Virulence of Emerging Clostridium difficile
|
|
|
- Erick Knight
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Virulence of Emerging Clostridium difficile Jimmy D. Ballard, Ph.D. Professor and Chairman Department of Microbiology and Immunology University of Oklahoma HSC
2 TcdB 027/NAP1/BI A Toxin Better Than a Very Good Toxin
3
4 Epidemic CDAD North American PFGE Type 1 (NAP1) Restriction Endonuclease Assay type BI Ribotype 027 NAP1/BI/027 Strain Nomenclature TcdB HV = TcdB produced by NAP1/BI/027 Strains TcdB HIST = TcdB produced strains commonly encountered before 2003
5 Epidemic/Hypervirulent C. difficile? Epidemic/Emerging ( Mortality, Recurrence) Wilcox et al. CID 55(8) Miller et al. CID 50 McDonald et al. NEJ 353 (23) Marsh et al. JCM 50 (12) Loo et al. NEJ 353 (23) Goorhuis et al. CID 45 (6) Petrella et al. CID 55 (3) Non-Hypervirulent Wilson et al. CID 50 (12) Morgan et al. PloS One 3 (3) Cloud et al. CG&H 7 Walk et al. CID Oct. 2012
6 Mot (+) Mot (-) Aggregation (-) HV/Ep Aggregation (+) Hist HV/Ep Hist Flagella CwpV PaLoc CDT: Binary Toxin Gyrase Hist tcdr tcdb tcde tcda tcdc cdtr gyra Fq S HV/Ep tcdr tcdb tcde tcda cdtr cdta cdtb gyra Fq R 3247 core genes 505 variant genes Sporulation? Toxin Levels?
7 C. difficile PaLoc Comparison of C. difficile Pathogenicity Locus between Historical and Hypervirulent Strain DNA Homology 100% 93% 99% 98% 95% Protein tcdd tcdb tcde tcda tcdc Similarity 100% 96% 100% 99% Identity 100% 92% 99% 98%
8 MLD Large Clostridial Toxin 270 kda Glucosyltransferase TcdB Major virulence factor Found in all clinically relevant isolates Immunity to the TcdB provides protection from CDI TcdB(-) strains are attenuated in virulence W D D D H C E E GTD CPD TMD CROP
9 TcdB TcdB Cellular Intoxication by TcdB/TcdA RME Glc UDP Rho Rac Cdc42 UDP-Glc IP 6 H + UDP H + IP 6 H + H + H + H +
10 W D D GTD % Identity
11 D H C 698 CPD % Identity
12 E E TMD % Identity
13 CROP % Identity
14 Impact of TcdB on Zebrafish TcdB HIST TcdB HV 10 nm 1 nm Untreated Hamm et al. (2006) PNAS Lanis et al. (2010) PLoS Pathogens
15 No difference in enzymatic activity of TcdB HIST and TcdB HV No correlative difference in cell binding between TcdB HIST and TcdB HV TcdB HV gains access to the cytoplasm (translocates) more rapidly than TcdB HIST
16 Organ Pathologies in TcdB-Treated Mice Liver Spleen Bone Marrow Brain TcdB HIST TcdB HV
17 Survival of TcdB Treated Mice
18 Cysteine Protease Activity of Autoproteoytic Bacterial Toxins Egerer and Satchell, PLoS Path 2010
19 Differences in autoproteolytic activity between various CPDs C. sordellii Lethal Toxin requires low ph for processing TcdA is much less efficient at processing despite equal IP6 affinity MARTX toxins reset to process multiple substrates
20 Enhanced processing of TcdB HV IP6 (μm) TcdB TcdB TcdB HIST TcdB TcdB TcdB TcdB HIST EC 50 IP6 = 9.20 ± 1.70 μm TcdB HV EC 50 IP6 = 4.97 ± μm TcdB HV TcdB Lanis et al. Mol. Micro. 2012
21 Activation of the Cysteine Protease Domain (CPD) Shen et al. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2011 Pruitt et al. (2009) JBC, 284, 33
22 TcdB HIST can exist in an activated unprocessed form Time (min) TcdB TcdB HIST Fluorescence TcdB Coomassie TcdB HV Fluorescence TcdB TcdB Coomassie TcdB HIST binds more probe in the unprocessed form than TcdB HV Lanis et al. Mol. Micro. 2012
23 TcdB HIST is predominantly labeled in the uncleaved form AWP19 (μm) TcdB TcdB HIST Fluorescence TcdB Coomassie TcdB HV Fluorescence TcdB TcdB Coomassie The intermediate form of TcdB HV is only evident with high concentrations of probe Lanis et al. Mol. Micro. 2012
24 TcdB HV shows enhanced affinity for intramolecular substrate TcdB HV IP6 TcdB HIST Key TcdB Substrate (Enzymatic Domain) AWP19 probe / Inhibitor Lanis et al. Mol. Micro. 2012
25 Differences in Cell Entry TcdB HV TcdB HIST H + H + H + H + H + H + H + H + H + H + H + H+ H+ H+ H + IP 6 IP 6 H+ IP 6 IP 6
26 % of Max TcdB CTERM Interactions (4 C) c-term 027 c-term HIST HV FL4-H TcdB CROP * + CROP + CROP
27 % of Max TcdB CTERM Interactions (37 C) c-term 027 c-term HV HIST FL4-H TcdB CROP * + CROP + CROP
28 TcdB Neutralization with TcdB HIST CTD antiserum * TcdB HIST +serum TcdB HV + serum
29 Solid Phase Peptide ELISA Solid Phase Peptide ELISA TcdB N- -C Enzymatic Domain CP D Translocation C-terminal antigenic region (Receptor Binding Domain) Peptides
30
31 % Viability TcdB HIST CTD HIST CTD HV >CTD HIST
32 Mot (+) Mot (-) Aggregation (-) HV/Ep Aggregation (+) Hist HV/Ep Hist Flagella CwpV Hist PaLoc tcdr tcdb tcde tcda tcdc CDT: Binary Toxin cdtr Gyrase gyra Fq S 078 HV/Ep tcdr tcdb tcde tcda cdtr cdta cdtb gyra Fq R core genes 505 variant genes
33 Sequence Comparison TcdB 078,012,027 Ribotype GTD CPD TMD CROP AA differences Green, match to 012 Red and blue, different in all strains White 078, 027 identical Yellow, unique to % Identity % Identity % Identity
34 Conclusion TcdB HV is a more potent toxin than TcdB HIST TcdB HV undergoes more efficient autoprocessing than TcdB HIST TcdB HV and TcdB HIST vary in putative neutralizing epitopes within the CTD The CTD of TcdB HV may contribute to more efficient cell entry TcdB 078 sequence varies from TcdB HV and TcdB HIST
35 Acknowledgements Ballard Research Group Soumitra Barua, Ph.D. Jason Larabee, Ph.D. Jonathan Hunt, Ph.D. Logan Hightower Jordi Lanis Latisha Heinlen, M.D., Ph.D. Collaborators Judith James, M.D., Ph.D. (OMRF) Aimee Shen, Ph.D. University of Vermont
Clostridium difficile Toxins: Mechanism of Action and Role in Disease
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Apr. 2005, p. 247 263 Vol. 18, No. 2 0893-8512/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.18.2.247 263.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Clostridium
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Apr. 2005, p. 247 263 Vol. 18, No. 2 0893-8512/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.18.2.247 263.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Clostridium
STRUCTURAL AND FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS OF CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE TOXINS A AND B. Rory Nelson Pruitt. Dissertation. Submitted to the Faculty of the
 STRUCTURAL AND FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS OF CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE TOXINS A AND B By Rory Nelson Pruitt Dissertation Submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Vanderbilt University in partial fulfillment
