Add Up and Cross Over
|
|
|
- Doris Neal
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Add Up and Cross Over Sordaria Genetics Simulation Introduction SCIENTIFIC BIO FAX! Crossing over occurs during meiosis I. During crossing over, homologous pairs of chromosomes exchange sections of DNA that contain the same genes. It is important to note that crossing over does not have to occur during each generation, nor does it always take place at the same point of exchange. Over time, however, crossing over leads to a greater variety of genes in a population and contributes to a diversity of characteristics and increased fitness of the population. This is reflected in the ability of the population to adapt to changes in the environment. Concepts Genetic diversity Gene mapping Crossing over Meiosis Background During sexual reproduction hyphae of different haploid S. fimicola come into contact allowing cells in the hyphae to fuse and form a single cell with two nuclei, one from each individual. This fused cell is called a dikaryon. The dikaryon is not considered diploid since the two nuclei are from separate fungi and the nuclei are not fused together. The dikaryon cells undergo multiple rounds of mitosis to form a mass of cells. This mass of cells can exist for years without undergoing fusion of the nuclei. Sexual reproduction occurs when some of the dikaryon nuclei fuse. After fusion the fruiting body forms and meiosis occurs, creating the asci and ascospores, which are haploid cells. The ascospores form inside the tight confines of the tube-like ascus. The ascospores actually line up in order based on which cell produced that particular ascospore. In 1956, a geneticist named Lindsay S. Olive ( ) published an article about crossing over in S. fimicola. Dr. Olive used ultraviolet light to cause mutations in the genes of S. fimicola. After numerous trials, Dr. Olive produced a mutation in the gene that produced the pigment in the ascospore. The production of the black pigment is either greatly reduced or completely repressed in the mutated strain of S. Fimicola. A reduction in the amount of black pigment results in gray asco spores. An absence of black pigment results in tan ascospores. By collecting the gray or tan ascospores, Dr. Olive was able to produce true breeding fungi much like Mendel s peas. Recall that each ascospore can be traced back to the parent chromosome. The pattern of black and tan ascospores shows whether crossing over occurred during meiosis. Observe Figure 1. Note that the diagram of the ascus indicates eight ascospores in each ascus, not the expected four cells. This is because each of the four haploid daughter cells undergoes a single mitosis after the end of meiosis II. So, each daughter cell produces a clone of itself. These clones reside next to each other within the ascus. If the cells come from parents with identical pigment genes, the ascus will contain eight spores that are the same color whether black or tan. If the cells come from parents with each pigment type, but crossing over did not occur, the spores will appear as four black, wild-type and four tan, mutant spores (4b:4t) (see Figure 1a). If crossing over of the pigment gene between a black wild-type and a tan mutant occurred during meiosis I, the four spores will have one of two possible patterns: 2:2:2:2 or 2:4:2. Each of the numbers can be either tan or black. This is written out as 2b:2t:2b:2t or 2t:2b:2t:2b and 2b:4t:2b or 2t:4b:2t. (See Figure 1b and 1 c) Flinn Scientific, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Publication No
2 Ascus phenotype Ascus phenotype Ascus phenotype Figure 1a. Figure 1b. Figure 1c. Non-crossover ascus 4b:4t Crossover ascus 2b:2t:2b:2t Crossover ascus 2b:4t:2b Materials Sordaria Cards, 5 Pencil Safety Precautions Although this activity is considered nonhazardous, please follow all laboratory safety guidelines. Procedure 1. Begin with one of the five Sordaria cards assigned. Categorize each ascus containing both black and tan ascospore beginning at the twelve o clock position. Note: Do not categorize any single-colored asci. single-colored asci are not the result of sexual reproduction between a tan mutant and a black wild type S. fimicola and will not be used to calculate the frequency of crossing over or the map distance. 2. Tally the results on the Counting Crossing Over Worksheet corresponding to the correct color arrangement for each ascus. Note: Refer to Figures 1a 1c for schematics of possible two-colored asci. 3. Categorize all of the two-colored asci on the first card. 4. Repeat steps 1 3 with the four remaining cards, compiling all the data. 5. Complete the calculations and data analysis on the Counting Crossing Over Worksheet. AP Biology Curriculum Enduring Understanding Essential knowledge 3.A.3: The chromosomal basis of inheritance provides an understanding of the pattern of passage (transmission) of genes from parent to offspring. Essential knowledge 3.C.1: Changes in genotype can result in changes in phenotype. Essential knowledge 3.C.2: Biological systems have multiple processes that increase genetic variation Flinn Scientific, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
3 Tips Published sources cite between 26 and 28 map units as the distance between the tan mutant gene and the centromere. Use this activity as an introduction for the Advanced Placement Biology Investigation 7 Part 5. References Olive, L. S. Genetics of Sordaria fimicola; American Journal of Botany, 1956, 43, Cassell, P., Mertens, T. R., A Laboratory Exercise on the Genetics of Ascospore Color in Sordaria fimicola; The American Biology Teacher, 1968, 30, The Tree of Life Web project (accessed August 2010). Biology: Lab Manual; College Entrance Examination Board: Kits covering the same topic as Add Up and Cross Over are available from Flinn Scientific, Inc. Catalog No. FB1973 FB2001 Description Counting Crossing Over Sordaria Genetics Student Activity Kit Sordaria Genetics Student Laboratory Kit Consult your Flinn Scientific Catalog/Reference Manual for current prices Flinn Scientific, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
