Supplemental Information: Govindaraghavan, Lad and Osmani
|
|
|
- Marylou Gibbs
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplemental Information: Govindaraghavan, Lad and Osmani Table S1: List of strains used in this study Strain Name Genotype (all strains also carry vea1) Source MG190 nima7; pyrg89; argb2; ndc80-cr::pyroa AF (pyroa4?); MG183 X CDS719 tuba-gfp; chaa1; GCP3-GFP::riboB AF (riboa1?) MG300 tuba-gfp; An-H1-chRFP::pyroA AF ; pyrg89; argb2; MG210 X HA365 nira14?; nica2? nicb8? MG298 nima7; H1-chRFP::pyroA AF (pyroa4); argb2; GFP-tub; MG210 X HA365 pyrg89; nira14?; nica2? nicb8?; wa2 or wa3 MG224 argb2; pyrg89; se15; GFP-tub; CR-AN162; pyroa4; MG199 X MC39 nica2? nicb8?; nira14? MG227 nima7; argb2; se15; GFP-tub; CR-AN162; pyroa4; MG199 X MC39 pyrg89; nica2? nicb8?; nira14?; wa2 or wa3 MG228 nima7; argb2; se15; GFP-tub; CR-AN162; pyroa4; MG199 X MC39 pyrg89; nica2? nicb8?; nira14?; wa2 or wa3 MG294 nima7; argb2; AN162-GFP; fib-cr::pyrg AF (pyrg89); MG198 X SO1064 se15?; nira14?, wa3 MG296 argb2; AN162-GFP; fib-cr::pyrg AF (pyrg89); se15?; MG198 X SO1064 nira14?; wa3 MG321 nima7; GFP-tub; nup49-chrfp::pyroa AF (pyroa4?); MG199 X CDS838 argb2; pyrg89; nira14?; se15?; nica2? nicb8?; wa3 MG378 nima7; GFP-tub; HP1-chRFP::pyroA AF (pyroa4); argb2; MG199 X KF28 pyrg89; nica2? nicb8?; se15?; nira14?; wa3 MG273 argb2; pyrg89; ya::nls-dsred; GFP-tub; pyroa4; MG199 X AY02 nica2? nicb8? MG229 nima7; argb2; pyrg89; ya::nls-dsred; GFP-tub; MG199 X AY02 pyroa4; nica2? nicb8? R153 pyroa4; wa3 (1) MG313 nima7; An-mad2::pyrG AF (pyrg89); pyroa4; GFP-tub; MG229 X CDS611 ya::nls-dsred; nica2? nicb8?; ya2 MG310 nima1; argb2; pyroa4; pyrg89; GFP-tub; ya::nls- MG273 X SO338 DsRed; nica2? nicb8?; fwa1/wa2 MG308 nima5; GFP-tub; ya::nls-dsred; pyroa4; pyrg89; wa2 MG273 X CDS616 or wa3 MG381 nima7; An-mad2::pyrG AF (pyrg89); pyroa4; nira14?; MG277 X CDS629 nica2? nicb8?; chaa1 CDS790 nima7; argb2; wa3 SO114 x CDS735 CDS629 md2a::pyrg (pyrg89); pyroa4; chaa1 CDS565 x CDS459 (2) Note: Question marks (?) refer to nutritional markers mutations that have not been tested for, but may be present in the strain. 1. Osmani AH, McGuire SL, O'Donnell KL, Pu RT, Osmani SA Role of the cellcycle-regulated NIMA protein kinase during G2 and mitosis: evidence for two pathways of mitotic regulation. Cold Spring Harbor symposia on quantitative biology 56: De Souza CP, Hashmi SB, Nayak T, Oakley B, Osmani SA Mlp1 acts as a mitotic scaffold to spatially regulate spindle assembly checkpoint proteins in Aspergillus nidulans. Molecular biology of the cell 20:
2 Fig S1: Normal nucleolar segregation and nuclear envelope dynamics during Wt (strain MG296) mitosis at 35 C. The nuclear envelope marked by GFP-AN162 exhibits a double restriction generating three membrane bound compartments at 4. The nucleolar protein, fibrillarin-cr, is seen to locate within the middle compartment, and undergoes disassembly and reassembly to generate two daughter nucleoli. 2
3 Fig S2: Cells with reduced NIMA function show a prolonged mitosis. (A) Quantitation of the average time spent in mitosis measured by spindle formation in Wt (n=13) and nima7 (n=21) cells at 35 C. Strains: Wt MG224, nima7 MG190, MG227, and MG229. (B) Box plot showing the distribution of time in mitosis for Wt and nima7 cells. The bottom and top of the box represent the 25th and 75th percentile and the band near the middle of the box is the 50th percentile (or the median). (C) The mitotic delay in cells with partial NIMA function is independent of the nima allele used. The quantitation of time in mitosis for Wt (n=15) and three different temperature sensitive alleles of nima nima7 (n=19), nima5 (n=12) and nima1 (n=31), at their respective semi-permissive temperatures, as indicated. Strains: Wt MG224, nima1 MG310, nima5 MG308, nima7 MG229. 3
4 Fig S3: Apparently successful first mitosis in nima7 cells (A) may be followed by a defective second mitosis (B) (71%, n=7). The same cell going through two rounds of mitosis is shown. Nuclear transport is marked by NLS-DsRed and spindle formation by GFP-Tub (strain MG229). In (A), mitosis is apparently successful with two daughter nuclei formed. In (B), both nuclei attempt the second mitoses and start to form mitotic spindles. However, the spindle in the nucleus to the left (n1) fails to elongate and this nucleus does not release its NLS-DsRed. The nucleus to the right (n2) completes mitosis after spindle formation and NLS-DsRed release but generates two nuclei of unequal size with the arrowhead indicating the micronucleus formed. Bars, 5μm. 4
5 Fig S4: Mitotic arrest in nima7 cells in the absence of spindles (A) A box and whiskers plot showing the variability in the time interval between the entry of GFP-tub into the nucleus and the dispersal of NLS-DsRed in nima7 (n=41) cells at 35 C as compared to Wt cells (n=25). The difference in time interval between nuclear entry of GFP-Tub and the release of NLS-DsRed between Wt and nima7 cells is highly significant (p value is 0.00 by unpaired t test). (B) A box and whiskers plot showing the length of SAC mediated mitotic arrest in the absence of spindles as represented by the time interval between the entry of GFP-tub into the nucleus and the reimport of NLS-DsRed at mitotic exit for Wt (n=25) cells and nima7 (n=41) cells at the semi-permissive temperature. The difference in mitotic arrest time between Wt and nima7 is not significant; p value > 0.01 using unpaired t-test. For (A) and (B), the bottom and top of the box represent the 25th and 75th percentile and the band near the middle of the box is the 50th percentile (or the median). 5
6 Supplementary Movie Information Movie S1: The configuration of the nuclear envelope and nucleolus in cells with partial NIMA function. The movie shows two nuclei, one of which (on the right in frame 1) has a distinct protrusion of the nucleus visualized by the nuclear envelope marked in green with GFP-AN0162 and the nucleolus in red with fibrillarin-cr. This rotation was generated from a movie with 8 Z sections that are 0.8 µm apart and 10 times points that are 1 min apart. Each time point is rotated through 360 in 10 degree increments. 6
Table S1. Aspergillus nidulans strains used in this study Strain Genotype Derivation
