulphate and half of Urea were applied at the time of final land preparation. The remaining urea was top dressed at 30 days after seedlings emergence. Necessary intercultural operation was taken during cropping period for proper growth and development of the plants recommended by Khaleque (1985). Thinning and first weeding was done at 10 days after emergence (DAE). The second weeding was done at 30 DAE followed by application of urea by top dressing. Irrigation was given at regular interval when necessary. For suppression of aphid population Malathion 57 EC was applied three times as foliar spray at an interval of days after seedling emergence (Khaleque, 1985). Data were collected from five randomly selected competitive plants of each of the entries on the characters days to 1st flowering, days to 50% flowering, number of primary branches per plant, days to 80% maturity, plant height at maturity (cm), length of inflorescence (cm), number of siliqua per plant, length of Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education 115
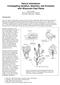
3 siliqua (cm), number of seeds per siliqua, 1000-seed weight (g), anther length (mm), anther breadth (mm), length of filament (mm), length of stamen (mm), seed yield per plant (g). Out crossing rate (%) was determined for CMS lines using the following formula- All data were analyzed using SAS statistical package version 9.01 (2008) to find out the variation among the different genotypes by F-test. Treatment means were separated by Duncan s Multiple Range Test (DMRT) at 5% level of probability for interpretation of the results (Steel and Torrie, 1980). 3. Results and Discussion 3.1 Performance of different pollen parents (B. napus genotypes) First flowering Variation due to genotypes was statistically significant for this character (Table 1). In Nap2019 first flower opened at 30 days after sowing which was statistically similar with Nap9901 (30.33 days), Nap9906 (30.67 days), Nap205 (30.67 days), Nap2012 (31 days) and Nap94006 (31.67 days). The maximum duration (36.33 days) for first opening of flower was required by genotype Nap2013, which was statistically identical to Nap9908 (35 days) but significantly different to the rest of the genotypes. Genotypes having minimum days to flowering are considered good genotypes for earliness. Considering days to flowering, the genotype Nap2013 could be considered as early and quick growing cultivar Anther length and breadth The mean square due to genotypes revealed significant variation existed among the genotypes for anther length and breadth (Table 1). The genotype Nap9907 and Nap9905 were found to produce the longest (2.815) and the shortest (2.075) anther, respectively. On the other hand, maximum anther breadth was observed in Nap9907 (0.918) and minimum in the genotype Nap2037 (0.697). Anther size is directly related to number of pollen grains inside anther. Genotype with larger anther contained more pollen grains which can be produced more seed per plant (Plate 1). The genotype Nap9907 with higher anther length and breadth can be produced more pollen grains inside anther. Several authors (Banga and Labana, 1985; Chen et al., 1993; Sodhi et al., 1993; Hu et al., 1992) found anther development in the pollen parent or maintainer line was normal Length of filament The difference in filament length among the genotypes was observed to be statistically significant. The longest filament (8.41) was recorded in Nap0130 while the shortest (5.41) was in Nap2012 (Table 1). The shortest filament producing genotypes were Nap2001, Nap206, Nap2037, Nap205, Nap2057, Nap012, Nap94006, Nap2066, Nap2019 and Nap9905. The genotype Nap0130 produced the longest filament was found to be statistically different from rest of the twenty genotypes. Filament length can increase the cross pollination rate and improve the seed production. The genotypes with longer filament can be produced more seed compared to the genotypes with shorter filament. Sixty two percent of the genotypes under study which include 13 genotypes produced filament length varying from 6.10 mm to 6.80 mm Length of stamen Stamen length showed significant variation and ranged from mm to mm (Table 1). The longest stamen was observed in Nap0130 (10.92). The genotype Nap2012 produced the shortest (7.913) stamen and was statistically similar to the genotypes Nap9905, Nap205, Nap206, Nap2057, Nap2037, Nap94006, Nap012, Nap2022 and BARI Sarisha-8. Stamen length could be influenced the pollination and seed production in Brassica napus % flowering Significant variation was observed for days to 50% flowering among the pollen parents under investigation. The maximum days to 50% flowering was observed in Nap2013 (43.33) followed by Nap2057(39.33) which did not differ significantly from Nap206, Nap9907, Nap108, Nap205, Nap2001, Nap2066, Nap94006, Nap2022, Nap9908, Nap9905, Nap2037 and Nap9904. The lowest days to 50% flowering was taken by Nap2019 (34.33) which was statistically similar to the Nap9906, Nap2012 and Nap0130. About two third of the genotypes produced 50% flowering within days after sowing (Table 2). The differences in days to 50% flowering might be due to the genetical factors of the genotype concerned. The genotype Nap2019 can be selected as parent during the development of short duration Brassica napus variety. 116
4 3.1.6 Primary branches per plant Marked variation was exhibited in respect of number of primary branches per plant. The maximum number (4.17) of primary branches per plant was produced by the genotype Nap9908 and the minimum (2.67) in Nap0130 (Table 2). Seventeen genotypes bearing the primary branches ranged from 3.0 to 3.8. Ghosh and Chatterjee (1988) found that the productivity of mustard per unit of area significantly affected by number of primary branches per plant in 8 different elite varieties of Indian mustard % maturity The analysis of variance for this character showed significant differences among the genotypes (Table 2). The minimum duration (95.67 days) for 80% maturity was required by the genotype Nap9906 followed by BARI Sarisha-8 (96.33 days) and the maximum duration by Nap2013 (109.7days). As maturity days concerned, two genotypes were taken less than 100 days for 80% maturity, exhibiting earliness Plant height at maturity Analysis of variance revealed marked variation among the genotypes in respect of plant height (Table 2). Plant height at maturity varied from to 114.7cm. The tallest plant was produced by the genotype Nap2022 (114.7cm) followed by the genotypes Nap9908 (105.3cm) and Nap9907 (101.2cm). The height of the plant was found to be minimum in Nap2057 (81.67cm) closely followed by Nap 9906 (84.34cm). More than 75% genotypes attained height of plant within the range between and 98.67cm. For plant height at maturity, 13 genotypes were of short stature with plant height ranged from to 98.67cm and remaining eight genotypes with long stature with plant height ranged from cm to 114.7cm. The variation in plant height of different varieties of canola may be attributed to their genetic potential (Sana et al., 2003) Length of inflorescence Length of inflorescence showed a wide range of variation among the genotypes evaluated in this study. The longest (70.0) inflorescence was found in the genotype Nap2001 (Table 2) which was statistically identical with Nap2022, Nap2012, Nap9904, Nap108, BARI Sarisha-8, Nap2037, and Nap9905. The smallest inflorescence was found in Nap9906 (48.67) followed in increasing order by Nap94006, Nap9901, Nap2066, Nap205, Nap2057 and Nap012. In respect of length of inflorescence 61.9% of the genotypes under study varied from 59.17cm to cm. The yield increase in brassica could be attributed to increased inflorescence length as it can be accommodate more number of siliqua Siliqua per plant The significant variation was observed for number of siliqua produced per plant and it was varied from to The highest number of siliqua per plant was produced by Nap2066 (285.8) and the other genotypes were statistically identical with that of the former being placed in the order of Nap9907 (279.1), Nap2001 (273.2), Nap108 (264.0), Nap9908 (259.8), Nap206 (201.3), Nap2037 (199.3), Nap2057 (191.5) and Nap012 (188.0). The lowest number of siliqua per plant (121.5) was produced in Nap9906 which was statistically similar to all the genotypes except Nap2066, Nap9907, Nap2001, Nap108 and Nap9908 (Table 2) Length of siliqua The difference in siliqua length among the genotypes was observed to be statistically significant. The longest siliqua (6.58) was produced by the genotype Nap9906 followed by Nap2037 (6.47) while the shortest by Nap0130 (5.26) followed by Nap9905 (5.27) (Table 2). The smallest siliqua producing genotype was statistically identical with those of Nap9905, Nap2001, Nap9901, Nap012, Nap2022 and BARI Sarisha-8. The longest siliqua producing genotypes was statistically similar with those of the Nap2037, Nap94006, Nap206, Nap108, Nap2057, Nap2066, Nap2019, Nap9908 and Nap9904. Wide variability in respect of siliqua length was exhibited among the genotypes Seeds per siliqua Statistical difference could be detected from Table 2 regarding the number of seeds per siliqua among the various B. napus genotypes. It varied from to The maximum number (23.86) of seeds per siliqua was recorded in the genotype Nap94006 followed by the genotypes Nap9906 (23.74) and Nap205 (23.67). The minimum number (17.33) of seeds per siliqua was found in the genotypes Nap9901 and other six genotypes were statistically identical with that of minimum seed producing genotype being placed in the order of Nap2001, Nap012, Nap0130, Nap108, Nap9905 and Nap2012. Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education 117
