The Potassium Ion Channel: Rahmat Muhammad
|
|
|
- Flora Williams
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Potassium Ion Channel: Rahmat Muhammad
2 Ions: Cell volume regulation Electrical impulse formation (e.g. sodium, potassium)
3 Lipid membrane: the dielectric barrier Pro: compartmentalization Con: Dielectric barrier Solution: water filled pores
4 The Pore Theory Traced as far back as the 1840s in attempt to explain osmosis Pores would pass water and small particles
5 Ions in the squid axon 1952: Hodgkin and Huxley describe action potential propagation Describe changes in Na+ and K+ permeability Hodgkin and Keynes isotopic K+ flux-ratio experiments: ions cross the membrane along a chain of negative charges or through narrow tubes or channels in which they are constrained to move in single file [with] several ions in the channel at any moment.
6 The debates of Ions pass through aqueous pores called channels Ion channels are proteins The channels for Na+ and K+ are different They have gates that open and close them in response to changing membrane voltage
7 Early ideas of channel architecture and selectivity: Binstock and Armstrong: TEA+ Derived K+ flux to be about one K+ ion per microsecond Armstrong and Hille using C9+, a TEA variant, proposed idea of gates :
8 Objections How can a channel be selective? If the ion stuck too tightly it would block rather than permeate Armstrong, 1971:
9 Enter Rod MacKinnon: How does a small scorpion toxin inhibit a potassium channel? Scorpion toxin occludes the potassium channel s ion pathway How does the potassium channel select potassium over sodium while still conducting it near the diffusion limit?
10 Shaker is cloned 1987: Shaker First potassium channel gene cloned Little information about the channel structure Used scorpion toxin to identify which of the amino acids form the ion pathway Using methods such as site directed mutagenesis, they reached a number of important conclusions about the potassium channel architecture
11 K+ channel before crystallography The channel contains four identical subunits arranged in a symmetric ring around a central pore Pore loop (P-Loop): short amino acid segment between two transmembrane helices that dips into the membrane without crossing it P-Loop has the signature sequence : Thr-Val Val-Gly-Tyr-Gly This signature sequence is responsible for potassium selectivity The four pore loops, one from each subunit, meet near the channel s central axis to form the narrowest point along the ion pathway
12 Meanwhile more K+ channels are cloned Signature sequence used as a key to find potassium channels even in bacteria
13 Why the KscA potassium channel? Hyrdophobicity plot shows two closely related varieties of K+ channels Although KscA is a 2TM channel, its amino acid sequence is closer to those of eukaryotic 6TM channels
14 X-ray crystallography Protein preparation Crystallization Solve the structure Measurement of native diffraction data Obtaining heavy atom derivatives Measurement and analysis of derivative data Calculation of phases Map interpretation and model building Model refinement
15 Protein Preparation Obtain sufficient quantities of material Overexpression of KscA in E.Coli Homogenous and active Crystallization Rate limiting step May require additives such as heavy atoms May require removing something
16 Electron density maps of KscA K+ channel Solved to a resolution of 3.2 Å Minimum separation of two groups in the electron-density plot that can be distinguished from one another At this resolution the path of the polypeptide backbone can be traced
17 K+ channels is a tetramer
18 Pore helices N+ N+ N+ N+ C- C- C- C-
19 Mutagenesis studies on Shaker: Mapping onto the KcsA structure Conotoxin or agatoxin2 External TEA site Internal TEA site
20 General properties of the ion conduction pore Both intracellular and extracellular entryways are negatively charge Polar main chain atoms Hydrophobic Polar atoms
21 General properties of the ion conduction pore Overall length of the pore is 45 Å External pore: ~12 Å long, ~2.5 Å across Cavity: ~10 Å across Internal pore: ~18 Å long
22 K+ ion positions in the pore Li Å,, Na Å Rb Å,, Cs Å,, K Å
23 The Cavity and Internal Pore Why is there an ion in the 10 Å diameter cavity? Electrostatic considerations Lipid bilayer Low dielectric bilayer
24 The Cavity and Internal Pore Stabilizing the ion at the cavity center: Surround the ion with polarizable water Negative electrostatic potential from four pore helices N N + C + C - - C - N + C - N +
25 The Cavity and Internal Pore What is the significance of the hydrophobic lining? Achieve a high throughput by having a relatively inert surface over most of the length of the pore
26 The selectivity filter Electron density in the selectivity filter Continuous ridge of electron density attributable to the main chain
27 The selectivity filter The structure of KcsA at a resolution of 2.0 A (Zhou et al Nature.. 414:43-48.) 48.) four internal binding sites (P1-P4) P4) and two external (P0 and P5)
28 The selectivity filter Two essential features of the selectivity filter: Main chain atoms create a stack of sequential oxygen rings Side chains pointing away from the pore interact with residues from the pore helix to hold the pore open
29 K+ ion selectivity model: 1998 Upon entering the selectivity filter, the ion dehydrates Carbonyl oxygen atoms act as surrogate water and compensate for cost of dehydration Selectivity filter is held open as if to prevent it from accommodating a Na+ ion
30 K+ ion selectivity model: 1971
31 K+ ion conductance model At 150 mm K+, selectivity filter contains two ions separated by ~7.5 Å
32 Summary The K+ channel pore is constructed of an inverted teepee with the selectivity filter held at its wide end The selectivity filter is ~2.5 A wide and 12 A long whereas the rest of the pore is wider with a relatively inert hydrophobic lining A large water filled cavity and helix dipoles help to overcome the high electrostatic energy barrier The K+ selectivity filter is lined by carbonyl oxygen atoms providing multiple closely spaced binding sites Two K+ ions at close proximity repel each other to counteract strong protein-ion ion interaction and allow for rapid conduction
33 Current and Future studies What are the conformational changes that underlie pore opening in K+ channels? MthK,, a Ca+ gated K+ channel crystallized in open state (Jiang( et al Nature. 417: Inner helices expand its intracellular diameter in the opened state What are the changes that underlie voltage sensitivity? KvAP,, a voltage gated K+ channel was crystallized (Jiang( et al Nature. 423:33-41) The electric field pulls on a charged helix-turn turn- helix structure on the channel s perimeter to bring about a conformation change
Molecular Basis of K + Conduction and Selectivity
 The Structure of the Potassium Channel: Molecular Basis of K + Conduction and Selectivity -Doyle, DA, et al. The structure of the potassium channel: molecular basis of K + conduction and selectivity. Science
The Structure of the Potassium Channel: Molecular Basis of K + Conduction and Selectivity -Doyle, DA, et al. The structure of the potassium channel: molecular basis of K + conduction and selectivity. Science
Potassium channel gating and structure!