STRUCTURAL AND FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS OF CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE TOXINS A AND B By Rory Nelson Pruitt Dissertation Submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Vanderbilt University in partial fulfillment
Genetic characteristics of toxigenic Clostridia and toxin gene evolution
 Genetic characteristics of toxigenic Clostridia and toxin gene evolution Michel Popoff, Philippe Bouvet To cite this version: Michel Popoff, Philippe Bouvet. Genetic characteristics of toxigenic Clostridia
Genetic characteristics of toxigenic Clostridia and toxin gene evolution Michel Popoff, Philippe Bouvet To cite this version: Michel Popoff, Philippe Bouvet. Genetic characteristics of toxigenic Clostridia
About OMICS Group Conferences
 About OMICS Group OMICS Group International is an amalgamation of Open Access publications and worldwide international science conferences and events. Established in the year 2007 with the sole aim of
About OMICS Group OMICS Group International is an amalgamation of Open Access publications and worldwide international science conferences and events. Established in the year 2007 with the sole aim of
Binary Bacterial Toxins
 Binary Bacterial Toxins C2- and VIP-Toxin Michael Leuber Biotechnology University Würzburg 1 Bacterial Toxins (1) Porin-like toxins (2) Toxins that bind to or modify existing ion channels (3) Toxins with
Binary Bacterial Toxins C2- and VIP-Toxin Michael Leuber Biotechnology University Würzburg 1 Bacterial Toxins (1) Porin-like toxins (2) Toxins that bind to or modify existing ion channels (3) Toxins with
Structure and mode of action of clostridial glucosylating toxins: the ABCD model
 Review Structure and mode of action of clostridial glucosylating toxins: the ABCD model Thomas Jank and Klaus Aktories Institut für Experimentelle und Klinische Pharmakologie und Toxikologie der Albert-Ludwigs-Universität
Review Structure and mode of action of clostridial glucosylating toxins: the ABCD model Thomas Jank and Klaus Aktories Institut für Experimentelle und Klinische Pharmakologie und Toxikologie der Albert-Ludwigs-Universität
CRISPR-SeroSeq: A Developing Technique for Salmonella Subtyping
 Department of Biological Sciences Seminar Blog Seminar Date: 3/23/18 Speaker: Dr. Nikki Shariat, Gettysburg College Title: Probing Salmonella population diversity using CRISPRs CRISPR-SeroSeq: A Developing
Department of Biological Sciences Seminar Blog Seminar Date: 3/23/18 Speaker: Dr. Nikki Shariat, Gettysburg College Title: Probing Salmonella population diversity using CRISPRs CRISPR-SeroSeq: A Developing
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11419 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of innate immune signaling pathways induced by intracellular Salmonella in cultured macrophages. a, During the infection Salmonella
doi:10.1038/nature11419 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of innate immune signaling pathways induced by intracellular Salmonella in cultured macrophages. a, During the infection Salmonella
NAME: Microbiology BI234 MUST be written and will not be accepted as a typed document. 1.
 Chapter 3 Study Guide Explain the 3 main characteristics that help differentiate prokaryotes from eukaryotes. What are the 7 structures/substances found in all bacterial cells? What are 8 specific structures
Chapter 3 Study Guide Explain the 3 main characteristics that help differentiate prokaryotes from eukaryotes. What are the 7 structures/substances found in all bacterial cells? What are 8 specific structures
RANK. Alternative names. Discovery. Structure. William J. Boyle* SUMMARY BACKGROUND
 RANK William J. Boyle* Department of Cell Biology, Amgen, Inc., One Amgen Center Drive, Thousand Oaks, CA 91320-1799, USA * corresponding author tel: 805-447-4304, fax: 805-447-1982, e-mail: bboyle@amgen.com
RANK William J. Boyle* Department of Cell Biology, Amgen, Inc., One Amgen Center Drive, Thousand Oaks, CA 91320-1799, USA * corresponding author tel: 805-447-4304, fax: 805-447-1982, e-mail: bboyle@amgen.com
Peptide-derived Inhibitors of Protein-Protein Interactions
 Peptide-derived Inhibitors of Protein-Protein Interactions Sven Hennig Department of Chemistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam 1 Biomolecular recognitions Classification via interaction
Peptide-derived Inhibitors of Protein-Protein Interactions Sven Hennig Department of Chemistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam 1 Biomolecular recognitions Classification via interaction
Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg Lapets ASSAY and Drug Development Technologies 2004, 2:
 1 3/1/2005 A Quantitative Cell-Based High-Content Screening Assay for the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Specific Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg
1 3/1/2005 A Quantitative Cell-Based High-Content Screening Assay for the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Specific Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg
Supplementary figure 1 Application of tmfret in LeuT. (a) To assess the feasibility of using tmfret for distance-dependent measurements in LeuT, a
 Supplementary figure 1 Application of tmfret in LeuT. (a) To assess the feasibility of using tmfret for distance-dependent measurements in LeuT, a series of tmfret-pairs comprised of single cysteine mutants
Supplementary figure 1 Application of tmfret in LeuT. (a) To assess the feasibility of using tmfret for distance-dependent measurements in LeuT, a series of tmfret-pairs comprised of single cysteine mutants
Proteomics. Areas of Interest
 Introduction to BioMEMS & Medical Microdevices Proteomics and Protein Microarrays Companion lecture to the textbook: Fundamentals of BioMEMS and Medical Microdevices, by Prof., http://saliterman.umn.edu/
Introduction to BioMEMS & Medical Microdevices Proteomics and Protein Microarrays Companion lecture to the textbook: Fundamentals of BioMEMS and Medical Microdevices, by Prof., http://saliterman.umn.edu/
Bacterial Morphology and Structure م.م رنا مشعل
 Bacterial Morphology and Structure م.م رنا مشعل SIZE OF BACTERIA Unit for measurement : Micron or micrometer, μm: 1μm=10-3 mm Size: Varies with kinds of bacteria, and also related to their age and external
Bacterial Morphology and Structure م.م رنا مشعل SIZE OF BACTERIA Unit for measurement : Micron or micrometer, μm: 1μm=10-3 mm Size: Varies with kinds of bacteria, and also related to their age and external
Binary Bacterial Toxins: Biochemistry, Biology, and Applications of Common Clostridium and Bacillus Proteins
 MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS, Sept. 2004, p. 373 402 Vol. 68, No. 3 1092-2172/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.68.3.373 402.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights
MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS, Sept. 2004, p. 373 402 Vol. 68, No. 3 1092-2172/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.68.3.373 402.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights
Microbiology / Active Lecture Questions Chapter 10 Classification of Microorganisms 1 Chapter 10 Classification of Microorganisms
 1 2 Bergey s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology differs from Bergey s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology in that the former a. groups bacteria into species. b. groups bacteria according to phylogenetic
1 2 Bergey s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology differs from Bergey s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology in that the former a. groups bacteria into species. b. groups bacteria according to phylogenetic
Received 12 May 2011/Returned for modification 8 June 2011/Accepted 10 July 2011
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Oct. 2011, p. 3913 3921 Vol. 79, No. 10 0019-9567/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/iai.05372-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Membrane Translocation
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Oct. 2011, p. 3913 3921 Vol. 79, No. 10 0019-9567/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/iai.05372-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Membrane Translocation
Ch 3. Bacteria and Archaea
 Ch 3 Bacteria and Archaea SLOs for Culturing of Microorganisms Compare and contrast the overall cell structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. List structures all bacteria possess. Describe three basic
Ch 3 Bacteria and Archaea SLOs for Culturing of Microorganisms Compare and contrast the overall cell structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. List structures all bacteria possess. Describe three basic
ENCODE DCC Antibody Validation Document
 ENCODE DCC Antibody Validation Document Date of Submission Name: Email: Lab Antibody Name: Target: Company/ Source: Catalog Number, database ID, laboratory Lot Number Antibody Description: Target Description:
ENCODE DCC Antibody Validation Document Date of Submission Name: Email: Lab Antibody Name: Target: Company/ Source: Catalog Number, database ID, laboratory Lot Number Antibody Description: Target Description:
Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice Supplementary Figure 2.
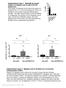 Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice. Percentage of marginal zone B cells in the spleen of wild-type mice (+/+), mice homozygous for cpm or pri
Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice. Percentage of marginal zone B cells in the spleen of wild-type mice (+/+), mice homozygous for cpm or pri
Succinate (Succinic Acid) Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
 Succinate (Succinic Acid) Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA3955 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background...
Succinate (Succinic Acid) Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA3955 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background...
Host-Pathogen interaction-ii. Pl Path 604 PN Sharma Department of Plant Pathology CSK HPKV, Palampur
 Host-Pathogen interaction-ii Pl Path 604 PN Sharma Department of Plant Pathology CSK HPKV, Palampur-176062 It was originally believed that gene-for-gene resistance was conferred by a direct interaction
Host-Pathogen interaction-ii Pl Path 604 PN Sharma Department of Plant Pathology CSK HPKV, Palampur-176062 It was originally believed that gene-for-gene resistance was conferred by a direct interaction
Lactacystin. 3. Biological activity 5-9) 1) Lactacystin inhibits cell cycle progression 5) and induces neurite outgrowth in Neuro 2a cells 1).
 1. Discovery, producing organism and structure 1-4) was originally isolated from a broth of treptomyces lactacystinicus strain M-6519 T while screening for neurite outgrowth inducers in euro 2a, a cell
1. Discovery, producing organism and structure 1-4) was originally isolated from a broth of treptomyces lactacystinicus strain M-6519 T while screening for neurite outgrowth inducers in euro 2a, a cell
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 GP2 Type I-piliated bacteria FAE M cell M cell pocket idc T cell mdc Generation of antigenspecific T cells Induction of antigen-specific mucosal immune response Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic diagram
GP2 Type I-piliated bacteria FAE M cell M cell pocket idc T cell mdc Generation of antigenspecific T cells Induction of antigen-specific mucosal immune response Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic diagram
Pathogenic effects of glucosyltransferase from Clostridium difficile toxins
 Pathogens and Disease, 74, 2016, ftw024 doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftw024 Advance Access Publication Date: 4 April 2016 Minireview MINIREVIEW Pathogenic effects of glucosyltransferase from Clostridium difficile
Pathogens and Disease, 74, 2016, ftw024 doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftw024 Advance Access Publication Date: 4 April 2016 Minireview MINIREVIEW Pathogenic effects of glucosyltransferase from Clostridium difficile
SPHERO TM Magnetic Particles
 SPHER TM Particles SPHER TM Microparticles provide high quality and reproducible results for your application Allow for rapid and reliable binding between the target and magnetic particle Consists of a
SPHER TM Particles SPHER TM Microparticles provide high quality and reproducible results for your application Allow for rapid and reliable binding between the target and magnetic particle Consists of a
Structure based drug design and LIE models for GPCRs
 Structure based drug design and LIE models for GPCRs Peter Kolb kolb@docking.org Shoichet Lab ACS 237 th National Meeting, March 24, 2009 p.1/26 [Acknowledgements] Brian Shoichet John Irwin Mike Keiser
Structure based drug design and LIE models for GPCRs Peter Kolb kolb@docking.org Shoichet Lab ACS 237 th National Meeting, March 24, 2009 p.1/26 [Acknowledgements] Brian Shoichet John Irwin Mike Keiser
WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT?
