[Byline: Erica Bree Rosenblum1*, Jamie Voyles2, Thomas J. Poorten1, Jason E. Stajich3,4
|
|
|
- Peregrine Stafford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chytrid fungus, frogs - worldwide: review article To: (05) Zoonoses, general; (23) Veterinary education ************************************************* CHYTRID FUNGUS, FROGS - WORLDWIDE: REVIEW ARTICLE ************************************************** A ProMED-mail post Date: 29 Jan 2010 Source: PLoS Pathogens [edited] < The Deadly Chytrid Fungus: A Story of an Emerging Pathogen -- Emerging infectious diseases present a great challenge for the health of both humans and wildlife. The increasing prevalence of drug-resistant fungal pathogens in humans [1] and recent outbreaks of novel fungal pathogens in wildlife populations [2] underscore the need to better understand the origins and mechanisms of fungal pathogenicity. One of the most dramatic examples of fungal impacts on vertebrate populations is the effect of the amphibian disease chytridiomycosis, caused by the chytrid fungus _Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis_ (_Bd_). Amphibians around the world are experiencing unprecedented population losses and local extinctions [3]. While there are multiple causes of amphibian declines, many catastrophic die-offs are attributed to _Bd_ [4],[5]. The chytrid pathogen has been documented in hundreds of amphibian species, and reports of Bd 's impact on additional species and in additional geographic regions are accumulating at an alarming rate (e.g., see < _Bd_ is a microbial, aquatic fungus with distinct life stages. The motile stage, called a zoospore, swims using a flagellum and initiates the colonization of frog skin. Within the host epidermal cells, a zoospore forms a spherical thallus, which matures and produces new zoospores by dividing asexually, renewing the cycle of infection when zoospores are released to the skin surface [Figure 1 -- see the original article at the Source URL for figures]. _Bd_ is considered an emerging pathogen, discovered and described only a decade ago [6],[7]. Despite intensive ecological study of _Bd_ over the last decade, a number of unanswered questions remain. Here we summarize what has been recently learned about this lethal pathogen. _Bd_ is a member of a basal group of fungi, the Chytridiomycota, and is the only known member of its order (the Rhizophydiales) to parasitize vertebrates. _Bd_ is phylogenetically distant from any of the other ~1000 chytrid species [8], and the lack of close relatives capable of parasitizing vertebrates suggests that _Bd_ pathogenicity evolved relatively recently. Further, population genetic data on _Bd_ isolates collected from different amphibian populations around the world suggest that _Bd_ is a recently spread pathogen rather than being endemic with altered relationships with hosts due to environmental change [9],[10]. Africa was initially proposed as the geographic origin because the earliest evidence of _Bd_ is from skin samples from African clawed frogs (_Xenopus laevis_) collected in African clawed frogs were traded globally for decades (from the 1930s-1960s) for pregnancy assays in humans [11]. Although based on a small sample size, recent population genetic work shows reduced genetic diversity of isolates from African clawed frogs and, instead, high allelic diversity in North American isolates collected from bullfrogs (_Rana catesbeiana_) [10],[12]. Although additional genetic work is needed, these studies suggest that _Bd_'s origin may not be in Africa. Anthropogenic spread of _Bd_ is a plausible explanation for at least some introductions [11],[13]. Some amphibian species that are traded globally may serve as disease reservoirs because they can carry _Bd_ infections without morbidity. A number of mysteries remain about how _Bd_ has dispersed to and persisted in remote pristine environments where anthropogenic introduction is unlikely. If _Bd_ can survive independently of
2 amphibian hosts, it must use non-amphibian organic materials as nutrient resources. Although _Bd_ DNA has been detected in water bodies [14] and on rocks [15], conclusive evidence of _Bd_ persistence in the environment is lacking. In infected amphibians, _Bd_ is found in the cells of the epidermis and pathological abnormalities include a thickening of the outer layer of skin [6]. Cutaneous fungal infections in other vertebrates are not typically lethal, but amphibian skin is unique because it is physiologically active, tightly regulating the exchange of respiratory gases, water, and electrolytes. Thus, the physiological importance of the skin makes amphibians particularly vulnerable to skin infections. It has been hypothesized that _Bd_ disrupts normal regulatory functioning of frog skin, and evidence suggests that electrolyte depletion and osmotic imbalance that occurs in amphibians with severe chytridiomycosis are sufficient to cause mortality [16],[17]. The molecular factors influencing _Bd_ pathogenicity and virulence have yet to be conclusively identified. Some evidence suggests that _Bd_ enzymatic activity directly influences pathogenesis. The initial penetration of _Bd_ into amphibian epidermal cells likely requires digestive enzymes. In culture, _Bd_ secretes extracellular proteases that degrade casein and gelatin [18],[19]. At the molecular level, genomic research into _Bd_ is revealing intriguing expression patterns in genes such as those for serine protease and fungalysin metallopeptidase [20], 2 gene families involved in pathogenesis in other fungal pathogens. Full genomes of 2 _Bd_ isolates have recently been sequenced, providing new resources for the study of molecular mechanisms of pathogenicity [21]. Several studies have shown variation in virulence among _Bd_ isolates. In experimental infections, differences in frog survival have been observed when exposed to different _Bd_ isolates (e.g., [22],[23]). Initial proteomic work suggests that _Bd_ isolates differ in their proteome profiles [23]. However, controlled infection experiments with reciprocal host isolate treatments and paired genomic and proteomic studies are necessary to identify the functional determinants of _Bd_ virulence. Species, populations, and individuals vary widely in susceptibility to chytridiomycosis. Mortality rates in laboratory infection experiments can range from 0 percent to 100 percent, depending on the species (e.g., [22],[24]), age of animals [25], and temperature regime [26]. In the wild, some species and populations are extirpated while others, those that survive initial declines, persist with various levels of infection (e.g., [27],[28]). While the disease dynamics are undoubtedly influenced by local environmental conditions, particularly temperature, inherent differences in host susceptibility and behavior are also important. Colonization by _Bd_ and subsequent disease development may be influenced by host defense mechanisms, such as secretions of antimicrobial peptides [29] or bacterial commensals with anti-fungal properties [30]. Some species-specific behavioral characteristics such as microhabitat selection, basking, aggregating in retreat sites, or association with water bodies may also affect the likelihood of infection and disease [31],[32]. Despite many gaps in our understanding of chytridiomycosis, we are beginning to unravel important elements of this lethal disease and make progress towards amphibian conservation. Multiple conservation strategies have been proposed and are currently being implemented to mitigate the threat of chytridiomycosis. These plans include efforts to limit the spread of the disease, invest in captive breeding programs for highly vulnerable amphibians, and advance basic disease research. Continued research on the biology of both the host and the pathogen is necessary, and efforts to catalog and preserve the _Bd_ isolates for ongoing research are particularly important (see < and < [33]). The conservation challenges we face with chytridiomycosis -- and other emerging pathogens -- are best confronted by increasing our knowledge of disease processes from both host and pathogen perspectives. [Byline: Erica Bree Rosenblum1*, Jamie Voyles2, Thomas J. Poorten1, Jason E. Stajich3,4