 Reading: Potassium channel gating and structure Hille (3rd ed.) chapts 10, 13, 17 Doyle et al. The Structure of the Potassium Channel: Molecular Basis of K1 Conduction and Selectivity. Science 280:70-77
Reading: Potassium channel gating and structure Hille (3rd ed.) chapts 10, 13, 17 Doyle et al. The Structure of the Potassium Channel: Molecular Basis of K1 Conduction and Selectivity. Science 280:70-77
Membrane Protein Channels
 Membrane Protein Channels Potassium ions queuing up in the potassium channel Pumps: 1000 s -1 Channels: 1000000 s -1 Pumps & Channels The lipid bilayer of biological membranes is intrinsically impermeable
Membrane Protein Channels Potassium ions queuing up in the potassium channel Pumps: 1000 s -1 Channels: 1000000 s -1 Pumps & Channels The lipid bilayer of biological membranes is intrinsically impermeable
I. MEMBRANE POTENTIALS
 I. MEMBRANE POTENTIALS Background to Nerve Impulses We have all heard that nerve impulses are electrical impulses. Stimuli at one end of a nerve cell are communicated to the far end of the nerve cell through
I. MEMBRANE POTENTIALS Background to Nerve Impulses We have all heard that nerve impulses are electrical impulses. Stimuli at one end of a nerve cell are communicated to the far end of the nerve cell through
Module Membrane Biogenesis and Transport Lecture 15 Ion Channels Dale Sanders
 Module 0220502 Membrane Biogenesis and Transport Lecture 15 Ion Channels Dale Sanders 9 March 2009 Aims: By the end of the lecture you should understand The principles behind the patch clamp technique;
Module 0220502 Membrane Biogenesis and Transport Lecture 15 Ion Channels Dale Sanders 9 March 2009 Aims: By the end of the lecture you should understand The principles behind the patch clamp technique;
Secondary Structure. Bioch/BIMS 503 Lecture 2. Structure and Function of Proteins. Further Reading. Φ, Ψ angles alone determine protein structure
 Bioch/BIMS 503 Lecture 2 Structure and Function of Proteins August 28, 2008 Robert Nakamoto rkn3c@virginia.edu 2-0279 Secondary Structure Φ Ψ angles determine protein structure Φ Ψ angles are restricted
Bioch/BIMS 503 Lecture 2 Structure and Function of Proteins August 28, 2008 Robert Nakamoto rkn3c@virginia.edu 2-0279 Secondary Structure Φ Ψ angles determine protein structure Φ Ψ angles are restricted
Homology models of the tetramerization domain of six eukaryotic voltage-gated potassium channels Kv1.1-Kv1.6
 Homology models of the tetramerization domain of six eukaryotic voltage-gated potassium channels Kv1.1-Kv1.6 Hsuan-Liang Liu* and Chin-Wen Chen Department of Chemical Engineering and Graduate Institute
Homology models of the tetramerization domain of six eukaryotic voltage-gated potassium channels Kv1.1-Kv1.6 Hsuan-Liang Liu* and Chin-Wen Chen Department of Chemical Engineering and Graduate Institute
Ion Channel Structure and Function (part 1)
 Ion Channel Structure and Function (part 1) The most important properties of an ion channel Intrinsic properties of the channel (Selectivity and Mode of Gating) + Location Physiological Function Types
Ion Channel Structure and Function (part 1) The most important properties of an ion channel Intrinsic properties of the channel (Selectivity and Mode of Gating) + Location Physiological Function Types
Building a Homology Model of the Transmembrane Domain of the Human Glycine α-1 Receptor
 Building a Homology Model of the Transmembrane Domain of the Human Glycine α-1 Receptor Presented by Stephanie Lee Research Mentor: Dr. Rob Coalson Glycine Alpha 1 Receptor (GlyRa1) Member of the superfamily
Building a Homology Model of the Transmembrane Domain of the Human Glycine α-1 Receptor Presented by Stephanie Lee Research Mentor: Dr. Rob Coalson Glycine Alpha 1 Receptor (GlyRa1) Member of the superfamily
BME 5742 Biosystems Modeling and Control
 BME 5742 Biosystems Modeling and Control Hodgkin-Huxley Model for Nerve Cell Action Potential Part 1 Dr. Zvi Roth (FAU) 1 References Hoppensteadt-Peskin Ch. 3 for all the mathematics. Cooper s The Cell
BME 5742 Biosystems Modeling and Control Hodgkin-Huxley Model for Nerve Cell Action Potential Part 1 Dr. Zvi Roth (FAU) 1 References Hoppensteadt-Peskin Ch. 3 for all the mathematics. Cooper s The Cell
Structure and Function of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels at Atomic Resolution
 Structure and Function of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels at Atomic Resolution Royal Society of Chemistry Cambridge UK, March 2013 William A. Catterall, Department of Pharmacology, University of Washington
Structure and Function of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels at Atomic Resolution Royal Society of Chemistry Cambridge UK, March 2013 William A. Catterall, Department of Pharmacology, University of Washington
Lecture 10 : Neuronal Dynamics. Eileen Nugent
 Lecture 10 : Neuronal Dynamics Eileen Nugent Origin of the Cells Resting Membrane Potential: Nernst Equation, Donnan Equilbrium Action Potentials in the Nervous System Equivalent Electrical Circuits and
Lecture 10 : Neuronal Dynamics Eileen Nugent Origin of the Cells Resting Membrane Potential: Nernst Equation, Donnan Equilbrium Action Potentials in the Nervous System Equivalent Electrical Circuits and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Table of Contents Page Supplementary Table 1. Diffraction data collection statistics 2 Supplementary Table 2. Crystallographic refinement statistics 3 Supplementary Fig. 1. casic1mfc packing in the R3
Table of Contents Page Supplementary Table 1. Diffraction data collection statistics 2 Supplementary Table 2. Crystallographic refinement statistics 3 Supplementary Fig. 1. casic1mfc packing in the R3
Electrical Properties of the Membrane
 BIOE 2520 Electrical Properties of the Membrane Reading: Chapter 11 of Alberts et al. Stephen Smith, Ph.D. 433 Biotech Center shs46@pitt.edu Permeability of Lipid membrane Lipid bilayer is virtually impermeable
BIOE 2520 Electrical Properties of the Membrane Reading: Chapter 11 of Alberts et al. Stephen Smith, Ph.D. 433 Biotech Center shs46@pitt.edu Permeability of Lipid membrane Lipid bilayer is virtually impermeable
SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION. Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course. Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C7: BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS
 2757 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C7: BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2013 Monday, 17 June, 2.30 pm 5.45 pm 15
2757 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C7: BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2013 Monday, 17 June, 2.30 pm 5.45 pm 15
THE BIT OF information in nerves is the action potential, a
 34 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NANOBIOSCIENCE, VOL. 4, NO. 1, MARCH 2005 Voltage-Gated Ion Channels Francisco Bezanilla Abstract Voltage-dependent ion channels are membrane proteins that conduct ions at high
34 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NANOBIOSCIENCE, VOL. 4, NO. 1, MARCH 2005 Voltage-Gated Ion Channels Francisco Bezanilla Abstract Voltage-dependent ion channels are membrane proteins that conduct ions at high
TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANE
 TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANE The plasma membrane functions to isolate the inside of the cell from its environment, but isolation is not complete. A large number of molecules constantly transit between the
TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANE The plasma membrane functions to isolate the inside of the cell from its environment, but isolation is not complete. A large number of molecules constantly transit between the
Dynamic hydration valve controlled ion permeability and
 1 Dynamic hydration valve controlled ion permeability and stability of NaK channel Rong Shen 1, *, Wanlin Guo 1, * & Wenyu Zhong 1 1 Institute of Nano Science, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,
1 Dynamic hydration valve controlled ion permeability and stability of NaK channel Rong Shen 1, *, Wanlin Guo 1, * & Wenyu Zhong 1 1 Institute of Nano Science, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,
Overview of ion channel proteins. What do ion channels do? Three important points:
 Overview of ion channel proteins Protein Structure Membrane proteins & channels Specific channels Several hundred distinct types Organization Evolution We need to consider 1. Structure 2. Functions 3.