5 seed weight The genotypes differ significantly in respect of 1000-seed weight (Table 2). It was observed that the genotype Nap2022 (4.64) was superior but statistically similar to the genotypes Nap2057 (4.58), BARI Sarisha-8 (4.38), and Nap108 (4.18). The minimum weight of 1000-seed were obtained in the genotype Nap9907 (3.05) which was statistically identical with Nap012 (3.20), Nap205 (3.23), Nap2013 (3.41) and Nap9905 (3.52). More than 50% of the genotypes varied from 3.62g to 4.11g in respect of 1000-seed weight but they were statistically similar. Several investigators (Hashem et al., 1998; Om et al., 1998 & Sana, et al., 2003) found significant differences for 1000-seed weight among different brassica varieties Seed yield per plant The genotypes showed significant differences for seed yield per plant. The highest seed yield (19.43 g) per plant was recorded in the genotype Nap2066 followed by Nap9907 (15.48 g) that was statistically similar. Thus higher seed yield potential of these genotypes can be attributed to this parameter. The lowest seed yield per plant was produced in the genotype Nap9905 (5.90 g) that was statistically identical with all the genotypes under studied except Nap2066, Nap9907, Nap9908, Nap108 and Nap2057. Chen et al. (1995) recorded 7.2 g seed yield per plant in B. napus. Reddy and Reddy (1998) and Khoshnazar et al. (2000) have also been reported significant differences in seed yield in different varieties of brassica species. 3.2 Performance of CMS lines From the Table 3 it was found that the first flower opened at days after sowing in CMSZ 1 and 50% plants of this line were flowered within 45 days after sowing. In case of CMSZ 2 first flower opened at days and 50% flower opened within days after sowing. The anther length of CMSZ 1 and CMSZ 2 were mm and mm, respectively. The anther breadth of CMSZ 1 was mm and CMSZ 2 was mm. Chen et al. (1993, 1995) observed two type of stamen in CMS B. juncea var. tumida, stamens without an anther, and stamens with thin and degenerate anthers. The length of filament was mm in CMSZ 1 and mm in CMSZ 2. Stamen length of CMSZ 1 and CMSZ 2 were mm and mm, respectively. The CMS plants produced small and slender anther and shorter filament in compare to pollen parents (Plate 1c-e). Jones and Clarke (1943) showed male sterility associated with morphological abnormality anther and filament. Chen et al. (1993) was also found CMS line with no anthers or had silk-like structure of stamen with few pollen grains which show lowered vigour and lacking normal external structure in tuber mustard. Male sterile plants were identified by several authors (Banga and Labana, 1985; Sodhi et al., 1993; Hu et al., 1992) based on small flower, small filament, lack of anther, silk like stamen with vestigial and indehiscent anthers. Banga and Amandeep (1995) observed variation in flower traits in different nuclear backgrounds of siifolia CMS system. The out crossing rate of CMSZ 1 was 40.31% and CMSZ 2 was 47.96%. Hackenberg and Kohler (1996) assessed variation in parental lines of rapeseed with regard to out crossing. Results showed that the partially out crossing rate was very high. Branching habit is an important character that contributes to seed yield in B. napus. Zhu et al. (1999) found that the seed production potentiality was similar between male sterile line and their male or pollen parents. In case of CMS plants the number of primary branches per plant was found 3.67 in CMSZ 1 and 3.50 CMSZ 2. Time required for days to 80% maturity of CMSZ 1 and CMSZ 2 were and , respectively. The average plant height of CMSZ 1 was 95 cm and CMSZ 2 was cm. The length of inflorescence was and in CMSZ 1 and CMSZ 2, respectively. The number of siliqua per plant was found in CMSZ 1 and in CMSZ 2. The longer siliqua (6.28 cm) was produced by CMSZ 1 than CMSZ 2 (6.28 cm). The average number of seeds per siliqua was found in g and g in CMSZ 1 and CMSZ 2, respectively. CMSZ 1 produced the smallest seeds and 1000-seed weight was 2.97 g. but in CMSZ 2, the 1000-seed weight was found in 3.43 g. The seed yield per plant of CMSZ 1 and CMSZ 2 was recorded g and g, respectively. Seed production capabilities of cytoplasmic male sterile cabbage derived from Ogura CMS radish was observed by Zhu et al. (1999). Seed production capabilities in cross and backcross descendants ranged from 4.1 to 20.8 seeds per pod, respectively. But seed production potentiality was similar between male sterile material and their backcross male parents (Plate 1a-b). The genotype Nap2019 was found early for days to 1 st flowering and the genotype Nap9906 for days to 80% maturity. Anther and stamen of pollen parents were longer as compare to CMS line and its test cross progenies. The genotypes Nap9908, Nap2066, Nap94006 and Nap9906 produced the highest number of primary branches/plant, number of siliqua/plant, number of seeds/siliqua and the longest siliqua. The genotype Nap2066 produced the highest seed yield per plant (19.43 g) and it was the lowest in Nap9905 (5.90 g). 118
6 In CMS plants (CMSZ 1 and CMSZ 2 ) produced small and slender anther, short filament and abnormal pollen grain as compare to pollen parent. Out crossing rate was 40.31% and 47.96% in CMSZ 1 and CMSZ 2, respectively. Hackenberg and Kohler (1996) assessed variation in parental lines of rapeseed with regard to out crossing and found similar results. 4. Conclusion From the present study it can be concluded that pollen parent with desirable performance can be test cross with CMS lines to develop new CMS lines or restorer lines depending on gene presence in their genome. On the basis of yield contributing characters and higher seed yield potential, the genotypes Nap2066, Nap9906, Nap94006 and Nap2022 are recommended for test cross with CMS line develop maintainer or restorer lines. Information on morph-physiological, floral and yield traits of pollen as well as CMS parent can helps to identify suitable genotypes for commercial hybrids. The CMS parents CMSZ 2 having higher out crossing rate can be used for future Brassica napus hybrid breeding program. References Anonymous. (1999). FAO Production Year Book. Food and Agricultural Organization of United Nations, Rome 00108, Italy. 53, 115. Anonymous. (2007). Statistical Year Book of Bangladesh Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics, Ministry of Planning, Government of the People s Republic of Bangladesh, Dhaka. Banga, S.K., & Amandeep. (1995). Assessment of siifolia cytoplasmic male sterility in Brassica juncea (L) Coss. Crop Improv., 22, Banga, S.S., & Labana, K.S. (1985). Male sterility in Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L.) Cross. IV Genetics of MS-4. Can. J. Genet. Cytol., 27, Barrett, S.C.H, & Eckert, C. (1990). Variation and evolution of mating systems in seed plants. In: Kawano S (ed) Biological approaches and evolutionary trends in plants. Academic Press. Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, Publishers, New York, pp BBS. (2008). Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics. Statistical Division, Ministry of Planning, People s Republic of Bangladesh. Dhaka, Bangladesh. Chen, Z.J., Gao, Q.K., Wo, G.L., Wang, B.L., Sun, W.G., & Gong, L. (1993). Morphology and genetic variation of flower of cytoplasmic male sterile in tuber mustard. Acta Agiculturae Zhejiangensis, 5(3), Chen, Z.J., Gao, Q.K., Wo, G.L., Wang, B.L., Sun, W.G., & Gong, L. (1993). Morphology and genetic variation of flower of cytoplasmic male sterile in tuber mustard. Acta Agiculturae Zhejiangensis, 5(3), Chen, Z.J., Zhang, M.F., Wang, B.L., Dong, W.H., & Huang, S.Q. (1995). Study of fertility and agronomic traits in cytoplasmically male sterile lines of Indian mustard. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 22(1), Dudley, L.S., Mazer, S.J., & Galusky, P. (2007). The joint evolution of mating system, floral traits and life history in Clarkia (Onagraceae): genetic constraints vs independent evolution. J Evol Biol., 20, Ghosh, R., & Chatterjee, B. (1988). Contribution of Primary Branches to Grain Yield of Indian Mustard (Brassica juncea L.). Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, 38(1), Goodwillie, C., Sargent, R.D., Eckert, C.G., Elle, E., Geber, M.A., Johnston, M.O., Kalisz, S., Moeller, D.A., Ree, R.H., Vallejo-Marin, M., & Winn, A.A. (2009). Correlated evolution of mating system and floral display traits in flowering plants and its implications for the distribution of mating system variation. New Phytol, 185, Hackenberg, E. M., & Kohler, W. (1996). Use of isozyme analysis in the breeding of synthetic rapeseed cultivar. Plant Breeding, 115(6), Hashem, A., Majumdar, M.N.A., Hamid, A., & Hossain, M.M. (1998). Drought stress effects on seed yield, yield attributes, growth, cell membrane stability and gas exchange of synthesized Brassica napus L. J. Agron. Crop Sci., 180, Hu, Q., Qian, X.Z., & Wu, X.M. (1992). A preliminary investigation of the fertility types of cytoplasm in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Oil Crops of China, 4, Jones, H., & Clarke, A. (1943). Inheritance of male sterility in the onion and the production of hybrid seed. Proceedings of American Society of Horticultural Science, 43, Khaleque, M.A. (1985). A Guide Book on Production of Oil crops in Bangladesh. DAE and FAO/UNDP Project BGD/79/034, Strengthening the Agricultural Extension Service Khamarbari, Farmgate, Dhaka, p. 3. Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education 119
