Cellular Respiration
|
|
|
- Ashley Harmon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
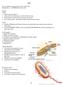
1 Elijah Banks Diamond Adams Raequon Mack Rilajah Baynes Cellular Respiration Cellular respiration is the process where organisms burn food to produce energy. The starting material of cellular respiration is glucose, which has energy stored in its chemical bonds. You can imagine glucose as a cellular piece of coal, full of energy, but useless when you want to power a source. Just as burning coal produces heat and energy in the form of electricity, the chemical processes of respiration convert the energy in glucose into a usable form. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the usable form of energy produced by respiration. For example, ATP is like the electricity that could power the stereo: it contains the same energy as coal, but it s easier to transport and is just what s needed when the cell needs some power to carry out a process. Photosynthesis makes the glucose that is used for cellular respiration to make ATP. The glucose is then turned back into carbon dioxide, which is used in photosynthesis. Water is being broken down to form oxygen during photosynthesis, in cellular respiration oxygen is combined with hydrogen to form water. While photosynthesis requires carbon dioxide and releases oxygen, cellular respiration requires oxygen and releases carbon dioxide. It is the released oxygen that is used by us and most other organisms for cellular respiration. Here s a visual to get a better understanding of what goes on during cellular respiration.
2 1. Plants and animals exchange materials through the processes of photosynthesis and respiration. Which of these statements is true about the way these two processes are related? a) The products of photosynthesis prevent respiration b) The products of photosynthesis are also the products of respiration c) The reactants of photosynthesis are also the reactants of respiration d) The product of photosynthesis are the reactants of respiration 2. What are the products of photosynthesis and reactants of respiration? a) ATP and ADP b) Water and Oxygen c) Glucose and Oxygen d) Hormones 3. What is the first step of cellular respiration?
3 a) Glycolysis b) Link reaction c) krebs cycle d) Electron transport chain 4. Explain the role of chloroplast in photosynthesis and why it is important. 5. Compare and contrast aerobic and anaerobic respiration ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS 1. What is the energy molecule used by all living things? 2. What are the reactants and products for cellular respiration? Homeostasis and transport All body systems work together to maintain homeostasis. Passive transport (including diffusion and osmosis) is the movement of materials across the cell membrane without cellular energy. The movement of materials against a concentration differences is known as active transport. Cell transport helps cells maintain homeostasis by keeping conditions within normal ranges inside all of an organism's cells. A cell seeks to maintain homeostasis within the cell therefore osmosis will occur. The cell will change the concentration of water within the cell to match the concentration of water outside the cell. Exocytosis is the reverse process, where a cell expels large particles, usually waste from cellular processes. These processes both require energy but are important for the cell to maintain homeostasis. Endocytosis is a form of active transport in which a cell transports molecules (such as proteins) into the cell by engulfing them in an
4 energy-using process.(atp) Endocytosis and exocytosis can occur in the same cell. It is how a cell transports and exports material in and out. 1. Which is an example of a homeostasis mechanism? a) Sweating when you become cold b) Shivering when you are cold c) Releasing urine and feces d) Wearing less clothes since it is warm 2. Compare and contrast hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic solutions. 3. Two solutions are placed on either side of a selectively permeable membrane. The membrane is permeable to solute. There is a higher concentration of solute particles on the left side of the membrane. In which direction will the solute particles move? Why? 4. How would the body respond to an increased environmental temperature? a) Hairs on body erect
5 b) Sweating c) shivering d) become sleepy 5) Which hormone regulate the amount of glucose in the blood? a) Pepsin b) Trypsin c) Insulin d) Glycine ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS 1.. How do the body systems coordinate & interact to maintain homeostasis of the whole organism? 2. How does disease always represent a loss of homeostasis? Theory of Evolution The theory of evolution by natural selection, first formulated in Darwin's book "On the Origin of Species" in 1859, is the process by which organisms change over time as a result of changes in heritable physical or behavioral traits. Changes that allow an organism to better adapt to its environment will help it survive and have more offspring. Evolution by natural selection is
6 one of the best substantiated theories in the history of science, supported by evidence from a wide variety of scientific disciplines, including paleontology, geology, genetics and developmental biology. All life on Earth is connected and related to each other and this diversity of life is a product of modifications of populations by natural selection, where some traits were favored in and environment over others. The other theory is that that there was a greater being who created men and women and we developed from there. Here s a link to a video for a better explanation What is the study of the early development of an organism? a) Fossils b) Embryology c) Homologous 2. What did the theory of evolution state, and which statement was true? a. People are created from god
7 b. Every specie comes from an earlier specie c. The human species evolved from chimpanzees d. People evolve not population 3. True or false? a dolphin fin and a human arm are homologous structure a. True b. False 4. In your own words describe what the theory of evolution is stating. 5. What s the biggest difference between homologous and analogous structures? Explain. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS 1. What is meant by evolution? 2. Are certain lines of evidence for evolution stronger than others? Cell growth and Reproduction Cell growth and reproduction can also be known as the cell cycle. The cell cycle describes the stages of a single cell s life. There are three main stages which are interphase, nuclear division, and cytokinesis. Interphase is the longest stage in the cell cycle because during the G1 stage the cell grows and then replicates DNA in the S stage and ready to divide in the G2 stage. There are two types of cellular reproduction, mitosis and meiosis. These processes are responsible for creating two different types of cells. Mitosis is a process that creates a nearly exact copy of the original cell. Somatic cells, which include nearly all human cells, are created by this process. Meiosis is a different form of reproduction that leads to the production of germ cells, or sex cells. he goal of cellular reproduction is to reproduce a copy of a preexisting cell. Cells achieve this by first copying their contents and then dividing them so each of the resulting two cells has the same components. These processes are a part of a larger cell cycle that also
8 includes periods of preparation for synthesizing copies of cellular components and division. This cycle occurs continuously in most organisms. 1. What role does cytokinesis play in the cell cycle? a) Nuclear division b) Copying DNA c) The final stage d) All of the above 2. How many phases is Mitosis duplicated of in the nucleus? a) 4 b) 3 c) 1 d) Prophase 3. DNA replication consists of one old strand and one new strand. a) False b) True 4. What is one difference between the parent cell and daughter cell that results from mitosis?
9 5. What happens when the chromatids separate? ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS 1. How does life result from chemical structure and function? 2. How does life result from cellular structure and function? Genetics The human body is made of some 50 trillion to 100 trillion cells, which form the basic units of life and combine to form more complex tissues and organs. Inside each cell, genes make up a blueprint for protein production that determines how the cell will function. Genes also determine physical characteristics or traits. The complete set of some 20,000 to 25,000 genes is called the genome. Only a tiny fraction of the total genome sets the human body apart from those of other animals. Chromosomes carry hereditary, genetic information in long strings of DNA called genes. Humans have 22 numbered pairs of chromosomes and a single pair of sex chromosomes XX in females and XY in males. Each chromosome pair includes one inherited from the father and one from the mother. If unwound, the microscopic DNA strands in one cell s nucleus would stretch to over six feet in length.