 CHAPTER 9 THE CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF BACTERIAL ANATOMY WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? Bacterial structures play a significant role in the five steps required for infection OVERVIEW The Clinical Signifcance of
CHAPTER 9 THE CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF BACTERIAL ANATOMY WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? Bacterial structures play a significant role in the five steps required for infection OVERVIEW The Clinical Signifcance of
Insights into the mechanism of botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) receptor binding and substrate cleavage from a structural perspective
 Insights into the mechanism of botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) receptor binding and substrate cleavage from a structural perspective Axel Brunger Stanford University Conference on New Frontiers in Microbiology
Insights into the mechanism of botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) receptor binding and substrate cleavage from a structural perspective Axel Brunger Stanford University Conference on New Frontiers in Microbiology
MOLECULAR DRUG TARGETS
 MOLECULAR DRUG TARGETS LEARNING OUTCOMES At the end of this session student shall be able to: List different types of druggable targets Describe forces involved in drug-receptor interactions Describe theories
MOLECULAR DRUG TARGETS LEARNING OUTCOMES At the end of this session student shall be able to: List different types of druggable targets Describe forces involved in drug-receptor interactions Describe theories
Enhancing hydrogen production of microalgae by redirecting electrons from photosystem I to hydrogenase
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary information for Enhancing hydrogen production of microalgae
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary information for Enhancing hydrogen production of microalgae
SPHERO TM Magnetic Particles
 56 27845 Irma Lee Circle, Lake Forest, IL 645 SPHER TM Magnetic SPHER TM Magnetic Microparticles provide high quality and reproducible results for your application Allow for rapid and reliable binding
56 27845 Irma Lee Circle, Lake Forest, IL 645 SPHER TM Magnetic SPHER TM Magnetic Microparticles provide high quality and reproducible results for your application Allow for rapid and reliable binding
Caspase Activation as a Versatile Assay Platform for Detection of Cytotoxic. Bacterial Toxins
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 3 July 2013 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.01161-13 Copyright 2013, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Caspase Activation as
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 3 July 2013 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.01161-13 Copyright 2013, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Caspase Activation as
Biology of Salmonella David Holden
 Biology of Salmonella David Holden Lecture 2 life on the inside trafficking and phagolysosomal avoidance PhoP/Q and the SPI-2 T3SS control of SPI-2 effector translocation effector function analysis at
Biology of Salmonella David Holden Lecture 2 life on the inside trafficking and phagolysosomal avoidance PhoP/Q and the SPI-2 T3SS control of SPI-2 effector translocation effector function analysis at
Glucosylation of Rho GTPases by Clostridium difficile toxin A triggers apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells
 Journal of Medical Microbiology (2008), 57, 765 770 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.47769-0 Glucosylation of Rho GTPases by Clostridium difficile toxin A triggers apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells Ralf Gerhard,
Journal of Medical Microbiology (2008), 57, 765 770 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.47769-0 Glucosylation of Rho GTPases by Clostridium difficile toxin A triggers apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells Ralf Gerhard,
Processing of Cry3Bb1 and Cry34Ab1/Cry35Ab1 in the Diabrotica midgut
 COST Action 862 Bacterial Toxins for Insect Control Working Group 3 Integrated Pest Management Workshop Bt-toxins against Diabrotica: Potential and prospective use in Europe University of Kiel, Salzau
COST Action 862 Bacterial Toxins for Insect Control Working Group 3 Integrated Pest Management Workshop Bt-toxins against Diabrotica: Potential and prospective use in Europe University of Kiel, Salzau
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005
 7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
Lecture 2: Read about the yeast MAT locus in Molecular Biology of the Gene. Watson et al. Chapter 10. Plus section on yeast as a model system Read
 Lecture 2: Read about the yeast MAT locus in Molecular Biology of the Gene. Watson et al. Chapter 10. Plus section on yeast as a model system Read chapter 22 and chapter 10 [section on MATing type gene
Lecture 2: Read about the yeast MAT locus in Molecular Biology of the Gene. Watson et al. Chapter 10. Plus section on yeast as a model system Read chapter 22 and chapter 10 [section on MATing type gene
Cross-Protection Against Salmonella enteritidis
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Apr. 1968, p. 1343-1349 Copyright 1968 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 95, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. Cross-Protection Against Salmonella enteritidis Infection in Mice FRANK
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Apr. 1968, p. 1343-1349 Copyright 1968 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 95, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. Cross-Protection Against Salmonella enteritidis Infection in Mice FRANK
Translation Part 2 of Protein Synthesis
 Translation Part 2 of Protein Synthesis IN: How is transcription like making a jello mold? (be specific) What process does this diagram represent? A. Mutation B. Replication C.Transcription D.Translation
Translation Part 2 of Protein Synthesis IN: How is transcription like making a jello mold? (be specific) What process does this diagram represent? A. Mutation B. Replication C.Transcription D.Translation
Apoptosis Detection Using the BD Accuri C6 Flow Cytometer
 Apoptosis Detection Using the BD Accuri C6 Flow Cytometer Stacey Roys, Marketing Applications Specialist, BD Biosciences Cyndy Lane, Senior Product Manager, BD Biosciences 23-14519-00 Outline What is apoptosis?
Apoptosis Detection Using the BD Accuri C6 Flow Cytometer Stacey Roys, Marketing Applications Specialist, BD Biosciences Cyndy Lane, Senior Product Manager, BD Biosciences 23-14519-00 Outline What is apoptosis?
Cell Cycle Control in the Fission Yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe
 Journal of Generul Microbiology ( 1989, 131, 2 123-2 127. Printed in Great Britain 2123 Cell Cycle Control in the Fission Yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe The Tenth Fleming Lecture ByPAUL NURSE Imperial
Journal of Generul Microbiology ( 1989, 131, 2 123-2 127. Printed in Great Britain 2123 Cell Cycle Control in the Fission Yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe The Tenth Fleming Lecture ByPAUL NURSE Imperial
William D. Singer, Ph.D.