 Supplemental Material De Souza et al., 211 Table S1. Aspergillus nidulans strains used in this study Strain Genotype Derivation CDS295 pyrg89; pyroa4; pyrg Af ::son promotor::gfp-son nup98/nup96 ; chaa1
Supplemental Material De Souza et al., 211 Table S1. Aspergillus nidulans strains used in this study Strain Genotype Derivation CDS295 pyrg89; pyroa4; pyrg Af ::son promotor::gfp-son nup98/nup96 ; chaa1
Copy Number Suppressors of the Aspergillus nidulans nima1 Mitotic Kinase Display Distinctive and Highly Dynamic Cell Cycle-Regulated Locations
 EUKARYOTIC CELL, Dec. 2008, p. 2087 2099 Vol. 7, No. 12 1535-9778/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/ec.00278-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Copy Number Suppressors of
EUKARYOTIC CELL, Dec. 2008, p. 2087 2099 Vol. 7, No. 12 1535-9778/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/ec.00278-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Copy Number Suppressors of
A redundant function for the N-terminal tail of Ndc80 in kinetochore-microtubule interaction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
 Genetics: Published Articles Ahead of Print, published on July 30, 2012 as 10.1534/genetics.112.143818 A redundant function for the N-terminal tail of Ndc80 in kinetochore-microtubule interaction in Saccharomyces
Genetics: Published Articles Ahead of Print, published on July 30, 2012 as 10.1534/genetics.112.143818 A redundant function for the N-terminal tail of Ndc80 in kinetochore-microtubule interaction in Saccharomyces
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005
 7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
Supporting Information
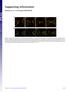 Supporting Information Fleissner et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907039106 Fig. S1. (A) MAK-2-GFP localized to CATs tips is not bound by membrane. his-3::pccg1 mak-2-gfp; mak-2 strain labeled with membrane dye FM4
Supporting Information Fleissner et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907039106 Fig. S1. (A) MAK-2-GFP localized to CATs tips is not bound by membrane. his-3::pccg1 mak-2-gfp; mak-2 strain labeled with membrane dye FM4
In eukaryotes, chromosomes are
 Extra View Nucleus 4:4, 261 266; July/August 2013; 2013 Landes Bioscience Extra View The dynamic nature of the nuclear envelope Lessons from closed mitosis James T Arnone, Alison D Walters and Orna Cohen-Fix*
Extra View Nucleus 4:4, 261 266; July/August 2013; 2013 Landes Bioscience Extra View The dynamic nature of the nuclear envelope Lessons from closed mitosis James T Arnone, Alison D Walters and Orna Cohen-Fix*
Potential Link between the NIMA Mitotic Kinase and Nuclear Membrane Fission during Mitotic Exit in Aspergillus nidulans
 EUKARYOTIC CELL, Dec. 2004, p. 1433 1444 Vol. 3, No. 6 1535-9778/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/EC.3.6.1433 1444.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Potential Link between
EUKARYOTIC CELL, Dec. 2004, p. 1433 1444 Vol. 3, No. 6 1535-9778/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/EC.3.6.1433 1444.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Potential Link between
-Tubulin Plays an Essential Role in the Coordination of Mitotic Events V
 Molecular Biology of the Cell Vol. 15, 1374 1386, March 2004 -Tubulin Plays an Essential Role in the Coordination of Mitotic Events V Natalie L. Prigozhina, C. Elizabeth Oakley, Amanda M. Lewis, Tania
Molecular Biology of the Cell Vol. 15, 1374 1386, March 2004 -Tubulin Plays an Essential Role in the Coordination of Mitotic Events V Natalie L. Prigozhina, C. Elizabeth Oakley, Amanda M. Lewis, Tania
3.a.2- Cell Cycle and Meiosis
 Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. 3.a.2- Cell Cycle and Meiosis EU 3.A: Heritable information provides for continuity of life.
Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. 3.a.2- Cell Cycle and Meiosis EU 3.A: Heritable information provides for continuity of life.
A Few Terms: When and where do you want your cells to divide?
 Today: - Lab 4 Debrief - Mitosis - Lunch -Meiosis Other: Blood Drive Today! TIME: 11:00am 1:00pm + 2:00pm 5:00pm PLACE: Baxter Events Center Thinking About Mitosis When and where do you want your cells
Today: - Lab 4 Debrief - Mitosis - Lunch -Meiosis Other: Blood Drive Today! TIME: 11:00am 1:00pm + 2:00pm 5:00pm PLACE: Baxter Events Center Thinking About Mitosis When and where do you want your cells
DURING the transition from interphase into mitosis,
 INVESTIGATION The Set1/COMPASS Histone H3 Methyltransferase Helps Regulate Mitosis With the CDK1 and NIMA Mitotic Kinases in Aspergillus nidulans Meera Govindaraghavan,*, Sarah Lea Anglin, Aysha H. Osmani,
INVESTIGATION The Set1/COMPASS Histone H3 Methyltransferase Helps Regulate Mitosis With the CDK1 and NIMA Mitotic Kinases in Aspergillus nidulans Meera Govindaraghavan,*, Sarah Lea Anglin, Aysha H. Osmani,
Three different fusions led to three basic ideas: 1) If one fuses a cell in mitosis with a cell in any other stage of the cell cycle, the chromosomes
 Section Notes The cell division cycle presents an interesting system to study because growth and division must be carefully coordinated. For many cells it is important that it reaches the correct size
Section Notes The cell division cycle presents an interesting system to study because growth and division must be carefully coordinated. For many cells it is important that it reaches the correct size
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Overexpression of YFP::GPR-1 in the germline.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Overexpression of YFP::GPR-1 in the germline. The pie-1 promoter and 3 utr were used to express yfp::gpr-1 in the germline. Expression levels from the yfp::gpr-1(cai 1.0)-expressing
Supplementary Figure 1 Overexpression of YFP::GPR-1 in the germline. The pie-1 promoter and 3 utr were used to express yfp::gpr-1 in the germline. Expression levels from the yfp::gpr-1(cai 1.0)-expressing
5.1 Cell Division and the Cell Cycle
 5.1 Cell Division and the Cell Cycle Lesson Objectives Contrast cell division in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Identify the phases of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Explain how the cell cycle is controlled.