10 1. What are the similarities between dominant allele and recessive allele? 2. What chromosomes are the sex-linked genes determined by? a) X b) Y c) Neither d) Both 3. What makes homozygous and heterozygous different? 4. What is a gene? a) The combination of alleles in an organism s b) A DNA sequence that specifies a protein c) An appearance of a trait d) None of the above 5. What inherits one of each allele explain? a) Homozygous
11 b) Recessive c) Heterozygous d) Dominant ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS 1. What is DNA? 2. What is the difference between DNA and RNA? Basic Biological Principles Prokaryotic cells have been proven to have been evolved before eukaryotic cells. Just as plant cells prokaryotic cells have cell walls also. Thye use them as protectants since cell walls have single organism or building blocks. Don t forget that prokaryotic cells DNA isn t found in the nucleus but in a region around it (nuclear). If you are still confused as to what prokaryotes some examples are bacteria and archaea. One last thing important about this cell is that it uses cell respiration for energy. Now for eukaryotic cells, they are made up of cells just as prokaryotic. A few huge difference between these two cells are their size (eukaryotic cells are more vast) and this cell has a nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have double membranes to protect them. Or in other words a single complex cell. Here s a visual of what prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells actually look like and how they work.
12 Both cells contain a ribosome which is basically another form of protein which is called RNA instead. Both these cells also use cilia and flagella to move around and or transport. Both plant and animal cells are considered eukaryotic. In each cell, the cytoplasm helps cellular growth, metabolism, and replication. 1. What do both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have in common? a. They are both organisms made up of cells b. They both use cell respiration for energy c. Prokaryotes are bigger than eukaryotes d. Prokaryotes lack something while eukaryotes make it up what is it? 2. Which cell has a nucleus? a. Prokaryote b. Eukaryote c. Bacteria d. Lysosomes 3. Which cell has ribosomes? a. Prokaryote b. Eukaryote c. Both cells contain ribosomes 4. Which of the following questions are false about prokaryotes/eukaryotes, explain why the following question is false? a. Both are surrounded around a cell membrane
13 b. Prokaryotic cells are larger than eukaryotic c. Both can move around with cilla and or flagella d. Prokaryotic cells contain cell walls 5. Which of the following question(s) are false about prokaryotes/eukaryotes explain why the following question(s) are false. a. Eukaryotic cells are larger than prokaryotic b. The dna of a eukaryotic cell is found in the nucleus c. Both animal and plant cells are eukaryotic d. Eukaryotic is an organism with is a single cell that has a complex structure ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS 1. What are the similarities between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? 2. What do the functions of membrane proteins include? The Chemical Basis of LIfe. Here s some information about the chemical bases of life. Polar bonds are covalent which is basically sharing atoms where the forming bonds of electrons are unbalanced or unequally shared. For example, these bonds are unequal which causes it to be polar. Living organism only use a small percentage to carry out their functions. There are six important elements which are hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and calcium. Now for ions which are charged elements that are brought up from the gain or loss of electrons from a neutral atom or molecule. Some atoms that gain and lose are sodium and fluorine. Bonding from atoms and ions can be covalent which basically means bonds formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms. Atoms are important units of chemical matter. Atoms contain a nucleus. It also contains positively charged protons and uncharged neutrons. Nonpolar bonds are molecules that share electrons with one another. Another important concept is chemical reactions which is a substance or substances
14 that are converted into one or more new substances. Here s a better understanding of each bond. Which molecule(s) are polar? a. Water b. Carbon c. Oxygen d. None of the above 2. What are polar bonds? a. Hydrophobic b. Hydrophilic c. Semipermeable d. Permeable 3. Which isn t a part of the plasma membrane? a. Amino acids b. Fatty acids c. Nucleic acids d. Phosphates 4. Explain why water molecules are polar. 5. Explain how biological macromolecules form from monomers.
15 KEY TERMS Basic Biological Principles Eukaryote - A type of organism composed of one or more cells containing a membrane-bound nucleus Nucleus- A membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells functioning to maintain the integrity of the genetic material and, through the expression of that material, controlling and regulating cellular activities. Cell- The basic unit of structure and function for all living organisms Prokaryote- A single-celled organism that lacks a membrane-bound nucleus and specialized organelles. A subunit within a cell that has a specialized function. Tissue- An anatomical unit composed of cells organized to perform a similar function. -multicellular- Made up of more than one cell. Ribosome- A cellular structure composed of RNA and proteins that is the site of protein synthesis in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Plasma membrane- A thin, phospholipid and protein molecule bilayer that encapsulates a cell and controls the movement of materials in and out of the cell through active or passive transport. Organ- A n anatomical unit composed of tissues serving a common function. \ The Chemical Basis Of Life Matter- a substance or a material) from which objects are made. Element- A substance that cannot be decomposed into simpler substances by chemical means, and is made up of atoms all with identical number of protons. Compound- A material made up of two or more parts or elements. Atom- The smallest possible unit of an element that still has all the chemical properties of that element Proton- a subatomic particle with a positive electric charge. Protons are found in the nucleus of every atom. Electron- an elementary particle that is a fundamental constituent of matter Nucleus- is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells Ion- an atom or group of atoms that carries a positive or negative electric charge as a result of having lost or gained one or more electrons see anion, cation Covalent bond- A chemical bond formed by the sharing of one or more electrons, especially pairs of electrons, between atoms. Polar molecule- an asymmetric molecule with non-uniform positive and negative charges Non polar molecule- when electrons are shared equally by the atoms, and there is no resulting charge Hydrogen bond- a weak chemical bond between an electronegative atom, such as fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen, and a hydrogen atom bound to another electronegative atom Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
16 Photosynthesis- a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that can later be released to fuel the organisms' activities. Cellular respiration- a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products. Pigment- a material that changes the color of reflected or transmitted light as the result of wavelength-selective absorption. Nadp- a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as lipid and nucleic acid synthesis, which require NADPH as a reducing agent. Glycolysis- the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C₆H₁₂O₆, into pyruvate, CH₃COCOO + H+. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules ATP and NADH. Nad- a coenzyme found in all living cells. Atp- a complex organic chemical that participates in many processes. Cell Transportation and Homeostasis Semi-permeable- allowing certain substances to pass through it but not others, especially allowing the passage of a solvent but not of certain solutes. Passive transport- a movement of ions and other atomic or molecular substances across cell membranes without need of energy input. Diffusion- the net movement of molecules or atoms from a region of high concentration with high chemical potential to a region of low concentration with low chemical potential. Osmosis- the spontaneous net movement of solvent molecules through a semi-permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides Hypotonic solution- is any solution that has a lower osmotic pressure than another solution Hypertonic solution- a particular type of solution that has a greater concentration of solutes on the outside of a cell when compared with the inside of a cell. Isotonic solution- to two solutions having the same osmotic pressure across a semipermeable membrane. Active transport- t he movement of ions or molecules across a cell membrane into a region of higher concentration, assisted by enzymes and requiring energy. Endocytosis- the taking in of matter by a living cell by invagination of its membrane to form a vacuole. Exocytosis- a form of active transport in which a cell transports molecules out of the cell by expelling them through an energy-dependent process. Homeostasis- as the maintenance or regulation of the stable condition, or its equilibrium; or simply as the balance of bodily functions.