4 Add Up and Cross Over Worksheet Data Table Color combinations Tally Marks Total Non-crossover Asci 4b:4t 4t:4b Crossover Asci 2b:2t:2b:2t 2t:2b:2t:2b 2b:4t:2b 2t:4b:2t Name: Post-Lab Questions and Calculations 1. Take the sum of the tally marks for each combination. Record each result in the Total column. 2. Determine the total number of non-crossover asci counted. 3. Determine the total number of crossover asci counted. 4. Determine the total number of hybrid asci counted. 5. Recall that each ascus contains eight spores because the four haploid spores underwent an additional mitosis. a correction to the totals must be performed to compensate for that extra mitotic event. Divide each of the numbers calculated in steps 3 4 by 2. Record the corrected values below. 5. Determine the map distance between the gene for spore color and the centromere using Equation 1. Report the result in map units. However, keep in mind that each ascus contains 8 spores because the four haploid spores underwent an additional mitotic event after meiosis. To account for this, the map distance found in Equation 1 needs to be halved (Equation 2). corrected number of crossover asci Map distance = 100 Equation 1 corrected total number of asci counted Map distance Equation Was the number of each type of crossover phenotype observed relatively constant or equal? Explain why you would expect these numbers to be constant. 7. A similar technique can be used to determine the distance between two genes on a single chromosome. In this laboratory a color mutation was used as the gene of interest. What is the benefit for using a color mutant gene for learning about map units Flinn Scientific, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
5 Flinn Scientific, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Add Up and Cross Over Sordaria Genetics Simulation
 Introduction Add Up and Cross Over Sordaria Genetics Simulation Publication No. Crossing over occurs during metaphase I of meiosis. During crossing over, homologous pairs of chromosomes exchange sections
Introduction Add Up and Cross Over Sordaria Genetics Simulation Publication No. Crossing over occurs during metaphase I of meiosis. During crossing over, homologous pairs of chromosomes exchange sections
Investigation 7: Cell Division Part B: Meiosis and Crossing Over
 Background Investigation 7: Cell Division Part B: Meiosis and Crossing Over Ascomycota are a diverse group of fungi including the familiar single-celled baker s yeast, the complex morel mushroom, and the
Background Investigation 7: Cell Division Part B: Meiosis and Crossing Over Ascomycota are a diverse group of fungi including the familiar single-celled baker s yeast, the complex morel mushroom, and the
Research Question How are gametes produced?
 Name Date AP Biology Unit 3 Research Question How are gametes produced? Background Meiosis resembles mitosis but serves a very different purpose. Meiosis is a cell division resulting in the halving, or
Name Date AP Biology Unit 3 Research Question How are gametes produced? Background Meiosis resembles mitosis but serves a very different purpose. Meiosis is a cell division resulting in the halving, or
MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION PART I: SIMULATION OF MEIOSIS EVOLUTION. Activity #9
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION Unit 1 Part 7 Chapter 13 Activity #9 NAME DATE PERIOD MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION Meiosis involves two successive nuclear divisions that produce four haploid cells. Meiosis I is the reduction
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION Unit 1 Part 7 Chapter 13 Activity #9 NAME DATE PERIOD MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION Meiosis involves two successive nuclear divisions that produce four haploid cells. Meiosis I is the reduction
Meiosis and Tetrad Analysis Lab
 Meiosis and Tetrad Analysis Lab Objectives: - Explain how meiosis and crossing over result in the different arrangements of ascospores within asci. - Learn how to calculate the map distance between a gene
Meiosis and Tetrad Analysis Lab Objectives: - Explain how meiosis and crossing over result in the different arrangements of ascospores within asci. - Learn how to calculate the map distance between a gene
AP Lab Seven: Mitosis and Meiosis
 AP Biology AP Lab Seven: Mitosis and Meiosis Name In this lab we will investigate the stages of mitosis and meiosis and explore different properties of cell reproduction. You will be working with microscopes
AP Biology AP Lab Seven: Mitosis and Meiosis Name In this lab we will investigate the stages of mitosis and meiosis and explore different properties of cell reproduction. You will be working with microscopes
Which of these best predicts the outcome of the changes illustrated in the diagrams?
 1. The diagrams below show two different scenarios for a pair of homologous chromosomes, known as a tetrad, undergoing a change where segments of DNA switch on parts of the chromosomes. In each scenario,
1. The diagrams below show two different scenarios for a pair of homologous chromosomes, known as a tetrad, undergoing a change where segments of DNA switch on parts of the chromosomes. In each scenario,
Introduction. Key Concepts I: Mitosis. AP Biology Laboratory 3 Mitosis & Meiosis
 Virtual Student Guide http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/index.html AP Biology Laboratory 3 Mitosis & Meiosis Introduction For organisms to grow and reproduce, cells must divide. Mitosis
Virtual Student Guide http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/index.html AP Biology Laboratory 3 Mitosis & Meiosis Introduction For organisms to grow and reproduce, cells must divide. Mitosis
Topic 10. Meiosis I. The Process of Meiosis
 Topic 10. Meiosis I. The Process of Meiosis Meiosis is a process of two sequenced nuclear divisions neither of which is identical to mitosis. Meiosis always begins with a nucleus with two sets of chromosomes
Topic 10. Meiosis I. The Process of Meiosis Meiosis is a process of two sequenced nuclear divisions neither of which is identical to mitosis. Meiosis always begins with a nucleus with two sets of chromosomes
Evolution Canyons occur naturally as a valley between two mountains where one slope, the
 Meiosis and Genetic Diversity in Sordaria fimicola Haley DeMartin Lab Section 001 Due October 27, 2014 Introduction Several Evolution Canyons exist in Lower Nahal Oren, Mount Carmel, Israel. These Evolution
Meiosis and Genetic Diversity in Sordaria fimicola Haley DeMartin Lab Section 001 Due October 27, 2014 Introduction Several Evolution Canyons exist in Lower Nahal Oren, Mount Carmel, Israel. These Evolution