Overview of ion channel proteins Protein Structure Membrane proteins & channels Specific channels Several hundred distinct types Organization Evolution We need to consider 1. Structure 2. Functions 3.
Electrophysiology of the neuron
 School of Mathematical Sciences G4TNS Theoretical Neuroscience Electrophysiology of the neuron Electrophysiology is the study of ionic currents and electrical activity in cells and tissues. The work of
School of Mathematical Sciences G4TNS Theoretical Neuroscience Electrophysiology of the neuron Electrophysiology is the study of ionic currents and electrical activity in cells and tissues. The work of
LETTERS. Atomic structure of a Na 1 - and K 1 -conducting channel. Ning Shi 1, Sheng Ye 1, Amer Alam 1, Liping Chen 1 & Youxing Jiang 1
 Vol 440 23 March 2006 doi:10.1038/nature04508 Atomic structure of a Na 1 - and K 1 -conducting channel Ning Shi 1, Sheng Ye 1, Amer Alam 1, Liping Chen 1 & Youxing Jiang 1 Ion selectivity is one of the
Vol 440 23 March 2006 doi:10.1038/nature04508 Atomic structure of a Na 1 - and K 1 -conducting channel Ning Shi 1, Sheng Ye 1, Amer Alam 1, Liping Chen 1 & Youxing Jiang 1 Ion selectivity is one of the
A SURPRISING CLARIFICATION OF THE MECHANISM OF ION-CHANNEL VOLTAGE- GATING
 A SURPRISING CLARIFICATION OF THE MECHANISM OF ION-CHANNEL VOLTAGE- GATING AR. PL. Ashok Palaniappan * An intense controversy has surrounded the mechanism of voltage-gating in ion channels. We interpreted
A SURPRISING CLARIFICATION OF THE MECHANISM OF ION-CHANNEL VOLTAGE- GATING AR. PL. Ashok Palaniappan * An intense controversy has surrounded the mechanism of voltage-gating in ion channels. We interpreted
Advanced Higher Biology. Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins
 Advanced Higher Biology Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins Membrane Structure Phospholipid bilayer Transmembrane protein Integral protein Movement of Molecules Across Membranes Phospholipid
Advanced Higher Biology Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins Membrane Structure Phospholipid bilayer Transmembrane protein Integral protein Movement of Molecules Across Membranes Phospholipid
Chapter 12: Intracellular sorting
 Chapter 12: Intracellular sorting Principles of intracellular sorting Principles of intracellular sorting Cells have many distinct compartments (What are they? What do they do?) Specific mechanisms are
Chapter 12: Intracellular sorting Principles of intracellular sorting Principles of intracellular sorting Cells have many distinct compartments (What are they? What do they do?) Specific mechanisms are
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. doi: /nature07461
 Figure S1 Electrophysiology. a ph-activation of. Two-electrode voltage clamp recordings of Xenopus oocytes expressing in comparison to waterinjected oocytes. Currents were recorded at 40 mv. The ph of
Figure S1 Electrophysiology. a ph-activation of. Two-electrode voltage clamp recordings of Xenopus oocytes expressing in comparison to waterinjected oocytes. Currents were recorded at 40 mv. The ph of
Protein Structure. W. M. Grogan, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES
 Protein Structure W. M. Grogan, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the structure and characteristic properties of typical proteins. 2. List and describe the four levels of structure found in proteins. 3. Relate
Protein Structure W. M. Grogan, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the structure and characteristic properties of typical proteins. 2. List and describe the four levels of structure found in proteins. 3. Relate
Quantitative Electrophysiology
 ECE 795: Quantitative Electrophysiology Notes for Lecture #1 Tuesday, September 18, 2012 1. INTRODUCTION TO EXCITABLE CELLS Historical perspective: Bioelectricity first discovered by Luigi Galvani in 1780s
ECE 795: Quantitative Electrophysiology Notes for Lecture #1 Tuesday, September 18, 2012 1. INTRODUCTION TO EXCITABLE CELLS Historical perspective: Bioelectricity first discovered by Luigi Galvani in 1780s
Channels can be activated by ligand-binding (chemical), voltage change, or mechanical changes such as stretch.
 1. Describe the basic structure of an ion channel. Name 3 ways a channel can be "activated," and describe what occurs upon activation. What are some ways a channel can decide what is allowed to pass through?
1. Describe the basic structure of an ion channel. Name 3 ways a channel can be "activated," and describe what occurs upon activation. What are some ways a channel can decide what is allowed to pass through?