3 1 Department of Biological Sciences, University of Idaho, Moscow, Idaho, United States of America 2 School of Public Health, Tropical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sciences, James Cook University, Townsville, Queensland, Australia 3 Department of Plant and Microbial Biology, University of California, Berkeley, California, United States of America 4 Department of Plant Pathology and Microbiology, University of California, Riverside, California, United States of America Editor: Hiten D. Madhani, University of California San Francisco, United States of America] Citation: - Rosenblum EB, Voyles J, Poorten TJ, Stajich JE (2010) The Deadly Chytrid Fungus: A Story of an Emerging Pathogen. PLoS Pathog 6(1): e doi: /journal.ppat References: --- [See the original article at the Source URL for links to these articles] 1 Warnock DW (2006) Fungal diseases: an evolving public health challenge. Med Mycol 44: 697? Blehert DS, Hicks AC, Behr M, Meteyer CU, Berlowski-Zier BM, et al. (2009) Bat white-nose syndrome: an emerging fungal pathogen? Science 323: 227? Stuart SN, Chanson JS, Cox NA, Young BE, Rodrigues ASL, et al. (2004) Status and trends of amphibian declines and extinctions worldwide. Science 306: Lips KR, Brem F, Brenes R, Reeve JD, Alford RA, et al. (2006) Emerging infectious disease and the loss of biodiversity in a Neotropical amphibian community. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103: 3165? Schloegel L, Hero JM, Berger L, Speare R, McDonald KR, et al. (2006) The decline of the sharp-snouted day frog (Taudactylus acutirostris): the first documented case of extinction by infection in a free-ranging wildlife species? EcoHealth 3: Berger L, Speare R, Daszak P, Green DE, Cunningham AA, et al. (1998) Chytridiomycosis causes amphibian mortality associated with population declines in the rain forests of Australia and Central America. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95: Longcore JE, Pessier AP, Nichols DK (1999) Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis gen et sp nov, a chytrid pathogenic to amphibians. Mycologia 91: James TY, Letcher PM, Longcore JE, Mozley-Standridge SE, Porter D, et al. (2006) A molecular phylogeny of the flagellated fungi
4 (Chytridiomycota) and description of a new phylum (Blastocladiomycota). Mycologia 98: Morehouse EA, James TY, Ganley ARD, Vilgalys R, Berger L, et al. (2003) Multilocus sequence typing suggests the chytrid pathogen of amphibians is a recently emerged clone. Mol Ecol 12: James TY, Litvintseva AP, Vilgalys R, Morgan JAT, Taylor JW, et al. (2009) Rapid global expansion of the fungal disease chytridiomycosis into declining and healthy amphibian populations. PLoS Pathog e : doi: /journal.ppat Weldon C, du Preez LH, Hyatt AD, Muller R, Speare R (2004) Origin of the amphibian chytrid fungus. Emerg Infect Dis 10: Goka K, Yokoyama J, Une Y, Kuroki T, Suzuki K, Nakahara M, Kobayashi A, Inaba S, Mizutani T, Hyatt AD (2009) Amphibian chytridiomycosis in Japan: distribution, haplotypes and possible route of entry into Japan. Molecular Ecology 18: Fisher MC, Garner TWJ (2007) The relationship between the emergence of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, the international trade in amphibians and introduced amphibian species. Fungal Biol Rev 21: Kirshtein JD, Anderson CW, Wood JS, Longcore JE, Voytek MA (2007) Quantitative PCR detection of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis DNA from sediments and water. Dis Aquat Org 77: Walker SF, Salas MB, Jenkins D, Garner TWJ, Cunningham AA, et al. (2007) Environmental detection of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis in a temperate climate. Dis Aquat Org 77: Voyles J, Berger L, Young S, Speare R, Webb R, et al. (2007) Electrolyte depletion and osmotic imbalance in amphibians with chytridiomycosis. Dis Aquat Org 77: 113? Voyles J, Young S, Berger L, Campbell C, Voyles WF, Dinudom A, Cook, Webb R, Alford RA, Skerratt LF, Speare R (2009) Pathogenesis of chytridiomycosis, a cause of catastrophic amphibian declines. Science 326: Piotrowski JS, Annis SL, Longcore JE (2004) Physiology of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, a chytrid pathogen of amphibians. Mycologia 96: Symonds EP, Trott DJ, Bird PS, Mills P (2008) Growth characteristics and enzyme activity in
5 Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis isolates. Mycopathologia 166: Rosenblum EB, Stajich JE, Maddox N, Eisen MB (2008) Global gene expression profiles for life stages of the deadly amphibian pathogen Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105: Rosenblum EB, Fisher MC, James TY, Stajich JE, Longcore JE, Gentry LR, Poorten TJ (2009) A molecular perspective: biology of the emerging pathogen Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis. Dis Aquat Org. doi: /dao Berger L, Marantelli G, Skerratt LL, Speare R (2005) Virulence of the amphibian chytrid fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis varies with the strain. Dis Aquat Org 68: Fisher MC, Bosch J, Yin Z, Stead DA, Walker J, et al. (2009) Proteomic and phenotypic profiling of the amphibian pathogen Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis shows that genotype is linked to virulence. Mol Ecol 18: Daszak P, Strieby A, Cunningham AA, Longcore JE, Brown CC, et al. (2004) Experimental evidence that the bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana) is a potential carrier of chytridiomycosis, an emerging fungal disease of amphibians. Herpetolog J 14: Lamirande EW, Nichols DK (2002) Effects of host age on susceptibility to cutaneous chytridiomycosis in blue-and-yellow poison dart frogs (Dendrobates tinctorius). St. Paul, Minnesota.: pp In Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on the Pathology of Reptiles and Amphibians, 18?19 April Woodhams DC, Alford RA, Marantelli G (2003) Emerging disease of amphibians cured by elevated body temperature. Dis Aquat Org 55: Retallick RWR, McCallum H, Speare R (2004) Endemic infection of the amphibian chytrid fungus in a frog community post-decline. PLoS Biol 2: e351. doi: /journal.pbio Briggs CJ, Vredenburg VT, Knapp RA, Rachowicz LJ (2005) Investigating the population-level effects of chytridiomycosis: An emerging infectious disease of amphibians. Ecology 86: Woodhams DC, Ardipradja K, Alford RA, Marantelli G, Reinert LK, et al. (2007) Resistance to chytridiomycosis varies among amphibian species and is correlated with skin peptide defenses. Anim Conserv 10:
6 30 Harris RN, James TY, Lauer A, Simon MA, Patel A (2006) Amphibian pathogen Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis is inhibited by the cutaneous bacteria of Amphibian species. Ecohealth 3: Lips KR, Reeve JD, Witters LR (2003) Ecological traits predicting amphibian population declines in Central America. Conserv Biol 17: Rowley JJL, Alford RA (2007) Behaviour of Australian rainforest stream frogs may affect the transmission of chytridiomycosis. Dis Aquat Org 77: Voyles J, Cashins SD, Rosenblum EB, Pushendorf R (2009) Preserving pathogens for wildlife conservation: a case for action on amphibian declines. Oryx 43: Communicated by: Mark A. Jensen <maj@fortinbras.us> [This article is a brief summary of a wide variety of research. It appears to be almost a summary type of article. - Mod.TG] [see also: 2009 Chytrid fungus, frog - South Korea Chytrid fungus, frog - Philippines: (Luzon) Chytrid fungus, frogs - Panama Chytrid fungus, frogs - Spain (Majorca) Chytrid fungus, frogs - Japan (02): wild frogs Chytrid fungus, frogs - Japan Chytrid fungus, amphibian - worldwide Chytrid fungus, frogs - worldwide: possible source Chytrid fungus, frogs - South Africa Chytrid fungus, frogs - UK (England) Chytrid fungus, frogs: background Chytrid fungus, frogs - USA (Colorado) (02) Chytrid fungus, frogs - USA (Arizona & Colorado) ]
Evolution and pathogenicity in the deadly chytrid pathogen of amphibians. Erica Bree Rosenblum UC Berkeley
 Evolution and pathogenicity in the deadly chytrid pathogen of amphibians Erica Bree Rosenblum UC Berkeley Emerging infectious disease Emerging infectious disease EID events have risen significantly over
Evolution and pathogenicity in the deadly chytrid pathogen of amphibians Erica Bree Rosenblum UC Berkeley Emerging infectious disease Emerging infectious disease EID events have risen significantly over
Distribution Limits of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis: A Case Study in the Rocky Mountains, USA
 Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 45(4), 2009, pp. 1198 1202 # Wildlife Disease Association 2009 Distribution Limits of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis: A Case Study in the Rocky Mountains, USA Blake R. Hossack,
Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 45(4), 2009, pp. 1198 1202 # Wildlife Disease Association 2009 Distribution Limits of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis: A Case Study in the Rocky Mountains, USA Blake R. Hossack,
Herpetological Review
 Herpetological Review chytrid fungus in American bullfrogs (Lithobates catesbeianus) along the platte River, nebraska, usa mary J. harner Platte River Whooping Crane Critical Habitat Maintenance Trust,
Herpetological Review chytrid fungus in American bullfrogs (Lithobates catesbeianus) along the platte River, nebraska, usa mary J. harner Platte River Whooping Crane Critical Habitat Maintenance Trust,
Introduction. Abstract
 Temperature alters reproductive life history patterns in Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, a lethal pathogen associated with the global loss of amphibians Jamie Voyles 1,4, Leah R. Johnson 2,3, Cheryl J.