17 Theory of Evolution Evolution- change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. Theory- a supposition or a system of ideas intended to explain something, especially one based on general principles independent of the thing to be explained. Fossils- any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Adaption- the dynamic evolutionary process that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Common descent- There is strong quantitative support for the theory that all living organisms on Earth are descended from a common ancestor. Homeostasis structures- Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis Cell growth Anaphase- the stage of meiotic or mitotic cell division in which the chromosomes move away from one another to opposite poles of the spindle. Cell cycle- t he series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication of its DNA to produce two daughter cells. Cell division- the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells Cytokinesis- the cytoplasmic division of a cell at the end of mitosis or meiosis, bringing about the separation into two daughter cells Centromere- the region of a chromosome to which the microtubules of the spindle attach, via the kinetochore, during cell division Homologous- similar in position, structure, and evolutionary origin but not necessarily in function. Interphase- the resting phase between successive mitotic divisions of a cell, or between the first and second divisions of meiosis. Metaphase- the second stage of cell division, between prophase and anaphase, during which the chromosomes become attached to the spindle fibers. Mitosis- a part of the cell cycle when replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Prophase- the first stage of cell division, before metaphase, during which the chromosomes become visible as paired chromatids and the nuclear envelope disappears. Telophase- the final phase of cell division, between anaphase and interphase, in which the chromatids or chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell and two nuclei are formed. Genes Alleles- one of two or more alternative forms of a gene that arise by mutation and are found at the same place on a chromosome.
18 Amino acids- are organic compounds containing amine and carboxyl functional groups, along with a side chain specific to each amino acid Chromosomes- a DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. Dna- a molecule that carries the genetic instructions used in the growth, development, functioning and reproduction of all known living organisms and many viruses. Eukaryotic- any organism whose cells have a cell nucleus and other organelles enclosed within membranes. Genetics- the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in living organisms. Genes- a sequence of DNA or RNA which codes for a molecule that has a function.
19 ANSWER KEY: Bioenergetics: Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration 1) D 2) C 3) A 4) Chloroplasts absorb sunlight and use it with water and carbon dioxide gas to produce food for the plant. Chloroplasts capture light energy from the sun to produce the free energy stored in ATP and NADPH through a process called photosynthesis. 5) The difference between aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration is aerobic respiration requires oxygen in order to generate energy molecule ATP, whereas anaerobic respiration synthesize ATP by using the electron transport chain, with inorganic molecules other than oxygen. Homeostasis and Transport 1) B 2) Hypertonic solutions have a greater solute concentration than the cell, causing water to move out of the cell. Hypotonic solutions have a lower concentration of solution than the cell, causing water to move in to the cell. Isotonic solutions have an equal concentration of solute inside and outside the cell, causing no net gain or loss of water 3) The molecules will move to the right side until equilibrium is reached, then continue to move back and forth with no net change in concentration. This will occur because the membrane is soluble to solute, which will move from high to low concentration. 4) B 5) C Theory of Revolution 1) B 2) B 3) A 4) It s basically saying that everyone and everything evolved from a related species that was around before. 5) Both these structures are based around the same thing but have different functions. Basic Biological principles 1. A 2. B 3. C
20 4. B is false because eukaryotic cells are far more vast and or larger than prokaryotic 5. B is false because it s not found in the nucleus, but in a area or region near it The Chemical Basis of LIfe. 1. A 2. A 3. C 4. Water molecules are polar because it s unbalanced one side is negatively charged while the other is charged positively. 5. Most of the macromolecules are made up by building blocks which are called monomers. Cell Growth 1. C B 4. The difference is the daughter cell has sister chromatids and the parent cell does not. 5. When it separates each chromatid is joined to one centromere. Genes 1. The similarities between dominant alleles and recessive allele are that they both can be expressed based on if the individual inherits copies of alleles. 2. D 3. Homozygous means the same alleles and heterozygous means different alleles. 4. A DNA sequence that specifies a protein and is a unit of heredity that is transferred from a parent to offspring 5. Heterozygous which is basically a pair of genes where one is dominant and one is recessive and or different from one another
2. Cellular and Molecular Biology
 2. Cellular and Molecular Biology 2.1 Cell Structure 2.2 Transport Across Cell Membranes 2.3 Cellular Metabolism 2.4 DNA Replication 2.5 Cell Division 2.6 Biosynthesis 2.1 Cell Structure What is a cell?
2. Cellular and Molecular Biology 2.1 Cell Structure 2.2 Transport Across Cell Membranes 2.3 Cellular Metabolism 2.4 DNA Replication 2.5 Cell Division 2.6 Biosynthesis 2.1 Cell Structure What is a cell?
Biology Mid-Year Review Packet This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES.
 Name: Period: Date: Biology Mid-Year Review Packet This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES. Topics: Observations & Inferences Making A Hypothesis Characteristics of Life
Name: Period: Date: Biology Mid-Year Review Packet This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES. Topics: Observations & Inferences Making A Hypothesis Characteristics of Life
Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018
 Class: Date: Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Hooke s discovery of cells was made observing a. living
Class: Date: Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Hooke s discovery of cells was made observing a. living
Biology Unit 3 Exam DO NOT WRITE ON THIS EXAM. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Biology Unit 3 Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Water moves into a cell placed in a(n) solution. a. osmotic c. hypotonic b. hypertonic
Biology Unit 3 Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Water moves into a cell placed in a(n) solution. a. osmotic c. hypotonic b. hypertonic
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Name Date Class CHAPTER 5 TEST PREP PRETEST Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each
Name Date Class CHAPTER 5 TEST PREP PRETEST Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each
Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2014
 Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2014 Biomolecules and Enzymes (Chapter 2) 8 questions Macromolecules, Biomolecules, Organic Compunds Elements *From the Periodic Table of Elements Subunits Monomers,
Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2014 Biomolecules and Enzymes (Chapter 2) 8 questions Macromolecules, Biomolecules, Organic Compunds Elements *From the Periodic Table of Elements Subunits Monomers,
Notes: Cell Processes 1. Movement across cell membrane 2. Photosynthesis 3. Cellular respiration 4. Cell cycle
 Notes: Cell Processes 1. Movement across cell membrane 2. Photosynthesis 3. Cellular respiration 4. Cell cycle AMDG 1. Notes: Movement across a cell membrane Cell Membrane-see picture in text book What
Notes: Cell Processes 1. Movement across cell membrane 2. Photosynthesis 3. Cellular respiration 4. Cell cycle AMDG 1. Notes: Movement across a cell membrane Cell Membrane-see picture in text book What
Number of questions TEK (Learning Target) Biomolecules & Enzymes
 Unit Biomolecules & Enzymes Number of questions TEK (Learning Target) on Exam 8 questions 9A I can compare and contrast the structure and function of biomolecules. 9C I know the role of enzymes and how
Unit Biomolecules & Enzymes Number of questions TEK (Learning Target) on Exam 8 questions 9A I can compare and contrast the structure and function of biomolecules. 9C I know the role of enzymes and how
Anaphase. Third phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Animal Cell
 Anaphase Third phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Animal Cell Antony Van Leevwenhoek 1643- Dutch microscope maker and merchant, observed and described
Anaphase Third phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Animal Cell Antony Van Leevwenhoek 1643- Dutch microscope maker and merchant, observed and described
To help you complete this review activity and to help you study for your test, you should read SC State Standards B
 Name: Test Date: PAGE: Biology I: Unit 3 Cell Structure Review for Unit Test Directions: You should use this as a guide to help you study for your test. You should also read through your notes, worksheets,
Name: Test Date: PAGE: Biology I: Unit 3 Cell Structure Review for Unit Test Directions: You should use this as a guide to help you study for your test. You should also read through your notes, worksheets,
BIO 210 Chapter 4 Physiology of Cells. By Beth Wyatt, Jack Bagwell, & John McGill. Introduction