 William D. Singer, Ph.D. billsinger@dcccd.edu EDUCATION AND TRAINING University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center; Dallas, Texas 1991-1995 ~ Postdoctoral Studies, Cellular Signal Transduction University
William D. Singer, Ph.D. billsinger@dcccd.edu EDUCATION AND TRAINING University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center; Dallas, Texas 1991-1995 ~ Postdoctoral Studies, Cellular Signal Transduction University
Enzyme function: the transition state. Enzymes & Kinetics V: Mechanisms. Catalytic Reactions. Margaret A. Daugherty A B. Lecture 16: Fall 2003
 Lecture 16: Enzymes & Kinetics V: Mechanisms Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 Enzyme function: the transition state Catalytic Reactions A B Catalysts (e.g. enzymes) act by lowering the transition state
Lecture 16: Enzymes & Kinetics V: Mechanisms Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 Enzyme function: the transition state Catalytic Reactions A B Catalysts (e.g. enzymes) act by lowering the transition state
Catalytic Reactions. Intermediate State in Catalysis. Lecture 16: Catalyzed reaction. Uncatalyzed reaction. Enzymes & Kinetics V: Mechanisms
 Enzyme function: the transition state Catalytic Reactions Lecture 16: Enzymes & Kinetics V: Mechanisms Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 A B Catalysts (e.g. enzymes) act by lowering the transition state
Enzyme function: the transition state Catalytic Reactions Lecture 16: Enzymes & Kinetics V: Mechanisms Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 A B Catalysts (e.g. enzymes) act by lowering the transition state
Molecular Biology (9)
 Molecular Biology (9) Translation Mamoun Ahram, PhD Second semester, 2017-2018 1 Resources This lecture Cooper, Ch. 8 (297-319) 2 General information Protein synthesis involves interactions between three
Molecular Biology (9) Translation Mamoun Ahram, PhD Second semester, 2017-2018 1 Resources This lecture Cooper, Ch. 8 (297-319) 2 General information Protein synthesis involves interactions between three
Caspase 3-mediated cleavage of the vacuolar proton-pumping ATPase subunit ATP6V1B2
 Caspase 3-mediated cleavage of the vacuolar proton-pumping ATPase subunit ATP6V1B2 Usnish Majumdar Mentored by Prof. James Mandell, M.D., Ph.D. UVa Medical Center, Department of Pathology Supported by
Caspase 3-mediated cleavage of the vacuolar proton-pumping ATPase subunit ATP6V1B2 Usnish Majumdar Mentored by Prof. James Mandell, M.D., Ph.D. UVa Medical Center, Department of Pathology Supported by
Lecture 2, 5/12/2001: Local alignment the Smith-Waterman algorithm. Alignment scoring schemes and theory: substitution matrices and gap models
 Lecture 2, 5/12/2001: Local alignment the Smith-Waterman algorithm Alignment scoring schemes and theory: substitution matrices and gap models 1 Local sequence alignments Local sequence alignments are necessary
Lecture 2, 5/12/2001: Local alignment the Smith-Waterman algorithm Alignment scoring schemes and theory: substitution matrices and gap models 1 Local sequence alignments Local sequence alignments are necessary
Apoptosis & Autophagy
 SPETSAI SUMMER SCHOOL 2010 Host Microbe Interactions Cellular Response to Infection: Apoptosis & Autophagy Christoph Dehio There are many ways to die Apoptosis: Historical perspective Process of programmed
SPETSAI SUMMER SCHOOL 2010 Host Microbe Interactions Cellular Response to Infection: Apoptosis & Autophagy Christoph Dehio There are many ways to die Apoptosis: Historical perspective Process of programmed
Computer Immunlogy. Primary response: Antigen has not been seen before by the immune system.
 Computer Immunlogy http://www.cheniere.org/images/rife/rife20.jpg Primary response: Antigen has not been seen before by the immune system. Detection of Pathogens via Affinity Maturation Trillions of lymphocytes
Computer Immunlogy http://www.cheniere.org/images/rife/rife20.jpg Primary response: Antigen has not been seen before by the immune system. Detection of Pathogens via Affinity Maturation Trillions of lymphocytes
Rex-Family Repressor/NADH Complex
 Kasey Royer Michelle Lukosi Rex-Family Repressor/NADH Complex Part A The biological sensing protein that we selected is the Rex-family repressor/nadh complex. We chose this sensor because it is a calcium
Kasey Royer Michelle Lukosi Rex-Family Repressor/NADH Complex Part A The biological sensing protein that we selected is the Rex-family repressor/nadh complex. We chose this sensor because it is a calcium
Immunomicroarray for multipathogens
 Funding period: Jan 3-Feb ultipathogen screening and /or confirmation via microarray detection Arun Bhunia, ark organ, Shu-I Tu Center for Food Safety and Engineering, Purdue University ERRC, Wyndmoor,
Funding period: Jan 3-Feb ultipathogen screening and /or confirmation via microarray detection Arun Bhunia, ark organ, Shu-I Tu Center for Food Safety and Engineering, Purdue University ERRC, Wyndmoor,
Lecture Notes for Fall Network Modeling. Ernest Fraenkel
 Lecture Notes for 20.320 Fall 2012 Network Modeling Ernest Fraenkel In this lecture we will explore ways in which network models can help us to understand better biological data. We will explore how networks
Lecture Notes for 20.320 Fall 2012 Network Modeling Ernest Fraenkel In this lecture we will explore ways in which network models can help us to understand better biological data. We will explore how networks
Role of Surface Charge of Inhibitors on Amyloid Beta Fibrillation
 Supporting Information Role of Surface Charge of Inhibitors on Amyloid Beta Fibrillation SWATHI SUDHAKAR, PANDURANGAN KALIPILLAI, POORNIMA BUDIME SANTHOSH, ETHAYARAJA MANI* POLYMER ENGINEERING AND COLLOID
Supporting Information Role of Surface Charge of Inhibitors on Amyloid Beta Fibrillation SWATHI SUDHAKAR, PANDURANGAN KALIPILLAI, POORNIMA BUDIME SANTHOSH, ETHAYARAJA MANI* POLYMER ENGINEERING AND COLLOID
MicroReview. Regulation of toxin production in the pathogenic clostridia. Summary. Introduction
 Molecular Microbiology (2014) 91(2), 221 231 doi:10.1111/mmi.12469 First published online 6 December 2013 MicroReview Regulation of toxin production in the pathogenic clostridia Glen P. Carter,* Jackie
Molecular Microbiology (2014) 91(2), 221 231 doi:10.1111/mmi.12469 First published online 6 December 2013 MicroReview Regulation of toxin production in the pathogenic clostridia Glen P. Carter,* Jackie
MAPK kinase kinase regulation of SAPK/JNK pathways
 MAPK kinase kinase regulation of SAPK/JNK pathways Lisa Stalheim and Gary L. Johnson Abstract SAPK/JNK members of the MAPK family are regulated by at least fourteen known MAPK kinase kinases (MKKKs). In
MAPK kinase kinase regulation of SAPK/JNK pathways Lisa Stalheim and Gary L. Johnson Abstract SAPK/JNK members of the MAPK family are regulated by at least fourteen known MAPK kinase kinases (MKKKs). In
Microcalorimetry for the Life Sciences
 Microcalorimetry for the Life Sciences Why Microcalorimetry? Microcalorimetry is universal detector Heat is generated or absorbed in every chemical process In-solution No molecular weight limitations Label-free
Microcalorimetry for the Life Sciences Why Microcalorimetry? Microcalorimetry is universal detector Heat is generated or absorbed in every chemical process In-solution No molecular weight limitations Label-free
Bacillus anthracis. Clostridium botulinum Clostridium perfringens and other, but never Gram-negative microbes
 SPORES (endospores) the spore is formed inside the parent vegetative cell hence the name endospores The spore is a dehydrated, multishelled structure that protects and allows the bacteria to exist in suspended
SPORES (endospores) the spore is formed inside the parent vegetative cell hence the name endospores The spore is a dehydrated, multishelled structure that protects and allows the bacteria to exist in suspended
Ribosome readthrough
 Ribosome readthrough Starting from the base PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Eukaryotic translation can be divided into four stages: Initiation, Elongation, Termination and Recycling During translation, the ribosome
Ribosome readthrough Starting from the base PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Eukaryotic translation can be divided into four stages: Initiation, Elongation, Termination and Recycling During translation, the ribosome
The Salmonella SPI2 Effector SseI Mediates Long-Term Systemic Infection by Modulating Host Cell Migration
 The Salmonella SPI2 Effector SseI Mediates Long-Term Systemic Infection by Modulating Host Cell Migration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
The Salmonella SPI2 Effector SseI Mediates Long-Term Systemic Infection by Modulating Host Cell Migration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Supplementary Figure 1. Biochemical and sequence alignment analyses the
 Supplementary Figure 1. Biochemical and sequence alignment analyses the interaction of OPTN and TBK1. (a) Analytical gel filtration chromatography analysis of the interaction between TBK1 CTD and OPTN(1-119).