7 Khoshanazar, P.R., Ahmadi, M.R., & Ghanndha, M.R. (2000). A study of adaptation and yield capacity of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) cultivars and tines. Iranian J. Agri. Sci., 31, Mondal, M.R.I., Hossain, M.A., Ali, M.H., & Begum, F. (2001). Oil seed production in Bangladesh: Constrains and opportunities. A paper presented on the 7 th Biennial Agronomy Conference on 18 th April Bangladesh Society of Agronomy. p. 45. Ogura, H. (1968). Studies on the new male sterility in Japanese radish, with special reference to the utilization of this sterility towards the practical raising of hybrid seeds. Mem Fac Agric Kagoshima Univ, 6, Om, P., Das, T.K., Singh, H.B., & Singh, N. (1999). Performance of three Brassica species as affected by time of sowing and nitrogen, I. Yield attributes and yield. Annals Agri. Res., 20, Reddy, C.S., & Reddy, P.R. (1998). Performance of mustard varieties on alfisols of Rayataseema Region of Andhra Pradesh. J. Oilseeds Res., 15, Sana, M.A., Ali, M., Malik, A., Saleem, M.F., & Rafiq, M. (2003). Comparative yield potential and oil contents of different canola cultivars (Brassica napus L.), Pakistan Journal of Agronomy, 2(1), 1-7. SAS. (2008). SAS/STAT User Installation Guide for SAS Foundation for Microsoft Windows. SAS Institute Inc., Copyright 2003, Cary, North Carolina, USA. Sodhi, Y.S., Pradhan, A.K., Mukhopadhyay, A., & Pental, D. (1993). Stability of Ogura cytoplasmic male sterility in three Indian cultivars of radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Indian J. Agric. Sci., 63(7), Steel, R.G.D., & Torrie, J.H. (1980). Principle and Procedures of Statistics: A Biometrical Approach. Second Edition, Mc. Graw Hill Book Co. Inc., New York. Zhu, Y.Y., Yso, W.Y., Xiaoguang, Wu., Gong, J., Shem, F.Y., & Jin, J. (1999). Effect of genetic background on seeding capability of cytoplasmic male sterile materials in broccoli (Brassica oleracea var. cymosa). Acta Agricultura Shanghai, 15(4), Table 1. Flowering characteristics of pollen parents (parents from where pollen was collected) Pollen plants Days to 1 st flowering Anther length (mm) Anther breadth (mm) Filament length (mm) Stamen length (mm) Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap BARI Sarisa F- value ** ** ** ** ** LSD (0.05) CV (%) Significance at 0.01(**) level 120
8 Table 2. Mean performance of 21 pollen parents (B. napus genotypes) for yield contributing characters Genotype No. of Plant Length Seed Days to Days to Length of No. of No. of primary height at of 1000seed yield 50% 80% inflorescence siliqua seeds branches maturity siliqua weight (g) /plant flowering maturity (cm) /plant /siliqua /plant (cm) (cm) (g) Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap Nap BARI Sarisha F- value ** * ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** LSD (0.05) CV (%) Significance at 0.05 (*) and 0.01 (**) level Table 3. Performance of CMS lines for flower and yield characteristics Characters CMSZ 1 CMSZ 2 Days to 1 st flowering Days to 50% flowering Anther length (mm) Anther breadth (mm) Length of filament (mm) Length of stamen (mm) Out crossing rate (%) No. of primary branches per plant Days to 80% maturity Plant height at maturity (cm) Length of inflorescence (cm) No. of siliqua per plant Length of siliqua (cm) No. of seeds per siliqua seed weight (g) Seed yield per plant (g) Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education 121
9 a b c d e Pollen CMS plant Fertile Sterile F 1 Fertile Sterile Plate 1. Showing a) flowering of pollen parent and CMS plant in the field, b) CMS plant with siliqua as a result of out crossing, c) pollen parent and CMS plant, d) flowers from pollen parent, CMS and F 1 plant e) anthers from pollen parent and CMS plant 122
Combining Ability and Heterosis in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivars
 J. Agr. Sci. Tech. (2010) Vol. 12: 223-231 Combining Ability and Heterosis in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivars M. Rahimi 1, B. Rabiei 1*, H. Samizadeh 1, and A. Kafi Ghasemi 1 ABSTRACT Quantitative valuations
J. Agr. Sci. Tech. (2010) Vol. 12: 223-231 Combining Ability and Heterosis in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivars M. Rahimi 1, B. Rabiei 1*, H. Samizadeh 1, and A. Kafi Ghasemi 1 ABSTRACT Quantitative valuations
MULTIVARIATE ANALYSIS IN ONION (Allium cepa L.)
 ISSN 0258-7122 Bangladesh J. Agril. Res. 37(4): 573-582, December 2012 MULTIVARIATE ANALYSIS IN ONION (Allium cepa L.) M. H. RASHID 1, A. K. M. A. ISLAM 2, M. A. K. MIAN 3 T. HOSSAIN 4 AND M. E. KABIR
ISSN 0258-7122 Bangladesh J. Agril. Res. 37(4): 573-582, December 2012 MULTIVARIATE ANALYSIS IN ONION (Allium cepa L.) M. H. RASHID 1, A. K. M. A. ISLAM 2, M. A. K. MIAN 3 T. HOSSAIN 4 AND M. E. KABIR
ABSTRACT: 54 BREEDING OF HYBRID SOYBEAN ZAYOUDOU NO.1
 ABSTRACT: 54 BREEDING OF HYBRID SOYBEAN ZAYOUDOU NO.1 ZHANG L, DAI O, HUANG Z, LI J, ZHANG L, HU C, YANG J 1.Crop Research Institute of Anhui Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2.Key Laboratory of Crop
ABSTRACT: 54 BREEDING OF HYBRID SOYBEAN ZAYOUDOU NO.1 ZHANG L, DAI O, HUANG Z, LI J, ZHANG L, HU C, YANG J 1.Crop Research Institute of Anhui Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2.Key Laboratory of Crop
INVESTIGATING YIELD AND YIELD COMPONENT OF WINTER RAPESEED CULTIVARS AT BOJNORD-IRAN
 Indian Journal of Fundamental and Applied Life Sciences ISSN: 2231 6345 (Online) INVESTIGATING YIELD AND YIELD COMPONENT OF WINTER RAPESEED CULTIVARS AT BOJNORD-IRAN Souri Khabazan, *Amir Behzad Bazrgar,
Indian Journal of Fundamental and Applied Life Sciences ISSN: 2231 6345 (Online) INVESTIGATING YIELD AND YIELD COMPONENT OF WINTER RAPESEED CULTIVARS AT BOJNORD-IRAN Souri Khabazan, *Amir Behzad Bazrgar,
Genetic study and selection in F4 generation of rice (Oryza sativa L.)
 Published with Open Access at Journal BiNET Vol. 09, Issue 01: 768-774 Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research Home page: www.journalbinet.com/jbar-journal.html Genetic study and selection in F4
Published with Open Access at Journal BiNET Vol. 09, Issue 01: 768-774 Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research Home page: www.journalbinet.com/jbar-journal.html Genetic study and selection in F4
Keywords: CGMS, combining ability, fertility restoration, heterosis, pigeonpea. Introduction
 Sri Lanka Journal of Food and Agriculture (2015) Byregowda et al. 1(2): 1-8 ISSN 2424-6913 Research Paper Identification of fertility restorers, stable combiners and heterotic combinations across environments
Sri Lanka Journal of Food and Agriculture (2015) Byregowda et al. 1(2): 1-8 ISSN 2424-6913 Research Paper Identification of fertility restorers, stable combiners and heterotic combinations across environments
GENETIC VARIABILITY AND CHARACTER ASSOCIATION IN INDIAN MUSTARD [BRASSICA JUNCEA (L) CZERNS & COSS]
![GENETIC VARIABILITY AND CHARACTER ASSOCIATION IN INDIAN MUSTARD [BRASSICA JUNCEA (L) CZERNS & COSS] GENETIC VARIABILITY AND CHARACTER ASSOCIATION IN INDIAN MUSTARD [BRASSICA JUNCEA (L) CZERNS & COSS]](/thumbs/82/86432454.jpg) Agric. Sci. Digest., 34 (3) : 183-188, 2014 doi:10.5958/0976-0547.2014.00998.7 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.arccjournals.com GENETIC VARIABILITY AND CHARACTER ASSOCIATION IN INDIAN MUSTARD
Agric. Sci. Digest., 34 (3) : 183-188, 2014 doi:10.5958/0976-0547.2014.00998.7 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.arccjournals.com GENETIC VARIABILITY AND CHARACTER ASSOCIATION IN INDIAN MUSTARD
Estimation of Genotypic and Phenotypic Coefficients Variation of Yield and its Contributing Characters of Brassica rapa L.
 American-Eurasian J. Agric. & Environ. Sci., 15 (10): 09-034, 015 ISSN 1818-6769 IDOSI Publications, 015 DOI: 10.589/idosi.aejaes.015.15.10.170 Estimation of Genotypic and Phenotypic Coefficients Variation
American-Eurasian J. Agric. & Environ. Sci., 15 (10): 09-034, 015 ISSN 1818-6769 IDOSI Publications, 015 DOI: 10.589/idosi.aejaes.015.15.10.170 Estimation of Genotypic and Phenotypic Coefficients Variation
IN SUNFLOWER (HELIANTHUS ANNUUS L.)