2. Look at the table below. How many of these asci contain a spore arrangement that resulted from crossing over?
 INS 2007-08 Pre-lab III Questions 1. The cell cycle in a certain cell type has the duration of 16 hours. The nuclei of 660 cells showed 13 cells in anaphase. What is the approximate duration of anaphase
INS 2007-08 Pre-lab III Questions 1. The cell cycle in a certain cell type has the duration of 16 hours. The nuclei of 660 cells showed 13 cells in anaphase. What is the approximate duration of anaphase
INS Biology Lab 5 Pre-Lab Name:
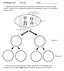 INS Biology Lab 5 Pre-Lab Name: 1. Diagram one possible fate of the chromosomes (assuming no crossover) during meiosis, starting with a hypothetical diploid cell containing two pairs of homologous chromosomes:
INS Biology Lab 5 Pre-Lab Name: 1. Diagram one possible fate of the chromosomes (assuming no crossover) during meiosis, starting with a hypothetical diploid cell containing two pairs of homologous chromosomes:
Ch 11.Introduction to Genetics.Biology.Landis
 Nom Section 11 1 The Work of Gregor Mendel (pages 263 266) This section describes how Gregor Mendel studied the inheritance of traits in garden peas and what his conclusions were. Introduction (page 263)
Nom Section 11 1 The Work of Gregor Mendel (pages 263 266) This section describes how Gregor Mendel studied the inheritance of traits in garden peas and what his conclusions were. Introduction (page 263)
UNIT 3: GENETICS 1. Inheritance and Reproduction Genetics inheritance Heredity parent to offspring chemical code genes specific order traits allele
 UNIT 3: GENETICS 1. Inheritance and Reproduction Genetics the study of the inheritance of biological traits Heredity- the passing of traits from parent to offspring = Inheritance - heredity is controlled
UNIT 3: GENETICS 1. Inheritance and Reproduction Genetics the study of the inheritance of biological traits Heredity- the passing of traits from parent to offspring = Inheritance - heredity is controlled
Virtual Lab 7 Mitosis and Meiosis
 Name Period Assignment # Virtual Lab 7 Mitosis and Meiosis http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/lab3/intro.html Click Next 1) What are 4 processes that require mitosis? a. b. c. d. 2)
Name Period Assignment # Virtual Lab 7 Mitosis and Meiosis http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/lab3/intro.html Click Next 1) What are 4 processes that require mitosis? a. b. c. d. 2)
Genes, Mutations and Diseases: Understanding the Origins of Genetic Disorders through Experiential Learning
 Genes, Mutations and Diseases: Understanding the Origins of Genetic Disorders through Experiential Learning A five week series of lessons and experiments designed for cohesiveness as unit, but can be done
Genes, Mutations and Diseases: Understanding the Origins of Genetic Disorders through Experiential Learning A five week series of lessons and experiments designed for cohesiveness as unit, but can be done
GENERAL SAFETY: Follow your teacher s directions. Do not work in the laboratory without your teacher s supervision.
 Name: Bio AP Lab: Cell Division B: Mitosis & Meiosis (Modified from AP Biology Investigative Labs) BACKGROUND: One of the characteristics of living things is the ability to replicate and pass on genetic
Name: Bio AP Lab: Cell Division B: Mitosis & Meiosis (Modified from AP Biology Investigative Labs) BACKGROUND: One of the characteristics of living things is the ability to replicate and pass on genetic
Teaching unit: Meiosis: The Steps to Creating Life
 Lesson Title: Meiosis Teacher s Name: I. Identification Course title: Biology/Life Science Teaching unit: Meiosis: The Steps to Creating Life CDE Standards Addressed: Biology/Life Sciences a. Students
Lesson Title: Meiosis Teacher s Name: I. Identification Course title: Biology/Life Science Teaching unit: Meiosis: The Steps to Creating Life CDE Standards Addressed: Biology/Life Sciences a. Students
Mitosis and Meiosis Winter Break Assignment
 Mitosis and Meiosis Winter Break Assignment AP Biology Objective FOLLOW ALL INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY AND BE SURE TO COMPLETE ALL PARTS OF THE ASSIGNMENT! This assignment is worth 100 points (the same as
Mitosis and Meiosis Winter Break Assignment AP Biology Objective FOLLOW ALL INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY AND BE SURE TO COMPLETE ALL PARTS OF THE ASSIGNMENT! This assignment is worth 100 points (the same as
What is a sex cell? How are sex cells made? How does meiosis help explain Mendel s results?