Temperature alters reproductive life history patterns in Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, a lethal pathogen associated with the global loss of amphibians Jamie Voyles 1,4, Leah R. Johnson 2,3, Cheryl J.
Spread of Chytridiomycosis Has Caused the Rapid Global Decline and Extinction of Frogs
 EcoHealth 4, 125 134, 2007 DOI: 10.1007/s10393-007-0093-5 Ó 2007 EcoHealth Journal Consortium Spread of Chytridiomycosis Has Caused the Rapid Global Decline and Extinction of Frogs Lee Francis Skerratt,
EcoHealth 4, 125 134, 2007 DOI: 10.1007/s10393-007-0093-5 Ó 2007 EcoHealth Journal Consortium Spread of Chytridiomycosis Has Caused the Rapid Global Decline and Extinction of Frogs Lee Francis Skerratt,
Effect of Temperature on Host Response to Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis Infection in the Mountain Yellow-legged Frog (Rana muscosa)
 Effect of Temperature on Host Response to Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis Infection in the Mountain Yellow-legged Frog (Rana muscosa) Authors: Sara E. Andre, John Parker, and Cheryl J. Briggs Source: Journal
Effect of Temperature on Host Response to Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis Infection in the Mountain Yellow-legged Frog (Rana muscosa) Authors: Sara E. Andre, John Parker, and Cheryl J. Briggs Source: Journal
Use of Immunohistochemistry to Diagnose Chytridiomycosis in Dyeing Poison Dart Frogs (Dendrobates tinctorius)
 Use of Immunohistochemistry to Diagnose Chytridiomycosis in Dyeing Poison Dart Frogs (Dendrobates tinctorius) Author(s): Tracy Van Ells, James Stanton, Ann Strieby, Peter Daszak, Alex D. Hyatt, and Corrie
Use of Immunohistochemistry to Diagnose Chytridiomycosis in Dyeing Poison Dart Frogs (Dendrobates tinctorius) Author(s): Tracy Van Ells, James Stanton, Ann Strieby, Peter Daszak, Alex D. Hyatt, and Corrie
The ecology and impact of chytridiomycosis: an emerging disease of amphibians
 Review The ecology and impact of chytridiomycosis: an emerging disease of amphibians A. Marm Kilpatrick 1, Cheryl J. Briggs 2 and Peter Daszak 3 1 Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, University
Review The ecology and impact of chytridiomycosis: an emerging disease of amphibians A. Marm Kilpatrick 1, Cheryl J. Briggs 2 and Peter Daszak 3 1 Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, University
Comparative analysis of anti-bd bacteria from six Malagasy frog species of Ranomafana National Park
 James Madison University JMU Scholarly Commons Senior Honors Projects, 2010-current Honors College Spring 2015 Comparative analysis of anti-bd bacteria from six Malagasy frog species of Ranomafana National
James Madison University JMU Scholarly Commons Senior Honors Projects, 2010-current Honors College Spring 2015 Comparative analysis of anti-bd bacteria from six Malagasy frog species of Ranomafana National
Chytridiomycosis: a global threat to amphibians
 Rev. sci. tech. Off. int. Epiz., 2013, 32 (3),... -... Chytridiomycosis: a global threat to amphibians P.L.L. Pereira (1)*, A.M.C. Torres M. Hijosa-Valsero (2) & E. Bécares (2) (1), D.F.M. Soares (1),
Rev. sci. tech. Off. int. Epiz., 2013, 32 (3),... -... Chytridiomycosis: a global threat to amphibians P.L.L. Pereira (1)*, A.M.C. Torres M. Hijosa-Valsero (2) & E. Bécares (2) (1), D.F.M. Soares (1),
Species-level correlates of susceptibility to the pathogenic amphibian fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis in the United States
 Biodivers Conserv (2011) 20:1911 1920 DOI 10.1007/s10531-011-0066-4 ORIGINAL PAPER Species-level correlates of susceptibility to the pathogenic amphibian fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis in the United
Biodivers Conserv (2011) 20:1911 1920 DOI 10.1007/s10531-011-0066-4 ORIGINAL PAPER Species-level correlates of susceptibility to the pathogenic amphibian fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis in the United
INVESTIGATING THE POPULATION-LEVEL EFFECTS OF CHYTRIDIOMYCOSIS: AN EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASE OF AMPHIBIANS
 Ecology, 86(12), 2005, pp. 3149 3159 2005 by the Ecological Society of America INVESTIGATING THE POPULATION-LEVEL EFFECTS OF CHYTRIDIOMYCOSIS: AN EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASE OF AMPHIBIANS CHERYL J. BRIGGS,
Ecology, 86(12), 2005, pp. 3149 3159 2005 by the Ecological Society of America INVESTIGATING THE POPULATION-LEVEL EFFECTS OF CHYTRIDIOMYCOSIS: AN EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASE OF AMPHIBIANS CHERYL J. BRIGGS,
Amphibian chytridiomycosis: strategies for captive management and conservation
 REVIEW: AMPHIBIANS & CHYTRIDIOMYCOSIS: STRATEGIES FOR CAPTIVE MANAGEMENT 85 Int. Zoo Yb. (2007) 41: 85 95 DOI:10.1111/j.1748-1090.2007.00010.x Amphibian chytridiomycosis: strategies for captive management
REVIEW: AMPHIBIANS & CHYTRIDIOMYCOSIS: STRATEGIES FOR CAPTIVE MANAGEMENT 85 Int. Zoo Yb. (2007) 41: 85 95 DOI:10.1111/j.1748-1090.2007.00010.x Amphibian chytridiomycosis: strategies for captive management
Principal Investigator: Roland Knapp; Co-principal Investigator: Vance Vredenburg
 P092: Effectiveness of reintroductions and probiotic treatment as tools to restore the endangered Sierra Nevada yellow-legged frog (Rana sierrae) to the Lake Tahoe Basin Project period: July 1, 2012 to
P092: Effectiveness of reintroductions and probiotic treatment as tools to restore the endangered Sierra Nevada yellow-legged frog (Rana sierrae) to the Lake Tahoe Basin Project period: July 1, 2012 to
Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis not found in rainforest frogs along an altitudinal gradient of Papua New Guinea
 Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis not found in rainforest frogs along an altitudinal gradient of Papua New Guinea Author Dahl, Chris, Kiatik, Ismale, Baisen, Ismale, Bronikowski, Ed, C. Fleischer, Robert,
Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis not found in rainforest frogs along an altitudinal gradient of Papua New Guinea Author Dahl, Chris, Kiatik, Ismale, Baisen, Ismale, Bronikowski, Ed, C. Fleischer, Robert,
EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASE AS A PROXIMATE CAUSE OF AMPHIBIAN MASS MORTALITY
 Ecology, 87(7), 2006, pp. 1671 1683 Ó 2006 by the Ecological Society of America EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASE AS A PROXIMATE CAUSE OF AMPHIBIAN MASS MORTALITY LARA J. RACHOWICZ, 1,5 ROLAND A. KNAPP, 2 JESS
Ecology, 87(7), 2006, pp. 1671 1683 Ó 2006 by the Ecological Society of America EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASE AS A PROXIMATE CAUSE OF AMPHIBIAN MASS MORTALITY LARA J. RACHOWICZ, 1,5 ROLAND A. KNAPP, 2 JESS
Tasmanian Frog and Chytrid monitoring 2014: Executive summary
 Tasmanian Frog and Chytrid monitoring 2014: Executive summary December 2014 Supported and funded by: Full citation Sinn, D. and Philips, A. (2014). Tasmanian Frog and Chytrid monitoring 2014: sound recording,
Tasmanian Frog and Chytrid monitoring 2014: Executive summary December 2014 Supported and funded by: Full citation Sinn, D. and Philips, A. (2014). Tasmanian Frog and Chytrid monitoring 2014: sound recording,
Possible modes of dissemination of the amphibian chytrid Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis in the environment
 DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 65: 181 186, 2005 Published July 18 Dis Aquat Org Possible modes of dissemination of the amphibian chytrid Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis in the environment Megan L.
DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 65: 181 186, 2005 Published July 18 Dis Aquat Org Possible modes of dissemination of the amphibian chytrid Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis in the environment Megan L.
ENVIRONMENTAL DNA (EDNA) SAMPLING FOR AMPHIBIAN PATHOGENS
 SEPARC Information Sheet #19 ENVIRONMENTAL DNA (EDNA) SAMPLING FOR AMPHIBIAN PATHOGENS Introduction to Environmental DNA Sampling: By: Todd W. Pierson and Ariel A. Horner The isolation and identification
SEPARC Information Sheet #19 ENVIRONMENTAL DNA (EDNA) SAMPLING FOR AMPHIBIAN PATHOGENS Introduction to Environmental DNA Sampling: By: Todd W. Pierson and Ariel A. Horner The isolation and identification
Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis: Chytrid disease
 Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis: Chytrid disease FISH497 Fall 2008 Aquatic Invasion Ecology Final Report By: Dave Lawrence Section 1. Diagnostic information Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, commonly called
Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis: Chytrid disease FISH497 Fall 2008 Aquatic Invasion Ecology Final Report By: Dave Lawrence Section 1. Diagnostic information Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, commonly called
Integrative and objective science is the best link between amphibian decline research and conservation on the ground
 Alytes, 2012, 29 (1 4): 119-132. 119 Integrative and objective science is the best link between amphibian decline research and conservation on the ground Carlos A. Navas a, Catherine R. Bevier b & Ana
Alytes, 2012, 29 (1 4): 119-132. 119 Integrative and objective science is the best link between amphibian decline research and conservation on the ground Carlos A. Navas a, Catherine R. Bevier b & Ana
Do emerging infectious diseases have a role in the decline and extinction of species? 1. Global loss of biodiversity 2. Emerging infectious diseases
 The Role of Infectious Disease in Amphibian Population Decline and Extinction James P. Collins School of Life Sciences Arizona State University University of Tennessee Department of Forestry, Wildlife
The Role of Infectious Disease in Amphibian Population Decline and Extinction James P. Collins School of Life Sciences Arizona State University University of Tennessee Department of Forestry, Wildlife
Altitudinal distribution of chytrid (Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis) infection in subtropical Australian frogs
 Austral Ecology (2008) 33, 22 32 Altitudinal distribution of chytrid (Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis) infection in subtropical Australian frogs KERRY M. KRIGER* AND JEAN-MARC HERO Griffith University,
Austral Ecology (2008) 33, 22 32 Altitudinal distribution of chytrid (Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis) infection in subtropical Australian frogs KERRY M. KRIGER* AND JEAN-MARC HERO Griffith University,
A genetic survey of the amphibian pathogen Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis collected in British Columbia, Canada and Peninsular Malaysia
 A genetic survey of the amphibian pathogen Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis collected in British Columbia, Canada and Peninsular Malaysia by Jonathon LeBlanc BSc, Brock University, 2004 BA, Brock University,
A genetic survey of the amphibian pathogen Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis collected in British Columbia, Canada and Peninsular Malaysia by Jonathon LeBlanc BSc, Brock University, 2004 BA, Brock University,
PROMOTING AMPHIBIAN CONSERVATION THROUGH THE COLLEGE CLASSROOM: DETECTION OF BATRACHOCHYTRIUM DENDROBATIDIS AMONG LOCAL AMPHIBIANS
 Herpetological Conservation and Biology 7(3):462 469. Submitted: 6 May 2012; Accepted: 24 September 2012; Published: 31 December 2012. PROMOTING AMPHIBIAN CONSERVATION THROUGH THE COLLEGE CLASSROOM: DETECTION
Herpetological Conservation and Biology 7(3):462 469. Submitted: 6 May 2012; Accepted: 24 September 2012; Published: 31 December 2012. PROMOTING AMPHIBIAN CONSERVATION THROUGH THE COLLEGE CLASSROOM: DETECTION
Title: Predation by zooplankton on Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis: Biological control of the
 Title: Predation by zooplankton on Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis: Biological control of the deadly amphibian chytrid fungus? Authors: Julia C. Buck, 1* Lisa Truong, 2 Andrew R. Blaustein 1 Affiliations:
Title: Predation by zooplankton on Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis: Biological control of the deadly amphibian chytrid fungus? Authors: Julia C. Buck, 1* Lisa Truong, 2 Andrew R. Blaustein 1 Affiliations:
Chapter 4. Probability Theory. 4.1 Probability theory Events
 Chapter 4 Probability Theory Probability theory is a branch of mathematics that is an essential component of statistics. It originally evolved from efforts to understand the odds and probabilities involved
Chapter 4 Probability Theory Probability theory is a branch of mathematics that is an essential component of statistics. It originally evolved from efforts to understand the odds and probabilities involved
Predation by zooplankton on Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis: biological control of the deadly amphibian chytrid fungus?
 Biodivers Conserv (2011) 20:3549 3553 DOI 10.1007/s10531-011-0147-4 ORIGINAL PAPER Predation by zooplankton on Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis: biological control of the deadly amphibian chytrid fungus?
Biodivers Conserv (2011) 20:3549 3553 DOI 10.1007/s10531-011-0147-4 ORIGINAL PAPER Predation by zooplankton on Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis: biological control of the deadly amphibian chytrid fungus?
Resistance, tolerance and environmental transmission dynamics determine host extinction risk in a load-dependent amphibian disease
 LETTER Ecology Letters, (2017) 20: 1169 1181 doi: 10.1111/ele.12814 Resistance, tolerance and environmental transmission dynamics determine host extinction risk in a load-dependent amphibian disease Mark
LETTER Ecology Letters, (2017) 20: 1169 1181 doi: 10.1111/ele.12814 Resistance, tolerance and environmental transmission dynamics determine host extinction risk in a load-dependent amphibian disease Mark
EFFECTS OF CANOPY COVER ON THE LANDSCAPE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF AN AMPHIBIAN CHYTRID FUNGUS STACY ELIZABETH BEYER THESIS
 EFFECTS OF CANOPY COVER ON THE LANDSCAPE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF AN AMPHIBIAN CHYTRID FUNGUS BY STACY ELIZABETH BEYER THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science
EFFECTS OF CANOPY COVER ON THE LANDSCAPE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF AN AMPHIBIAN CHYTRID FUNGUS BY STACY ELIZABETH BEYER THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science
ACADEMIC POSITIONS 2017-present Assistant Professor, Department of Biology, Eastern Washington University, Cheney, WA
 Jenifer B. Walke, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Biology, Eastern Washington University 258 Science Building, Cheney, WA 99004-2440 Phone: 509-359-4750; E-mail: jwalke@ewu.edu Website: WalkeLab.com
Jenifer B. Walke, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Biology, Eastern Washington University 258 Science Building, Cheney, WA 99004-2440 Phone: 509-359-4750; E-mail: jwalke@ewu.edu Website: WalkeLab.com
Evan H Campbell Grant Northeast Amphibian Research and Monitoring Initiative US Geological Survey Patuxent Wildlife Research Center
 Evan H Campbell Grant Northeast Amphibian Research and Monitoring Initiative US Geological Survey Patuxent Wildlife Research Center New England Chapter of the Wildlife Society Spring Workshop 2015 Color
Evan H Campbell Grant Northeast Amphibian Research and Monitoring Initiative US Geological Survey Patuxent Wildlife Research Center New England Chapter of the Wildlife Society Spring Workshop 2015 Color
Only skin deep: shared genetic response to the deadly chytrid fungus in susceptible frog species
 Molecular Ecology (2012) 21, 3110 3120 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2012.05481.x FROM THE COVER Only skin deep: shared genetic response to the deadly chytrid fungus in susceptible frog species ERICA BREE ROSENBLUM,*
Molecular Ecology (2012) 21, 3110 3120 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2012.05481.x FROM THE COVER Only skin deep: shared genetic response to the deadly chytrid fungus in susceptible frog species ERICA BREE ROSENBLUM,*
Amphibian species traits, evolutionary history, and environment predict. Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis infection patterns, but not extinction risk
 Final version published as Greenberg, D.A., W. J. Palen, & A. Ø. Mooers. 2017. Linking species traits and evolutionary history to Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis infection risk, intensity, and extinction
Final version published as Greenberg, D.A., W. J. Palen, & A. Ø. Mooers. 2017. Linking species traits and evolutionary history to Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis infection risk, intensity, and extinction
What Drives Chytrid Infections in Newt Populations? Associations with Substrate, Temperature, and Shade
 EcoHealth 7, 526 536, 2010 DOI: 10.1007/s10393-010-0358-2 Ó 2010 International Association for Ecology and Health Original Contribution What Drives Chytrid Infections in Newt Populations? Associations
EcoHealth 7, 526 536, 2010 DOI: 10.1007/s10393-010-0358-2 Ó 2010 International Association for Ecology and Health Original Contribution What Drives Chytrid Infections in Newt Populations? Associations
Transmission of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis within and between amphibian life stages
 DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 61: 75 83, 2004 Published October 21 Dis Aquat Org Transmission of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis within and between amphibian life stages Lara J. Rachowicz*, Vance T.
DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 61: 75 83, 2004 Published October 21 Dis Aquat Org Transmission of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis within and between amphibian life stages Lara J. Rachowicz*, Vance T.
Annual assessment of Chytrid fungus prevalence amongst endangered native Fijian ground frog populations on Viwa Fiji Islands Project ID:
 Annual assessment of Chytrid fungus prevalence amongst endangered native Fijian ground frog populations on Viwa Fiji Islands Project ID: 29.07.09 Final Report Submitted by Dr. Edward Narayan Fiji Islands
Annual assessment of Chytrid fungus prevalence amongst endangered native Fijian ground frog populations on Viwa Fiji Islands Project ID: 29.07.09 Final Report Submitted by Dr. Edward Narayan Fiji Islands
Kingdom Fungi. Announcements
 Kingdom Fungi Announcements Friday lab: Fungi & Lichen Bring a Lichen to ID! Do prelab Quiz #4 Friday Study Prokaryotes & Protists Mushroom Fest extra credit due Fri Email me or bring to lab Endosymbiosis
Kingdom Fungi Announcements Friday lab: Fungi & Lichen Bring a Lichen to ID! Do prelab Quiz #4 Friday Study Prokaryotes & Protists Mushroom Fest extra credit due Fri Email me or bring to lab Endosymbiosis
Applying Critical Thinking to the Amphibian Decline Problem
 Network of Conservation Educators & Practitioners Applying Critical Thinking to the Amphibian Decline Problem Author(s): Ana L. Porzecanski and Adriana Bravo Source: Lessons in Conservation, Vol. 8, Issue
Network of Conservation Educators & Practitioners Applying Critical Thinking to the Amphibian Decline Problem Author(s): Ana L. Porzecanski and Adriana Bravo Source: Lessons in Conservation, Vol. 8, Issue
Host species determines whether infection load increases beyond disease-causing thresholds following exposure to the amphibian chytrid fungus
 Host species determines whether infection load increases beyond disease-causing thresholds following exposure to the amphibian chytrid fungus M. P. Stockwell, J. Clulow & M. J. Mahony Animal Conservation.
Host species determines whether infection load increases beyond disease-causing thresholds following exposure to the amphibian chytrid fungus M. P. Stockwell, J. Clulow & M. J. Mahony Animal Conservation.
From The Cover: Emerging infectious disease and the loss of biodiversity in a Neotropical amphibian community
 From The Cover: Emerging infectious disease and the loss of biodiversity in a Neotropical amphibian community Karen R. Lips, Forrest Brem, Roberto Brenes, John D. Reeve, Ross A. Alford, Jamie Voyles, Cynthia
From The Cover: Emerging infectious disease and the loss of biodiversity in a Neotropical amphibian community Karen R. Lips, Forrest Brem, Roberto Brenes, John D. Reeve, Ross A. Alford, Jamie Voyles, Cynthia
Spatial dynamics and population impacts of disease in threatened amphibians
 Spatial dynamics and population impacts of disease in threatened amphibians Benjamin Scheele Submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy of The Australian National
Spatial dynamics and population impacts of disease in threatened amphibians Benjamin Scheele Submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy of The Australian National
Sciences Graduate Program, Oregon State University, 104 Wilkinson Hall, Corvallis, OR 97330, USA; and
 Functional Ecology 2014, 28, 569 578 doi: 10.1111/1365-2435.12194 Temporal patterns in immunity, infection load and disease susceptibility: understanding the drivers of host responses in the amphibian-chytrid
Functional Ecology 2014, 28, 569 578 doi: 10.1111/1365-2435.12194 Temporal patterns in immunity, infection load and disease susceptibility: understanding the drivers of host responses in the amphibian-chytrid
MICROORGANISMS AND AMPHIBIANS
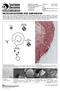 The life cycle of the chytrid fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis begins with a motile zoospore, which is the infective stage of this pathogen. During the course of infection, chytrid zoospores enter
The life cycle of the chytrid fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis begins with a motile zoospore, which is the infective stage of this pathogen. During the course of infection, chytrid zoospores enter
BIOL 101 Introduction to Biological Research Techniques I
 BIOL 101 Introduction to Biological Research Techniques I 1. Develop a research plan including hypothesis, controls and procedures. 2. Conduct a primary literature review relating to their research project.
BIOL 101 Introduction to Biological Research Techniques I 1. Develop a research plan including hypothesis, controls and procedures. 2. Conduct a primary literature review relating to their research project.