 Recent Research in Science and Technology 2009, 1(5): 202 206 ISSN: 2076-5061 www.recent-science.com GENETICS & GENOMICS USING LINE X TESTER ANALYSIS FOR EARLINESS AND PLANT HEIGHT TRAITS IN SUNFLOWER
Recent Research in Science and Technology 2009, 1(5): 202 206 ISSN: 2076-5061 www.recent-science.com GENETICS & GENOMICS USING LINE X TESTER ANALYSIS FOR EARLINESS AND PLANT HEIGHT TRAITS IN SUNFLOWER
Seed production potential of ICRISAT-bred parental lines of two sorghum hybrids in the central Rift-valley of Ethiopia
 Seed production potential of ICRISAT-bred parental lines of two sorghum hybrids in the central Rift-valley of Ethiopia Asfaw Adugna* and Tesfaye Tesso Melkassa Agricultural Research Center, PO Box 436,
Seed production potential of ICRISAT-bred parental lines of two sorghum hybrids in the central Rift-valley of Ethiopia Asfaw Adugna* and Tesfaye Tesso Melkassa Agricultural Research Center, PO Box 436,
Breeding strategy for improvement of flower and seed yields in safflower
 Breeding strategy for improvement of flower and seed yields in safflower Vrijendra Singh, N. M. Kolekar and N. Nimbkar Nimbkar Agricultural Research Institute, Lonand Road, Phaltan 415523, Maharashtra,
Breeding strategy for improvement of flower and seed yields in safflower Vrijendra Singh, N. M. Kolekar and N. Nimbkar Nimbkar Agricultural Research Institute, Lonand Road, Phaltan 415523, Maharashtra,
HETEROSIS AND HERITABILITY STUDIES FOR SUPERIOR SEGREGANTS SELECTION IN CHICKPEA
 Pak. J. Bot., 39(7): 2443-2449, 2007. HETEROSIS AND HERITABILITY STUDIES FOR SUPERIOR SEGREGANTS SELECTION IN CHICKPEA AHMED BAKHSH *, SHAHID RIAZ MALIK **, UMER IQBAL ** AND WAHEED ARSHAD * * PMAS Arid
Pak. J. Bot., 39(7): 2443-2449, 2007. HETEROSIS AND HERITABILITY STUDIES FOR SUPERIOR SEGREGANTS SELECTION IN CHICKPEA AHMED BAKHSH *, SHAHID RIAZ MALIK **, UMER IQBAL ** AND WAHEED ARSHAD * * PMAS Arid
MAGNITUDE OF HETEROSIS AND HERITABILITY IN SUNFLOWER OVER ENVIRONMENTS
 Pak. J. Bot., 40(1): 301-308, 2008. MAGNITUDE OF HETEROSIS AND HERITABILITY IN SUNFLOWER OVER ENVIRONMENTS HAKIM KHAN 1, HIDAYAT-UR-RAHMAN 2, * HABIB AHMAD 3, HAIDAR ALI 4, INAMULLAH 3 AND MUKHTAR ALAM
Pak. J. Bot., 40(1): 301-308, 2008. MAGNITUDE OF HETEROSIS AND HERITABILITY IN SUNFLOWER OVER ENVIRONMENTS HAKIM KHAN 1, HIDAYAT-UR-RAHMAN 2, * HABIB AHMAD 3, HAIDAR ALI 4, INAMULLAH 3 AND MUKHTAR ALAM
USING LINE TESTER ANALYSIS TO DEVELOP NEW SOURCE OF CYTOPLASMIC MALE STERILE LINE IN HYBRID RICE
 Plant Archives Vol. 17 No. 1, 2017 pp. 753-759 ISSN 0972-5210 USING LINE TESTER ANALYSIS TO DEVELOP NEW SOURCE OF CYTOPLASMIC MALE STERILE LINE IN HYBRID RICE M. I. Abo Youssef, M. S. Abd El Aty 1, S.
Plant Archives Vol. 17 No. 1, 2017 pp. 753-759 ISSN 0972-5210 USING LINE TESTER ANALYSIS TO DEVELOP NEW SOURCE OF CYTOPLASMIC MALE STERILE LINE IN HYBRID RICE M. I. Abo Youssef, M. S. Abd El Aty 1, S.
Study of Genetic Diversity in Some Newly Developed Rice Genotypes
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 10 (2017) pp. 2693-2698 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.610.317
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 10 (2017) pp. 2693-2698 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.610.317
Pollen fertility Vs Spikelet fertility in F2 of a CMS based hybrids in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under Aerobic condition
 Research Article Pollen fertility Vs Spikelet fertility in F of a CMS based hybrids in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under Aerobic condition N.Naresh Babu,N.Shivakumar and Shailaja Hittalmani Abstract : Identification
Research Article Pollen fertility Vs Spikelet fertility in F of a CMS based hybrids in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under Aerobic condition N.Naresh Babu,N.Shivakumar and Shailaja Hittalmani Abstract : Identification
Genetic Divergence Studies for the Quantitative Traits of Paddy under Coastal Saline Ecosystem
 J. Indian Soc. Coastal Agric. Res. 34(): 50-54 (016) Genetic Divergence Studies for the Quantitative Traits of Paddy under Coastal Saline Ecosystem T. ANURADHA* Agricultural Research Station, Machilipatnam
J. Indian Soc. Coastal Agric. Res. 34(): 50-54 (016) Genetic Divergence Studies for the Quantitative Traits of Paddy under Coastal Saline Ecosystem T. ANURADHA* Agricultural Research Station, Machilipatnam
Heritability, Correlation and Path Coefficient Analysis in Twenty Ber Genotypes
 Academic Journal of Plant Sciences 3 (): 9-98, 010 ISSN 1995-8986 IDOSI Publications, 010 Heritability, Correlation and Path Coefficient Analysis in Twenty Ber Genotypes 1 3 3 M.N. Islam, M.M. Hossain,
Academic Journal of Plant Sciences 3 (): 9-98, 010 ISSN 1995-8986 IDOSI Publications, 010 Heritability, Correlation and Path Coefficient Analysis in Twenty Ber Genotypes 1 3 3 M.N. Islam, M.M. Hossain,
Exploration of combining ability for yield and morpholo-physical traits in hybrid rice (Oryza sativa L.)
 2017; SP1: 644648 EISS: 22784136 PISS: 23498234 JPP 2017; SP1: 644648 Madhru Grace Minz Deepak Sharma Exploration of combining ability for yield and morpholophysical traits in hybrid rice (Oryza sativa
2017; SP1: 644648 EISS: 22784136 PISS: 23498234 JPP 2017; SP1: 644648 Madhru Grace Minz Deepak Sharma Exploration of combining ability for yield and morpholophysical traits in hybrid rice (Oryza sativa
Diallel Analysis in Taramira (Eruca sativa)
 Journal of Oilseed Brassica, 2(1): 2934, Jan 2011 Journal of Oilseed Brassica, 2(1) : 2011 29 Diallel Analysis in Taramira (Eruca sativa) K.C. Sharma, J.P. Kumhar, E.V.D. Sastry and M.L. Jakhar* Abstract
Journal of Oilseed Brassica, 2(1): 2934, Jan 2011 Journal of Oilseed Brassica, 2(1) : 2011 29 Diallel Analysis in Taramira (Eruca sativa) K.C. Sharma, J.P. Kumhar, E.V.D. Sastry and M.L. Jakhar* Abstract
Combining ability analysis for yield components and physiological traits in rice
 I J P INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PLANT SCIENCES SVolume 7 Issue 2 July, 2012 295-300 RESEARCH ARTICLE Combining ability analysis for yield components and physiological traits in rice D. ADILAKSHMI AND P.
I J P INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PLANT SCIENCES SVolume 7 Issue 2 July, 2012 295-300 RESEARCH ARTICLE Combining ability analysis for yield components and physiological traits in rice D. ADILAKSHMI AND P.
CHARACTER ASSOCIATION AND PATH ANALYSIS IN GARLIC (Allium sativum L) FOR YIELD AND ITS ATTRIBUTES
 SAARC J. Agri., 11(1): 45-52 (2013) CHARACTER ASSOCIATION AND PATH ANALYSIS IN GARLIC (Allium sativum L) FOR YIELD AND ITS ATTRIBUTES S. R. Singh, N. A. Ahmed, S. Lal, Asima Amin 1, Mudasir Amin 5 S. A.
SAARC J. Agri., 11(1): 45-52 (2013) CHARACTER ASSOCIATION AND PATH ANALYSIS IN GARLIC (Allium sativum L) FOR YIELD AND ITS ATTRIBUTES S. R. Singh, N. A. Ahmed, S. Lal, Asima Amin 1, Mudasir Amin 5 S. A.
Qualities of monogerm male-sterile sugar beet lines
 RESEARCH PAPER International Journal of Agronomy and Agricultural Research (IJAAR) ISSN: 2223-7054 (Print) 2225-3610 (Online) http://www.innspub.net Vol. 8, No. 4, p. 81-86, 2016 Qualities of monogerm
RESEARCH PAPER International Journal of Agronomy and Agricultural Research (IJAAR) ISSN: 2223-7054 (Print) 2225-3610 (Online) http://www.innspub.net Vol. 8, No. 4, p. 81-86, 2016 Qualities of monogerm
Prediction and Validation of Three Cross Hybrids in Maize (Zea mays L.)