 CHAPTER 6 3 Meiosis SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a sex cell? How are sex cells made? How does meiosis help explain
CHAPTER 6 3 Meiosis SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a sex cell? How are sex cells made? How does meiosis help explain
1. The diagram below shows two processes (A and B) involved in sexual reproduction in plants and animals.
 1. The diagram below shows two processes (A and B) involved in sexual reproduction in plants and animals. Which statement best explains how these processes often produce offspring that have traits not
1. The diagram below shows two processes (A and B) involved in sexual reproduction in plants and animals. Which statement best explains how these processes often produce offspring that have traits not
THREE MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES INTRODUCTION
 THREE MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS OVERVIEW In this lab you will investigate the processes of mitosis and rneiosis: 1. You will use prepared slides of onion root tips to study plant mitosis and to calculate the
THREE MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS OVERVIEW In this lab you will investigate the processes of mitosis and rneiosis: 1. You will use prepared slides of onion root tips to study plant mitosis and to calculate the
THREE MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS
 OVERVEW THREE MTOSS AND MEOSS n this lab you will investigate the processes of mitosis and meiosis: 1. You will use prepared slides of onion root tips to study plant mitosis and to calculate the relative
OVERVEW THREE MTOSS AND MEOSS n this lab you will investigate the processes of mitosis and meiosis: 1. You will use prepared slides of onion root tips to study plant mitosis and to calculate the relative
Meiosis. Activity. Procedure Part I:
 Activity The purpose of meiosis, a cell division process, is to create gametes with genetic variability for use in sexual reproduction. These gametes, or the sperm and egg, are then used in the process
Activity The purpose of meiosis, a cell division process, is to create gametes with genetic variability for use in sexual reproduction. These gametes, or the sperm and egg, are then used in the process
genome a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another gene the passing of traits from one generation to the next
 genetics the study of heredity heredity sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait genome a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another gene trait the passing
genetics the study of heredity heredity sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait genome a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another gene trait the passing
Meiosis. Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and meiosis II
 Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION PART I: MEIOSIS
 MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION Meiosis involves two successive nuclear divisions that produce four haploid cells. Meiosis I is the reduction division. It is this first division that reduces the chromosome number
MEIOSIS LAB INTRODUCTION Meiosis involves two successive nuclear divisions that produce four haploid cells. Meiosis I is the reduction division. It is this first division that reduces the chromosome number
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION & MEIOSIS
 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION & MEIOSIS Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. Offspring resemble their parents more than they do less closely related individuals of the
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION & MEIOSIS Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. Offspring resemble their parents more than they do less closely related individuals of the
For a species to survive, it must REPRODUCE! Ch 13 NOTES Meiosis. Genetics Terminology: Homologous chromosomes
 For a species to survive, it must REPRODUCE! Ch 13 NOTES Meiosis Genetics Terminology: Autosomes Somatic cell Gamete Karyotype Homologous chromosomes Meiosis Sex chromosomes Diploid Haploid Zygote Synapsis
For a species to survive, it must REPRODUCE! Ch 13 NOTES Meiosis Genetics Terminology: Autosomes Somatic cell Gamete Karyotype Homologous chromosomes Meiosis Sex chromosomes Diploid Haploid Zygote Synapsis
Outline for today s lecture (Ch. 13)
 Outline for today s lecture (Ch. 13) Sexual and asexual life cycles Meiosis Origins of Genetic Variation Independent assortment Crossing over ( recombination ) Heredity Transmission of traits between generations
Outline for today s lecture (Ch. 13) Sexual and asexual life cycles Meiosis Origins of Genetic Variation Independent assortment Crossing over ( recombination ) Heredity Transmission of traits between generations
Introduction to Genetics
 Chapter 11 Introduction to Genetics Section 11 1 The Work of Gregor Mendel (pages 263 266) This section describes how Gregor Mendel studied the inheritance of traits in garden peas and what his conclusions
Chapter 11 Introduction to Genetics Section 11 1 The Work of Gregor Mendel (pages 263 266) This section describes how Gregor Mendel studied the inheritance of traits in garden peas and what his conclusions
Labs 7 and 8: Mitosis, Meiosis, Gametes and Genetics
 Biology 107 General Biology Labs 7 and 8: Mitosis, Meiosis, Gametes and Genetics In Biology 107, our discussion of the cell has focused on the structure and function of subcellular organelles. The next
Biology 107 General Biology Labs 7 and 8: Mitosis, Meiosis, Gametes and Genetics In Biology 107, our discussion of the cell has focused on the structure and function of subcellular organelles. The next
Meiosis. Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and meiosis II
 Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
Chromosome Chr Duplica Duplic t a ion Pixley
 Chromosome Duplication Pixley Figure 4-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Figure 4-72 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Interphase During mitosis (cell division),
Chromosome Duplication Pixley Figure 4-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Figure 4-72 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Interphase During mitosis (cell division),