 BIO 210 Chapter 4 Physiology of Cells By Beth Wyatt, Jack Bagwell, & John McGill Introduction The living must exchange materials with the nonliving. How does this happen? Cell transport Two major types
BIO 210 Chapter 4 Physiology of Cells By Beth Wyatt, Jack Bagwell, & John McGill Introduction The living must exchange materials with the nonliving. How does this happen? Cell transport Two major types
CORE CONCEPTS & TERMINOLOGY FALL 2010
 CORE CONCEPTS & TERMINOLOGY FALL 2010 The following concepts and terms will be covered by all BIO 120 lecture instructors. Presentation of additional concepts is left to the discretion of the individual
CORE CONCEPTS & TERMINOLOGY FALL 2010 The following concepts and terms will be covered by all BIO 120 lecture instructors. Presentation of additional concepts is left to the discretion of the individual
NAME: PERIOD: The Cell and Its Functions
 NAME: PERIOD: The Cell and Its Functions Directions: Using your notes and book as a guide, complete the following questions to review everything we have learned about cells, their parts, and any functions
NAME: PERIOD: The Cell and Its Functions Directions: Using your notes and book as a guide, complete the following questions to review everything we have learned about cells, their parts, and any functions
Biology Midterm Test Review
 Biology Midterm Test Review Levels of Organization 1. Put these levels of organization in order from simplest to most complex (smallest to largest): cell, community, atom, organism, biosphere, organ system,
Biology Midterm Test Review Levels of Organization 1. Put these levels of organization in order from simplest to most complex (smallest to largest): cell, community, atom, organism, biosphere, organ system,
Biology Spring Final Exam Study Guide
 Name: Hour: Basic Biology Skills Graphing Know the keys to creating a graph Know how to interpret a graph Independent variable Dependent variable Biology Spring Final Exam Study Guide Levels of Organization
Name: Hour: Basic Biology Skills Graphing Know the keys to creating a graph Know how to interpret a graph Independent variable Dependent variable Biology Spring Final Exam Study Guide Levels of Organization
Philipsburg-Osceola Area School District Science Department. Standard(s )
 Philipsburg-Osceola Area School District Science Department Course Name: Biology Grade Level: 10 Timelin e Big Ideas Essential Questions Content/ Concepts Skills/ Competencies Standard(s ) Eligible Content
Philipsburg-Osceola Area School District Science Department Course Name: Biology Grade Level: 10 Timelin e Big Ideas Essential Questions Content/ Concepts Skills/ Competencies Standard(s ) Eligible Content
Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle
 Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
Study Guide: Fall Final Exam H O N O R S B I O L O G Y : U N I T S 1-5
 Study Guide: Fall Final Exam H O N O R S B I O L O G Y : U N I T S 1-5 Directions: The list below identifies topics, terms, and concepts that will be addressed on your Fall Final Exam. This list should
Study Guide: Fall Final Exam H O N O R S B I O L O G Y : U N I T S 1-5 Directions: The list below identifies topics, terms, and concepts that will be addressed on your Fall Final Exam. This list should
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Name Date Class CHAPTER 5 DIRECTED READING Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Section 5-1: Energy and Living Things Energy Flows Between Organisms in Living Systems In the space provided, write the
Name Date Class CHAPTER 5 DIRECTED READING Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Section 5-1: Energy and Living Things Energy Flows Between Organisms in Living Systems In the space provided, write the
Name: Life Science Review Packet. Cell Structure and Function: What Defines Life:
 Name: Life Science Review Packet What Defines Life: An is anything capable of carrying on the processes or characteristics of life. = using materials from the surroundings to make more of oneself, or becoming
Name: Life Science Review Packet What Defines Life: An is anything capable of carrying on the processes or characteristics of life. = using materials from the surroundings to make more of oneself, or becoming
Honors Biology Midterm Review
 Honors Biology Midterm Review 1. CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE Match each item in the boxes with a characteristic a. Reproduction (DNA) 1-passing DNA on to 1, 5 offspring b. Homeostasis 2-trait that helps 7,
Honors Biology Midterm Review 1. CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE Match each item in the boxes with a characteristic a. Reproduction (DNA) 1-passing DNA on to 1, 5 offspring b. Homeostasis 2-trait that helps 7,
B I O. 1. B I O A N A L Y Z E T H E C E L L A S A L I V I N G S Y S T E M.
 Goal 1 B I O. 1. 1 U N D E R S T A N D T H E R E L A T I O N S H I P B E T W E E N T H E S T R U C T U R E S A N D F U N C T I O N S O F C E L L S A N D T H E I R O R G A N E L L E S. B I O. 1. 2 A N A
Goal 1 B I O. 1. 1 U N D E R S T A N D T H E R E L A T I O N S H I P B E T W E E N T H E S T R U C T U R E S A N D F U N C T I O N S O F C E L L S A N D T H E I R O R G A N E L L E S. B I O. 1. 2 A N A
Biology 1 Semester Review
 Chapter 1 What is Science? 1 1 What Is Science? Key Concept The goal of science is to investigate and understand the natural world, to explain events in the natural world, and to use those explanations
Chapter 1 What is Science? 1 1 What Is Science? Key Concept The goal of science is to investigate and understand the natural world, to explain events in the natural world, and to use those explanations
Curriculum Map. Biology, Quarter 1 Big Ideas: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes (BIO1.LS1)
 1 Biology, Quarter 1 Big Ideas: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes (BIO1.LS1) Focus Standards BIO1.LS1.2 Evaluate comparative models of various cell types with a focus on organic molecules
1 Biology, Quarter 1 Big Ideas: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes (BIO1.LS1) Focus Standards BIO1.LS1.2 Evaluate comparative models of various cell types with a focus on organic molecules
Midterm Review Guide. Unit 1 : Biochemistry: 1. Give the ph values for an acid and a base. 2. What do buffers do? 3. Define monomer and polymer.
 Midterm Review Guide Name: Unit 1 : Biochemistry: 1. Give the ph values for an acid and a base. 2. What do buffers do? 3. Define monomer and polymer. 4. Fill in the Organic Compounds chart : Elements Monomer
Midterm Review Guide Name: Unit 1 : Biochemistry: 1. Give the ph values for an acid and a base. 2. What do buffers do? 3. Define monomer and polymer. 4. Fill in the Organic Compounds chart : Elements Monomer
Honors Biology Fall Final Exam Study Guide
 Honors Biology Fall Final Exam Study Guide Helpful Information: Exam has 100 multiple choice questions. Be ready with pencils and a four-function calculator on the day of the test. Review ALL vocabulary,
Honors Biology Fall Final Exam Study Guide Helpful Information: Exam has 100 multiple choice questions. Be ready with pencils and a four-function calculator on the day of the test. Review ALL vocabulary,
Name: Date: Period: Biology End of Course Vocabulary 1. This is an organism s unique role in the environment that includes the habitat, function, and
 1. This is an organism s unique role in the environment that includes the habitat, function, and activities of the organism. a. Niche 2. This is a inter-species relationship in which one species benefits
1. This is an organism s unique role in the environment that includes the habitat, function, and activities of the organism. a. Niche 2. This is a inter-species relationship in which one species benefits
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION. Chapter 10
 CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
Honors Biology Midterm Exam Study Guide--January 2019
 Objective Response Reflection 3 = I totally know this! :) 2 = I remember this somewhat 1 = I don't remember this at all Explain the difference between independent and dependent variables. Explain what
Objective Response Reflection 3 = I totally know this! :) 2 = I remember this somewhat 1 = I don't remember this at all Explain the difference between independent and dependent variables. Explain what
Chemistry of Life Cells & Bioprocesses CRT Review
 Chemistry of Life Cells & Bioprocesses CRT Review Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life macromolecules - The four types of macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins Types of Macromolecules
Chemistry of Life Cells & Bioprocesses CRT Review Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life macromolecules - The four types of macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins Types of Macromolecules
GREENCASTLE ANTRIM SCHOOL DISTRICT Planned Course Board Approved February 16, 2012 Course Title: Biology Grade Level(s) 10 11th
 GREENCASTLE ANTRIM SCHOOL DISTRICT Planned Course Board Approved February 16, 2012 Course Title: Biology Grade Level(s) 10 11th Course Materials: Primary Source(s) Supplemental Source(s) Course Materials:
GREENCASTLE ANTRIM SCHOOL DISTRICT Planned Course Board Approved February 16, 2012 Course Title: Biology Grade Level(s) 10 11th Course Materials: Primary Source(s) Supplemental Source(s) Course Materials:
2015 FALL FINAL REVIEW
 2015 FALL FINAL REVIEW Biomolecules & Enzymes Illustrate table and fill in parts missing 9A I can compare and contrast the structure and function of biomolecules. 9C I know the role of enzymes and how
2015 FALL FINAL REVIEW Biomolecules & Enzymes Illustrate table and fill in parts missing 9A I can compare and contrast the structure and function of biomolecules. 9C I know the role of enzymes and how
Name Date Period Unit 1 Basic Biological Principles 1. What are the 7 characteristics of life?