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.183
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.183
Development of male-sterile lines in sorghum
 Development of male-sterile lines in sorghum A Ashok Kumar, Belum VS Reddy, P Sanjana Reddy and B Ramaiah International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics, Patancheru 502 324, Andhra Pradesh,
Development of male-sterile lines in sorghum A Ashok Kumar, Belum VS Reddy, P Sanjana Reddy and B Ramaiah International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics, Patancheru 502 324, Andhra Pradesh,
ESTIMATION OF GENETIC DIVERSITY IN LENTIL GERMPLASM
 AGRIVITA VOLUME 33 No. 2 JUNE-2011 ISSN : 0126-0537 103 ESTIMATION OF GENETIC DIVERSITY IN LENTIL GERMPLASM A.K.M.M Alam 1*), R. Podder 1) and A. Sarker 2) 1) Pulses Research Centre, Bangladesh Agricultural
AGRIVITA VOLUME 33 No. 2 JUNE-2011 ISSN : 0126-0537 103 ESTIMATION OF GENETIC DIVERSITY IN LENTIL GERMPLASM A.K.M.M Alam 1*), R. Podder 1) and A. Sarker 2) 1) Pulses Research Centre, Bangladesh Agricultural
A species of plants. In maize 20 genes for male sterility are listed by
 THE INTERRELATION OF PLASMAGENES AND CHROMO- GENES IN POLLEN PRODUCTION IN MAIZE DONALD F. JONES Connecticut Agricultural Experiment Station, New Haven, Connecticut Received January 24, 195 IV INHERITED
THE INTERRELATION OF PLASMAGENES AND CHROMO- GENES IN POLLEN PRODUCTION IN MAIZE DONALD F. JONES Connecticut Agricultural Experiment Station, New Haven, Connecticut Received January 24, 195 IV INHERITED
Lodging-Resistance Breeding of Platycodon grandiflorus Using Distant Hybridization
 American Journal of Plant Sciences, 2015, 6, 2844-2849 Published Online November 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajps http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2015.618281 Lodging-Resistance Breeding
American Journal of Plant Sciences, 2015, 6, 2844-2849 Published Online November 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajps http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2015.618281 Lodging-Resistance Breeding
Raghavendra P and S. Hittalmani * Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, University of Agricultural Sciences GKVK, Bangalore , India
 SAARC J. Agri., 13(2): 198-213 (2015) GENETIC PARAMETERS OF TWO BC 2 F 1 POPULATIONS FOR DEVELOPMENT OF SUPERIOR MALE STERILE LINES PERTAINING TO MORPHO-FLORAL TRAITS FOR AEROBIC RICE (Oryza sativa L.)
SAARC J. Agri., 13(2): 198-213 (2015) GENETIC PARAMETERS OF TWO BC 2 F 1 POPULATIONS FOR DEVELOPMENT OF SUPERIOR MALE STERILE LINES PERTAINING TO MORPHO-FLORAL TRAITS FOR AEROBIC RICE (Oryza sativa L.)
Variability, Heritability and Genetic Advance Analysis in Bread Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Genotypes
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 2687-2691 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.321
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 2687-2691 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.321
COMBINING ABILITY ANALYSIS OF SOME YIELD COMPONENTS IN RICE (ORYZA SATIVA L.)
 COMBINING ABILITY ANALYSIS OF SOME YIELD COMPONENTS IN RICE (ORYZA SATIVA L.) Verica Ilieva*, Natalija Markova*, Dobre Andov**, Danica Andreevska** * Goce Delcev University, Faculty of Agriculture, Goce
COMBINING ABILITY ANALYSIS OF SOME YIELD COMPONENTS IN RICE (ORYZA SATIVA L.) Verica Ilieva*, Natalija Markova*, Dobre Andov**, Danica Andreevska** * Goce Delcev University, Faculty of Agriculture, Goce
GENETIC DIVERGENCE IN PEA (PISUM SATIVUM L.)
 Plant Archives Vol. 14 No. 2, 2014 pp. 887-891 ISSN 0972-5210 GENETIC DIVERGENCE IN PEA (PISUM SATIVUM L.) B. Senthamizh Selvi*, J. Rajangam and R. Muthuselvi Horticultural Research Station, Tamil Nadu
Plant Archives Vol. 14 No. 2, 2014 pp. 887-891 ISSN 0972-5210 GENETIC DIVERGENCE IN PEA (PISUM SATIVUM L.) B. Senthamizh Selvi*, J. Rajangam and R. Muthuselvi Horticultural Research Station, Tamil Nadu
Genetic Divergence of Advanced Mutant Breeding Lines, In Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) Assessed Through D 2 Statistics
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 3133-3139 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.609.387
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 3133-3139 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.609.387
Effect of Growth Habit on Agronomic Characters in Faba Bean
 ORIGINAL SCIENTIFIC PAPER 43 Effect of Growth Habit on Agronomic Characters in Faba Bean Salvador NADAL 1 * Alfonso CABELLO 2 Fernando FLORES 2 María Teresa MORENO 1 SUMMARY A change in growth habit in
ORIGINAL SCIENTIFIC PAPER 43 Effect of Growth Habit on Agronomic Characters in Faba Bean Salvador NADAL 1 * Alfonso CABELLO 2 Fernando FLORES 2 María Teresa MORENO 1 SUMMARY A change in growth habit in
Investigation of Correlation and Board Sense Heritability in Tritipyrum Lines under Normal and Drought Stress Conditions
 American-Eurasian J. Agric. & Environ. Sci., 3 (): 07-, 03 ISSN 88-6769 IDOSI Publications, 03 DOI: 0.589/idosi.aejaes.03.3.0.333 Investigation of Correlation and Board Sense Heritability in Tritipyrum
American-Eurasian J. Agric. & Environ. Sci., 3 (): 07-, 03 ISSN 88-6769 IDOSI Publications, 03 DOI: 0.589/idosi.aejaes.03.3.0.333 Investigation of Correlation and Board Sense Heritability in Tritipyrum
EXTENT OF HETEROTIC EFFECTS FOR SEED YIELD AND COMPONENT CHARACTERS IN CASTOR (RICINUS COMMUNIS L.) UNDER SEMI RABI CONDITION
 Indian J. Agric. Res.., 47 (4) : 368-372, 2013 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.arccjournals.com / indianjournals.com EXTENT OF HETEROTIC EFFECTS FOR SEED YIELD AND COMPONENT CHARACTERS IN
Indian J. Agric. Res.., 47 (4) : 368-372, 2013 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.arccjournals.com / indianjournals.com EXTENT OF HETEROTIC EFFECTS FOR SEED YIELD AND COMPONENT CHARACTERS IN
Genetic variability, Heritability and Genetic Advance for Yield, Yield Related Components of Brinjal [Solanum melongena (L.
 Available online at www.ijpab.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5404 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (5): 872-878 (2017) Research Article Genetic variability, Heritability and Genetic
Available online at www.ijpab.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5404 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (5): 872-878 (2017) Research Article Genetic variability, Heritability and Genetic
Characterization of ICRISAT-bred restorer parents of pearl millet
 Characterization of ICRISAT-bred restorer parents of pearl millet SK Gupta 1 *, Ranjana Bhattacharjee 1,2, KN Rai 1 and M Suresh Kumar 1 1. International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics
Characterization of ICRISAT-bred restorer parents of pearl millet SK Gupta 1 *, Ranjana Bhattacharjee 1,2, KN Rai 1 and M Suresh Kumar 1 1. International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics
QUANTITATIVE INHERITANCE OF SOME PHYSIOLOGICAL TRAITS FOR SPRING WHEAT UNDER TWO DIFFERENT POPULATION DENSITIES
 Pak. J. Bot., 40(2): 581-587, 2008. QUANTITATIVE INHERITANCE OF SOME PHYSIOLOGICAL TRAITS FOR SPRING WHEAT UNDER TWO DIFFERENT POPULATION DENSITIES SYED EJAZ-UL-HASSAN * AND IHSAN KHALIQ ** * Tobacco Research
Pak. J. Bot., 40(2): 581-587, 2008. QUANTITATIVE INHERITANCE OF SOME PHYSIOLOGICAL TRAITS FOR SPRING WHEAT UNDER TWO DIFFERENT POPULATION DENSITIES SYED EJAZ-UL-HASSAN * AND IHSAN KHALIQ ** * Tobacco Research
Genetic divergence studies for fibre yield traits in roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa l.) In terai zone of West Bengal
 Journal Crop and Weed, 11(Special Issue):90-94(015) Genetic divergence studies for fibre yield traits in roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa l.) In terai zone of West Bengal 1 N. HARI SATYANARAYANA, S. MUKHERJEE,
Journal Crop and Weed, 11(Special Issue):90-94(015) Genetic divergence studies for fibre yield traits in roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa l.) In terai zone of West Bengal 1 N. HARI SATYANARAYANA, S. MUKHERJEE,
Assessment of Genetic Variation in Selected Germplasm of White Jute (Corchorus capsularis L.)
 Pertanika J. Trop. Agric. Sci. 39 (1): 41-53 (2016) TROPICAL AGRICULTURAL SCIENCE Journal homepage: http://www.pertanika.upm.edu.my/ Assessment of Genetic Variation in Selected Germplasm of White Jute
Pertanika J. Trop. Agric. Sci. 39 (1): 41-53 (2016) TROPICAL AGRICULTURAL SCIENCE Journal homepage: http://www.pertanika.upm.edu.my/ Assessment of Genetic Variation in Selected Germplasm of White Jute
Genetic Variability, Coefficient of Variance, Heritability and Genetic Advance of Some Gossypium hirsutum L. Accessions
 Journal of Agricultural Science; Vol. 7, No. 2; 2015 ISSN 1916-9752 E-ISSN 1916-9760 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Genetic Variability, Coefficient of Variance, Heritability and
Journal of Agricultural Science; Vol. 7, No. 2; 2015 ISSN 1916-9752 E-ISSN 1916-9760 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Genetic Variability, Coefficient of Variance, Heritability and
Effect of different modes of pollination on seed set of mustard (Brassica juncea L.) sown on different sowing dates
 2018; 6(2): 1889-1893 E-ISSN: 2320-7078 P-ISSN: 2349-6800 JEZS 2018; 6(2): 1889-1893 2018 JEZS Received: 05-01-2018 Accepted: 07-02-2018 Manju Devi Harish Kumar Sharma Effect of different modes of pollination
2018; 6(2): 1889-1893 E-ISSN: 2320-7078 P-ISSN: 2349-6800 JEZS 2018; 6(2): 1889-1893 2018 JEZS Received: 05-01-2018 Accepted: 07-02-2018 Manju Devi Harish Kumar Sharma Effect of different modes of pollination
Pak. J. Agri., Agril. Engg., Vet. Sci., 2013, 29 (1) ISSN Pak. J. Agri., Agril. Engg., Vet. Sci., 2013, 29 (1): 13-23
 ISSN 1023-1072 : 13-23 HETEROSIS OF SOME YIELD AND ITS RELATED CHARACTERS IN AROMATIC RICE (ORYZA SATIVA L.) VARIETIES AND THEIR F 1 HYBRIDS UNDER LOWLAND AND UPLAND ENVIRONMENTS 1 A. D. Jarwar 1, Q. D.