Supplementary Figure 1. Biochemical and sequence alignment analyses the interaction of OPTN and TBK1. (a) Analytical gel filtration chromatography analysis of the interaction between TBK1 CTD and OPTN(1-119).
Signal Transduction. Dr. Chaidir, Apt
 Signal Transduction Dr. Chaidir, Apt Background Complex unicellular organisms existed on Earth for approximately 2.5 billion years before the first multicellular organisms appeared.this long period for
Signal Transduction Dr. Chaidir, Apt Background Complex unicellular organisms existed on Earth for approximately 2.5 billion years before the first multicellular organisms appeared.this long period for
Microbial Genetics, Mutation and Repair. 2. State the function of Rec A proteins in homologous genetic recombination.
 Answer the following questions 1. Define genetic recombination. Microbial Genetics, Mutation and Repair 2. State the function of Rec A proteins in homologous genetic recombination. 3. List 3 types of bacterial
Answer the following questions 1. Define genetic recombination. Microbial Genetics, Mutation and Repair 2. State the function of Rec A proteins in homologous genetic recombination. 3. List 3 types of bacterial
Microplate-Based Measurements of Target Engagement in Live Cells With CETSA - a Reflection on Screen Results and Quantitative Interpretations
 Microplate-Based Measurements of Target Engagement in Live Cells With CETSA - a Reflection on Screen Results and Quantitative Interpretations Thomas Lundbäck Karolinska Institutet ELRIG Drug Discovery
Microplate-Based Measurements of Target Engagement in Live Cells With CETSA - a Reflection on Screen Results and Quantitative Interpretations Thomas Lundbäck Karolinska Institutet ELRIG Drug Discovery
Assessment of toxicological properties and establishment of risk profiles - genotoxic properties of selected spice compounds
 Assessment of toxicological properties and establishment of risk profiles - genotoxic properties of selected spice compounds Frankfurt/Main, September 25 th 212 V.J. Koller 1, V. Auwärter 2, G. Zlabinger
Assessment of toxicological properties and establishment of risk profiles - genotoxic properties of selected spice compounds Frankfurt/Main, September 25 th 212 V.J. Koller 1, V. Auwärter 2, G. Zlabinger
Structural and functional aspects of gastric proton pump, H +,K + -ATPase
 Kazuhiro ABE, Ph. D. E-mail:kabe@cespi.nagoya-u.ac.jp Structural and functional aspects of gastric proton pump, H +,K + -ATPase In response to food intake, ph of our stomach reaches around 1. This highly
Kazuhiro ABE, Ph. D. E-mail:kabe@cespi.nagoya-u.ac.jp Structural and functional aspects of gastric proton pump, H +,K + -ATPase In response to food intake, ph of our stomach reaches around 1. This highly
Carri-Lyn Mead Thursday, January 13, 2005 Terry Fox Laboratory, Dr. Dixie Mager
 Investigating Trends in Transposable Element Insertion within Regulatory Regions Carri-Lyn Mead cmead@bcgsc.ca Thursday, January 13, 2005 Terry Fox Laboratory, Dr. Dixie Mager Outline Transposable Element
Investigating Trends in Transposable Element Insertion within Regulatory Regions Carri-Lyn Mead cmead@bcgsc.ca Thursday, January 13, 2005 Terry Fox Laboratory, Dr. Dixie Mager Outline Transposable Element
Cell Death & Trophic Factors II. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cell Death & Trophic Factors II Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Remember? Neurotrophins are cell survival factors that neurons get from their target cells! There is a
Cell Death & Trophic Factors II Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Remember? Neurotrophins are cell survival factors that neurons get from their target cells! There is a
Problem Set 5 Question 1
 2.32 Problem Set 5 Question As discussed in class, drug discovery often involves screening large libraries of small molecules to identify those that have favorable interactions with a certain druggable
2.32 Problem Set 5 Question As discussed in class, drug discovery often involves screening large libraries of small molecules to identify those that have favorable interactions with a certain druggable
ADAM FAMILY. ephrin A INTERAZIONE. Eph ADESIONE? PROTEOLISI ENDOCITOSI B A RISULTATO REPULSIONE. reverse. forward
 ADAM FAMILY - a family of membrane-anchored metalloproteases that are known as A Disintegrin And Metalloprotease proteins and are key components in protein ectodomain shedding Eph A INTERAZIONE B ephrin
ADAM FAMILY - a family of membrane-anchored metalloproteases that are known as A Disintegrin And Metalloprotease proteins and are key components in protein ectodomain shedding Eph A INTERAZIONE B ephrin
Nuclear import of DNA: genetic modification of plants
 Nuclear import of DNA: genetic modification of plants gene delivery by Agrobacterium tumefaciens T. Tzfira & V. Citovsky. 2001. Trends in Cell Biol. 12: 121-129 VirE2 binds ssdna in vitro forms helical
Nuclear import of DNA: genetic modification of plants gene delivery by Agrobacterium tumefaciens T. Tzfira & V. Citovsky. 2001. Trends in Cell Biol. 12: 121-129 VirE2 binds ssdna in vitro forms helical
Drosophila Apoptosis and the Regulation of the Caspase Cascade
 Drosophila Apoptosis and the Regulation of the Caspase Cascade Kate Stafford March 18, 2005 Abstract The caspase cascade in Drosophila is controlled primarily by DIAP1 (Drosophila inhibitor of apoptosis),
Drosophila Apoptosis and the Regulation of the Caspase Cascade Kate Stafford March 18, 2005 Abstract The caspase cascade in Drosophila is controlled primarily by DIAP1 (Drosophila inhibitor of apoptosis),
Lecture 10: Cyclins, cyclin kinases and cell division
 Chem*3560 Lecture 10: Cyclins, cyclin kinases and cell division The eukaryotic cell cycle Actively growing mammalian cells divide roughly every 24 hours, and follow a precise sequence of events know as
Chem*3560 Lecture 10: Cyclins, cyclin kinases and cell division The eukaryotic cell cycle Actively growing mammalian cells divide roughly every 24 hours, and follow a precise sequence of events know as
Dr. William S. Mellon School of Pharmacy University of Wisconsin-Madison 425 N. Charter Street Madison, WI