Neurobiology Biomed 509 Ion Channels
 eurobiology Biomed 509 Ion hannels References: Luo 2.4, 2.4 2., (3.20 3.2), M 2.8 I. ores vs. carriers In order for hydrophilic ions to transit the hydrophobic membrane, they need to have a specific pathway
eurobiology Biomed 509 Ion hannels References: Luo 2.4, 2.4 2., (3.20 3.2), M 2.8 I. ores vs. carriers In order for hydrophilic ions to transit the hydrophobic membrane, they need to have a specific pathway
The potassium channel: Structure, selectivity and diffusion
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 112, NUMBER 18 8 MAY 2000 The potassium channel: Structure, selectivity and diffusion T. W. Allen a) Protein Dynamics Unit, Department of Chemistry, Australian National
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 112, NUMBER 18 8 MAY 2000 The potassium channel: Structure, selectivity and diffusion T. W. Allen a) Protein Dynamics Unit, Department of Chemistry, Australian National
Particle-Based Simulation of Bio-Electronic Systems
 Particle-Based Simulation of Bio-Electronic Systems Alex Smolyanitsky, and Marco Saraniti Arizona State University Outline Particle-based Brownian dynamics simulations for bioelectronic systems Complex-field
Particle-Based Simulation of Bio-Electronic Systems Alex Smolyanitsky, and Marco Saraniti Arizona State University Outline Particle-based Brownian dynamics simulations for bioelectronic systems Complex-field
Supplementary Figure S1. Urea-mediated buffering mechanism of H. pylori. Gastric urea is funneled to a cytoplasmic urease that is presumably attached
 Supplementary Figure S1. Urea-mediated buffering mechanism of H. pylori. Gastric urea is funneled to a cytoplasmic urease that is presumably attached to HpUreI. Urea hydrolysis products 2NH 3 and 1CO 2
Supplementary Figure S1. Urea-mediated buffering mechanism of H. pylori. Gastric urea is funneled to a cytoplasmic urease that is presumably attached to HpUreI. Urea hydrolysis products 2NH 3 and 1CO 2
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11054 Supplementary Fig. 1 Sequence alignment of Na v Rh with NaChBac, Na v Ab, and eukaryotic Na v and Ca v homologs. Secondary structural elements of Na v Rh are indicated above the
doi:10.1038/nature11054 Supplementary Fig. 1 Sequence alignment of Na v Rh with NaChBac, Na v Ab, and eukaryotic Na v and Ca v homologs. Secondary structural elements of Na v Rh are indicated above the
Particles with opposite charges (positives and negatives) attract each other, while particles with the same charge repel each other.
 III. NEUROPHYSIOLOGY A) REVIEW - 3 basic ideas that the student must remember from chemistry and physics: (i) CONCENTRATION measure of relative amounts of solutes in a solution. * Measured in units called
III. NEUROPHYSIOLOGY A) REVIEW - 3 basic ideas that the student must remember from chemistry and physics: (i) CONCENTRATION measure of relative amounts of solutes in a solution. * Measured in units called
A Model of Voltage Gating Developed Using the KvAP Channel Crystal Structure
 Biophysical Journal Volume 87 October 2004 2255 2270 2255 A Model of Voltage Gating Developed Using the KvAP Channel Crystal Structure Indira H. Shrivastava, Stewart R. Durell, and H. Robert Guy Laboratory
Biophysical Journal Volume 87 October 2004 2255 2270 2255 A Model of Voltage Gating Developed Using the KvAP Channel Crystal Structure Indira H. Shrivastava, Stewart R. Durell, and H. Robert Guy Laboratory
Packing of Secondary Structures
 7.88 Lecture Notes - 4 7.24/7.88J/5.48J The Protein Folding and Human Disease Professor Gossard Retrieving, Viewing Protein Structures from the Protein Data Base Helix helix packing Packing of Secondary
7.88 Lecture Notes - 4 7.24/7.88J/5.48J The Protein Folding and Human Disease Professor Gossard Retrieving, Viewing Protein Structures from the Protein Data Base Helix helix packing Packing of Secondary
Lecture 2. Excitability and ionic transport
 Lecture 2 Excitability and ionic transport Selective membrane permeability: The lipid barrier of the cell membrane and cell membrane transport proteins Chemical compositions of extracellular and intracellular
Lecture 2 Excitability and ionic transport Selective membrane permeability: The lipid barrier of the cell membrane and cell membrane transport proteins Chemical compositions of extracellular and intracellular
Basics of protein structure
 Today: 1. Projects a. Requirements: i. Critical review of one paper ii. At least one computational result b. Noon, Dec. 3 rd written report and oral presentation are due; submit via email to bphys101@fas.harvard.edu
Today: 1. Projects a. Requirements: i. Critical review of one paper ii. At least one computational result b. Noon, Dec. 3 rd written report and oral presentation are due; submit via email to bphys101@fas.harvard.edu
Energetics of Ion Permeation in an Open-Activated TRPV1 Channel
 Biophysical Journal, Volume 111 Supplemental Information Energetics of Ion Permeation in an Open-Activated TRPV1 Channel Christian Jorgensen, Simone Furini, and Carmen Domene Supporting Material Energetics
Biophysical Journal, Volume 111 Supplemental Information Energetics of Ion Permeation in an Open-Activated TRPV1 Channel Christian Jorgensen, Simone Furini, and Carmen Domene Supporting Material Energetics
Neuroscience 201A Exam Key, October 7, 2014
 Neuroscience 201A Exam Key, October 7, 2014 Question #1 7.5 pts Consider a spherical neuron with a diameter of 20 µm and a resting potential of -70 mv. If the net negativity on the inside of the cell (all
Neuroscience 201A Exam Key, October 7, 2014 Question #1 7.5 pts Consider a spherical neuron with a diameter of 20 µm and a resting potential of -70 mv. If the net negativity on the inside of the cell (all
Biochemistry,530:,, Introduc5on,to,Structural,Biology, Autumn,Quarter,2015,
 Biochemistry,530:,, Introduc5on,to,Structural,Biology, Autumn,Quarter,2015, Course,Informa5on, BIOC%530% GraduateAlevel,discussion,of,the,structure,,func5on,,and,chemistry,of,proteins,and, nucleic,acids,,control,of,enzyma5c,reac5ons.,please,see,the,course,syllabus,and,
Biochemistry,530:,, Introduc5on,to,Structural,Biology, Autumn,Quarter,2015, Course,Informa5on, BIOC%530% GraduateAlevel,discussion,of,the,structure,,func5on,,and,chemistry,of,proteins,and, nucleic,acids,,control,of,enzyma5c,reac5ons.,please,see,the,course,syllabus,and,
Transporters and Membrane Motors Nov 15, 2007
 BtuB OM vitamin B12 transporter F O F 1 ATP synthase Human multiple drug resistance transporter P-glycoprotein Transporters and Membrane Motors Nov 15, 2007 Transport and membrane motors Concentrations
BtuB OM vitamin B12 transporter F O F 1 ATP synthase Human multiple drug resistance transporter P-glycoprotein Transporters and Membrane Motors Nov 15, 2007 Transport and membrane motors Concentrations
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 www.nature.com/nature 1 Figure S1 Sequence alignment. a Structure based alignment of the plgic of E. chrysanthemi (ELIC), the acetylcholine binding protein from the snail Lymnea stagnalis (AchBP, PDB code
www.nature.com/nature 1 Figure S1 Sequence alignment. a Structure based alignment of the plgic of E. chrysanthemi (ELIC), the acetylcholine binding protein from the snail Lymnea stagnalis (AchBP, PDB code
LESSON 2.2 WORKBOOK How do our axons transmit electrical signals?