ISSN 1023-1072 : 13-23 HETEROSIS OF SOME YIELD AND ITS RELATED CHARACTERS IN AROMATIC RICE (ORYZA SATIVA L.) VARIETIES AND THEIR F 1 HYBRIDS UNDER LOWLAND AND UPLAND ENVIRONMENTS 1 A. D. Jarwar 1, Q. D.
Evaluation of Taro (Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott.) Germplasm Using Multivariate Analysis
 150 Journal of Root Crops, 2011, Vol. 37 No. 2, pp. 150-154 Indian Society for Root Crops ISSN 0378-2409 Evaluation of Taro (Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott.) Germplasm Using Multivariate Analysis Central
150 Journal of Root Crops, 2011, Vol. 37 No. 2, pp. 150-154 Indian Society for Root Crops ISSN 0378-2409 Evaluation of Taro (Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott.) Germplasm Using Multivariate Analysis Central
Introduction to Plant Breeding. Master Gardener Training
 Introduction to Plant Breeding Master Gardener Training Start with a seed Germplasm Germplasm The greatest service which can be rendered to any country is to add a useful plant to its culture -Thomas Jefferson
Introduction to Plant Breeding Master Gardener Training Start with a seed Germplasm Germplasm The greatest service which can be rendered to any country is to add a useful plant to its culture -Thomas Jefferson
Germplasm. Introduction to Plant Breeding. Germplasm 2/12/2013. Master Gardener Training. Start with a seed
 Introduction to Plant Breeding Master Gardener Training Start with a seed Germplasm Germplasm The greatest service which can be rendered to any country is to add a useful plant to its culture -Thomas Jefferson
Introduction to Plant Breeding Master Gardener Training Start with a seed Germplasm Germplasm The greatest service which can be rendered to any country is to add a useful plant to its culture -Thomas Jefferson
Hacking Hybrid Plants and Seeds Dr. Art Trese, Ohio University. Presentation Credit: Dr. Art Trese, Ohio University
 Hacking Hybrid Plants and Seeds Dr. Art Trese, Ohio University Hybrid: In biology, hybrid means something different when applied to animals versus plants A) hybrid animals progeny of two different species
Hacking Hybrid Plants and Seeds Dr. Art Trese, Ohio University Hybrid: In biology, hybrid means something different when applied to animals versus plants A) hybrid animals progeny of two different species
COMBINING ABILITY ANALYSIS FOR CURED LEAF YIELD AND ITS COMPONENT TRAITS IN BIDI TOBACCO (NicotianatabacumL.)
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 3, 2016, 1373 1380 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMBINING ABILITY ANALYSIS FOR CURED LEAF YIELD AND ITS COMPONENT TRAITS IN
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 3, 2016, 1373 1380 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMBINING ABILITY ANALYSIS FOR CURED LEAF YIELD AND ITS COMPONENT TRAITS IN
Date Received: 09/15/2013; Date Revised: 10/05/2013; Date Published Online: 10/25/2013
 ARTICLE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL Advancements in Life Sciences Date Received: 09/15/2013; Date Revised: 10/05/2013; Date Published Online: 10/25/2013 Open Access Heritability, heterosis and heterobeltiosis
ARTICLE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL Advancements in Life Sciences Date Received: 09/15/2013; Date Revised: 10/05/2013; Date Published Online: 10/25/2013 Open Access Heritability, heterosis and heterobeltiosis
Genetic Analysis for Heterotic Traits in Bread Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Using Six Parameters Model
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 06 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.706.029
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 06 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.706.029
American Journal of Plant Biology. Performance of Brinjal (Solanum melongena) Genotypes through Genetic Variability Analysis
 Nishi NSB et al. American Journal of Plant Biology 2017, 3:22-30 Page 1 of 9 Research Article American Journal of Plant Biology http://ivyunion.org/index.php/ajplantbio/ Performance of Brinjal (Solanum
Nishi NSB et al. American Journal of Plant Biology 2017, 3:22-30 Page 1 of 9 Research Article American Journal of Plant Biology http://ivyunion.org/index.php/ajplantbio/ Performance of Brinjal (Solanum
Heterosis for flower and fruit traits in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.)
 African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 9(27), pp. 4144-4151, 5 July, 2010 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb ISSN 1684 5315 2010 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper Heterosis
African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 9(27), pp. 4144-4151, 5 July, 2010 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb ISSN 1684 5315 2010 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper Heterosis
Characterization of Rice (Oryza Sativa L.) Germplasm Through Various Agro-Morphological Traits
 Scientia Agriculturae www.pscipub.com/sa E-ISSN: 2310-953X / P-ISSN: 2311-0228 DOI: 10.15192/PSCP.SA.2015.9.2.8388 Sci. Agri. 9 (2), 2015: 83-88 PSCI Publications Characterization of Rice (Oryza Sativa
Scientia Agriculturae www.pscipub.com/sa E-ISSN: 2310-953X / P-ISSN: 2311-0228 DOI: 10.15192/PSCP.SA.2015.9.2.8388 Sci. Agri. 9 (2), 2015: 83-88 PSCI Publications Characterization of Rice (Oryza Sativa
Study of Genetic Divergence in Pea (Pisum sativum L.) based on Agro-Morphic Traits
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 11 (2017) pp. 3816-3821 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.611.448
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 11 (2017) pp. 3816-3821 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.611.448
HETEROSIS AND COMBINING ABILITY IN HYBRID RICE (Oryza sativa L.)
 HETEROSIS AND COMBINING ABILITY IN HYBRID RICE (Oryza sativa L.) B. S. Thorat 1, R. L. Kunkerkar 2, B. L. Thaware, M. M. Burondkar 4 and S. G. Bhave 5 1 M.Sc. (Agri.) Scholar, Dept. of Agril. Botany, 2
HETEROSIS AND COMBINING ABILITY IN HYBRID RICE (Oryza sativa L.) B. S. Thorat 1, R. L. Kunkerkar 2, B. L. Thaware, M. M. Burondkar 4 and S. G. Bhave 5 1 M.Sc. (Agri.) Scholar, Dept. of Agril. Botany, 2
Research Notes: G. B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology
 Volume 1 Article 6 4-1-1974 Research Notes: G. B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology G. B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology G. B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology G.
Volume 1 Article 6 4-1-1974 Research Notes: G. B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology G. B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology G. B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology G.