Heredity Variation Genetics Meiosis
 Genetics Warm Up Exercise: -Using your previous knowledge of genetics, determine what maternal genotype would most likely yield offspring with such characteristics. -Use the genotype that you came up with
Genetics Warm Up Exercise: -Using your previous knowledge of genetics, determine what maternal genotype would most likely yield offspring with such characteristics. -Use the genotype that you came up with
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics
 Chapter Test A CHAPTER 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics Part A: Multiple Choice In the space at the left, write the letter of the term, number, or phrase that best answers each question. 1. How many
Chapter Test A CHAPTER 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics Part A: Multiple Choice In the space at the left, write the letter of the term, number, or phrase that best answers each question. 1. How many
Lesson Overview Meiosis
 11.4 THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
11.4 THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
Ch. 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics. p
 Ch. 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics p. 270 - 10.1 Meiosis p. 270-276 Essential Question Main Idea! Meiosis produces haploid gametes Where are the instructions for each trait located in a cell?! On
Ch. 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics p. 270 - 10.1 Meiosis p. 270-276 Essential Question Main Idea! Meiosis produces haploid gametes Where are the instructions for each trait located in a cell?! On
Advance Organizer. Topic: Mendelian Genetics and Meiosis
 Name: Row Unit 8 - Chapter 11 - Mendelian Genetics and Meiosis Advance Organizer Topic: Mendelian Genetics and Meiosis 1. Objectives (What should I be able to do?) a. Summarize the outcomes of Gregor Mendel's
Name: Row Unit 8 - Chapter 11 - Mendelian Genetics and Meiosis Advance Organizer Topic: Mendelian Genetics and Meiosis 1. Objectives (What should I be able to do?) a. Summarize the outcomes of Gregor Mendel's
Objectives. Announcements. Comparison of mitosis and meiosis
 Announcements Colloquium sessions for which you can get credit posted on web site: Feb 20, 27 Mar 6, 13, 20 Apr 17, 24 May 15. Review study CD that came with text for lab this week (especially mitosis
Announcements Colloquium sessions for which you can get credit posted on web site: Feb 20, 27 Mar 6, 13, 20 Apr 17, 24 May 15. Review study CD that came with text for lab this week (especially mitosis
Name Date Class CHAPTER 10. Section 1: Meiosis
 Name Date Class Study Guide CHAPTER 10 Section 1: Meiosis In your textbook, read about meiosis I and meiosis II. Label the diagrams below. Use these choices: anaphase I anaphase II interphase metaphase
Name Date Class Study Guide CHAPTER 10 Section 1: Meiosis In your textbook, read about meiosis I and meiosis II. Label the diagrams below. Use these choices: anaphase I anaphase II interphase metaphase
Name Class Date. Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. 33
 Chapter 11 Introduction to Genetics Chapter Vocabulary Review Matching On the lines provided, write the letter of the definition of each term. 1. genetics a. likelihood that something will happen 2. trait
Chapter 11 Introduction to Genetics Chapter Vocabulary Review Matching On the lines provided, write the letter of the definition of each term. 1. genetics a. likelihood that something will happen 2. trait
biology Slide 1 of 35 End Show Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 biology 1 of 35 Do Now: Turn in mitosis worksheet Write down your homework http://www.richannel.org/collection s/2013/chromosome#/chromosome -2 http://www.richannel.org/collection s/2013/chromosome#/chromosome
biology 1 of 35 Do Now: Turn in mitosis worksheet Write down your homework http://www.richannel.org/collection s/2013/chromosome#/chromosome -2 http://www.richannel.org/collection s/2013/chromosome#/chromosome
Name Date Class. Meiosis I and Meiosis II
 Concept Mapping Meiosis I and Meiosis II Complete the events chains about meiosis I and meiosis II. These terms may be used more than once: chromosomes, condense, cytokinesis, equator, line up, nuclei,
Concept Mapping Meiosis I and Meiosis II Complete the events chains about meiosis I and meiosis II. These terms may be used more than once: chromosomes, condense, cytokinesis, equator, line up, nuclei,
Dr. Ramesh U4L3 Meiosis
 Dr. Ramesh U4L3 Meiosis The Cell Cycle and Cell Division: MEIOSIS The Cell Cycle and Cell Division KEY CONCEPT: Meiosis Halves the Nuclear Chromosome Content and Generates Diversity Organisms have two
Dr. Ramesh U4L3 Meiosis The Cell Cycle and Cell Division: MEIOSIS The Cell Cycle and Cell Division KEY CONCEPT: Meiosis Halves the Nuclear Chromosome Content and Generates Diversity Organisms have two
Meiosis produces haploid gametes.
 Section 1: produces haploid gametes. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions How does the reduction in chromosome number occur during meiosis? What are the stages of
Section 1: produces haploid gametes. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions How does the reduction in chromosome number occur during meiosis? What are the stages of
Lesson Overview Meiosis
 11.4 As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures? What cellular
11.4 As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures? What cellular
MEIOSIS C H A P T E R 1 3
 MEIOSIS CHAPTER 13 CENTRAL DOGMA OF BIOLOGY DNA RNA Protein OFFSPRING ACQUIRE GENES FROM PARENTS Genes are segments of DNA that program specific traits. Genetic info is transmitted as specific sequences
MEIOSIS CHAPTER 13 CENTRAL DOGMA OF BIOLOGY DNA RNA Protein OFFSPRING ACQUIRE GENES FROM PARENTS Genes are segments of DNA that program specific traits. Genetic info is transmitted as specific sequences
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Name: AP Biology Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Define the following terms: gene locus gamete male gamete female gamete
Name: AP Biology Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Define the following terms: gene locus gamete male gamete female gamete
THINK ABOUT IT. Lesson Overview. Meiosis. As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located.