 LESSON 2.2 WORKBOOK How do our axons transmit electrical signals? This lesson introduces you to the action potential, which is the process by which axons signal electrically. In this lesson you will learn
LESSON 2.2 WORKBOOK How do our axons transmit electrical signals? This lesson introduces you to the action potential, which is the process by which axons signal electrically. In this lesson you will learn
LUMINESCENCE RESONANCE ENERGY TRANSFER STUDIES OF THE SHAKER K + VOLTAGE-GATED ION CHANNEL DAVID JOHN POSSON DISSERTATION
 LUMINESCENCE RESONANCE ENERGY TRANSFER STUDIES OF THE SHAKER K + VOLTAGE-GATED ION CHANNEL BY DAVID JOHN POSSON B.S., University of Cincinnati, 1997 DISSERTATION Submitted in partial fulfillment of the
LUMINESCENCE RESONANCE ENERGY TRANSFER STUDIES OF THE SHAKER K + VOLTAGE-GATED ION CHANNEL BY DAVID JOHN POSSON B.S., University of Cincinnati, 1997 DISSERTATION Submitted in partial fulfillment of the
Universality of sensory-response systems
 excite.org(anism): Electrical Signaling Universality of sensory-response systems Three step process: sensation-integration-response Bacterial chemotaxis Madigan et al. Fig. 8.24 Rick Stewart (CBMG) Human
excite.org(anism): Electrical Signaling Universality of sensory-response systems Three step process: sensation-integration-response Bacterial chemotaxis Madigan et al. Fig. 8.24 Rick Stewart (CBMG) Human
Introduction to Physiology II: Control of Cell Volume and Membrane Potential
 Introduction to Physiology II: Control of Cell Volume and Membrane Potential J. P. Keener Mathematics Department Math Physiology p.1/23 Basic Problem The cell is full of stuff: Proteins, ions, fats, etc.
Introduction to Physiology II: Control of Cell Volume and Membrane Potential J. P. Keener Mathematics Department Math Physiology p.1/23 Basic Problem The cell is full of stuff: Proteins, ions, fats, etc.
Quantitative Electrophysiology
 ECE 795: Quantitative Electrophysiology Notes for Lecture #1 Wednesday, September 13, 2006 1. INTRODUCTION TO EXCITABLE CELLS Historical perspective: Bioelectricity first discovered by Luigi Galvani in
ECE 795: Quantitative Electrophysiology Notes for Lecture #1 Wednesday, September 13, 2006 1. INTRODUCTION TO EXCITABLE CELLS Historical perspective: Bioelectricity first discovered by Luigi Galvani in
Lecture 3 13/11/2018
 Lecture 3 13/11/2018 1 Plasma membrane ALL cells have a cell membrane made of proteins and lipids. protein channel Cell Membrane Layer 1 Layer 2 lipid bilayer protein pump Lipid bilayer allows water, carbon
Lecture 3 13/11/2018 1 Plasma membrane ALL cells have a cell membrane made of proteins and lipids. protein channel Cell Membrane Layer 1 Layer 2 lipid bilayer protein pump Lipid bilayer allows water, carbon
Transmembrane Domains (TMDs) of ABC transporters
 Transmembrane Domains (TMDs) of ABC transporters Most ABC transporters contain heterodimeric TMDs (e.g. HisMQ, MalFG) TMDs show only limited sequence homology (high diversity) High degree of conservation
Transmembrane Domains (TMDs) of ABC transporters Most ABC transporters contain heterodimeric TMDs (e.g. HisMQ, MalFG) TMDs show only limited sequence homology (high diversity) High degree of conservation
Central Dogma. modifications genome transcriptome proteome
 entral Dogma DA ma protein post-translational modifications genome transcriptome proteome 83 ierarchy of Protein Structure 20 Amino Acids There are 20 n possible sequences for a protein of n residues!
entral Dogma DA ma protein post-translational modifications genome transcriptome proteome 83 ierarchy of Protein Structure 20 Amino Acids There are 20 n possible sequences for a protein of n residues!
Supratim Ray
 Supratim Ray sray@cns.iisc.ernet.in Biophysics of Action Potentials Passive Properties neuron as an electrical circuit Passive Signaling cable theory Active properties generation of action potential Techniques
Supratim Ray sray@cns.iisc.ernet.in Biophysics of Action Potentials Passive Properties neuron as an electrical circuit Passive Signaling cable theory Active properties generation of action potential Techniques
The Membrane Potential
 The Membrane Potential Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.aw.com/bc) ** It is suggested that you carefully label each ion
The Membrane Potential Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.aw.com/bc) ** It is suggested that you carefully label each ion
Membrane Potentials, Action Potentials, and Synaptic Transmission. Membrane Potential
 Cl Cl - - + K + K+ K + K Cl - 2/2/15 Membrane Potentials, Action Potentials, and Synaptic Transmission Core Curriculum II Spring 2015 Membrane Potential Example 1: K +, Cl - equally permeant no charge
Cl Cl - - + K + K+ K + K Cl - 2/2/15 Membrane Potentials, Action Potentials, and Synaptic Transmission Core Curriculum II Spring 2015 Membrane Potential Example 1: K +, Cl - equally permeant no charge
Roderick MacKinnon: Okay. Thank you very much. It's a real pleasure to be here to tell you about potassium channels.