5.1 Cell Division and the Cell Cycle Lesson Objectives Contrast cell division in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Identify the phases of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Explain how the cell cycle is controlled.
16 The Cell Cycle. Chapter Outline The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression The Events of M Phase Meiosis and Fertilization
 The Cell Cycle 16 The Cell Cycle Chapter Outline The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression The Events of M Phase Meiosis and Fertilization Introduction Self-reproduction is perhaps
The Cell Cycle 16 The Cell Cycle Chapter Outline The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression The Events of M Phase Meiosis and Fertilization Introduction Self-reproduction is perhaps
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division
 Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Read Chapter 19 pages 651-663 663 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections these are in Chapter
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Read Chapter 19 pages 651-663 663 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections these are in Chapter
Reading Assignments. A. Systems of Cell Division. Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division
 Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Death Read Chapter 19 Cell Division Read Chapter 20 pages 659-672 672 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections)
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Death Read Chapter 19 Cell Division Read Chapter 20 pages 659-672 672 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections)
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division
 Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Death Read Chapter 19 Cell Division Read Chapter 20 pages 659-672 672 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections)
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Death Read Chapter 19 Cell Division Read Chapter 20 pages 659-672 672 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature09414 Supplementary Figure 1 FACS-isolated 8c hepatocytes are highly pure. a, Gating strategy for identifying hepatocyte populations based on DNA content. b, Detection of mchry and mchr9
doi:10.1038/nature09414 Supplementary Figure 1 FACS-isolated 8c hepatocytes are highly pure. a, Gating strategy for identifying hepatocyte populations based on DNA content. b, Detection of mchry and mchr9
Name Chapter 10: Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis Mrs. Laux Take home test #7 DUE: MONDAY, NOVEMBER 16, 2009 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A bacterial chromosome consists of: A. a linear DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. B. a circular DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. C. a circular DNA
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A bacterial chromosome consists of: A. a linear DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. B. a circular DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. C. a circular DNA
Life Sciences 1a: Section 3B. The cell division cycle Objectives Understand the challenges to producing genetically identical daughter cells
 Life Sciences 1a: Section 3B. The cell division cycle Objectives Understand the challenges to producing genetically identical daughter cells Understand how a simple biochemical oscillator can drive the
Life Sciences 1a: Section 3B. The cell division cycle Objectives Understand the challenges to producing genetically identical daughter cells Understand how a simple biochemical oscillator can drive the
Chapter 6: Cell Growth and Reproduction Lesson 6.1: The Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Chapter 6: Cell Growth and Reproduction Lesson 6.1: The Cell Cycle and Mitosis No matter the type of cell, all cells come from preexisting cells through the process of cell division. The cell may be the
Chapter 6: Cell Growth and Reproduction Lesson 6.1: The Cell Cycle and Mitosis No matter the type of cell, all cells come from preexisting cells through the process of cell division. The cell may be the
AP Biology - Cell cycle / division
 AP Biology - Cell cycle / division Quiz Directions 1. During which stage does DNA replication occur? A. Prophase B. Metaphase C. Anaphase D. none of these 2. At what phase in the cell cycle does DNA replication
AP Biology - Cell cycle / division Quiz Directions 1. During which stage does DNA replication occur? A. Prophase B. Metaphase C. Anaphase D. none of these 2. At what phase in the cell cycle does DNA replication
AP Biology. Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division
 QuickTime and and a TIFF TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are are needed needed to to see see this this picture. picture. Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
QuickTime and and a TIFF TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are are needed needed to to see see this this picture. picture. Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
Key Concepts. n Cell Cycle. n Interphase. n Mitosis. n Cytokinesis
 The Cell Cycle B-2.6: Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ); the phases of mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. Key
The Cell Cycle B-2.6: Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ); the phases of mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. Key
Biology: Life on Earth
 Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 11 The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction Cellular Reproduction Intracellular activity between one cell division to the next is the cell
Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 11 The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction Cellular Reproduction Intracellular activity between one cell division to the next is the cell
ACCELERATE ITS BIOCHEMICAL PROCESSES WHICH WERE SLOWED DOWN BY MITOSIS. THE LENGTH OF THE G1 PHASE CREATES THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN FAST DIVIDING
 CHAPTER 1: OVERVIEW OF THE CELL CYCLE THE THREE STAGES OF INTERPHASE: INTERPHASE BEFORE A CELL CAN ENTER CELL DIVISION, IT NEEDS TO PREPARE ITSELF BY REPLICATING ITS GENETIC INFORMATION AND ALL OF THE
CHAPTER 1: OVERVIEW OF THE CELL CYCLE THE THREE STAGES OF INTERPHASE: INTERPHASE BEFORE A CELL CAN ENTER CELL DIVISION, IT NEEDS TO PREPARE ITSELF BY REPLICATING ITS GENETIC INFORMATION AND ALL OF THE
A Role for NIMA in the Nuclear Localization of Cyclin B in Aspergillus nidulans
 University of Kentucky UKnowledge Biology Faculty Publications Biology 6-29-1998 A Role for NIMA in the Nuclear Localization of Cyclin B in Aspergillus nidulans L. Wu Pennsylvania State University S. A.
University of Kentucky UKnowledge Biology Faculty Publications Biology 6-29-1998 A Role for NIMA in the Nuclear Localization of Cyclin B in Aspergillus nidulans L. Wu Pennsylvania State University S. A.
Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division
 LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division The larger the cell, the more trouble the cell has moving nutrients and waste across the cell membrane. LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH 1. DNA/information
LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division The larger the cell, the more trouble the cell has moving nutrients and waste across the cell membrane. LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH 1. DNA/information
Chapter 2: Chromosomes and cellular reproduction
 Chapter 2: Chromosomes and cellular reproduction I. Contrast between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. See Figure 2.1 Nucleus absent Small diameter 1 to 10 µm Genome usually 1 circular molecule Small genome;
Chapter 2: Chromosomes and cellular reproduction I. Contrast between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. See Figure 2.1 Nucleus absent Small diameter 1 to 10 µm Genome usually 1 circular molecule Small genome;
Topic 6 Cell Cycle and Mitosis. Day 1
 Topic 6 Cell Cycle and Mitosis Day 1 Bell Ringer (5 minutes) *pick up worksheet by the door* Get out your homework and answer these questions on the back page: What do I need to do to pass my real EOC?
Topic 6 Cell Cycle and Mitosis Day 1 Bell Ringer (5 minutes) *pick up worksheet by the door* Get out your homework and answer these questions on the back page: What do I need to do to pass my real EOC?
Honors Biology Test Chapter 8 Mitosis and Meiosis
 Honors Biology Test Chapter 8 Mitosis and Meiosis 1. In mitosis, if a parent cell has 16 chromosomes, each daughter cell will have how many chromosomes? a. 64 b. 32 c. 16 d. 8 e. 4 2. Chromatids that are
Honors Biology Test Chapter 8 Mitosis and Meiosis 1. In mitosis, if a parent cell has 16 chromosomes, each daughter cell will have how many chromosomes? a. 64 b. 32 c. 16 d. 8 e. 4 2. Chromatids that are
Eucaryotic Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 4 Part II Eucaryotic Cell Structure and Function The Nucleus and Cell Division! Constant feature in eukaryotic cells! Place where the cell s genetic information and its control center Nuclear Structure!
Chapter 4 Part II Eucaryotic Cell Structure and Function The Nucleus and Cell Division! Constant feature in eukaryotic cells! Place where the cell s genetic information and its control center Nuclear Structure!
2. Which of the following are NOT prokaryotes? A) eubacteria B) archaea C) viruses D) ancient bacteria
 1. Which of the following statements is FALSE? A) Errors in chromosome separation are rarely a problem for an organism. B) Errors in chromosome separation can result in a miscarriage. C) Errors in chromosome
1. Which of the following statements is FALSE? A) Errors in chromosome separation are rarely a problem for an organism. B) Errors in chromosome separation can result in a miscarriage. C) Errors in chromosome
Lecture 10: Cyclins, cyclin kinases and cell division
 Chem*3560 Lecture 10: Cyclins, cyclin kinases and cell division The eukaryotic cell cycle Actively growing mammalian cells divide roughly every 24 hours, and follow a precise sequence of events know as
Chem*3560 Lecture 10: Cyclins, cyclin kinases and cell division The eukaryotic cell cycle Actively growing mammalian cells divide roughly every 24 hours, and follow a precise sequence of events know as
Modeling of snrnp Motion in the Nucleoplasm
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 008 Hannover Modeling of snrnp Motion in the Nucleoplasm Michaela Blažíková 1, Jan Malínský *,, David Staněk 3 and Petr Heřman 1 1 Charles University
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 008 Hannover Modeling of snrnp Motion in the Nucleoplasm Michaela Blažíková 1, Jan Malínský *,, David Staněk 3 and Petr Heřman 1 1 Charles University
AP Biology Fall Semester Set 1
 1. During which stage does DNA replication occur? A. Prophase B. Metaphase C. Anaphase D. none of these 2. At what phase in the cell cycle does DNA replication occur? A. G1 B. S C. G2 D. M 3. Which of
1. During which stage does DNA replication occur? A. Prophase B. Metaphase C. Anaphase D. none of these 2. At what phase in the cell cycle does DNA replication occur? A. G1 B. S C. G2 D. M 3. Which of
Dr. Mahmood S. Choudhery, PhD, Postdoc (USA) Assistant Professor Tissue Engineering & Regenerative Medicine King Edward Medical University
 CELL DIVISION Dr. Mahmood S. Choudhery, PhD, Postdoc (USA) Assistant Professor Tissue Engineering & Regenerative Medicine King Edward Medical University Cell Division The key roles of cell division Unicellular
CELL DIVISION Dr. Mahmood S. Choudhery, PhD, Postdoc (USA) Assistant Professor Tissue Engineering & Regenerative Medicine King Edward Medical University Cell Division The key roles of cell division Unicellular
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION. Chapter 10
 CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
An intracellular phase transition drives nucleolar assembly and size control
 An intracellular phase transition drives nucleolar assembly and size control Steph Weber Department of Biology McGill University Membranes spatially organize eukaryotic cells Cells also contain membraneless
An intracellular phase transition drives nucleolar assembly and size control Steph Weber Department of Biology McGill University Membranes spatially organize eukaryotic cells Cells also contain membraneless
Chromosome duplication and distribution during cell division
 CELL DIVISION AND HEREDITY Student Packet SUMMARY IN EUKARYOTES, HERITABLE INFORMATION IS PASSED TO THE NEXT GENERATION VIA PROCESSES THAT INCLUDE THE CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS /MEIOSIS AND FERTILIZATION Mitosis
CELL DIVISION AND HEREDITY Student Packet SUMMARY IN EUKARYOTES, HERITABLE INFORMATION IS PASSED TO THE NEXT GENERATION VIA PROCESSES THAT INCLUDE THE CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS /MEIOSIS AND FERTILIZATION Mitosis
Dr. Fred Cross, Rockefeller (KITP Bio Networks 3/26/2003) 1
 Outline Cell growth as the driver for cell cycle (in microbes): coordination of growth and division A basic principle organizing cell cycle control: why cyclin-dependent kinase activity must oscillate
Outline Cell growth as the driver for cell cycle (in microbes): coordination of growth and division A basic principle organizing cell cycle control: why cyclin-dependent kinase activity must oscillate
Describe the process of cell division in prokaryotic cells. The Cell Cycle
 The Cell Cycle Objective # 1 In this topic we will examine the cell cycle, the series of changes that a cell goes through from one division to the next. We will pay particular attention to how the genetic
The Cell Cycle Objective # 1 In this topic we will examine the cell cycle, the series of changes that a cell goes through from one division to the next. We will pay particular attention to how the genetic
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis. Chapter 11