Gene Action and Combining Ability in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Involving Indica and Tropical Japonica Genotypes
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 7 (2017) pp. 8-16 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.607.002
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 7 (2017) pp. 8-16 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.607.002
Study on Genetic Variability, Heritability and Genetic Advance in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Genotypes
 Available online at www.ijpab.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.3047 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (4): 511-515 (2017) Research Article Study on Genetic Variability, Heritability
Available online at www.ijpab.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.3047 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (4): 511-515 (2017) Research Article Study on Genetic Variability, Heritability
THE EFFECTS OF FOLIAR APPLICATION OF SALICYLIC ACID ON QUALITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE YIELD OF WHEAT UNDER SALINE CONDITIONS
 International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences. Vol., 2 (9), 366-370, 2011 Available online at http://www. irjabs.com 2011 THE EFFECTS OF FOLIAR APPLICATION OF SALICYLIC ACID ON QUALITATIVE
International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences. Vol., 2 (9), 366-370, 2011 Available online at http://www. irjabs.com 2011 THE EFFECTS OF FOLIAR APPLICATION OF SALICYLIC ACID ON QUALITATIVE
BREEDING, GENETICS, AND PHYSIOLOGY. Phenotypic Analysis of the 2006 MY2 Mapping Population in Arkansas
 BREEDING, GENETICS, AND PHYSIOLOGY Phenotypic Analysis of the 2006 MY2 Mapping Population in Arkansas E.J. Boza, K.A.K. Moldenhauer, R.D. Cartwright, S. Linscombe, J.H. Oard, and M.M. Blocker ABSTRACT
BREEDING, GENETICS, AND PHYSIOLOGY Phenotypic Analysis of the 2006 MY2 Mapping Population in Arkansas E.J. Boza, K.A.K. Moldenhauer, R.D. Cartwright, S. Linscombe, J.H. Oard, and M.M. Blocker ABSTRACT
Hairy s Inheritance: Investigating Variation, Selection, and Evolution with Wisconsin Fast Plants
 Introduction Hairy s Inheritance: Investigating Variation, Selection, and Evolution with Wisconsin Fast Plants Daniel Lauffer Wisconsin Fast Plants Program University of Wisconsin - Madison Since the dawn
Introduction Hairy s Inheritance: Investigating Variation, Selection, and Evolution with Wisconsin Fast Plants Daniel Lauffer Wisconsin Fast Plants Program University of Wisconsin - Madison Since the dawn
Meiosis and Mendel. Chapter 6
 Meiosis and Mendel Chapter 6 6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS Key Concept Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. Body Cells vs. Gametes You have body cells and gametes body cells
Meiosis and Mendel Chapter 6 6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS Key Concept Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. Body Cells vs. Gametes You have body cells and gametes body cells
Certification of PARENT LINES of Cytoplasmic Male Sterile (CMS) HYBRID WHEAT with Blended Parent Lines
 SECTION 12A Certification of PARENT LINES of Cytoplasmic Male Sterile (CMS) HYBRID WHEAT with Blended Parent Lines In this section, Cereals includes: Wheat which includes spring and winter Wheat, Einkorn,
SECTION 12A Certification of PARENT LINES of Cytoplasmic Male Sterile (CMS) HYBRID WHEAT with Blended Parent Lines In this section, Cereals includes: Wheat which includes spring and winter Wheat, Einkorn,
The Influence of Nectar Sugar Production on Insect Visitors to Flowers of Brassica rapa L. M.A. Taylor and A.R. Davis
 The Influence of Nectar Sugar Production on Insect Visitors to Flowers of Brassica rapa L. M.A. Taylor and A.R. Davis University of Saskatchewan, Department of Biology, 112 Science Place, Saskatoon, SK,
The Influence of Nectar Sugar Production on Insect Visitors to Flowers of Brassica rapa L. M.A. Taylor and A.R. Davis University of Saskatchewan, Department of Biology, 112 Science Place, Saskatoon, SK,
Estimates of Genetic variability, heritability and genetic advance of oat (Avena sativa L.) genotypes for grain and fodder yield
 Agricultural Science Research Journals Vol. 3(2), pp. 56-61, February 2013 Available online at http://www.resjournals.com/arj ISSN-L:2026-6073 2013 International Research Journals Full Length Research
Agricultural Science Research Journals Vol. 3(2), pp. 56-61, February 2013 Available online at http://www.resjournals.com/arj ISSN-L:2026-6073 2013 International Research Journals Full Length Research
EFFECT OF POLLINATION TIME AND CROSSING RATIO ON SEED YIELD AND QUALITY OF BRINJAL HYBRID UNDER DHARWAD REGION OF KARNATAKA
 Indian J. Agric. Res., 42 (1) : 7-12, 2008 EFFECT OF POLLINATION TIME AND CROSSING RATIO ON SEED YIELD AND QUALITY OF BRINJAL HYBRID UNDER DHARWAD REGION OF KARNATAKA Shivashankaragouda B. Patil, M.N.
Indian J. Agric. Res., 42 (1) : 7-12, 2008 EFFECT OF POLLINATION TIME AND CROSSING RATIO ON SEED YIELD AND QUALITY OF BRINJAL HYBRID UNDER DHARWAD REGION OF KARNATAKA Shivashankaragouda B. Patil, M.N.
Evaluation and classification of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L.) genotypes using principal component analysis
 Journal of Oilseed Brassica, 6 (1): 167-174, January 2015 Journal of Oilseed Brassica, 6 (1) Jan., 2015 167 Abstract Evaluation and classification of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L.) genotypes using
Journal of Oilseed Brassica, 6 (1): 167-174, January 2015 Journal of Oilseed Brassica, 6 (1) Jan., 2015 167 Abstract Evaluation and classification of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L.) genotypes using
Studies on Fertility Restoration Using Newly Derived Restorers in Sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.)
 Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.ci (218) 7(1): 2131-2135 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied ciences IN: 2319-776 Volume 7 Number 1 (218) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.ci (218) 7(1): 2131-2135 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied ciences IN: 2319-776 Volume 7 Number 1 (218) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original
Kentucky Seed Certification Standards. I. Explanation of General Standards as Applied to Corn Hybrids
 Kentucky Seed Certification Standards H Y B R I D C O R N I. Explanation of General Standards as Applied to Corn Hybrids A. The General Seed Certification Standards as adopted are basic and, together with
Kentucky Seed Certification Standards H Y B R I D C O R N I. Explanation of General Standards as Applied to Corn Hybrids A. The General Seed Certification Standards as adopted are basic and, together with
GENETIC DIVERGENCE OF A COLLECTION OF SPONGE GOURD (Luffa cylindrica L.)
 GENETIC DIVERGENCE OF A COLLECTION OF SPONGE GOURD (Luffa cylindrica L.) M. A. Gaffar 1, M. S. Hossain 2, Shamsunnaher 3 1 Agriculture Extension Officer, Department of Agricultural Extension, Narayanganj
GENETIC DIVERGENCE OF A COLLECTION OF SPONGE GOURD (Luffa cylindrica L.) M. A. Gaffar 1, M. S. Hossain 2, Shamsunnaher 3 1 Agriculture Extension Officer, Department of Agricultural Extension, Narayanganj
POSSIBILITY TO SELECT HETEROZYGOUS GENOTYPES BY POLLEN FERTILITY IN SEGREGATION HYBRID AND BACKCROSS PROGENIES CREATED based on NUCLEAR MALE STERILITY
 565 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 18 (No 4) 2012, 565-570 Agricultural Academy POSSIBILITY TO SELECT HETEROZYGOUS GENOTYPES BY POLLEN FERTILITY IN SEGREGATION HYBRID AND BACKCROSS PROGENIES
565 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 18 (No 4) 2012, 565-570 Agricultural Academy POSSIBILITY TO SELECT HETEROZYGOUS GENOTYPES BY POLLEN FERTILITY IN SEGREGATION HYBRID AND BACKCROSS PROGENIES
Estimation of Heterosis, Heterobeltiosis and Economic Heterosis in Dual Purpose Sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]
![Estimation of Heterosis, Heterobeltiosis and Economic Heterosis in Dual Purpose Sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] Estimation of Heterosis, Heterobeltiosis and Economic Heterosis in Dual Purpose Sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]](/thumbs/85/92593885.jpg) International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 5 (2017) pp. 990-1014 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.605.109
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 5 (2017) pp. 990-1014 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.605.109
Assessment of genetic variability for quantitative and qualitative traits in Rice Germplasm Accessions (Oryza sativa L.).
 Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 6 Special issue [] 27: 76-83 27 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 2277-88 Journal
Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 6 Special issue [] 27: 76-83 27 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 2277-88 Journal
$25 per bin, minimum $50 per on-site visit
 Adopted 2/11/2014 Revised 2/16/2015 Application and Fees Field applications must be submitted through the Oregon Seed Certification Service e-certification website at www.seedcert.oregonstate.edu. All
Adopted 2/11/2014 Revised 2/16/2015 Application and Fees Field applications must be submitted through the Oregon Seed Certification Service e-certification website at www.seedcert.oregonstate.edu. All
Genetic Parameters for Yield and Yield Components in F 1 Hybrids and Parents of Bell Pepper
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 03 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.703.308
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 03 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.703.308
Correlation and path coefficient analysis in tuberose
 Journal of Crop and Weed, 9(2):44-49(2013) Correlation and path coefficient analysis in tuberose VANLALRUATI, T. MANDAL AND S. PRADHAN Department of Floriculture and Landscaping, Faculty of Horticulture
Journal of Crop and Weed, 9(2):44-49(2013) Correlation and path coefficient analysis in tuberose VANLALRUATI, T. MANDAL AND S. PRADHAN Department of Floriculture and Landscaping, Faculty of Horticulture
Morphological Markers Related to Sex Expression in Papaya (Carica papaya L.)
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Soni et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (4): 526-531 (2017) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5132 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (4):
Available online at www.ijpab.com Soni et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (4): 526-531 (2017) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5132 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (4):
Prediction of leaf number by linear regression models in cassava
 J. Bangladesh Agril. Univ. 9(1): 49 54, 2011 ISSN 1810-3030 Prediction of leaf number by linear regression models in cassava M. S. A. Fakir, M. G. Mostafa, M. R. Karim and A. K. M. A. Prodhan Department
J. Bangladesh Agril. Univ. 9(1): 49 54, 2011 ISSN 1810-3030 Prediction of leaf number by linear regression models in cassava M. S. A. Fakir, M. G. Mostafa, M. R. Karim and A. K. M. A. Prodhan Department
Evaluation of drought stress effect in summer Safflower genotypes
 ISSN No. (Print): 0975-1130 ISSN No. (Online): 2249-3239 Evaluation of drought stress effect in summer Safflower genotypes Behnam Tahmasebpour*, Omid Sofalian**, Hasan Dehghanian*** and Seyed Sajad Hoseini****
ISSN No. (Print): 0975-1130 ISSN No. (Online): 2249-3239 Evaluation of drought stress effect in summer Safflower genotypes Behnam Tahmasebpour*, Omid Sofalian**, Hasan Dehghanian*** and Seyed Sajad Hoseini****
Effects of high plant populations on the growth and yield of winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus)
 Journal of Agricultural Science, Cambridge (1999), 132, 173 180. 1999 Cambridge University Press Printed in the United Kingdom 173 Effects of high plant populations on the growth and yield of winter oilseed
Journal of Agricultural Science, Cambridge (1999), 132, 173 180. 1999 Cambridge University Press Printed in the United Kingdom 173 Effects of high plant populations on the growth and yield of winter oilseed
Genetic Variability and Character Association in Some Native Orchid Species (Dendrobium spp.)