Skin sloughing rate increases with chytrid fungus infection load in a susceptible amphibian
 Functional Ecology 2015, 29, 674 682 doi: 10.1111/1365-2435.12370 Skin sloughing rate increases with chytrid fungus infection load in a susceptible amphibian Michel E.B. Ohmer*, Rebecca L. Cramp, Craig
Functional Ecology 2015, 29, 674 682 doi: 10.1111/1365-2435.12370 Skin sloughing rate increases with chytrid fungus infection load in a susceptible amphibian Michel E.B. Ohmer*, Rebecca L. Cramp, Craig
Mitigation of chytridiomycosis in amphibians
 Mitigation of chytridiomycosis in amphibians Mark Blooi Dissertation submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor in Veterinary Sciences (PhD) 2015 Promoters: Prof. Dr. F. Pasmans
Mitigation of chytridiomycosis in amphibians Mark Blooi Dissertation submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor in Veterinary Sciences (PhD) 2015 Promoters: Prof. Dr. F. Pasmans
Higher temperature variability increases the impact of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis and shifts interspecific interactions in tadpole mesocosms
 Higher temperature variability increases the impact of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis and shifts interspecific interactions in tadpole mesocosms Phineas T. Hamilton 1, Jean M.L. Richardson 1, Purnima Govindarajulu
Higher temperature variability increases the impact of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis and shifts interspecific interactions in tadpole mesocosms Phineas T. Hamilton 1, Jean M.L. Richardson 1, Purnima Govindarajulu
Ch 5. Evolution, Biodiversity, and Population Ecology. Part 1: Foundations of Environmental Science
 Ch 5 Evolution, Biodiversity, and Population Ecology Part 1: Foundations of Environmental Science PowerPoint Slides prepared by Jay Withgott and Heidi Marcum Copyright 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
Ch 5 Evolution, Biodiversity, and Population Ecology Part 1: Foundations of Environmental Science PowerPoint Slides prepared by Jay Withgott and Heidi Marcum Copyright 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
The Prevalence of Chytridiomycosis in the Southern Appalachians
 The Prevalence of Chytridiomycosis in the Southern Appalachians By Shem Kearney Blackley IV Honors Thesis Appalachian State University Submitted to the Department of Biology In partial fulfillment of the
The Prevalence of Chytridiomycosis in the Southern Appalachians By Shem Kearney Blackley IV Honors Thesis Appalachian State University Submitted to the Department of Biology In partial fulfillment of the
Microbiota: Its Evolution and Essence. Hsin-Jung Joyce Wu "Microbiota and man: the story about us
 Microbiota: Its Evolution and Essence Overview q Define microbiota q Learn the tool q Ecological and evolutionary forces in shaping gut microbiota q Gut microbiota versus free-living microbe communities
Microbiota: Its Evolution and Essence Overview q Define microbiota q Learn the tool q Ecological and evolutionary forces in shaping gut microbiota q Gut microbiota versus free-living microbe communities
Introduction: Catesbeiana 36(1): 35-42
 Determining the prevalence of Amphibian Chytrid Fungus (Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis) and Ranavirus at Long Branch Nature Center in Arlington, Virginia Catesbeiana 36(1): 35-42 Lauren Augustine and Matthew
Determining the prevalence of Amphibian Chytrid Fungus (Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis) and Ranavirus at Long Branch Nature Center in Arlington, Virginia Catesbeiana 36(1): 35-42 Lauren Augustine and Matthew
OCR (A) Biology A-level
 OCR (A) Biology A-level Topic 4.2: Biodiversity Notes Biodiversity is the variety of living organisms, over time the variety of life on Earth has become more extensive but now it is being threatened by
OCR (A) Biology A-level Topic 4.2: Biodiversity Notes Biodiversity is the variety of living organisms, over time the variety of life on Earth has become more extensive but now it is being threatened by
Bayesian inference for a population growth model of the chytrid fungus Philipp H Boersch-Supan, Sadie J Ryan, and Leah R Johnson September 2016
 Bayesian inference for a population growth model of the chytrid fungus Philipp H Boersch-Supan, Sadie J Ryan, and Leah R Johnson September 2016 1 Preliminaries This vignette illustrates the steps needed
Bayesian inference for a population growth model of the chytrid fungus Philipp H Boersch-Supan, Sadie J Ryan, and Leah R Johnson September 2016 1 Preliminaries This vignette illustrates the steps needed
4. Identify one bird that would most likely compete for food with the large tree finch. Support your answer. [1]
![4. Identify one bird that would most likely compete for food with the large tree finch. Support your answer. [1] 4. Identify one bird that would most likely compete for food with the large tree finch. Support your answer. [1]](/thumbs/84/91138454.jpg) Name: Topic 5B 1. A hawk has a genetic trait that gives it much better eyesight than other hawks of the same species in the same area. Explain how this could lead to evolutionary change within this species
Name: Topic 5B 1. A hawk has a genetic trait that gives it much better eyesight than other hawks of the same species in the same area. Explain how this could lead to evolutionary change within this species
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved.
 Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. AP Biology Unity and Diversity Blizzard Bag 2014-20151. The sawfish, also known as the carpenter shark, lives in estuaries off the coast of Australia. A scientist
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. AP Biology Unity and Diversity Blizzard Bag 2014-20151. The sawfish, also known as the carpenter shark, lives in estuaries off the coast of Australia. A scientist
CHYTRIDIOMYCOSIS caused by the fungal pathogen
 Copeia 2009, No. 4, 653 660 An Aquatic Disease on a Terrestrial Salamander: Individual and Population Level Effects of the Amphibian Chytrid Fungus, Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, onbatrachoseps attenuatus
Copeia 2009, No. 4, 653 660 An Aquatic Disease on a Terrestrial Salamander: Individual and Population Level Effects of the Amphibian Chytrid Fungus, Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, onbatrachoseps attenuatus
Georgia Performance Standards for Urban Watch Restoration Field Trips
 Georgia Performance Standards for Field Trips 6 th grade S6E3. Students will recognize the significant role of water in earth processes. a. Explain that a large portion of the Earth s surface is water,
Georgia Performance Standards for Field Trips 6 th grade S6E3. Students will recognize the significant role of water in earth processes. a. Explain that a large portion of the Earth s surface is water,
Distribution of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis and pathology in the skin of green tree frogs Litoria caerulea with severe chytridiomycosis
 DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 68: 65 70, 2005 Published December 30 Dis Aquat Org Distribution of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis and pathology in the skin of green tree frogs Litoria caerulea with
DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 68: 65 70, 2005 Published December 30 Dis Aquat Org Distribution of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis and pathology in the skin of green tree frogs Litoria caerulea with
Endemicity of chytridiomycosis features pathogen overdispersion
 Journal of Animal Ecology 26, 85, 86 86 doi:./365-2656.25 Endemicity of chytridiomycosis features pathogen overdispersion Laura F. Grogan,2 *, Andrea D. Phillott,3, Benjamin C. Scheele,4, Lee Berger, Scott
Journal of Animal Ecology 26, 85, 86 86 doi:./365-2656.25 Endemicity of chytridiomycosis features pathogen overdispersion Laura F. Grogan,2 *, Andrea D. Phillott,3, Benjamin C. Scheele,4, Lee Berger, Scott
Chytridiomycosis and Seasonal Mortality of Tropical Stream-Associated Frogs 15 Years after Introduction of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis
 Chytridiomycosis and Seasonal Mortality of Tropical Stream-Associated Frogs 15 Years after Introduction of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis Author Phillott, Andrea D., F. Grogan, Laura, Cashins, Scott D.,
Chytridiomycosis and Seasonal Mortality of Tropical Stream-Associated Frogs 15 Years after Introduction of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis Author Phillott, Andrea D., F. Grogan, Laura, Cashins, Scott D.,
Amphibian ranaviruses in Canada historical, current and future research directions. Danna M Schock, PhD Keyano College Fort McMurray, Alberta