 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Chapter 11 1 Sexual life cycle Made up of meiosis and fertilization Diploid cells Somatic cells of adults have 2 sets of chromosomes Haploid cells Gametes (egg and sperm)
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Chapter 11 1 Sexual life cycle Made up of meiosis and fertilization Diploid cells Somatic cells of adults have 2 sets of chromosomes Haploid cells Gametes (egg and sperm)
Cellular Division. copyright cmassengale
 Cellular Division 1 Cell Division All cells are derived from pre- existing cells New cells are produced for growth and to replace damaged or old cells Differs in prokaryotes (bacteria) and eukaryotes (protists,
Cellular Division 1 Cell Division All cells are derived from pre- existing cells New cells are produced for growth and to replace damaged or old cells Differs in prokaryotes (bacteria) and eukaryotes (protists,
Introduction: The Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Contents 1 Introduction: The Cell Cycle and Mitosis 2 Mitosis Review Introduction: The Cell Cycle and Mitosis The cell cycle refers to the a series of events that describe the metabolic processes of growth
Contents 1 Introduction: The Cell Cycle and Mitosis 2 Mitosis Review Introduction: The Cell Cycle and Mitosis The cell cycle refers to the a series of events that describe the metabolic processes of growth
Meiosis. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Meiosis Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction requires fertilization, a union of two cells from two individual organisms. If those two cells each contain one set of chromosomes, then the resulting cell
Meiosis Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction requires fertilization, a union of two cells from two individual organisms. If those two cells each contain one set of chromosomes, then the resulting cell
2 CELLS AND CELL DIVISION
 CHAPTER OUTLINE 2 CELLS AND CELL DIVISION THE CHEMISTRY OF CELLS CELL STRUCTURE REFLECTS FUNCTION There are two cellular domains: the plasma membrane and the cytoplasm. Organelles are specialized structures
CHAPTER OUTLINE 2 CELLS AND CELL DIVISION THE CHEMISTRY OF CELLS CELL STRUCTURE REFLECTS FUNCTION There are two cellular domains: the plasma membrane and the cytoplasm. Organelles are specialized structures
A. Incorrect! The Cell Cycle contains 4 distinct phases: (1) G 1, (2) S Phase, (3) G 2 and (4) M Phase.
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 21: Cell Cycle and Cell Death Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the cell cycle is correct? Question #1 (A) The Cell Cycle contains 3
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 21: Cell Cycle and Cell Death Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the cell cycle is correct? Question #1 (A) The Cell Cycle contains 3
AP Biology Unit 6 Practice Test 1. A group of cells is assayed for DNA content immediately following mitosis and is found to have an average of 8
 AP Biology Unit 6 Practice Test Name: 1. A group of cells is assayed for DNA content immediately following mitosis and is found to have an average of 8 picograms of DNA per nucleus. How many picograms
AP Biology Unit 6 Practice Test Name: 1. A group of cells is assayed for DNA content immediately following mitosis and is found to have an average of 8 picograms of DNA per nucleus. How many picograms
Cell Division. Binary Fission, Mitosis & Meiosis 2/9/2016. Dr. Saud Alamri
 Cell Division Binary Fission, Mitosis & Meiosis 1 Prokaryotic cells reproduce asexually by a type of cell division called binary fission 2 Prokaryotic chromosome Division into two daughter cells Plasma
Cell Division Binary Fission, Mitosis & Meiosis 1 Prokaryotic cells reproduce asexually by a type of cell division called binary fission 2 Prokaryotic chromosome Division into two daughter cells Plasma
Prof. Fahd M. Nasr. Lebanese university Faculty of sciences I Department of Natural Sciences.
 Prof. Fahd M. Nasr Lebanese university Faculty of sciences I Department of Natural Sciences fnasr@ul.edu.lb B3206 Microbial Genetics Eukaryotic M. G. The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a genetic model
Prof. Fahd M. Nasr Lebanese university Faculty of sciences I Department of Natural Sciences fnasr@ul.edu.lb B3206 Microbial Genetics Eukaryotic M. G. The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a genetic model
Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 8: Mechanisms of Cell Cycle Control and DNA Synthesis Gary Peter
 Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 8: Mechanisms of Cell Cycle Control and DNA Synthesis Gary Peter 9/10/2008 1 Learning Objectives Explain why a cell cycle was selected for during evolution
Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 8: Mechanisms of Cell Cycle Control and DNA Synthesis Gary Peter 9/10/2008 1 Learning Objectives Explain why a cell cycle was selected for during evolution
Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle
 Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division
 Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division The larger the cell, the more trouble the cell has moving nutrients and waste across the cell membrane. 1. DNA/information overload As a cell increases in size,
Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division The larger the cell, the more trouble the cell has moving nutrients and waste across the cell membrane. 1. DNA/information overload As a cell increases in size,
Place the definition s corresponding number to the vocabulary term.
 UNIT 5 CP BIOLOGY: ular Division Differentiation Stem UNIT 5 CP BIOLOGY: ular Division Differentiation Stem CP: 1. First phase of mitosis when chromatin condenses, the nuclear envelope breaks down, the
UNIT 5 CP BIOLOGY: ular Division Differentiation Stem UNIT 5 CP BIOLOGY: ular Division Differentiation Stem CP: 1. First phase of mitosis when chromatin condenses, the nuclear envelope breaks down, the
The Microscopic Observation of Mitosis in Plant and Animal Cells
 The Microscopic Observation of Mitosis in Plant and Animal Cells Prelab Assignment Before coming to lab, read carefully the introduction and the procedures for each part of the experiment, and then answer
The Microscopic Observation of Mitosis in Plant and Animal Cells Prelab Assignment Before coming to lab, read carefully the introduction and the procedures for each part of the experiment, and then answer
CELL CYCLE UNIT GUIDE- Due January 19, 2016
 CELL CYCLE UNIT GUIDE- Due January 19, 2016 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday January 4- No School 5-Cell Cycle/Mitosis 6-Cell Cycle/ Mitosis 7-Mitosis 8-Meiosis Reading Check Quiz #1 sections 5.1-5.5
CELL CYCLE UNIT GUIDE- Due January 19, 2016 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday January 4- No School 5-Cell Cycle/Mitosis 6-Cell Cycle/ Mitosis 7-Mitosis 8-Meiosis Reading Check Quiz #1 sections 5.1-5.5
Mitosis & Meiosis. PPT Questions. 4. Why must each new cell get a complete copy of the original cell s DNA?