 COLUMBIA columbia university DIGITAL KNOWLEDGE VENTURES Brain and Mind May 13, 2004 Roderick MacKinnon, MD Potassium Channels Introduction by Gerald Fischbach Gerald Fischbach: I would like to move on
COLUMBIA columbia university DIGITAL KNOWLEDGE VENTURES Brain and Mind May 13, 2004 Roderick MacKinnon, MD Potassium Channels Introduction by Gerald Fischbach Gerald Fischbach: I would like to move on
β1 Structure Prediction and Validation
 13 Chapter 2 β1 Structure Prediction and Validation 2.1 Overview Over several years, GPCR prediction methods in the Goddard lab have evolved to keep pace with the changing field of GPCR structure. Despite
13 Chapter 2 β1 Structure Prediction and Validation 2.1 Overview Over several years, GPCR prediction methods in the Goddard lab have evolved to keep pace with the changing field of GPCR structure. Despite
Neurophysiology. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 Neurophysiology Danil Hammoudi.MD ACTION POTENTIAL An action potential is a wave of electrical discharge that travels along the membrane of a cell. Action potentials are an essential feature of animal
Neurophysiology Danil Hammoudi.MD ACTION POTENTIAL An action potential is a wave of electrical discharge that travels along the membrane of a cell. Action potentials are an essential feature of animal
Supporting Material for. Microscopic origin of gating current fluctuations in a potassium channel voltage sensor
 Supporting Material for Microscopic origin of gating current fluctuations in a potassium channel voltage sensor J. Alfredo Freites, * Eric V. Schow, * Stephen H. White, and Douglas J. Tobias * * Department
Supporting Material for Microscopic origin of gating current fluctuations in a potassium channel voltage sensor J. Alfredo Freites, * Eric V. Schow, * Stephen H. White, and Douglas J. Tobias * * Department
Model Worksheet Teacher Key
 Introduction Despite the complexity of life on Earth, the most important large molecules found in all living things (biomolecules) can be classified into only four main categories: carbohydrates, lipids,
Introduction Despite the complexity of life on Earth, the most important large molecules found in all living things (biomolecules) can be classified into only four main categories: carbohydrates, lipids,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1737 Supplementary Table 1 variant Description FSEC - 2B12 a FSEC - 6A1 a K d (leucine) c Leucine uptake e K (wild-type like) K (Y18F) K (TS) K (TSY) K288A mutant, lipid facing side chain
doi:1.138/nature1737 Supplementary Table 1 variant Description FSEC - 2B12 a FSEC - 6A1 a K d (leucine) c Leucine uptake e K (wild-type like) K (Y18F) K (TS) K (TSY) K288A mutant, lipid facing side chain
Protein Folding & Stability. Lecture 11: Margaret A. Daugherty. Fall How do we go from an unfolded polypeptide chain to a
 Lecture 11: Protein Folding & Stability Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 How do we go from an unfolded polypeptide chain to a compact folded protein? (Folding of thioredoxin, F. Richards) Structure - Function
Lecture 11: Protein Folding & Stability Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 How do we go from an unfolded polypeptide chain to a compact folded protein? (Folding of thioredoxin, F. Richards) Structure - Function
Chapter 2: Neurons and Glia
 Chapter 2: Neurons and Glia The Prototypical Neuron The Soma Cytosol: watery fluid inside the cell Organelles: membrane-enclosed structures within the soma Cytoplasm: contents within a cell membrane, e.g.,
Chapter 2: Neurons and Glia The Prototypical Neuron The Soma Cytosol: watery fluid inside the cell Organelles: membrane-enclosed structures within the soma Cytoplasm: contents within a cell membrane, e.g.,
Membranes 2: Transportation
 Membranes 2: Transportation Steven E. Massey, Ph.D. Associate Professor Bioinformatics Department of Biology University of Puerto Rico Río Piedras Office & Lab: NCN#343B Tel: 787-764-0000 ext. 7798 E-mail:
Membranes 2: Transportation Steven E. Massey, Ph.D. Associate Professor Bioinformatics Department of Biology University of Puerto Rico Río Piedras Office & Lab: NCN#343B Tel: 787-764-0000 ext. 7798 E-mail:
Insights from Modeling Three-Dimensional Structures of the Human Potassium and Sodium Channels
 Insights from Modeling Three-Dimensional Structures of the Human Potassium and Sodium Channels Kuo-Chen Chou* Life Science Research Center, Shanghai Jiaotong University, Shanghai 200030, China, Tianjin
Insights from Modeling Three-Dimensional Structures of the Human Potassium and Sodium Channels Kuo-Chen Chou* Life Science Research Center, Shanghai Jiaotong University, Shanghai 200030, China, Tianjin
Review. Membrane proteins. Membrane transport
 Quiz 1 For problem set 11 Q1, you need the equation for the average lateral distance transversed (s) of a molecule in the membrane with respect to the diffusion constant (D) and time (t). s = (4 D t) 1/2
Quiz 1 For problem set 11 Q1, you need the equation for the average lateral distance transversed (s) of a molecule in the membrane with respect to the diffusion constant (D) and time (t). s = (4 D t) 1/2
CAP 5510 Lecture 3 Protein Structures
 CAP 5510 Lecture 3 Protein Structures Su-Shing Chen Bioinformatics CISE 8/19/2005 Su-Shing Chen, CISE 1 Protein Conformation 8/19/2005 Su-Shing Chen, CISE 2 Protein Conformational Structures Hydrophobicity
CAP 5510 Lecture 3 Protein Structures Su-Shing Chen Bioinformatics CISE 8/19/2005 Su-Shing Chen, CISE 1 Protein Conformation 8/19/2005 Su-Shing Chen, CISE 2 Protein Conformational Structures Hydrophobicity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11085 Supplementary Tables: Supplementary Table 1. Summary of crystallographic and structure refinement data Structure BRIL-NOP receptor Data collection Number of crystals 23 Space group
doi:10.1038/nature11085 Supplementary Tables: Supplementary Table 1. Summary of crystallographic and structure refinement data Structure BRIL-NOP receptor Data collection Number of crystals 23 Space group
Molecular Dynamics Investigation of the ω-current in the Kv1.2 Voltage Sensor Domains
 Molecular Dynamics Investigation of the ω-current in the Kv1.2 Voltage Sensor Domains Fatemeh Khalili-Araghi, Emad Tajkhorshid, Benoît Roux, and Klaus Schulten Department of Physics, Department of Biochemistry,
Molecular Dynamics Investigation of the ω-current in the Kv1.2 Voltage Sensor Domains Fatemeh Khalili-Araghi, Emad Tajkhorshid, Benoît Roux, and Klaus Schulten Department of Physics, Department of Biochemistry,
Ion channels. Part I Channel structure and gating
 Ion channels 7, 10, 12, & 14 Feb 14 Part I Channel structure and gating Dan Minor, Ph.D. Cardiovascular Research Institute University of California, San Francisco daniel.minor@ucsf.edu Ion Channels - Structures
Ion channels 7, 10, 12, & 14 Feb 14 Part I Channel structure and gating Dan Minor, Ph.D. Cardiovascular Research Institute University of California, San Francisco daniel.minor@ucsf.edu Ion Channels - Structures
The Membrane Potential
 The Membrane Potential Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) ** It is suggested that you carefully label each ion channel
The Membrane Potential Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) ** It is suggested that you carefully label each ion channel
4 Proteins: Structure, Function, Folding W. H. Freeman and Company
 4 Proteins: Structure, Function, Folding 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company CHAPTER 4 Proteins: Structure, Function, Folding Learning goals: Structure and properties of the peptide bond Structural hierarchy
4 Proteins: Structure, Function, Folding 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company CHAPTER 4 Proteins: Structure, Function, Folding Learning goals: Structure and properties of the peptide bond Structural hierarchy
Major Types of Association of Proteins with Cell Membranes. From Alberts et al