 Unit 1 Basic Biological Principles 1. What are the 7 characteristics of life? Eukaryotic cell parts you should be able a. to identify and label: Nucleus b. Nucleolus c. Rough/smooth ER Ribosomes d. Golgi
Unit 1 Basic Biological Principles 1. What are the 7 characteristics of life? Eukaryotic cell parts you should be able a. to identify and label: Nucleus b. Nucleolus c. Rough/smooth ER Ribosomes d. Golgi
Chapter Outline. The Living Cell. The Cell Theory. The Nature and Variety of Cells. Cell theory. Observing Cells: The Microscope
 Chapter Outline The Living Cell Chapter 21 The Nature and Variety of Cells How Does a Cell Work? Metabolism: Energy and Life Cell Division Great Idea: Life is based on chemistry, and chemistry takes place
Chapter Outline The Living Cell Chapter 21 The Nature and Variety of Cells How Does a Cell Work? Metabolism: Energy and Life Cell Division Great Idea: Life is based on chemistry, and chemistry takes place
The Process of Cell Division. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview The Process of Cell Division
 Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division Chromosomes genetic information passed from parent to offspring is carried by chromosomes. Chromosomes enable precise DNA separation during cell division.
Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division Chromosomes genetic information passed from parent to offspring is carried by chromosomes. Chromosomes enable precise DNA separation during cell division.
Find your notes, old notebook, and a pencil * On Thursday please bring a calculator!
 Find your notes, old notebook, and a pencil * On Thursday please bring a calculator! Describe Photosynthesis: Inputs & outputs? Equation? Factors that impact it What types of organisms do Plants do it
Find your notes, old notebook, and a pencil * On Thursday please bring a calculator! Describe Photosynthesis: Inputs & outputs? Equation? Factors that impact it What types of organisms do Plants do it
Biology 2018 Final Review. Miller and Levine
 Biology 2018 Final Review Miller and Levine bones blood cells elements All living things are made up of. cells If a cell of an organism contains a nucleus, the organism is a(n). eukaryote prokaryote plant
Biology 2018 Final Review Miller and Levine bones blood cells elements All living things are made up of. cells If a cell of an organism contains a nucleus, the organism is a(n). eukaryote prokaryote plant
The Cell in Action. The Exchange with the Environment, Cell Energy, and the Cell Cycle
 The Cell in Action The Exchange with the Environment, Cell Energy, and the Cell Cycle References Information and Most Images Holt Science & Technology, North Carolina, Grade 7. Holt, Rinehart and Winston:
The Cell in Action The Exchange with the Environment, Cell Energy, and the Cell Cycle References Information and Most Images Holt Science & Technology, North Carolina, Grade 7. Holt, Rinehart and Winston:
Biology Semester Review
 Chapter 1 The Science of Biology Biology Semester Review 1 1 What is Science? One goal of science is to provide natural explanations for events in the natural world. Science also aims to use those explanations
Chapter 1 The Science of Biology Biology Semester Review 1 1 What is Science? One goal of science is to provide natural explanations for events in the natural world. Science also aims to use those explanations
B-2 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of cells and their organelles.
 B-2 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of cells and their organelles. B-2.1 Recall the three major tenets of cell theory (all living things are composed of one
B-2 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of cells and their organelles. B-2.1 Recall the three major tenets of cell theory (all living things are composed of one
2. Draw two water molecules. Using a dotted line, show a hydrogen bond that could form between them.
 Biology Final Review Packet Directions: Answer the questions below. You may use any notes, worksheets, or your textbook to find the answers. The questions are divided up based on the different units we
Biology Final Review Packet Directions: Answer the questions below. You may use any notes, worksheets, or your textbook to find the answers. The questions are divided up based on the different units we
5. The cells in the liver that detoxify poison substances contain lots of a. smooth ER b. rough ER c. Golgi apparatus d. lysosomes e.
 Chapter 7 practice 1. What scientist originally came up with the term "cell"? a. von Leeuwenhoek d. Watson b. Hooke e. Virchow c. van der Waals 2. When you wish to look at the coat of a virus on the surface
Chapter 7 practice 1. What scientist originally came up with the term "cell"? a. von Leeuwenhoek d. Watson b. Hooke e. Virchow c. van der Waals 2. When you wish to look at the coat of a virus on the surface
BIO 2 GO! 3216a The Cell Organelles and Nucleus Function
 BIO 2 GO! 3216a The Cell Organelles and Nucleus Function The cell is the smallest unit of life. Each living cell has a nucleus which functions to control the actions of the rest of the cell. Upon successful
BIO 2 GO! 3216a The Cell Organelles and Nucleus Function The cell is the smallest unit of life. Each living cell has a nucleus which functions to control the actions of the rest of the cell. Upon successful
Please be aware that any form of plagiarism will result in penalties consistent with the CCPS Academic Dishonesty Policy.
 AP Biology Summer Assignment GENERAL DIRECTIONS: You can use e- textbook (Campbell Biology, AP Edition 9e) to find answers to the following questions. The instructions to register are already given to
AP Biology Summer Assignment GENERAL DIRECTIONS: You can use e- textbook (Campbell Biology, AP Edition 9e) to find answers to the following questions. The instructions to register are already given to
Now starts the fun stuff Cell structure and function
 Now starts the fun stuff Cell structure and function Cell Theory The three statements of the cell theory are: All organisms are composed of one or more cells and the processes of life occur in these cells.
Now starts the fun stuff Cell structure and function Cell Theory The three statements of the cell theory are: All organisms are composed of one or more cells and the processes of life occur in these cells.