 Dr. William S. Mellon School of Pharmacy University of Wisconsin-Madison 425 N. Charter Street Madison, WI 53706-1515 PHONE: 608 / 262-3196 FAX: 608 / 262-3997 email: WSMellon@facstaff.wisc.edu PUBLICATIONS
Dr. William S. Mellon School of Pharmacy University of Wisconsin-Madison 425 N. Charter Street Madison, WI 53706-1515 PHONE: 608 / 262-3196 FAX: 608 / 262-3997 email: WSMellon@facstaff.wisc.edu PUBLICATIONS
C a h p a t p e t r e r 6 E z n y z m y e m s
 Chapter 6 Enzymes 4. Examples of enzymatic reactions acid-base catalysis: give and take protons covalent catalysis: a transient covalent bond is formed between the enzyme and the substrate metal ion catalysis:
Chapter 6 Enzymes 4. Examples of enzymatic reactions acid-base catalysis: give and take protons covalent catalysis: a transient covalent bond is formed between the enzyme and the substrate metal ion catalysis:
Finding the Achilles Heel in Gram Negative Bacteria. Role of Medicinal Chemistry
 Finding the Achilles Heel in Gram Negative Bacteria. Role of Medicinal Chemistry Gabriele Costantino gabriele.costantino@unipr.it http://p4t.farmacia.unipr.it @gabrielecostan4 www.integrate-etn.eu Bacterial
Finding the Achilles Heel in Gram Negative Bacteria. Role of Medicinal Chemistry Gabriele Costantino gabriele.costantino@unipr.it http://p4t.farmacia.unipr.it @gabrielecostan4 www.integrate-etn.eu Bacterial
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10244 a O07391_MYCAV/127-243 NLPC_HAEIN/80-181 SPR_SHIFL/79-183 P74160_SYNY3/112-245 O24914_HELPY/301-437 Q51835_PORGI/68-178 DPP6_BACSH/163-263 YKFC_BACSU/185-292 YDHO_ECOLI/153-263
doi:10.1038/nature10244 a O07391_MYCAV/127-243 NLPC_HAEIN/80-181 SPR_SHIFL/79-183 P74160_SYNY3/112-245 O24914_HELPY/301-437 Q51835_PORGI/68-178 DPP6_BACSH/163-263 YKFC_BACSU/185-292 YDHO_ECOLI/153-263
Role as adhesin of muramidase released protein of Streptococcus s uis type 2
 2002, 25 (4) : 6771 Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University 2 1,2 1 3, (11, 210095 ; 21, 730070) : 2 (SS2) (MRP) : 11 HA9801 (MRP + ) SH006444 (MRP - ) HEp 2, MRP + MRP + ( P < 0105) 21 56 1 h ; DNase
2002, 25 (4) : 6771 Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University 2 1,2 1 3, (11, 210095 ; 21, 730070) : 2 (SS2) (MRP) : 11 HA9801 (MRP + ) SH006444 (MRP - ) HEp 2, MRP + MRP + ( P < 0105) 21 56 1 h ; DNase
Exam 4 April 15, 2005 CHEM 3511 Print Name: KEY Signature
 1) (8 pts) General Properties of Enzymes. Give four properties of enzymaticallycatalyzed reactions. The answers should indicate how enzymatic reactions differ from non-enzymatic reactions. Write four only
1) (8 pts) General Properties of Enzymes. Give four properties of enzymaticallycatalyzed reactions. The answers should indicate how enzymatic reactions differ from non-enzymatic reactions. Write four only
NMR study of complexes between low molecular mass inhibitors and the West Nile virus NS2B-NS3 protease
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2009 NMR study of complexes between low molecular mass inhibitors and the West Nile
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2009 NMR study of complexes between low molecular mass inhibitors and the West Nile
A Database of human biological pathways
 A Database of human biological pathways Steve Jupe - sjupe@ebi.ac.uk 1 Rationale Journal information Nature 407(6805):770-6.The Biochemistry of Apoptosis. Caspase-8 is the key initiator caspase in the
A Database of human biological pathways Steve Jupe - sjupe@ebi.ac.uk 1 Rationale Journal information Nature 407(6805):770-6.The Biochemistry of Apoptosis. Caspase-8 is the key initiator caspase in the
BACTERIAL PHYSIOLOGY SMALL GROUP. Monday, August 25, :00pm. Faculty: Adam Driks, Ph.D. Alan Wolfe, Ph.D.
 BACTERIAL PHYSIOLOGY SMALL GROUP Monday, August 25, 2014 1:00pm Faculty: Adam Driks, Ph.D. Alan Wolfe, Ph.D. Learning Goal To understand how bacterial physiology applies to the diagnosis and treatment
BACTERIAL PHYSIOLOGY SMALL GROUP Monday, August 25, 2014 1:00pm Faculty: Adam Driks, Ph.D. Alan Wolfe, Ph.D. Learning Goal To understand how bacterial physiology applies to the diagnosis and treatment
Phylogenomics. Gene History, Genome History and Organismal Phylogeny (genealogy of cellular life)
 Phylogenomics Gene History, Genome History and Organismal Phylogeny (genealogy of cellular life) The time will come I believe, though I shall not live to see it,when we shall have very fairly true genealogical
Phylogenomics Gene History, Genome History and Organismal Phylogeny (genealogy of cellular life) The time will come I believe, though I shall not live to see it,when we shall have very fairly true genealogical
Optimization of Immunoblot Protocol for Use with a Yeast Strain Containing the CDC7 Gene Tagged with myc
 OPTIMIZATION OF IMMUNOBLOT PROTOCOL 121 Optimization of Immunoblot Protocol for Use with a Yeast Strain Containing the CDC7 Gene Tagged with myc Jacqueline Bjornton and John Wheeler Faculty Sponsor: Anne
OPTIMIZATION OF IMMUNOBLOT PROTOCOL 121 Optimization of Immunoblot Protocol for Use with a Yeast Strain Containing the CDC7 Gene Tagged with myc Jacqueline Bjornton and John Wheeler Faculty Sponsor: Anne
depends on the translocation assembly module nanomachine
 ARTICLE NUMBER: 16064 DOI: 10.1038/NMICROBIOL.16.64 Effective assembly of fimbriae in Escherichia coli depends on the translocation assembly module nanomachine Christopher Stubenrauch 1, Matthew J. Belousoff
ARTICLE NUMBER: 16064 DOI: 10.1038/NMICROBIOL.16.64 Effective assembly of fimbriae in Escherichia coli depends on the translocation assembly module nanomachine Christopher Stubenrauch 1, Matthew J. Belousoff
Toxicological Targets. Russell L. Carr Department of Basic Sciences College of Veterinary Medicine
 Toxicological Targets Russell L. Carr Department of Basic Sciences College of Veterinary Medicine Toxicology Definitions = study of poisons Poison = any agent capable of producing a deleterious response
Toxicological Targets Russell L. Carr Department of Basic Sciences College of Veterinary Medicine Toxicology Definitions = study of poisons Poison = any agent capable of producing a deleterious response
Accelerated Stability of Peptides. Alisa K. Waterman, Ph.D. FreeThink Technologies, Inc.