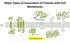 Major Types of Association of Proteins with Cell Membranes From Alberts et al Proteins Are Polymers of Amino Acids Peptide Bond Formation Amino Acid central carbon atom to which are attached amino group
Major Types of Association of Proteins with Cell Membranes From Alberts et al Proteins Are Polymers of Amino Acids Peptide Bond Formation Amino Acid central carbon atom to which are attached amino group
Electrostatic basis of valence selectivity in cationic channels
 Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1711 (25) 72 86 http://www.elsevier.com/locate/bba Electrostatic basis of valence selectivity in cationic channels Ben Corry a, T, Taira Vora b, Shin-Ho Chung b a Chemistry,
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1711 (25) 72 86 http://www.elsevier.com/locate/bba Electrostatic basis of valence selectivity in cationic channels Ben Corry a, T, Taira Vora b, Shin-Ho Chung b a Chemistry,
7.012 Problem Set 1 Solutions
 ame TA Section 7.012 Problem Set 1 Solutions Your answers to this problem set must be inserted into the large wooden box on wheels outside 68120 by 4:30 PM, Thursday, September 15. Problem sets will not
ame TA Section 7.012 Problem Set 1 Solutions Your answers to this problem set must be inserted into the large wooden box on wheels outside 68120 by 4:30 PM, Thursday, September 15. Problem sets will not
Voltage-clamp and Hodgkin-Huxley models
 Voltage-clamp and Hodgkin-Huxley models Read: Hille, Chapters 2-5 (best Koch, Chapters 6, 8, 9 See also Hodgkin and Huxley, J. Physiol. 117:500-544 (1952. (the source Clay, J. Neurophysiol. 80:903-913
Voltage-clamp and Hodgkin-Huxley models Read: Hille, Chapters 2-5 (best Koch, Chapters 6, 8, 9 See also Hodgkin and Huxley, J. Physiol. 117:500-544 (1952. (the source Clay, J. Neurophysiol. 80:903-913
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 9 - TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com K + K + K + K + CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: PRINCIPLES OF TRANSMEMBRANE TRANSPORT Membranes and Gradients Cells must be able to communicate across their membrane barriers to materials
!! www.clutchprep.com K + K + K + K + CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: PRINCIPLES OF TRANSMEMBRANE TRANSPORT Membranes and Gradients Cells must be able to communicate across their membrane barriers to materials
Nonselective Conduction in a Mutated NaK Channel with Three Cation-Binding Sites
 2106 Biophysical Journal Volume 103 November 2012 2106 2114 Nonselective Conduction in a Mutated NaK Channel with Three Cation-Binding Sites Simone Furini and Carmen Domene * Department of Medical Surgery
2106 Biophysical Journal Volume 103 November 2012 2106 2114 Nonselective Conduction in a Mutated NaK Channel with Three Cation-Binding Sites Simone Furini and Carmen Domene * Department of Medical Surgery
Membrane Proteins: 1. Integral proteins: 2. Peripheral proteins: 3. Amphitropic proteins:
 Membrane Proteins: 1. Integral proteins: proteins that insert into/span the membrane bilayer; or covalently linked to membrane lipids. (Interact with the hydrophobic part of the membrane) 2. Peripheral
Membrane Proteins: 1. Integral proteins: proteins that insert into/span the membrane bilayer; or covalently linked to membrane lipids. (Interact with the hydrophobic part of the membrane) 2. Peripheral
Membrane Protein Pumps
 Membrane Protein Pumps Learning objectives You should be able to understand & discuss: Active transport-na + /K + ATPase ABC transporters Metabolite transport by lactose permease 1. Ion pumps: ATP-driven
Membrane Protein Pumps Learning objectives You should be able to understand & discuss: Active transport-na + /K + ATPase ABC transporters Metabolite transport by lactose permease 1. Ion pumps: ATP-driven
Biophysics 490M Project
 Biophysics 490M Project Dan Han Department of Biochemistry Structure Exploration of aa 3 -type Cytochrome c Oxidase from Rhodobacter sphaeroides I. Introduction: All organisms need energy to live. They
Biophysics 490M Project Dan Han Department of Biochemistry Structure Exploration of aa 3 -type Cytochrome c Oxidase from Rhodobacter sphaeroides I. Introduction: All organisms need energy to live. They
3.3 Simulating action potentials
 6 THE HODGKIN HUXLEY MODEL OF THE ACTION POTENTIAL Fig. 3.1 Voltage dependence of rate coefficients and limiting values and time constants for the Hodgkin Huxley gating variables. (a) Graphs of forward
6 THE HODGKIN HUXLEY MODEL OF THE ACTION POTENTIAL Fig. 3.1 Voltage dependence of rate coefficients and limiting values and time constants for the Hodgkin Huxley gating variables. (a) Graphs of forward
Supplemental Information for: Characterizing the Membrane-Bound State of Cytochrome P450 3A4: Structure, Depth of Insertion and Orientation
 Supplemental Information for: Characterizing the Membrane-Bound State of Cytochrome P450 3A4: Structure, Depth of Insertion and Orientation Javier L. Baylon, Ivan L. Lenov, Stephen G. Sligar and Emad Tajkhorshid
Supplemental Information for: Characterizing the Membrane-Bound State of Cytochrome P450 3A4: Structure, Depth of Insertion and Orientation Javier L. Baylon, Ivan L. Lenov, Stephen G. Sligar and Emad Tajkhorshid
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure S1. Pulses >3mJ reduce membrane resistance in HEK cells. Reversal potentials in a representative cell for IR-induced currents with laser pulses of 0.74 to
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure S1. Pulses >3mJ reduce membrane resistance in HEK cells. Reversal potentials in a representative cell for IR-induced currents with laser pulses of 0.74 to
Patrick: An Introduction to Medicinal Chemistry 5e Chapter 04
 01) Which of the following statements is not true about receptors? a. Most receptors are proteins situated inside the cell. b. Receptors contain a hollow or cleft on their surface which is known as a binding
01) Which of the following statements is not true about receptors? a. Most receptors are proteins situated inside the cell. b. Receptors contain a hollow or cleft on their surface which is known as a binding
Ion Channels. 6 th December, Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology
 Ion Channels 6 th December, 2016 Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Introduction The ion channels of nerve cells are optimally
Ion Channels 6 th December, 2016 Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Introduction The ion channels of nerve cells are optimally
Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain
 Slide 1 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain Chapter 3: The Neuronal Membrane at Rest Slide 2 Introduction Action potential in the nervous system Action potential vs. resting potential Slide 3 Not at rest
Slide 1 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain Chapter 3: The Neuronal Membrane at Rest Slide 2 Introduction Action potential in the nervous system Action potential vs. resting potential Slide 3 Not at rest
Experimental Techniques in Protein Structure Determination
 Experimental Techniques in Protein Structure Determination Homayoun Valafar Department of Computer Science and Engineering, USC Two Main Experimental Methods X-Ray crystallography Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Experimental Techniques in Protein Structure Determination Homayoun Valafar Department of Computer Science and Engineering, USC Two Main Experimental Methods X-Ray crystallography Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Transport of glucose across epithelial cells: a. Gluc/Na cotransport; b. Gluc transporter Alberts
 Figure 7 a. Secondary transporters make up the largest subfamily of transport proteins. TAGI 2000. Nature 408, 796 1. Na+- or H+-coupled cotransporters - Secondary active transport 2/7-02 Energy released
Figure 7 a. Secondary transporters make up the largest subfamily of transport proteins. TAGI 2000. Nature 408, 796 1. Na+- or H+-coupled cotransporters - Secondary active transport 2/7-02 Energy released
Ch/APh2 Bioenergetics Section Lecture of May 19, The thermodynamics of biological energy production.