Biology Midterm Review
 Biology Midterm Review Unit 1 Keystone Objectives: A.1.1, A.1.2, B.4.1.1 1.1 Biology explores life from the global to the microscopic level. Put the levels of organization in order, starting with subatomic
Biology Midterm Review Unit 1 Keystone Objectives: A.1.1, A.1.2, B.4.1.1 1.1 Biology explores life from the global to the microscopic level. Put the levels of organization in order, starting with subatomic
Name Period. Final Exam Study Guide
 Name Period Chapter 6-1 Chromosomes Final Exam Study Guide 1. What is the structure of chromosomes(what are they made of and what is on them)? How many do we have? When are they copied? 2. What is an autosome
Name Period Chapter 6-1 Chromosomes Final Exam Study Guide 1. What is the structure of chromosomes(what are they made of and what is on them)? How many do we have? When are they copied? 2. What is an autosome
3 The Organization of Living Things
 CHAPTER 1 SECTION Cells: The Basic Units of Life 3 The Organization of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the advantages of
CHAPTER 1 SECTION Cells: The Basic Units of Life 3 The Organization of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the advantages of
Review Quizzes Chapters 6-10
 Review Quizzes Chapters 6-10 1. The product(s) of the light reactions of photosynthesis is/are a. pyruvate b. glucose c. ATP and NADPH d. CO 2 and H 2 O e. ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) 1. The product(s)
Review Quizzes Chapters 6-10 1. The product(s) of the light reactions of photosynthesis is/are a. pyruvate b. glucose c. ATP and NADPH d. CO 2 and H 2 O e. ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) 1. The product(s)
Compare cellular structure and their functions in prokaryote and eukaryote cells.
 Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards DNA molecules contain genetic information that is found in all cells. Genes are sections of DNA that code for proteins,
Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards DNA molecules contain genetic information that is found in all cells. Genes are sections of DNA that code for proteins,
Review: Each molecule of glucose yields up to 38 molecules of ATP
 Review: Each molecule of glucose yields up to 38 molecules of ATP Electron shuttle across membrane Mitochondrion Cytoplasm 2 NADH 2 NADH (or 2 FADH 2 ) 2 NADH 6 NADH 2 FADH 2 GLYCOLYSIS Glucose 2 Pyruvate
Review: Each molecule of glucose yields up to 38 molecules of ATP Electron shuttle across membrane Mitochondrion Cytoplasm 2 NADH 2 NADH (or 2 FADH 2 ) 2 NADH 6 NADH 2 FADH 2 GLYCOLYSIS Glucose 2 Pyruvate
Basic Biology. Content Skills Learning Targets Assessment Resources & Technology
 Teacher: Lynn Dahring Basic Biology August 2014 Basic Biology CEQ (tri 1) 1. What are the parts of the biological scientific process? 2. What are the essential molecules and elements in living organisms?
Teacher: Lynn Dahring Basic Biology August 2014 Basic Biology CEQ (tri 1) 1. What are the parts of the biological scientific process? 2. What are the essential molecules and elements in living organisms?
DO NOT WRITE ON THIS!! WRITE ON YOUR OWN PAPER
 BIOLOGY EOC REVIEW Photosynthesis 1. Identify inputs and/or outputs of matter and/or energy in photosynthesis using words and/or chemical formulas Sun + CO 2 + H 2O -> C 6H 12O 6 + O 2 Light Energy + Carbon
BIOLOGY EOC REVIEW Photosynthesis 1. Identify inputs and/or outputs of matter and/or energy in photosynthesis using words and/or chemical formulas Sun + CO 2 + H 2O -> C 6H 12O 6 + O 2 Light Energy + Carbon
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Cell Cycle and Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates itself. These
Cell Cycle and Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates itself. These
Biology EOC Review Study Questions
 Biology EOC Review Study Questions Microscopes and Characteristics of Life 1. How do you calculate total magnification on a compound light microscope? 2. What is the basic building block of all living
Biology EOC Review Study Questions Microscopes and Characteristics of Life 1. How do you calculate total magnification on a compound light microscope? 2. What is the basic building block of all living
Honors Biology summer assignment. Review the notes and study them. There will be a test on this information the 1 st week of class
 Honors Biology summer assignment Review the notes and study them. There will be a test on this information the 1 st week of class Biomolecules Molecules that make up living things. There are 4 molecules
Honors Biology summer assignment Review the notes and study them. There will be a test on this information the 1 st week of class Biomolecules Molecules that make up living things. There are 4 molecules
Cellular Division. copyright cmassengale
 Cellular Division 1 Cell Division All cells are derived from pre- existing cells New cells are produced for growth and to replace damaged or old cells Differs in prokaryotes (bacteria) and eukaryotes (protists,
Cellular Division 1 Cell Division All cells are derived from pre- existing cells New cells are produced for growth and to replace damaged or old cells Differs in prokaryotes (bacteria) and eukaryotes (protists,
Academic Biology: Midterm Review
 Academic Biology: Midterm Review Quarter #1 Chapter 1: The Science of Biology Biology the study of the living world Scientific Method Step 1: Observation Step 2: Forming a Question Step 3: Form a Hypothesis
Academic Biology: Midterm Review Quarter #1 Chapter 1: The Science of Biology Biology the study of the living world Scientific Method Step 1: Observation Step 2: Forming a Question Step 3: Form a Hypothesis
Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division
 Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The process of meiosis results in: A. the production of four identical cells B. no change in chromosome number from parental cells C. a doubling of
Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The process of meiosis results in: A. the production of four identical cells B. no change in chromosome number from parental cells C. a doubling of
 http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html 4A: Students will compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Robert Hooke (1665) Used a compound microscope to look at thin slices of cork (oak
http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html 4A: Students will compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Robert Hooke (1665) Used a compound microscope to look at thin slices of cork (oak
Cells. A. The iodine diffused into the bag. B. The starch was changed to sugar.
 Name: Date: 1. A student filled a bag of dialysis tubing with a milky-white starch solution and placed the bag in a beaker of iodine-water as shown in the diagram. An hour later, the student observed that
Name: Date: 1. A student filled a bag of dialysis tubing with a milky-white starch solution and placed the bag in a beaker of iodine-water as shown in the diagram. An hour later, the student observed that
Biology Mid-Term Study Guide
 Name: Date: Chapter 1: The Science of Biology 1. List the 8 characteristics of all living things: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 2. What is biology? 3. What is homeostasis? 4. Define sexual and asexual reproduction.
Name: Date: Chapter 1: The Science of Biology 1. List the 8 characteristics of all living things: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 2. What is biology? 3. What is homeostasis? 4. Define sexual and asexual reproduction.
CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location ALL CELLS DNA Common in Animals Uncommon in Plants Lysosome
 CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location is the material that contains the Carry genetic ALL CELLS information that determines material inherited characteristics.
CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location is the material that contains the Carry genetic ALL CELLS information that determines material inherited characteristics.
AP Biology - Summer Assignment
 Lorraine Dunigan 2016-2017 School Year duniganl@calvertnet.k12.md.us AP Biology - Summer Assignment GENERAL DIRECTIONS: You may use the internet, library, previous biology course notes, and/or textbooks
Lorraine Dunigan 2016-2017 School Year duniganl@calvertnet.k12.md.us AP Biology - Summer Assignment GENERAL DIRECTIONS: You may use the internet, library, previous biology course notes, and/or textbooks
CELL REPRODUCTION NOTES
 CELL REPRODUCTION NOTES CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION The adult human body produces roughly cells every day. WHY DO CELLS REPRODUCE? So that the organism can and As multicellular organisms grow larger, its
CELL REPRODUCTION NOTES CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION The adult human body produces roughly cells every day. WHY DO CELLS REPRODUCE? So that the organism can and As multicellular organisms grow larger, its
Cells. Every organism is made up of a cell or many cells Humans have ~ 100 TRILLION cells each!