 Amphibian ranaviruses in Canada historical, current and future research directions Danna M Schock, PhD Keyano College Fort McMurray, Alberta Thanks 1 1) host range and geographic range 3) validating &
Amphibian ranaviruses in Canada historical, current and future research directions Danna M Schock, PhD Keyano College Fort McMurray, Alberta Thanks 1 1) host range and geographic range 3) validating &
1 In 2006, the scientific journal, Nature, reported the discovery of a fossil from around 380 million
 1 In 2006, the scientific journal, Nature, reported the discovery of a fossil from around 380 million years ago. It was given the name Tiktaalik roseae. This fossil has some features in common with fish
1 In 2006, the scientific journal, Nature, reported the discovery of a fossil from around 380 million years ago. It was given the name Tiktaalik roseae. This fossil has some features in common with fish
BEFORE TAKING THIS MODULE YOU MUST ( TAKE BIO-4013Y OR TAKE BIO-
 2018/9 - BIO-4001A BIODIVERSITY Autumn Semester, Level 4 module (Maximum 150 Students) Organiser: Dr Harriet Jones Timetable Slot:DD This module explores life on Earth. You will be introduced to the major
2018/9 - BIO-4001A BIODIVERSITY Autumn Semester, Level 4 module (Maximum 150 Students) Organiser: Dr Harriet Jones Timetable Slot:DD This module explores life on Earth. You will be introduced to the major
Mechanisms behind the successful invasion of American Bullfrogs (Rana catesbeiana) in the Northwest United States
 Mechanisms behind the successful invasion of American Bullfrogs (Rana catesbeiana) in the Northwest United States Tiffany Garcia, Rebbecca Hill, Sarah Abdulkarim, and Chris Funk Department of Fisheries
Mechanisms behind the successful invasion of American Bullfrogs (Rana catesbeiana) in the Northwest United States Tiffany Garcia, Rebbecca Hill, Sarah Abdulkarim, and Chris Funk Department of Fisheries
Marine Resources Development Foundation/MarineLab Grades: 9, 10, 11, 12 States: AP Biology Course Description Subjects: Science
 Marine Resources Development Foundation/MarineLab Grades: 9, 10, 11, 12 States: AP Biology Course Description Subjects: Science Highlighted components are included in Tallahassee Museum s 2016 program
Marine Resources Development Foundation/MarineLab Grades: 9, 10, 11, 12 States: AP Biology Course Description Subjects: Science Highlighted components are included in Tallahassee Museum s 2016 program
Survival of three species of anuran metamorphs exposed to UV-B radiation and the pathogenic fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis
 DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 72: 163 169, 2006 Published October 17 Dis Aquat Org Survival of three species of anuran metamorphs exposed to UV-B radiation and the pathogenic fungus Batrachochytrium
DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 72: 163 169, 2006 Published October 17 Dis Aquat Org Survival of three species of anuran metamorphs exposed to UV-B radiation and the pathogenic fungus Batrachochytrium
Impact of a Chytrid-related mortality event on a population of the Green and Golden Bell Frog Litoria aurea
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2008 Impact of a Chytrid-related mortality event on a population of the Green and
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2008 Impact of a Chytrid-related mortality event on a population of the Green and
AMPHIBIAN AND REPTILE DISEASES
 528 AMPHIBIAN AND REPTILE DISEASES AMPHIBIAN AND REPTILE DISEASES Herpetological Review, 2015, 46(4), 528 532. 2015 by Society for the Study of Amphibians and Reptiles Infection Prevalence in Three Lowland
528 AMPHIBIAN AND REPTILE DISEASES AMPHIBIAN AND REPTILE DISEASES Herpetological Review, 2015, 46(4), 528 532. 2015 by Society for the Study of Amphibians and Reptiles Infection Prevalence in Three Lowland
Chapter 5 Evolution of Biodiversity. Sunday, October 1, 17
 Chapter 5 Evolution of Biodiversity CHAPTER INTRO: The Dung of the Devil Read and Answer Questions Provided Module 14 The Biodiversity of Earth After reading this module you should be able to understand
Chapter 5 Evolution of Biodiversity CHAPTER INTRO: The Dung of the Devil Read and Answer Questions Provided Module 14 The Biodiversity of Earth After reading this module you should be able to understand
Chapter 5 Evolution of Biodiversity
 Chapter 5 Evolution of Biodiversity Biodiversity What is biodiversity? How does evolution occur? What is an ecological niche? Earth is Home to a Tremendous Diversity of Species Ecosystem diversity the
Chapter 5 Evolution of Biodiversity Biodiversity What is biodiversity? How does evolution occur? What is an ecological niche? Earth is Home to a Tremendous Diversity of Species Ecosystem diversity the
Occurrence and Prevalence of Chytrid Fungus (Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis) in Amphibian Species of Alberta
 Occurrence and Prevalence of Chytrid Fungus (Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis) in Amphibian Species of Alberta Alberta Species at Risk Report No. 143 Occurrence and Prevalence of Chytrid Fungus (Batrachochytrium
Occurrence and Prevalence of Chytrid Fungus (Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis) in Amphibian Species of Alberta Alberta Species at Risk Report No. 143 Occurrence and Prevalence of Chytrid Fungus (Batrachochytrium
The ecology of chytridiomycosis in red-legged frog (Rana aurora) tadpoles. Phineas Hamilton B.Sc., University of Victoria, 2006
 The ecology of chytridiomycosis in red-legged frog (Rana aurora) tadpoles by Phineas Hamilton B.Sc., University of Victoria, 2006 A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree
The ecology of chytridiomycosis in red-legged frog (Rana aurora) tadpoles by Phineas Hamilton B.Sc., University of Victoria, 2006 A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree
UNIVERSIDADE ESTADUAL PAULISTA PLANO DE ENSINO DA DISCIPLINA
 Data Aprovação: 10/07/2013 Data Desativação: Nº Créditos : 5 Carga Horária Total: Carga Horária Teórica: Carga Horária Prática: Carga Horária Teórica/Prátical: Carga Horária Seminário: Carga Horária Laboratório:
Data Aprovação: 10/07/2013 Data Desativação: Nº Créditos : 5 Carga Horária Total: Carga Horária Teórica: Carga Horária Prática: Carga Horária Teórica/Prátical: Carga Horária Seminário: Carga Horária Laboratório:
Nowhere to hide: impact of a temperature-sensitive amphibian pathogen along an elevation gradient in the temperate zone
 Nowhere to hide: impact of a temperature-sensitive amphibian pathogen along an elevation gradient in the temperate zone ROLAND A. KNAPP, 1, CHERYL J. BRIGGS, 2 THOMAS C. SMITH, 2 AND JEFF R. MAURER 3,4
Nowhere to hide: impact of a temperature-sensitive amphibian pathogen along an elevation gradient in the temperate zone ROLAND A. KNAPP, 1, CHERYL J. BRIGGS, 2 THOMAS C. SMITH, 2 AND JEFF R. MAURER 3,4
PATHOGENICITY OF BATRACHOCHYTRIUM DENDROBATIDIS IN LARVAL AMBYSTOMATID SALAMANDERS
 Herpetological Conservation and Biology 5(2):174-182. Submitted: 18 December 2009; Accepted: 17 May 2010. PATHOGENICITY OF BATRACHOCHYTRIUM DENDROBATIDIS IN LARVAL AMBYSTOMATID SALAMANDERS MATTHEW D. VENESKY
Herpetological Conservation and Biology 5(2):174-182. Submitted: 18 December 2009; Accepted: 17 May 2010. PATHOGENICITY OF BATRACHOCHYTRIUM DENDROBATIDIS IN LARVAL AMBYSTOMATID SALAMANDERS MATTHEW D. VENESKY
California Subject Examinations for Teachers
 California Subject Examinations for Teachers TEST GUIDE SCIENCE SUBTEST II: LIFE SCIENCES Subtest Description This document contains the Life Sciences subject matter requirements arranged according to
California Subject Examinations for Teachers TEST GUIDE SCIENCE SUBTEST II: LIFE SCIENCES Subtest Description This document contains the Life Sciences subject matter requirements arranged according to
AMPHIBIAN CHYTRID FUNGUS (BATRACHOCHYTRIUM
 Herpetological Conservation and Biology 6(3):383 394. Submitted: 13 April 2010; Accepted: 16 September 2011; Published: 31 December 2011. AMPHIBIAN CHYTRID FUNGUS (BATRACHOCHYTRIUM DENDROBATIDIS) IN COASTAL
Herpetological Conservation and Biology 6(3):383 394. Submitted: 13 April 2010; Accepted: 16 September 2011; Published: 31 December 2011. AMPHIBIAN CHYTRID FUNGUS (BATRACHOCHYTRIUM DENDROBATIDIS) IN COASTAL
Michael J. Lannoo 1 *, Christopher Petersen 2, Robert E. Lovich 3, Priya Nanjappa\ Christopher Phillips5, Joseph C. Mitche1l 6, Irene Macallister 7
 1 Do frogs still get their kicks on Route 66? A transcontinental transect for amphibian Chytrid Fungus (Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis) infection on U.S. Department of Defense installations Michael J.
1 Do frogs still get their kicks on Route 66? A transcontinental transect for amphibian Chytrid Fungus (Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis) infection on U.S. Department of Defense installations Michael J.