 1. From where do new cells arise? Mitosis & Meiosis PPT Questions 2. Why does the body constantly make new cells? 3. Is cell division the same in all cells? Explain. 4. Why must each new cell get a complete
1. From where do new cells arise? Mitosis & Meiosis PPT Questions 2. Why does the body constantly make new cells? 3. Is cell division the same in all cells? Explain. 4. Why must each new cell get a complete
NUP2 AND A NEWLY DISCOVERED NUCLEAR PORE COMPLEX PROTEIN, NUPA, FUNCTION AT MITOTIC CHROMATIN CONTROLLED BY THE NIMA KINASE DISSERTATION
 NUP2 AND A NEWLY DISCOVERED NUCLEAR PORE COMPLEX PROTEIN, NUPA, FUNCTION AT MITOTIC CHROMATIN CONTROLLED BY THE NIMA KINASE DISSERTATION Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree
NUP2 AND A NEWLY DISCOVERED NUCLEAR PORE COMPLEX PROTEIN, NUPA, FUNCTION AT MITOTIC CHROMATIN CONTROLLED BY THE NIMA KINASE DISSERTATION Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree
Cell Cycle Regulation by Chlamydomonas Cyclin-Dependent Protein Kinases
 Plant Cell Advance Publication. Published on February 5, 2018, doi:10.1105/tpc.18.00103 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 IN BRIEF Cell Cycle Regulation by Chlamydomonas
Plant Cell Advance Publication. Published on February 5, 2018, doi:10.1105/tpc.18.00103 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 IN BRIEF Cell Cycle Regulation by Chlamydomonas
A&P 1 Cellular Anatomy, Division & Mitosis In-lab Guide Lab Exercises. In this "Lab Exercise", we will be looking at cellular anatomy and mitosis.
 A&P 1 Cellular Anatomy, Division & Mitosis In-lab Guide Lab Exercises In this "Lab Exercise", we will be looking at cellular anatomy and mitosis. Before trying to do these steps, we should have read the
A&P 1 Cellular Anatomy, Division & Mitosis In-lab Guide Lab Exercises In this "Lab Exercise", we will be looking at cellular anatomy and mitosis. Before trying to do these steps, we should have read the
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.9 MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: MITOSIS Mitosis is a type of cell division that produces daughter cells Interphase is the initial stage of the cell cycle, and is the period between divisions - G1, which
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: MITOSIS Mitosis is a type of cell division that produces daughter cells Interphase is the initial stage of the cell cycle, and is the period between divisions - G1, which
Partial Nuclear Pore Complex Disassembly during Closed Mitosis in Aspergillus nidulans
 Current Biology, Vol. 14, 1973 1984, November 23, 2004, 2004 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2004.10.050 Partial Nuclear Pore Complex Disassembly during Closed Mitosis in Aspergillus
Current Biology, Vol. 14, 1973 1984, November 23, 2004, 2004 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2004.10.050 Partial Nuclear Pore Complex Disassembly during Closed Mitosis in Aspergillus
The Process of Cell Division. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview The Process of Cell Division
 Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division Chromosomes genetic information passed from parent to offspring is carried by chromosomes. Chromosomes enable precise DNA separation during cell division.
Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division Chromosomes genetic information passed from parent to offspring is carried by chromosomes. Chromosomes enable precise DNA separation during cell division.
2:1 Chromosomes DNA Genes Chromatin Chromosomes CHROMATIN: nuclear material in non-dividing cell, composed of DNA/protein in thin uncoiled strands
 Human Heredity Chapter 2 Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis 2:1 Chromosomes DNA Genes Chromatin Chromosomes CHROMATIN: nuclear material in non-dividing cell, composed of DNA/protein in thin uncoiled strands
Human Heredity Chapter 2 Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis 2:1 Chromosomes DNA Genes Chromatin Chromosomes CHROMATIN: nuclear material in non-dividing cell, composed of DNA/protein in thin uncoiled strands
Passive. mechanisms. Active. mechanisms. Cell diffusion. Movement. Movement. Movement. Mechanisms that do not require cellular energy such as:
 Passive mechanisms Mechanisms that do not require cellular energy such as: Diffusion Facilitated diffusion Osmosis Filtration Active mechanisms Mechanisms that do require cellular energy such as: Active
Passive mechanisms Mechanisms that do not require cellular energy such as: Diffusion Facilitated diffusion Osmosis Filtration Active mechanisms Mechanisms that do require cellular energy such as: Active
Meiosis produces haploid gametes.
 Section 1: produces haploid gametes. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions How does the reduction in chromosome number occur during meiosis? What are the stages of
Section 1: produces haploid gametes. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions How does the reduction in chromosome number occur during meiosis? What are the stages of
CHAPTER 10 : CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION K C MEENA PGT BIOLOGY KVS
 CHAPTER 10 : CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION K C MEENA PGT BIOLOGY KVS Cell cycle It is a series of events that takes place in a cell, leading to the formation of two daughter cells from a single mother cell.
CHAPTER 10 : CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION K C MEENA PGT BIOLOGY KVS Cell cycle It is a series of events that takes place in a cell, leading to the formation of two daughter cells from a single mother cell.