 Cells Every organism is made up of a cell or many cells Humans have ~ 100 TRILLION cells each! History 1660 s Microscopes developed Allowed for the observation of cells for the first time Robert Hooke
Cells Every organism is made up of a cell or many cells Humans have ~ 100 TRILLION cells each! History 1660 s Microscopes developed Allowed for the observation of cells for the first time Robert Hooke
Principles of Cellular Biology
 Principles of Cellular Biology آشنایی با مبانی اولیه سلول Biologists are interested in objects ranging in size from small molecules to the tallest trees: Cell Basic building blocks of life Understanding
Principles of Cellular Biology آشنایی با مبانی اولیه سلول Biologists are interested in objects ranging in size from small molecules to the tallest trees: Cell Basic building blocks of life Understanding
7-1 Life Is Cellular. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 7-1 Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell What is the cell theory? The Discovery of the Cell The cell theory states: All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure
7-1 Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell What is the cell theory? The Discovery of the Cell The cell theory states: All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure
Do all living things grow, move, and breathe? All living things are made of what?
 All living things are made of what? Do all living things grow, move, and breathe? All living things respond to external conditions. This is called what? Which of the 7 traits of life is defined as the
All living things are made of what? Do all living things grow, move, and breathe? All living things respond to external conditions. This is called what? Which of the 7 traits of life is defined as the
Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 5: Cellular Reproduction
 Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 5: Cellular Reproduction NC Essential Standard: 1.2.2 Analyze how cells grow and reproduce in terms of interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis
Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 5: Cellular Reproduction NC Essential Standard: 1.2.2 Analyze how cells grow and reproduce in terms of interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis
PLEASE KEEP EACH EOC CHECK POINTS PAGE!! These will help you review for chapter tests as well as prepare for your EOC Exam!
 EOC Check Points Nature of Science 1. State the independent variable for the graph. 2. On which axis (X, Y) is the independent variable located? 3. State the dependent variable for the graph. 4. On which
EOC Check Points Nature of Science 1. State the independent variable for the graph. 2. On which axis (X, Y) is the independent variable located? 3. State the dependent variable for the graph. 4. On which
Hypothesis. Levels of organization. Theory. Controlled experiment. Homeostasis. ph scale. Characteristics of living things
 Hypothesis Quantitative & Qualitative observations Theory Levels of organization Controlled experiment Homeostasis Characteristics of living things ph scale Quantitative- involves numbers, counting, measuring
Hypothesis Quantitative & Qualitative observations Theory Levels of organization Controlled experiment Homeostasis Characteristics of living things ph scale Quantitative- involves numbers, counting, measuring
The Cell. What is a cell?
 The Cell What is a cell? The Cell What is a cell? Structure which makes up living organisms. The Cell Theory l All living things are composed of cells. l Cells are the basic unit of life. l Cells come
The Cell What is a cell? The Cell What is a cell? Structure which makes up living organisms. The Cell Theory l All living things are composed of cells. l Cells are the basic unit of life. l Cells come
Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction
 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Human Development: Mitosis and Meiosis Division of the Cell Before a cell grows too large, it divides into two new daughter cells in a process called cell division.
Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Human Development: Mitosis and Meiosis Division of the Cell Before a cell grows too large, it divides into two new daughter cells in a process called cell division.
Joy of Science Experience the evolution of the Universe, Earth and Life
 Joy of Science Experience the evolution of the Universe, Earth and Life Review Introduction Main contents Group discussions Unless otherwise noted, pictures are taken from wikipedia.org Review 1 Organic
Joy of Science Experience the evolution of the Universe, Earth and Life Review Introduction Main contents Group discussions Unless otherwise noted, pictures are taken from wikipedia.org Review 1 Organic
MIDTERM EXAM Figure 7-1
 No. MIDTERM EXAM 2014 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Mark your response on your answer sheet. (1 point each) 1. Which of the following is
No. MIDTERM EXAM 2014 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Mark your response on your answer sheet. (1 point each) 1. Which of the following is
8/25/ Opening Questions: Are all living things made of cells? What are at least five things you know about cells?
 Chapter 3 The Cell: Module Hyperlinks 3.1 Cells are the fundamental units of life 3.2 Plant vs. animal cells 3.3 Membranes: structure 3.4 Membranes: function 3.5 The nucleus 3.6 Organelles in protein production
Chapter 3 The Cell: Module Hyperlinks 3.1 Cells are the fundamental units of life 3.2 Plant vs. animal cells 3.3 Membranes: structure 3.4 Membranes: function 3.5 The nucleus 3.6 Organelles in protein production
Name: Date: Hour: Unit Four: Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosis. Monomer Polymer Example Drawing Function in a cell DNA
 Unit Four: Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosis I. Concept Review A. Why is carbon often called the building block of life? B. List the four major macromolecules. C. Complete the chart below. Monomer Polymer
Unit Four: Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosis I. Concept Review A. Why is carbon often called the building block of life? B. List the four major macromolecules. C. Complete the chart below. Monomer Polymer
Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis
 Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis 6:1 Chromosomes DNA GENES CHROMATIN/CHROMOSOMES CHROMOSOMES/CHROMATIN are made of units called GENES. GENES are made of a compound called deoxyribonucleic acid or
Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis 6:1 Chromosomes DNA GENES CHROMATIN/CHROMOSOMES CHROMOSOMES/CHROMATIN are made of units called GENES. GENES are made of a compound called deoxyribonucleic acid or
BIOLOGY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC
 BIOLOGY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE FUNDAMENTAL PROCESSES OF ALL LIVING THINGS DEPEND ON A VARIETY OF SPECIALIZED CELL STRUCTURES AND CHEMICAL PROCESSES. First Semester Benchmarks:
BIOLOGY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE FUNDAMENTAL PROCESSES OF ALL LIVING THINGS DEPEND ON A VARIETY OF SPECIALIZED CELL STRUCTURES AND CHEMICAL PROCESSES. First Semester Benchmarks:
Stamford Public Schools Science Department District Midterm Examination REVIEW
 Stamford Public Schools Science Department District Midterm Examination REVIEW 2013-2014 CP Biology Student Name: School/Teacher: Date: SPS CP Biology Midterm Review, January 2014 Page 1 Dear Biology Student,
Stamford Public Schools Science Department District Midterm Examination REVIEW 2013-2014 CP Biology Student Name: School/Teacher: Date: SPS CP Biology Midterm Review, January 2014 Page 1 Dear Biology Student,
Why mitosis?
 Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotes. Prokaryotes (i.e., archaea and bacteria) divide via binary fission. Mitosis is the process by which the somatic cells of all multicellular organisms multiply. Somatic
Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotes. Prokaryotes (i.e., archaea and bacteria) divide via binary fission. Mitosis is the process by which the somatic cells of all multicellular organisms multiply. Somatic
1. A cell with 10 chromosomes undergoes mitosis. How many daughter cells are created? Each daughter cell has chromosomes. 2, 10 / 10, 2 / 1, 10 / 2,
 Test Review (12/7) 1. A cell with 10 chromosomes undergoes mitosis. How many daughter cells are created? Each daughter cell has chromosomes. 2, 10 / 10, 2 / 1, 10 / 2, 20 2. 5. What structure is responsible
Test Review (12/7) 1. A cell with 10 chromosomes undergoes mitosis. How many daughter cells are created? Each daughter cell has chromosomes. 2, 10 / 10, 2 / 1, 10 / 2, 20 2. 5. What structure is responsible
Key Concepts. n Cell Cycle. n Interphase. n Mitosis. n Cytokinesis
 The Cell Cycle B-2.6: Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ); the phases of mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. Key
The Cell Cycle B-2.6: Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ); the phases of mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. Key
Wake Acceleration Academy - Biology Note Guide Unit 3: Cell Structures and Functions
 Wake Acceleration Academy - Biology Note Guide Unit 3: Cell Structures and Functions Extra Resources Website: http://waa-science.weebly.com Module 1: Overview of Cell Structures and Functions Vocabulary
Wake Acceleration Academy - Biology Note Guide Unit 3: Cell Structures and Functions Extra Resources Website: http://waa-science.weebly.com Module 1: Overview of Cell Structures and Functions Vocabulary
Passive. mechanisms. Active. mechanisms. Cell diffusion. Movement. Movement. Movement. Mechanisms that do not require cellular energy such as:
 Passive mechanisms Mechanisms that do not require cellular energy such as: Diffusion Facilitated diffusion Osmosis Filtration Active mechanisms Mechanisms that do require cellular energy such as: Active
Passive mechanisms Mechanisms that do not require cellular energy such as: Diffusion Facilitated diffusion Osmosis Filtration Active mechanisms Mechanisms that do require cellular energy such as: Active
Notes Chapter 4 Cell Reproduction. That cell divided and becomes two, two become four, four become eight, and so on.