 Notes THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
Notes THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
Heredity Variation Genetics Meiosis
 Genetics Warm Up Exercise: -Using your previous knowledge of genetics, determine what maternal genotype would most likely yield offspring with such characteristics. -Use the genotype that you came up with
Genetics Warm Up Exercise: -Using your previous knowledge of genetics, determine what maternal genotype would most likely yield offspring with such characteristics. -Use the genotype that you came up with
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles
 Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Meiosis and Mendel. Chapter 6
 Meiosis and Mendel Chapter 6 6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS Key Concept Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. Body Cells vs. Gametes You have body cells and gametes body cells
Meiosis and Mendel Chapter 6 6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS Key Concept Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. Body Cells vs. Gametes You have body cells and gametes body cells
Section 11 1 The Work of Gregor Mendel
 Chapter 11 Introduction to Genetics Section 11 1 The Work of Gregor Mendel (pages 263 266) What is the principle of dominance? What happens during segregation? Gregor Mendel s Peas (pages 263 264) 1. The
Chapter 11 Introduction to Genetics Section 11 1 The Work of Gregor Mendel (pages 263 266) What is the principle of dominance? What happens during segregation? Gregor Mendel s Peas (pages 263 264) 1. The
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics
 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics Mitosis is a form of asexual reproduction This means that it only requires 1 organism (ex. Skin cells dividing) For growth and repair in somatic (body) cells! Results
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics Mitosis is a form of asexual reproduction This means that it only requires 1 organism (ex. Skin cells dividing) For growth and repair in somatic (body) cells! Results
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction. Chapter 10. Halving the Chromosome Number. Homologous Pairs
 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 10 Outline Reduction in Chromosome Number Homologous Pairs Meiosis Overview Genetic Recombination Crossing-Over Independent Assortment Fertilization Meiosis I Meiosis
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 10 Outline Reduction in Chromosome Number Homologous Pairs Meiosis Overview Genetic Recombination Crossing-Over Independent Assortment Fertilization Meiosis I Meiosis
Modeling Genetic Variation in Gametes PSI AP Biology
 Modeling Genetic Variation in Gametes PSI AP Biology Name: Objective Students will model the processes of gamete formation that increase genetic variation: independent assortment, crossing-over, and fertilization.
Modeling Genetic Variation in Gametes PSI AP Biology Name: Objective Students will model the processes of gamete formation that increase genetic variation: independent assortment, crossing-over, and fertilization.
Sexual Reproduction ( Cell Division ) - Chromosome # s
 Sexual Reproduction ( Cell Division ) - Chromosome # s somatic cells: all the cells in the body except for specialized sex cells each somatic cell has a specific # of chromosomes - ( humans have 46, 23
Sexual Reproduction ( Cell Division ) - Chromosome # s somatic cells: all the cells in the body except for specialized sex cells each somatic cell has a specific # of chromosomes - ( humans have 46, 23
AP Biology Unit 6 Practice Test 1. A group of cells is assayed for DNA content immediately following mitosis and is found to have an average of 8
 AP Biology Unit 6 Practice Test Name: 1. A group of cells is assayed for DNA content immediately following mitosis and is found to have an average of 8 picograms of DNA per nucleus. How many picograms
AP Biology Unit 6 Practice Test Name: 1. A group of cells is assayed for DNA content immediately following mitosis and is found to have an average of 8 picograms of DNA per nucleus. How many picograms
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview: Hereditary Similarity and Variation
 Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview: Hereditary Similarity and Variation Living organisms Are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind Biology, 7 th Edition Neil Campbell
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview: Hereditary Similarity and Variation Living organisms Are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind Biology, 7 th Edition Neil Campbell
THE WORK OF GREGOR MENDEL
 GENETICS NOTES THE WORK OF GREGOR MENDEL Genetics-. - Austrian monk- the father of genetics- carried out his work on. Pea flowers are naturally, which means that sperm cells fertilize the egg cells in
GENETICS NOTES THE WORK OF GREGOR MENDEL Genetics-. - Austrian monk- the father of genetics- carried out his work on. Pea flowers are naturally, which means that sperm cells fertilize the egg cells in
Essential Questions. Meiosis. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education
 Essential Questions How does the reduction in chromosome number occur during meiosis? What are the stages of meiosis? What is the importance of meiosis in providing genetic variation? Meiosis Vocabulary
Essential Questions How does the reduction in chromosome number occur during meiosis? What are the stages of meiosis? What is the importance of meiosis in providing genetic variation? Meiosis Vocabulary
Problem Set 3 10:35 AM January 27, 2011
 BIO322: Genetics Douglas J. Burks Department of Biology Wilmington College of Ohio Problem Set 3 Due @ 10:35 AM January 27, 2011 Chapter 4: Problems 3, 5, 12, 23, 25, 31, 37, and 41. Chapter 5: Problems
BIO322: Genetics Douglas J. Burks Department of Biology Wilmington College of Ohio Problem Set 3 Due @ 10:35 AM January 27, 2011 Chapter 4: Problems 3, 5, 12, 23, 25, 31, 37, and 41. Chapter 5: Problems
CHAPTER 3 VOCABULARY (for now)
 3.1 Meiosis CHAPTER 3 VOCABULARY (for now) VOCABULARY WORD VOCABULARY WORD diploid number Independent assortment haploid number gametes homologous chromosomes zygote genetic diversity Crossing over Sexual
3.1 Meiosis CHAPTER 3 VOCABULARY (for now) VOCABULARY WORD VOCABULARY WORD diploid number Independent assortment haploid number gametes homologous chromosomes zygote genetic diversity Crossing over Sexual
Bellwork. Many organisms reproduce via asexual and sexual reproduction. How would we look if we reproduced mitotically?