 Ch/APh2 Bioenergetics Section Lecture of May 19, 2009 Introduction to bioenergetics. The thermodynamics of biological energy production. Kinetic aspects of bioenergetic processes. Energy transfer Electron
Ch/APh2 Bioenergetics Section Lecture of May 19, 2009 Introduction to bioenergetics. The thermodynamics of biological energy production. Kinetic aspects of bioenergetic processes. Energy transfer Electron
Biomedical Instrumentation
 ELEC ENG 4BD4: Biomedical Instrumentation Lecture 5 Bioelectricity 1. INTRODUCTION TO BIOELECTRICITY AND EXCITABLE CELLS Historical perspective: Bioelectricity first discovered by Luigi Galvani in 1780s
ELEC ENG 4BD4: Biomedical Instrumentation Lecture 5 Bioelectricity 1. INTRODUCTION TO BIOELECTRICITY AND EXCITABLE CELLS Historical perspective: Bioelectricity first discovered by Luigi Galvani in 1780s
Perspective Coupled Movements in Voltage-gated Ion Channels
 Perspective Coupled Movements in Voltage-gated Ion Channels Richard Horn Department of Physiology, Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, PA 19107 Ion channels, like most other proteins, are designed
Perspective Coupled Movements in Voltage-gated Ion Channels Richard Horn Department of Physiology, Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, PA 19107 Ion channels, like most other proteins, are designed
Voltage-clamp and Hodgkin-Huxley models
 Voltage-clamp and Hodgkin-Huxley models Read: Hille, Chapters 2-5 (best) Koch, Chapters 6, 8, 9 See also Clay, J. Neurophysiol. 80:903-913 (1998) (for a recent version of the HH squid axon model) Rothman
Voltage-clamp and Hodgkin-Huxley models Read: Hille, Chapters 2-5 (best) Koch, Chapters 6, 8, 9 See also Clay, J. Neurophysiol. 80:903-913 (1998) (for a recent version of the HH squid axon model) Rothman
Biochemistry Prof. S. DasGupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur. Lecture - 06 Protein Structure IV
 Biochemistry Prof. S. DasGupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Lecture - 06 Protein Structure IV We complete our discussion on Protein Structures today. And just to recap
Biochemistry Prof. S. DasGupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Lecture - 06 Protein Structure IV We complete our discussion on Protein Structures today. And just to recap
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature17991 Supplementary Discussion Structural comparison with E. coli EmrE The DMT superfamily includes a wide variety of transporters with 4-10 TM segments 1. Since the subfamilies of the
doi:10.1038/nature17991 Supplementary Discussion Structural comparison with E. coli EmrE The DMT superfamily includes a wide variety of transporters with 4-10 TM segments 1. Since the subfamilies of the
4. The Michaelis-Menten combined rate constant Km, is defined for the following kinetic mechanism as k 1 k 2 E + S ES E + P k -1
 Fall 2000 CH 595C Exam 1 Answer Key Multiple Choice 1. One of the reasons that enzymes are such efficient catalysts is that a) the energy level of the enzyme-transition state complex is much higher than
Fall 2000 CH 595C Exam 1 Answer Key Multiple Choice 1. One of the reasons that enzymes are such efficient catalysts is that a) the energy level of the enzyme-transition state complex is much higher than
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE. Lecture 9. Biology Department Concordia University. Dr. S. Azam BIOL 266/
 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE Lecture 9 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University RED BLOOD CELL MEMBRANE PROTEINS The Dynamic Nature of the Plasma Membrane SEM of human erythrocytes
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE Lecture 9 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University RED BLOOD CELL MEMBRANE PROTEINS The Dynamic Nature of the Plasma Membrane SEM of human erythrocytes
Neurons and the membrane potential. N500 John Beggs 23 Aug, 2016
 Neurons and the membrane potential N500 John Beggs 23 Aug, 2016 My background, briefly Neurons Structural elements of a typical neuron Figure 1.2 Some nerve cell morphologies found in the human
Neurons and the membrane potential N500 John Beggs 23 Aug, 2016 My background, briefly Neurons Structural elements of a typical neuron Figure 1.2 Some nerve cell morphologies found in the human
Closing In on the Resting State of the Shaker K + Channel
 Article Closing In on the Resting State of the Shaker K + Channel Medha M. Pathak, 1,8,9 Vladimir Yarov-Yarovoy, 4,8 Gautam Agarwal, 2 Benoît Roux, 6 Patrick Barth, 5 Susy Kohout, 3 Francesco Tombola,
Article Closing In on the Resting State of the Shaker K + Channel Medha M. Pathak, 1,8,9 Vladimir Yarov-Yarovoy, 4,8 Gautam Agarwal, 2 Benoît Roux, 6 Patrick Barth, 5 Susy Kohout, 3 Francesco Tombola,
Membrane proteins Porins: FadL. Oriol Solà, Dimitri Ivancic, Daniel Folch, Marc Olivella
 Membrane proteins Porins: FadL Oriol Solà, Dimitri Ivancic, Daniel Folch, Marc Olivella INDEX 1. INTRODUCTION TO MEMBRANE PROTEINS 2. FADL: OUTER MEMBRANE TRANSPORT PROTEIN 3. MAIN FEATURES OF FADL STRUCTURE
Membrane proteins Porins: FadL Oriol Solà, Dimitri Ivancic, Daniel Folch, Marc Olivella INDEX 1. INTRODUCTION TO MEMBRANE PROTEINS 2. FADL: OUTER MEMBRANE TRANSPORT PROTEIN 3. MAIN FEATURES OF FADL STRUCTURE
K versus Na Ions in a K Channel Selectivity Filter: A Simulation Study
 Biophysical Journal Volume 83 August 2002 633 645 633 K versus Na Ions in a K Channel Selectivity Filter: A Simulation Study Indira H. Shrivastava, D. Peter Tieleman, Philip C. Biggin, and Mark S. P. Sansom
Biophysical Journal Volume 83 August 2002 633 645 633 K versus Na Ions in a K Channel Selectivity Filter: A Simulation Study Indira H. Shrivastava, D. Peter Tieleman, Philip C. Biggin, and Mark S. P. Sansom