 The Agriculturists 10 (1): 1-9 (01) A Scientific Journal of Krishi Foundation ISSN-179-511 Genetic Variability and Character Association in Some Native Orchid Species (Dendrobium spp.) M. Moniruzzaman
The Agriculturists 10 (1): 1-9 (01) A Scientific Journal of Krishi Foundation ISSN-179-511 Genetic Variability and Character Association in Some Native Orchid Species (Dendrobium spp.) M. Moniruzzaman
C.v. Dr. Mohammed Ali Hussein
 C.v. Dr. Mohammed Ali Hussein - Dr Mohammed Ali Hussien Al- Falahe Email: dr.mohammed1953@yahoo.com Tele : 07507718671. - Was born in Baghdad Iraq 1953. - Graduated from Al-Nasar primary school in 1966.
C.v. Dr. Mohammed Ali Hussein - Dr Mohammed Ali Hussien Al- Falahe Email: dr.mohammed1953@yahoo.com Tele : 07507718671. - Was born in Baghdad Iraq 1953. - Graduated from Al-Nasar primary school in 1966.
Correlation and Path Analysis Study in Dolichos Bean (Lablab purpureus L.)
 Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2017) 6(9): 22282235 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 23197706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 22282235 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2017) 6(9): 22282235 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 23197706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 22282235 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com
Correlation, path and cluster analysis in hyacinth bean (Lablab purpureus L. Sweet)
 Available online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com ISSN 1686-9141 Correlation, path and cluster analysis in hyacinth bean (Lablab purpureus L. Sweet) Singh, ramod K. 1*, Rai, N. 1, Lal, Hira 1, Bhardwaj, D.R.
Available online http://www.ijat-aatsea.com ISSN 1686-9141 Correlation, path and cluster analysis in hyacinth bean (Lablab purpureus L. Sweet) Singh, ramod K. 1*, Rai, N. 1, Lal, Hira 1, Bhardwaj, D.R.
ASSESSMENT OF GENETIC DIVERSITY IN MUSTARD GENOTYPES
 Plant Archives Vol. 18 No. 2, 2018 pp. 2091-2096 e-issn:2581-6063 (online), ISSN:0972-5210 ASSESSMENT OF GENETIC DIVERSITY IN MUSTARD GENOTYPES Ravi Nagda 1, Nidhi Dubey 2 *, Harshal Avinashe 3 and Dattesh
Plant Archives Vol. 18 No. 2, 2018 pp. 2091-2096 e-issn:2581-6063 (online), ISSN:0972-5210 ASSESSMENT OF GENETIC DIVERSITY IN MUSTARD GENOTYPES Ravi Nagda 1, Nidhi Dubey 2 *, Harshal Avinashe 3 and Dattesh
1 Mendel and His Peas
 CHAPTER 3 1 Mendel and His Peas SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is heredity? How did Gregor Mendel study heredity? National
CHAPTER 3 1 Mendel and His Peas SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is heredity? How did Gregor Mendel study heredity? National
Arpna Kumari and Vedna Kumari
 2018; 7(7): 290-296 ISSN (E): 2277-7695 ISSN (P): 2349-8242 NAAS Rating: 5.03 TPI 2018; 7(7): 290-296 2018 TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 28-05-2018 Accepted: 30-06-2018 Arpna Kumari Department
2018; 7(7): 290-296 ISSN (E): 2277-7695 ISSN (P): 2349-8242 NAAS Rating: 5.03 TPI 2018; 7(7): 290-296 2018 TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 28-05-2018 Accepted: 30-06-2018 Arpna Kumari Department
RFLP facilitated analysis of tiller and leaf angles in rice (Oryza sativa L.)
 Euphytica 109: 79 84, 1999. 1999 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 79 RFLP facilitated analysis of tiller and leaf angles in rice (Oryza sativa L.) Zhikang Li 1,2,3, Andrew H. Paterson
Euphytica 109: 79 84, 1999. 1999 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 79 RFLP facilitated analysis of tiller and leaf angles in rice (Oryza sativa L.) Zhikang Li 1,2,3, Andrew H. Paterson
Abstract =20, R 2 =25 15, S 2 = 25 25, S 3
 Plant Archives Vol. 16 No. 2, 2016 pp. 575-579 ISSN 0972-5210 EVALUATION OF INFLUENCE OF RHIZOME SIZE AND PLANT SPACING ON GROWTH AND YIELD ATTRIBUTES OF GINGER (ZINGIBER OFFICINALE ROSC.) CV. MARAN IN
Plant Archives Vol. 16 No. 2, 2016 pp. 575-579 ISSN 0972-5210 EVALUATION OF INFLUENCE OF RHIZOME SIZE AND PLANT SPACING ON GROWTH AND YIELD ATTRIBUTES OF GINGER (ZINGIBER OFFICINALE ROSC.) CV. MARAN IN
Character Association and Path Coefficient Analysis in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.)
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 1966-1972 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.233
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 1966-1972 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.233
Growth Pattern of Mungbean at Different Planting Distance
 Academic Journal of Plant Sciences 4 (): 0-, 0 ISSN 995-898 IDOSI Publications, 0 Growth Pattern of Mungbean at Different Planting Distance K.U. Ahamed, Kamrun Nahar, Mirza Hasanuzzaman and Golam Faruq
Academic Journal of Plant Sciences 4 (): 0-, 0 ISSN 995-898 IDOSI Publications, 0 Growth Pattern of Mungbean at Different Planting Distance K.U. Ahamed, Kamrun Nahar, Mirza Hasanuzzaman and Golam Faruq
Jeopardy. Final Jeopardy. Topic 1 Topic 2 Topic 3 Topic 4 Topic 5 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400
 Jeopardy Topic 1 Topic 2 Topic 3 Topic 4 Topic 5 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 Final Jeopardy 1 - $100 n Although
Jeopardy Topic 1 Topic 2 Topic 3 Topic 4 Topic 5 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 Final Jeopardy 1 - $100 n Although
Available online at
 Available online at www.ijpab.com ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 3 (1): 143-149 (2015) INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE & APPLIED BIOSCIENCE Research Article variability, Correlation and Path analysis
Available online at www.ijpab.com ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 3 (1): 143-149 (2015) INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE & APPLIED BIOSCIENCE Research Article variability, Correlation and Path analysis
Genetic variability, Heritability and Morphological Characterization in. Bitter gourd (Momordica charantia L.)
 Available online at www.ijpab.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5710 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (4): 1322-1327 (2017) Research Article Genetic variability, Heritability and
Available online at www.ijpab.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5710 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (4): 1322-1327 (2017) Research Article Genetic variability, Heritability and
FORECASTING COARSE RICE PRICES IN BANGLADESH
 Progress. Agric. 22(1 & 2): 193 201, 2011 ISSN 1017-8139 FORECASTING COARSE RICE PRICES IN BANGLADESH M. F. Hassan*, M. A. Islam 1, M. F. Imam 2 and S. M. Sayem 3 Department of Agricultural Statistics,
Progress. Agric. 22(1 & 2): 193 201, 2011 ISSN 1017-8139 FORECASTING COARSE RICE PRICES IN BANGLADESH M. F. Hassan*, M. A. Islam 1, M. F. Imam 2 and S. M. Sayem 3 Department of Agricultural Statistics,
1 Mendel and His Peas
 CHAPTER 5 1 Mendel and His Peas SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is heredity? How did Gregor Mendel study heredity? National
CHAPTER 5 1 Mendel and His Peas SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is heredity? How did Gregor Mendel study heredity? National
Improvement of Photosynthetic Capacity in Soybean Variety
 Improvement of Photosynthetic Capacity in Soybean Variety By MUTSUO OJIMA Crop Division, Chugoku National Agricultural Experiment Station The demand for soybean as protein and oil resources is increasing
Improvement of Photosynthetic Capacity in Soybean Variety By MUTSUO OJIMA Crop Division, Chugoku National Agricultural Experiment Station The demand for soybean as protein and oil resources is increasing
Partitioning of General and Specific Combining Ability Effects for Estimating Maternal and Reciprocal Effects
 Partitioning of General and Specific Combining Ability Effects for Estimating Maternal and Reciprocal Effects Galal M. A. Mahgoub Maize Research Department, Field Crops Research Institute. Agricultural
Partitioning of General and Specific Combining Ability Effects for Estimating Maternal and Reciprocal Effects Galal M. A. Mahgoub Maize Research Department, Field Crops Research Institute. Agricultural
Deflowering effect on vasculature and yield attributes in raceme of mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek]
![Deflowering effect on vasculature and yield attributes in raceme of mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek] Deflowering effect on vasculature and yield attributes in raceme of mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek]](/thumbs/77/76604295.jpg) AJCS 5(11):1339-1344 (2011) Deflowering effect on vasculature and yield attributes in raceme of mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek] M. Monjurul Alam Mondal 1, Md. Solaiman Ali Fakir 2, A.K.M.Azad-ud-doula
AJCS 5(11):1339-1344 (2011) Deflowering effect on vasculature and yield attributes in raceme of mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek] M. Monjurul Alam Mondal 1, Md. Solaiman Ali Fakir 2, A.K.M.Azad-ud-doula