 4.1 Cell Division and Mitosis Many organisms start as one cell. Notes Chapter 4 Cell Reproduction That cell divided and becomes two, two become four, four become eight, and so on. Many-celled organisms,
4.1 Cell Division and Mitosis Many organisms start as one cell. Notes Chapter 4 Cell Reproduction That cell divided and becomes two, two become four, four become eight, and so on. Many-celled organisms,
Cell Reproduction Review
 Name Date Period Cell Reproduction Review Explain what is occurring in each part of the cell cycle --- G 0, G1, S, G2, and M. 1 CELL DIVISION Label all parts of each cell in the cell cycle and explain
Name Date Period Cell Reproduction Review Explain what is occurring in each part of the cell cycle --- G 0, G1, S, G2, and M. 1 CELL DIVISION Label all parts of each cell in the cell cycle and explain
STEMscopedia: PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS
 B.L 14.2 and 14.3 Reflect Take a moment to think about all of the living things on Earth. There is great diversity among organisms, from microscopic bacteria to massive blue whales the largest animals
B.L 14.2 and 14.3 Reflect Take a moment to think about all of the living things on Earth. There is great diversity among organisms, from microscopic bacteria to massive blue whales the largest animals
Cell Theory Essential Questions
 Cells Vocab words 1. Cell 2. Cell theory 3. Nucleus 4. Eukaryote 5. Prokaryote 6. Organelle 7. Cytoplasm 8. Nuclear envelope 9. Chromatin 10. Chromosome 11. Nucleolus 12. Ribosome 13. Endoplasmic reticulum
Cells Vocab words 1. Cell 2. Cell theory 3. Nucleus 4. Eukaryote 5. Prokaryote 6. Organelle 7. Cytoplasm 8. Nuclear envelope 9. Chromatin 10. Chromosome 11. Nucleolus 12. Ribosome 13. Endoplasmic reticulum
Biology Quarter 2 Credit Recovery. Overview. Reference textbook: Glencoe Biology 2007, ISBN
 Biology Quarter 2 Credit Recovery Overview Reference textbook: Glencoe Biology 2007, ISBN 0-07-8695104 Pre-Assessment 3 English versions 1 Spanish version Module 15 Assignments 2 Labs 1 Answer Key document
Biology Quarter 2 Credit Recovery Overview Reference textbook: Glencoe Biology 2007, ISBN 0-07-8695104 Pre-Assessment 3 English versions 1 Spanish version Module 15 Assignments 2 Labs 1 Answer Key document
CELL BIOLOGY. Which of the following cell structures does not have membranes? A. Ribosomes B. Mitochondria C. Chloroplasts D.
 1 CELL BIOLOGY PROKARYOTIC and EUKARYOTIC SP/1. SP/2. SP/4. Plant and animal cells both have A. ribosomes, cell walls and mitochondria. B. Golgi apparatus, chromosomes and mitochondria. C. Golgi apparatus,
1 CELL BIOLOGY PROKARYOTIC and EUKARYOTIC SP/1. SP/2. SP/4. Plant and animal cells both have A. ribosomes, cell walls and mitochondria. B. Golgi apparatus, chromosomes and mitochondria. C. Golgi apparatus,
Biology Fall Final Review 2005/2006 Mrs. Nuño
 Biology Fall Final Review 2005/2006 Mrs. Nuño Unit 1: The Nature of Science (Chapter 1) 7 characteristics of life. 7 major themes of biology, including the definitions of science terms describing those
Biology Fall Final Review 2005/2006 Mrs. Nuño Unit 1: The Nature of Science (Chapter 1) 7 characteristics of life. 7 major themes of biology, including the definitions of science terms describing those
Stamford Public Schools Science Department District Midterm Examination REVIEW
 Stamford Public Schools Science Department District Midterm Examination REVIEW 2015-2016 Honors Biology Student Name: School/Teacher: Date: SPS Honors Biology Midterm Review, January 2016 Page 1 Dear Biology
Stamford Public Schools Science Department District Midterm Examination REVIEW 2015-2016 Honors Biology Student Name: School/Teacher: Date: SPS Honors Biology Midterm Review, January 2016 Page 1 Dear Biology
Peddie Summer Day School
 Peddie Summer Day School Course Syllabus: BIOLOGY Teacher: Mr. Jeff Tuliszewski Text: Biology by Miller and Levine, Prentice Hall, 2010 edition ISBN 9780133669510 Guided Reading Workbook for Biology ISBN
Peddie Summer Day School Course Syllabus: BIOLOGY Teacher: Mr. Jeff Tuliszewski Text: Biology by Miller and Levine, Prentice Hall, 2010 edition ISBN 9780133669510 Guided Reading Workbook for Biology ISBN
Ch. 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles
 Introduction Ch. 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles 2004-05 Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. -Offspring resemble their parents more than they do less closely
Introduction Ch. 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles 2004-05 Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. -Offspring resemble their parents more than they do less closely
CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE ORGANIZATION OF LIFE CELL THEORY TIMELINE
 CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE 1. composed of cells either uni/multi 2. reproduce sexual and/or asexual 3. contain DNA in cells 4. grow and develop 5. use material/energy in metabolic reactions 6. respond to
CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE 1. composed of cells either uni/multi 2. reproduce sexual and/or asexual 3. contain DNA in cells 4. grow and develop 5. use material/energy in metabolic reactions 6. respond to
Ladies and Gentlemen.. The King of Rock and Roll
 Ladies and Gentlemen.. The King of Rock and Roll Learning Objectives: The student is able to construct an explanation, using visual representations or narratives, as to how DNA in chromosomes is transmitted
Ladies and Gentlemen.. The King of Rock and Roll Learning Objectives: The student is able to construct an explanation, using visual representations or narratives, as to how DNA in chromosomes is transmitted
Answer Key- Biology Review for Fall Benchmark
 Name Class Answer Key- Biology Review for Fall Benchmark Definitions You should know what every word on this page means. Look through the entire review sheet and highlight any words you do not recognize.
Name Class Answer Key- Biology Review for Fall Benchmark Definitions You should know what every word on this page means. Look through the entire review sheet and highlight any words you do not recognize.
Cell Division. Genetic info must be copied. Each cell gets a complete copy of that info. It occurs in two main stages:
 10-2 Cell Division Key Questions: 1)What is the role of chromosomes in cell division? 2) What are the main events of the cell cycle? 3) What events occur during each of the four phases of mitosis? 4) How
10-2 Cell Division Key Questions: 1)What is the role of chromosomes in cell division? 2) What are the main events of the cell cycle? 3) What events occur during each of the four phases of mitosis? 4) How