Map of AP-Aligned Bio-Rad Kits with Learning Objectives
 Map of AP-Aligned Bio-Rad Kits with Learning Objectives Cover more than one AP Biology Big Idea with these AP-aligned Bio-Rad kits. Big Idea 1 Big Idea 2 Big Idea 3 Big Idea 4 ThINQ! pglo Transformation
Map of AP-Aligned Bio-Rad Kits with Learning Objectives Cover more than one AP Biology Big Idea with these AP-aligned Bio-Rad kits. Big Idea 1 Big Idea 2 Big Idea 3 Big Idea 4 ThINQ! pglo Transformation
Final Report Prepared by: Jonathan E. Kolby
 Investigation of Forest Canopies as Possible Safe Havens from Amphibian Chytrid Fungus (Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis): Hope in the Midst of a Global Amphibian Extinction Crisis Final Report Prepared
Investigation of Forest Canopies as Possible Safe Havens from Amphibian Chytrid Fungus (Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis): Hope in the Midst of a Global Amphibian Extinction Crisis Final Report Prepared
Science Unit Learning Summary
 Learning Summary Inheritance, variation and evolution Content Sexual and asexual reproduction. Meiosis leads to non-identical cells being formed while mitosis leads to identical cells being formed. In
Learning Summary Inheritance, variation and evolution Content Sexual and asexual reproduction. Meiosis leads to non-identical cells being formed while mitosis leads to identical cells being formed. In
OCR Biology Checklist
 Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Studying Life. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview. 1.3 Studying Life
 Lesson Overview 1.3 Characteristics of Living Things What characteristics do all living things share? Living things are made up of basic units called cells, are based on a universal genetic code, obtain
Lesson Overview 1.3 Characteristics of Living Things What characteristics do all living things share? Living things are made up of basic units called cells, are based on a universal genetic code, obtain
OCR Biology Checklist
 Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
ANIMAL ECOLOGY (A ECL)
 Animal Ecology (A ECL) 1 ANIMAL ECOLOGY (A ECL) Courses primarily for undergraduates: A ECL 312: Ecology (Cross-listed with BIOL, ENSCI). (3-3) Cr. 4. SS. Prereq: BIOL 211, BIOL 211L, BIOL 212, and BIOL
Animal Ecology (A ECL) 1 ANIMAL ECOLOGY (A ECL) Courses primarily for undergraduates: A ECL 312: Ecology (Cross-listed with BIOL, ENSCI). (3-3) Cr. 4. SS. Prereq: BIOL 211, BIOL 211L, BIOL 212, and BIOL
AP Biology Curriculum Framework
 AP Biology Curriculum Framework This chart correlates the College Board s Advanced Placement Biology Curriculum Framework to the corresponding chapters and Key Concept numbers in Campbell BIOLOGY IN FOCUS,
AP Biology Curriculum Framework This chart correlates the College Board s Advanced Placement Biology Curriculum Framework to the corresponding chapters and Key Concept numbers in Campbell BIOLOGY IN FOCUS,
A DISEASE ECOLOGIST S GUIDE TO EVOLUTION: EVIDENCE FROM HOST- PARASITE RELATIONSHIPS
 A DISEASE ECOLOGIST S GUIDE TO EVOLUTION: EVIDENCE FROM HOST- PARASITE RELATIONSHIPS SARAH A. ORLOFSKE TEACHING EVOLUTION WORKSHOP UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO BOULDER sarah.orlofske@colorado.edu Ph.D. Candidate
A DISEASE ECOLOGIST S GUIDE TO EVOLUTION: EVIDENCE FROM HOST- PARASITE RELATIONSHIPS SARAH A. ORLOFSKE TEACHING EVOLUTION WORKSHOP UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO BOULDER sarah.orlofske@colorado.edu Ph.D. Candidate
AP Biology Essential Knowledge Cards BIG IDEA 1
 AP Biology Essential Knowledge Cards BIG IDEA 1 Essential knowledge 1.A.1: Natural selection is a major mechanism of evolution. Essential knowledge 1.A.4: Biological evolution is supported by scientific
AP Biology Essential Knowledge Cards BIG IDEA 1 Essential knowledge 1.A.1: Natural selection is a major mechanism of evolution. Essential knowledge 1.A.4: Biological evolution is supported by scientific
The Prokaryotic World
 The Prokaryotic World A. An overview of prokaryotic life There is no doubt that prokaryotes are everywhere. By everywhere, I mean living in every geographic region, in extremes of environmental conditions,
The Prokaryotic World A. An overview of prokaryotic life There is no doubt that prokaryotes are everywhere. By everywhere, I mean living in every geographic region, in extremes of environmental conditions,
Valley Central School District 944 State Route 17K Montgomery, NY Telephone Number: (845) ext Fax Number: (845)
 Valley Central School District 944 State Route 17K Montgomery, NY 12549 Telephone Number: (845)457-2400 ext. 18121 Fax Number: (845)457-4254 Advance Placement Biology Presented to the Board of Education
Valley Central School District 944 State Route 17K Montgomery, NY 12549 Telephone Number: (845)457-2400 ext. 18121 Fax Number: (845)457-4254 Advance Placement Biology Presented to the Board of Education
The North American bullfrog as a reservoir for the spread of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis in Brazil
 Animal Conservation. Print ISSN 1367-9430 The North American bullfrog as a reservoir for the spread of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis in Brazil L. M. Schloegel 1,2, C. M. Ferreira 3, T. Y. James 4, M.
Animal Conservation. Print ISSN 1367-9430 The North American bullfrog as a reservoir for the spread of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis in Brazil L. M. Schloegel 1,2, C. M. Ferreira 3, T. Y. James 4, M.
7 th Grade Life Science Teaching & Learning Framework
 7 th Grade Science 7 th Grade Life Science Teaching & Learning Framework Quarter 1 Quarter 2 Quarter 3 Quarter 4 Unit 1 9 weeks Structure and Function of Cells S7L2. Obtain, evaluate, and describe how
7 th Grade Science 7 th Grade Life Science Teaching & Learning Framework Quarter 1 Quarter 2 Quarter 3 Quarter 4 Unit 1 9 weeks Structure and Function of Cells S7L2. Obtain, evaluate, and describe how
Purpose. Potential causes for amphibian declines in Puerto Rico. Three species presumably extinct! Long Term Data of Transect Surveys :
 Potential causes for amphibian declines in Puerto Rico Patricia A. Burrowes, Rafael L. Joglar and Ana Longo University of Puerto Rico Purpose Summarize findings on the current status of Puerto Rican Amphibians
Potential causes for amphibian declines in Puerto Rico Patricia A. Burrowes, Rafael L. Joglar and Ana Longo University of Puerto Rico Purpose Summarize findings on the current status of Puerto Rican Amphibians
EXAMgen Correlation to Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS)
 EXAMgen Correlation to Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) TEKS EXAMgen Biology 3rd Edition Outline 112.34 Biology *TEKS in red denote Readiness Standards ex: (B.4)(B)R *TEKS in green denote Supporting
EXAMgen Correlation to Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) TEKS EXAMgen Biology 3rd Edition Outline 112.34 Biology *TEKS in red denote Readiness Standards ex: (B.4)(B)R *TEKS in green denote Supporting
CHAPTER. Population Ecology
 CHAPTER 4 Population Ecology Chapter 4 TOPIC POPULATION ECOLOGY Indicator Species Serve as Biological Smoke Alarms Indicator species Provide early warning of damage to a community Can monitor environmental
CHAPTER 4 Population Ecology Chapter 4 TOPIC POPULATION ECOLOGY Indicator Species Serve as Biological Smoke Alarms Indicator species Provide early warning of damage to a community Can monitor environmental
Chapter 5. Evolution of Biodiversity
 Chapter 5. Evolution of Biodiversity I. Earth s tremendous diversity A. life comes in many forms B. Recall 1. we can think of biodiversity in three ways a) genetic diversity b) species diversity c) ecosystem
Chapter 5. Evolution of Biodiversity I. Earth s tremendous diversity A. life comes in many forms B. Recall 1. we can think of biodiversity in three ways a) genetic diversity b) species diversity c) ecosystem
Ecotoxicology of Declining Amphibian Populations
 Ecotoxicology of Declining Amphibian Populations Some Questions What does the term declining amphibians mean? decrease in number of individuals in an area decrease in number of sites occupied by breeding
Ecotoxicology of Declining Amphibian Populations Some Questions What does the term declining amphibians mean? decrease in number of individuals in an area decrease in number of sites occupied by breeding
Course Name: Biology Level: A Points: 5 Teacher Name: Claire E. Boudreau
 Course Name: Biology Level: A Points: 5 Teacher Name: Claire E. Boudreau Texts/Instructional Materials: Biology : Concepts and Connections 5 th edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor and Simon Pearson Syllabus:
Course Name: Biology Level: A Points: 5 Teacher Name: Claire E. Boudreau Texts/Instructional Materials: Biology : Concepts and Connections 5 th edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor and Simon Pearson Syllabus:
Rapid speciation following recent host shift in the plant pathogenic fungus Rhynchosporium
 Rapid speciation following recent host shift in the plant pathogenic fungus Rhynchosporium Tiziana Vonlanthen, Laurin Müller 27.10.15 1 Second paper: Origin and Domestication of the Fungal Wheat Pathogen
Rapid speciation following recent host shift in the plant pathogenic fungus Rhynchosporium Tiziana Vonlanthen, Laurin Müller 27.10.15 1 Second paper: Origin and Domestication of the Fungal Wheat Pathogen