 Accelerated Stability of Peptides Alisa K. Waterman, Ph.D. FreeThink Technologies, Inc. 1 Small Molecules Subject to chemical modifications such as oxidation, deamination, hydrolysis Chemical modifications
Accelerated Stability of Peptides Alisa K. Waterman, Ph.D. FreeThink Technologies, Inc. 1 Small Molecules Subject to chemical modifications such as oxidation, deamination, hydrolysis Chemical modifications
Studies on Pathogenesis and Immunity to Turkey Clostridial Dermatitis. K.V. Nagaraja and Anil Thachil
 Studies on Pathogenesis and Immunity to Turkey Clostridial Dermatitis K.V. Nagaraja and Anil Thachil Department of Veterinary and Biomedical Sciences, University of Minnesota, 1971 Commonwealth Ave, St.
Studies on Pathogenesis and Immunity to Turkey Clostridial Dermatitis K.V. Nagaraja and Anil Thachil Department of Veterinary and Biomedical Sciences, University of Minnesota, 1971 Commonwealth Ave, St.
Apoptosis in Mammalian Cells
 Apoptosis in Mammalian Cells 7.16 2-10-05 Apoptosis is an important factor in many human diseases Cancer malignant cells evade death by suppressing apoptosis (too little apoptosis) Stroke damaged neurons
Apoptosis in Mammalian Cells 7.16 2-10-05 Apoptosis is an important factor in many human diseases Cancer malignant cells evade death by suppressing apoptosis (too little apoptosis) Stroke damaged neurons
Chemical Exchange and Ligand Binding
 Chemical Exchange and Ligand Binding NMR time scale Fast exchange for binding constants Slow exchange for tight binding Single vs. multiple binding mode Calcium binding process of calcium binding proteins
Chemical Exchange and Ligand Binding NMR time scale Fast exchange for binding constants Slow exchange for tight binding Single vs. multiple binding mode Calcium binding process of calcium binding proteins
A. Reaction Mechanisms and Catalysis (1) proximity effect (2) acid-base catalysts (3) electrostatic (4) functional groups (5) structural flexibility
 (P&S Ch 5; Fer Ch 2, 9; Palm Ch 10,11; Zub Ch 9) A. Reaction Mechanisms and Catalysis (1) proximity effect (2) acid-base catalysts (3) electrostatic (4) functional groups (5) structural flexibility B.
(P&S Ch 5; Fer Ch 2, 9; Palm Ch 10,11; Zub Ch 9) A. Reaction Mechanisms and Catalysis (1) proximity effect (2) acid-base catalysts (3) electrostatic (4) functional groups (5) structural flexibility B.
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 21, 2005
 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 21, 2005 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books, a calculator, and notes but not computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 21, 2005 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books, a calculator, and notes but not computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write
Microbiology Helmut Pospiech
 Microbiology 20.03.2018 Helmut Pospiech The control of what gets in Passive transport along a concentration gradient often inefficient Active transport Requires energy consumption and what gets out ABC
Microbiology 20.03.2018 Helmut Pospiech The control of what gets in Passive transport along a concentration gradient often inefficient Active transport Requires energy consumption and what gets out ABC
5- Semaphorin-Plexin-Neuropilin
 5- Semaphorin-Plexin-Neuropilin 1 SEMAPHORINS-PLEXINS-NEUROPILINS ligands receptors co-receptors semaphorins and their receptors are known signals for: -axon guidance -cell migration -morphogenesis -immune
5- Semaphorin-Plexin-Neuropilin 1 SEMAPHORINS-PLEXINS-NEUROPILINS ligands receptors co-receptors semaphorins and their receptors are known signals for: -axon guidance -cell migration -morphogenesis -immune
C. elegans as an in vivo model to decipher microbial virulence. Centre d Immunologie de Marseille-Luminy
 C. elegans as an in vivo model to decipher microbial virulence Centre d Immunologie de Marseille-Luminy C. elegans : a model organism Mechanisms of apoptosis, RNA interference Neuronal function and development
C. elegans as an in vivo model to decipher microbial virulence Centre d Immunologie de Marseille-Luminy C. elegans : a model organism Mechanisms of apoptosis, RNA interference Neuronal function and development
Ch 4: Cellular Metabolism, Part 1
 Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Ch 4: Cellular Metabolism, Part 1 Energy as it relates to Biology Energy for synthesis and movement Energy transformation Enzymes and how they speed reactions Metabolism
Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Ch 4: Cellular Metabolism, Part 1 Energy as it relates to Biology Energy for synthesis and movement Energy transformation Enzymes and how they speed reactions Metabolism
Graduate Institute t of fanatomy and Cell Biology
 Cell Adhesion 黃敏銓 mchuang@ntu.edu.tw Graduate Institute t of fanatomy and Cell Biology 1 Cell-Cell Adhesion and Cell-Matrix Adhesion actin filaments adhesion belt (cadherins) cadherin Ig CAMs integrin
Cell Adhesion 黃敏銓 mchuang@ntu.edu.tw Graduate Institute t of fanatomy and Cell Biology 1 Cell-Cell Adhesion and Cell-Matrix Adhesion actin filaments adhesion belt (cadherins) cadherin Ig CAMs integrin
The Riboswitch is functionally separated into the ligand binding APTAMER and the decision-making EXPRESSION PLATFORM
 The Riboswitch is functionally separated into the ligand binding APTAMER and the decision-making EXPRESSION PLATFORM Purine riboswitch TPP riboswitch SAM riboswitch glms ribozyme In-line probing is used
The Riboswitch is functionally separated into the ligand binding APTAMER and the decision-making EXPRESSION PLATFORM Purine riboswitch TPP riboswitch SAM riboswitch glms ribozyme In-line probing is used
TE content correlates positively with genome size
 TE content correlates positively with genome size Mb 3000 Genomic DNA 2500 2000 1500 1000 TE DNA Protein-coding DNA 500 0 Feschotte & Pritham 2006 Transposable elements. Variation in gene numbers cannot
TE content correlates positively with genome size Mb 3000 Genomic DNA 2500 2000 1500 1000 TE DNA Protein-coding DNA 500 0 Feschotte & Pritham 2006 Transposable elements. Variation in gene numbers cannot