 Bellwork Many organisms reproduce via asexual and sexual reproduction. How would we look if we reproduced mitotically? SC.912.L.16.17 Meiosis Functions in Sexual Reproduction Other Standards Addressed:
Bellwork Many organisms reproduce via asexual and sexual reproduction. How would we look if we reproduced mitotically? SC.912.L.16.17 Meiosis Functions in Sexual Reproduction Other Standards Addressed:
Meiosis and Life Cycles - 1
 Meiosis and Life Cycles - 1 We have just finished looking at the process of mitosis, a process that produces cells genetically identical to the original cell. Mitosis ensures that each cell of an organism
Meiosis and Life Cycles - 1 We have just finished looking at the process of mitosis, a process that produces cells genetically identical to the original cell. Mitosis ensures that each cell of an organism
Chapter 11 INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS
 Chapter 11 INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS 11-1 The Work of Gregor Mendel I. Gregor Mendel A. Studied pea plants 1. Reproduce sexually (have two sex cells = gametes) 2. Uniting of male and female gametes = Fertilization
Chapter 11 INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS 11-1 The Work of Gregor Mendel I. Gregor Mendel A. Studied pea plants 1. Reproduce sexually (have two sex cells = gametes) 2. Uniting of male and female gametes = Fertilization
Comparing Mitosis And Meiosis Answer Key
 Comparing Answer Key Free PDF ebook Download: Comparing Answer Key Download or Read Online ebook comparing mitosis and meiosis answer key in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Mitosis & Compare
Comparing Answer Key Free PDF ebook Download: Comparing Answer Key Download or Read Online ebook comparing mitosis and meiosis answer key in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Mitosis & Compare
Chromosome duplication and distribution during cell division
 CELL DIVISION AND HEREDITY Student Packet SUMMARY IN EUKARYOTES, HERITABLE INFORMATION IS PASSED TO THE NEXT GENERATION VIA PROCESSES THAT INCLUDE THE CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS /MEIOSIS AND FERTILIZATION Mitosis
CELL DIVISION AND HEREDITY Student Packet SUMMARY IN EUKARYOTES, HERITABLE INFORMATION IS PASSED TO THE NEXT GENERATION VIA PROCESSES THAT INCLUDE THE CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS /MEIOSIS AND FERTILIZATION Mitosis
Lesson Overview 11.4 Meiosis
 Lesson Overview 11.4 Meiosis THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the
Lesson Overview 11.4 Meiosis THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Outline Overview: Variations on a Theme Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. Offspring resemble their parents
Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Outline Overview: Variations on a Theme Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. Offspring resemble their parents
Name: Period: EOC Review Part F Outline
 Name: Period: EOC Review Part F Outline Mitosis and Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences
Name: Period: EOC Review Part F Outline Mitosis and Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences
Meiosis. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Meiosis Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction requires fertilization, a union of two cells from two individual organisms. If those two cells each contain one set of chromosomes, then the resulting cell
Meiosis Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction requires fertilization, a union of two cells from two individual organisms. If those two cells each contain one set of chromosomes, then the resulting cell
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 10 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 10 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
Lesson 1 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis
 Lesson 1 Name Date Class A. What is sexual reproduction? 1. produces an offspring when genetic materials from two different sex cells combine. a. The female sex cell, a(n), forms in an ovary. b. The male
Lesson 1 Name Date Class A. What is sexual reproduction? 1. produces an offspring when genetic materials from two different sex cells combine. a. The female sex cell, a(n), forms in an ovary. b. The male
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis. Chapter 11
 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Chapter 11 1 Sexual life cycle Made up of meiosis and fertilization Diploid cells Somatic cells of adults have 2 sets of chromosomes Haploid cells Gametes (egg and sperm)
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Chapter 11 1 Sexual life cycle Made up of meiosis and fertilization Diploid cells Somatic cells of adults have 2 sets of chromosomes Haploid cells Gametes (egg and sperm)
Learning Objectives:
 Review! Why is cell division important?! What are the different types of cell division?! What are these useful for?! What are the products?! What is a somatic cell?! What is a sex cell?! What is a haploid
Review! Why is cell division important?! What are the different types of cell division?! What are these useful for?! What are the products?! What is a somatic cell?! What is a sex cell?! What is a haploid
Ladies and Gentlemen.. The King of Rock and Roll
 Ladies and Gentlemen.. The King of Rock and Roll Learning Objectives: The student is able to construct an explanation, using visual representations or narratives, as to how DNA in chromosomes is transmitted
Ladies and Gentlemen.. The King of Rock and Roll Learning Objectives: The student is able to construct an explanation, using visual representations or narratives, as to how DNA in chromosomes is transmitted
Name Class Date. KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have.
 Section 1: Chromosomes and Meiosis KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. VOCABULARY somatic cell autosome fertilization gamete sex chromosome diploid homologous
Section 1: Chromosomes and Meiosis KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. VOCABULARY somatic cell autosome fertilization gamete sex chromosome diploid homologous
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Variations on a Theme Living
13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Variations on a Theme Living
Introduction to Genetics
 Introduction to Genetics The Work of Gregor Mendel B.1.21, B.1.22, B.1.29 Genetic Inheritance Heredity: the transmission of characteristics from parent to offspring The study of heredity in biology is
Introduction to Genetics The Work of Gregor Mendel B.1.21, B.1.22, B.1.29 Genetic Inheritance Heredity: the transmission of characteristics from parent to offspring The study of heredity in biology is
Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
 Biology 110 Sec. 11 J. Greg Doheny Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Quiz Questions: 1. What word do you use to describe a chromosome or gene allele that we inherit from our Mother? From our Father?
Biology 110 Sec. 11 J. Greg Doheny Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Quiz Questions: 1. What word do you use to describe a chromosome or gene allele that we inherit from our Mother? From our Father?
Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1
 Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1 Introduction In this activity, you will learn how you inherited two copies of each gene, one from your mother and one from your father.
Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1 Introduction In this activity, you will learn how you inherited two copies of each gene, one from your mother and one from your father.
MGC New Life Christian Academy
 A. Meiosis Main Idea: Meiosis produces haploid gametes. Key Concept: Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces offspring that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent. Sexual
A. Meiosis Main Idea: Meiosis produces haploid gametes. Key Concept: Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces offspring that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent. Sexual
Cellular Reproduction. MXMS 7th Grade Science
 Cellular Reproduction MXMS 7th Grade Science What is cell division? 2 primary methods allow for cells to divide and reproduce themselves: A. Mitosis: produces identical offspring B. Meiosis: produces genetically
Cellular Reproduction MXMS 7th Grade Science What is cell division? 2 primary methods allow for cells to divide and reproduce themselves: A. Mitosis: produces identical offspring B. Meiosis: produces genetically
Chapter 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics
 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics Section 1: Meiosis Section 2: Mendelian Genetics Section 3: Gene Linkage and Polyploidy Click on a lesson name to select. Chromosomes and Chromosome Number! Human body
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics Section 1: Meiosis Section 2: Mendelian Genetics Section 3: Gene Linkage and Polyploidy Click on a lesson name to select. Chromosomes and Chromosome Number! Human body
Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1
 Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1 How does a child inherit one copy of each gene from each parent? Compare what you already know with this flowchart. 1. Fill in each blank
Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1 How does a child inherit one copy of each gene from each parent? Compare what you already know with this flowchart. 1. Fill in each blank
Cell division / Asexual reproduction
 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produces cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes same genetic information Asexual
Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produces cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes same genetic information Asexual
11-4 Meiosis Meiosis. Slide 1 of 35. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with
11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with
Cell Division: the process of copying and dividing entire cells The cell grows, prepares for division, and then divides to form new daughter cells.
 Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
Ch. 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles
 Introduction Ch. 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles 2004-05 Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. -Offspring resemble their parents more than they do less closely
Introduction Ch. 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles 2004-05 Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. -Offspring resemble their parents more than they do less closely
Learning Objectives LO 3.7 The student can make predictions about natural phenomena occurring during the cell cycle. [See SP 6.4]
![Learning Objectives LO 3.7 The student can make predictions about natural phenomena occurring during the cell cycle. [See SP 6.4] Learning Objectives LO 3.7 The student can make predictions about natural phenomena occurring during the cell cycle. [See SP 6.4]](/thumbs/94/118687827.jpg) Big Ideas 3.A.2: In eukaryotes, heritable information is passed to the next generation via processes that include the cell cycle and mitosis or meiosis plus fertilization. CHAPTER 13 MEIOSIS AND SEXUAL
Big Ideas 3.A.2: In eukaryotes, heritable information is passed to the next generation via processes that include the cell cycle and mitosis or meiosis plus fertilization. CHAPTER 13 MEIOSIS AND SEXUAL
4 Metaphase I 4 Anaphase I 4 Telophase I 2/4 Prophase II 2 Metaphase II 2 Anaphase II 2 Telophase II 2 Cytokinesis 2
 Meiosis What therefore God hath joined together, let not man put asunder Mark 10:6-9 Stage Table 1 Meiosis (Without Crossover Event) # Chromosomes Per Cell Prophase I 4 Metaphase I 4 Anaphase I 4 Telophase
Meiosis What therefore God hath joined together, let not man put asunder Mark 10:6-9 Stage Table 1 Meiosis (Without Crossover Event) # Chromosomes Per Cell Prophase I 4 Metaphase I 4 Anaphase I 4 Telophase
Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1
 Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1 Introduction In this activity, you will learn how you inherited two copies of each gene, one from your mother and one from your father.
Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1 Introduction In this activity, you will learn how you inherited two copies of each gene, one from your mother and one from your father.
DNA Structure and Function
 DNA Structure and Function Nucleotide Structure 1. 5-C sugar RNA ribose DNA deoxyribose 2. Nitrogenous Base N attaches to 1 C of sugar Double or single ring Four Bases Adenine, Guanine, Thymine, Cytosine
DNA Structure and Function Nucleotide Structure 1. 5-C sugar RNA ribose DNA deoxyribose 2. Nitrogenous Base N attaches to 1 C of sugar Double or single ring Four Bases Adenine, Guanine, Thymine, Cytosine
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
BIOLOGY. Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Variations on a Theme Living
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Variations on a Theme Living
Biology Kevin Dees. Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Reproduction Characteristic of all living things Reproduction also involves the transmission of traits from one generation to the next; inheritance Heredity Latin
Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Reproduction Characteristic of all living things Reproduction also involves the transmission of traits from one generation to the next; inheritance Heredity Latin
Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles. Reproduction
 Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Reproduction Characteristic of all living things Reproduction also involves the transmission of traits from one generation to the next; inheritance Heredity Latin
Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Reproduction Characteristic of all living things Reproduction also involves the transmission of traits from one generation to the next; inheritance Heredity Latin
2. Next, try to describe the cell cycle as follows: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis
 1. First, tell me something exciting you did over spring break! 2. Next, try to describe the cell cycle as follows: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis *Reminder*-Thursday
1. First, tell me something exciting you did over spring break! 2. Next, try to describe the cell cycle as follows: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis *Reminder*-Thursday