NCERT. not to be published CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION 10.1 CELL CYCLE 162 BIOLOGY
 162 BIOLOGY 10.1 Cell Cycle 10.2 M Phase 10.3 Significance of Mitosis 10.4 Meiosis 10.5 Significance of Meiosis CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION Are you aware that all organisms, even the largest,
162 BIOLOGY 10.1 Cell Cycle 10.2 M Phase 10.3 Significance of Mitosis 10.4 Meiosis 10.5 Significance of Meiosis CHAPTER 10 CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION Are you aware that all organisms, even the largest,
Mitosis, Not Just Open or Closed
 EUKARYOTIC CELL, Sept. 2007, p. 1521 1527 Vol. 6, No. 9 1535-9778/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/ec.00178-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Mitosis, Not Just Open or Closed
EUKARYOTIC CELL, Sept. 2007, p. 1521 1527 Vol. 6, No. 9 1535-9778/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/ec.00178-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Mitosis, Not Just Open or Closed
Essential Knowledge: In eukaryotes, heritable information is passed to the next generation via processes that include the cell cycle and mitosis OR
 Essential Knowledge: In eukaryotes, heritable information is passed to the next generation via processes that include the cell cycle and mitosis OR meiosis plus fertilization Objective: You will be able
Essential Knowledge: In eukaryotes, heritable information is passed to the next generation via processes that include the cell cycle and mitosis OR meiosis plus fertilization Objective: You will be able
The Gametic Cell Cycle
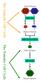 The Gametic Cell Cycle Diploid Parents MEIOSIS Haploid Gametes FERTILIZATION The Somatic Cell Cycle Diploid Zygote MITOSIS Diploid organism Activities of meiosis that differ from mitosis? Life cycle of
The Gametic Cell Cycle Diploid Parents MEIOSIS Haploid Gametes FERTILIZATION The Somatic Cell Cycle Diploid Zygote MITOSIS Diploid organism Activities of meiosis that differ from mitosis? Life cycle of
G 2 G 1. Cell Cycle. Cell Structure and Function. prophase. metaphase anaphase. telophase. cytokinesis. STAAR Biology: Assessment Activities
 STAAR Biology: Assessment Activities INTERPHASE G 2 prophase M metaphase MITOSIS anaphase telophase cytokinesis INTERPHASE G 1 S G 0 INTERPHASE Cell Structure and Function 91 STAAR Biology: Assessment
STAAR Biology: Assessment Activities INTERPHASE G 2 prophase M metaphase MITOSIS anaphase telophase cytokinesis INTERPHASE G 1 S G 0 INTERPHASE Cell Structure and Function 91 STAAR Biology: Assessment
E. Incorrect! At telophase II, cells are nearly completed with meiosis, with no cross-over.
 OAT Biology - Problem Drill 06: Mitosis and Meiosis Question No. 1 of 10 1. During meiosis, cross-over between homologous chromosomes occurs at the end of. Question #01 (A) Anaphase II (B) Metaphase I
OAT Biology - Problem Drill 06: Mitosis and Meiosis Question No. 1 of 10 1. During meiosis, cross-over between homologous chromosomes occurs at the end of. Question #01 (A) Anaphase II (B) Metaphase I
BIOLOGY. Chapter 10 CELL REPRODUCTION PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 BIOLOGY Chapter 10 CELL REPRODUCTION PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 10.1 A sea urchin begins life as a single cell that (a) divides to form two cells, visible by scanning electron microscopy. After
BIOLOGY Chapter 10 CELL REPRODUCTION PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 10.1 A sea urchin begins life as a single cell that (a) divides to form two cells, visible by scanning electron microscopy. After
THREE MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES INTRODUCTION
 THREE MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS OVERVIEW In this lab you will investigate the processes of mitosis and rneiosis: 1. You will use prepared slides of onion root tips to study plant mitosis and to calculate the
THREE MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS OVERVIEW In this lab you will investigate the processes of mitosis and rneiosis: 1. You will use prepared slides of onion root tips to study plant mitosis and to calculate the
3.2.2 All cells arise from other cells
 alevelbiology.co.uk SPECIFICATION Within multicellular organisms, not all cells retain the ability to divide. Eukaryotic cells that do retain the ability to divide show a cell cycle. DNA replication occurs
alevelbiology.co.uk SPECIFICATION Within multicellular organisms, not all cells retain the ability to divide. Eukaryotic cells that do retain the ability to divide show a cell cycle. DNA replication occurs
Three Myosins Contribute Uniquely to the Assembly and Constriction of the Fission Yeast Cytokinetic Contractile Ring
 Current Biology Supplemental Information Three Myosins Contribute Uniquely to the Assembly and Constriction of the Fission Yeast Cytokinetic Contractile Ring Caroline Laplante, Julien Berro, Erdem Karatekin,
Current Biology Supplemental Information Three Myosins Contribute Uniquely to the Assembly and Constriction of the Fission Yeast Cytokinetic Contractile Ring Caroline Laplante, Julien Berro, Erdem Karatekin,
Figure S1. Programmed cell death in the AB lineage occurs in temporally distinct
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Figure S1. Programmed cell death in the AB lineage occurs in temporally distinct waves. (A) A representative sub-lineage (ABala) of the C. elegans lineage tree (adapted from
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Figure S1. Programmed cell death in the AB lineage occurs in temporally distinct waves. (A) A representative sub-lineage (ABala) of the C. elegans lineage tree (adapted from
Kinesin-8 effects on mitotic microtubule dynamics contribute to spindle function in fission yeast
 Kinesin-8 effects on mitotic microtubule dynamics contribute to spindle function in fission yeast Zachary R. Gergely 1,2, Ammon Crapo 1, Loren E. Hough 1, J. Richard McIntosh 2, and Meredith D. Betterton
Kinesin-8 effects on mitotic microtubule dynamics contribute to spindle function in fission yeast Zachary R. Gergely 1,2, Ammon Crapo 1, Loren E. Hough 1, J. Richard McIntosh 2, and Meredith D. Betterton
THE WORK OF GREGOR MENDEL
 GENETICS NOTES THE WORK OF GREGOR MENDEL Genetics-. - Austrian monk- the father of genetics- carried out his work on. Pea flowers are naturally, which means that sperm cells fertilize the egg cells in
GENETICS NOTES THE WORK OF GREGOR MENDEL Genetics-. - Austrian monk- the father of genetics- carried out his work on. Pea flowers are naturally, which means that sperm cells fertilize the egg cells in
Mitosis and Meiosis for AP Biology
 Mitosis and Meiosis for AP Biology by Mark Anestis Practice problems for these concepts can be found at : Cell Division Review Questions for AP Biology Mitosis During mitosis, the fourth stage of the cell
Mitosis and Meiosis for AP Biology by Mark Anestis Practice problems for these concepts can be found at : Cell Division Review Questions for AP Biology Mitosis During mitosis, the fourth stage of the cell
Genetics Essentials Concepts and Connections 3rd Edition by Benjamin A Pierce Test Bank
 Genetics Essentials Concepts and Connections 3rd Edition by Benjamin A Pierce Test Bank Which of the following statements is FALSE? A) Errors in chromosome separation are rarely a problem for an organism.
Genetics Essentials Concepts and Connections 3rd Edition by Benjamin A Pierce Test Bank Which of the following statements is FALSE? A) Errors in chromosome separation are rarely a problem for an organism.
Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle
 Name Period Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle Overview: 1. What are the three key roles of cell division? State each role, and give an example. Key Role Example 2. What is meant by the cell cycle? Concept 12.1
Name Period Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle Overview: 1. What are the three key roles of cell division? State each role, and give an example. Key Role Example 2. What is meant by the cell cycle? Concept 12.1
Cell Division. Mitosis
 Cell division consists of two phases, nuclear division followed by cytokinesis. Nuclear division divides the genetic material in the nucleus, while cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm. There are two kinds
Cell division consists of two phases, nuclear division followed by cytokinesis. Nuclear division divides the genetic material in the nucleus, while cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm. There are two kinds
MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION PART I: SIMULATION OF MEIOSIS EVOLUTION. Activity #9
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION Unit 1 Part 7 Chapter 13 Activity #9 NAME DATE PERIOD MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION Meiosis involves two successive nuclear divisions that produce four haploid cells. Meiosis I is the reduction
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION Unit 1 Part 7 Chapter 13 Activity #9 NAME DATE PERIOD MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION Meiosis involves two successive nuclear divisions that produce four haploid cells. Meiosis I is the reduction
Human biology Laboratory. Cell division. Lecturer Maysam A Mezher
 Human biology Laboratory Cell division Lecturer Maysam A Mezher CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact
Human biology Laboratory Cell division Lecturer Maysam A Mezher CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact
Cell Division. Genetic info must be copied. Each cell gets a complete copy of that info. It occurs in two main stages:
 10-2 Cell Division Key Questions: 1)What is the role of chromosomes in cell division? 2) What are the main events of the cell cycle? 3) What events occur during each of the four phases of mitosis? 4) How
10-2 Cell Division Key Questions: 1)What is the role of chromosomes in cell division? 2) What are the main events of the cell cycle? 3) What events occur during each of the four phases of mitosis? 4) How
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer Cdc55 coordinates spindle assembly and chromosome disjunction during meiosis Citation for published version: Bizzari, F & Marston, AL 2011, 'Cdc55 coordinates spindle assembly
Edinburgh Research Explorer Cdc55 coordinates spindle assembly and chromosome disjunction during meiosis Citation for published version: Bizzari, F & Marston, AL 2011, 'Cdc55 coordinates spindle assembly
Lesson Overview Meiosis
 11.4 THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
11.4 THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
Role of the spindle-pole-body protein ApsB and the cortex protein ApsA in microtubule organization and nuclear migration in Aspergillus nidulans
 Research Article 3705 Role of the spindle-pole-body protein ApsB and the cortex protein ApsA in microtubule organization and nuclear migration in Aspergillus nidulans Daniel Veith 1,2, Nicole Scherr 1,2,
Research Article 3705 Role of the spindle-pole-body protein ApsB and the cortex protein ApsA in microtubule organization and nuclear migration in Aspergillus nidulans Daniel Veith 1,2, Nicole Scherr 1,2,
A diploid somatic cell from a rat has a total of 42 chromosomes (2n = 42). As in humans, sex chromosomes determine sex: XX in females and XY in males.
 Multiple Choice Use the following information for questions 1-3. A diploid somatic cell from a rat has a total of 42 chromosomes (2n = 42). As in humans, sex chromosomes determine sex: XX in females and
Multiple Choice Use the following information for questions 1-3. A diploid somatic cell from a rat has a total of 42 chromosomes (2n = 42). As in humans, sex chromosomes determine sex: XX in females and
Meiosis * OpenStax. This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0.
 OpenStax-CNX module: m45466 1 Meiosis * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able to: Abstract
OpenStax-CNX module: m45466 1 Meiosis * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able to: Abstract
Entry into mitosis is characterized by a dramatic
 Published Online: 29 September, 2008 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200801153 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on April 12, 2018 JCB: ARTICLE Grapes(Chk1) prevents nuclear CDK1 activation by delaying
Published Online: 29 September, 2008 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200801153 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on April 12, 2018 JCB: ARTICLE Grapes(Chk1) prevents nuclear CDK1 activation by delaying
Cell Growth and Division
 Cell Growth and Division Growth, Development, and Reproduction Q: How does a cell produce a new cell? 10.1 Why do cells divide? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER: Cells divide to produce more cells. WHAT I LEARNED
Cell Growth and Division Growth, Development, and Reproduction Q: How does a cell produce a new cell? 10.1 Why do cells divide? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER: Cells divide to produce more cells. WHAT I LEARNED
Ch. 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics. p
 Ch. 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics p. 270 - 10.1 Meiosis p. 270-276 Essential Question Main Idea! Meiosis produces haploid gametes Where are the instructions for each trait located in a cell?! On
Ch. 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics p. 270 - 10.1 Meiosis p. 270-276 Essential Question Main Idea! Meiosis produces haploid gametes Where are the instructions for each trait located in a cell?! On
BIOLOGY 1101 LAB 4: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS
 BIOLOGY 1101 LAB 4: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS READING: Please read chapter 8 in your text. INTRODUCTION: The nuclei of eukaryotic cells contain chromosomes along which genes are arranged. Genes are sections
BIOLOGY 1101 LAB 4: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS READING: Please read chapter 8 in your text. INTRODUCTION: The nuclei of eukaryotic cells contain chromosomes along which genes are arranged. Genes are sections
CELL REPRODUCTION VOCABULARY- CHAPTER 8 (33 words)
 CELL REPRODUCTION- CHAPTER 8 CELL REPRODUCTION VOCABULARY- CHAPTER 8 (33 words) 1. Chromosome 2. histone 3. chromatid 4. Centromere 5. chromatin 6. autosome 7. Sex chromosome 8. homologous chromosome 9.
CELL REPRODUCTION- CHAPTER 8 CELL REPRODUCTION VOCABULARY- CHAPTER 8 (33 words) 1. Chromosome 2. histone 3. chromatid 4. Centromere 5. chromatin 6. autosome 7. Sex chromosome 8. homologous chromosome 9.
10 CELL DIVISION AND MITOSIS
 10 CELL DIVISION AND MITOSIS Chapter Outline Why It Matters 10.1 THE CYCLE OF CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION: OVERVIEW The products of mitosis are genetic duplicates of the dividing cell Chromosomes are the
10 CELL DIVISION AND MITOSIS Chapter Outline Why It Matters 10.1 THE CYCLE OF CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION: OVERVIEW The products of mitosis are genetic duplicates of the dividing cell Chromosomes are the
