Eukaryotic cell. Other big difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA. Fundamentals. Eukaryotic Chromosomes and Cell Division
|
|
|
- Sabina Dawson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Eukaryotic cell 1) Review of haploid, diploid, mitosis and meiosis (for relevant reading, see Campbell pp and ) 2) Overview of sexual life cycles 3) Components of the eukaryotic cell 4) Overview of plant tissues Fundamentals Genes are DNA sequences that code for proteins Proteins catalyze reactions and make up structures Thus genes indirectly control every reaction and structure making up a cell Genes are carried together on chromosomes Other big difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA Eukaryotic genes are spread among multiple chromosomes. Almost all eukaryotic organisms are diploid at some stage in their life cycle. This means that they have two copies of each chromosome - one from mom and one from dad. Thus they also have two copies of each gene. Prokaryotic Chromosomes and Cell Division Prokaryotic Genomes Bacterial Chromosomes- Single strands of DNA Reproduction- Binary Fission (asexual) Eukaryotic Chromosomes and Cell Division Eukaryotic Genomes Organization of Eukaryotic Genomes: Complexity! Genomic size- each human cell has 3 meters of DNA!! Chromosomal structure- Fold that 3 m into something manageable Each Chromosome is one long strand of DNA Biparental inheritance - diploidy 1
2 Figure 13.x2 Human female chromosomes. Figure 13.x3 Human female chromosomes. Human bodies are diploid (2n=46 chromosomes. Human gametes, i.e. sperm and eggs, are haploid (n=23 chromosomes). Note: the human DNA shown here is in the form of separate chromosomes, rather than condensed into a nucleus. The chromosomes are arranged into homologous pairs. The Cell Cycle The Cell Cycle Figure 7.6 Interphase- 90% of most cells life Gap 1, Synthesis, Gap 2, and Mitotic Phase What is Mitosis? Cellular Division Three main functions of cell divisions Reproduction Growth and development Tissue renewal Mitosis is a process of cell division that preserves chromosome number (e.g., diploid to diploid, haploid to haploid, or dikaryotic to dikaryotic) and results in genetically identical cells Happens during a variety of processes, including simple growth, asexual reproduction Meiosis is the process of cell division whereby chromosome number is reduced by half (e.g. diploid to haploid) Happens during sexual reproduction Results in genetically variable haploid cells (usually spores or gametes) 2
3 Mitosis The Process of cell division that results in the production of 2 daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent cell from which they arose. Mitosis is for cell growth, development and repair (and reproduction in single cell organisms) Occurs in Somatic Tissues Parts of the Replicating Chromosome Phases of Mitosis Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase 3
4 Cytokinesis- Animals Cytokinesis- Plants Genetic Variation Lets look around the class at our variation in Phenotype (how our genes are expressed on the outside) Lots of variation exists why? Helps with survival- Hot Gene and Cold Gene Genetic Variation So variation is good for a population, how do we get it? Genetic Variation in Bacteria Antibiotic resistance from random mutations Genetic Variation Antibiotic Resistance 1 in a million genes per generation will mutate E. coli reproduces in 20 minutes (Generation Time) hours = 1,000,000 cells!!! If one of these cells mutated so it was resistant, how many resistant cells in 7 more hours? Genetic Variation So, for organisms with very short generation times, depending on mutations for genetic variation can be OK What is your generation time? Can t depend on mutations for variation too slow Why is there Sex? Provides a way to mix genes and get variation 4
5 Meiosis The process of cell division that results in the production of 4 haploid gametes that are genetically different from one another and from the parents. In Mitosis we made exact copies of the parent cells, with two sets of chromosomes In Meiosis the result is different cells with only one set of chromosomes Meiosis Gametogenesis- formation of the gametes Sperm= Spermatogenesis 1 cell = 4 sperm Egg= Oogenesis 1 cell = 1 egg +3 polar bodies Need to get Chromosome number in half! Fig Meiosis- Overview Meiosis I Meiosis II 5
6 Random Assortment How do we get our Genetic Variation? We have a set of chromosomes from mom and a set from dad, which of these gets into the gametes is random Four chromosome example- 2 2 =4 combos Humans have 23 chromosomes = over 8 million different combos from each parent x 2 23 =? Over 64 trillion different combinations of your parents genes!! Random Assortment Crossing Over How do we get our Genetic Variation? The exchange of corresponding segments between two homologous chromosomes. Scrambles up the genes Happens in Prophase I of Meiosis Figure example with one chromosome Crossing Over When Meiosis Has Errors Extra Chromosomes Down Syndrome 3 copies of Chromosome 21 1 in 700 births 6
7 Extra Chromosomes When Meiosis Has Errors Abnormal Number of Sex Chromosomes When Meiosis Has Errors Alteration of Chromosome Structure Four main types of structural changes Deletion, Duplication, Inversion, and Translocation Errors are a source of Variation Most errors are bad, but some can be good. New species can be developed from extra chromosome numbers (polyploid) Beneficial changes will persist, damaging ones will disappear 7
8 Polyploidy More than 2 sets of chromosomes (diploid) Very common in plants (50-60% of flowering plants!) Can occur as a result of non-disjunction during meiosis Can occur when cytokinesis fails (autopolyploidy) Can occur between two species-interspecific hybrid (autopolyploidy) Leads to reproductive failure (eg. With diploids) Can lead to new species - especially sympatric speciation Key points Mitosis results in production of genetically identical cells Involved in growth, asexual reproduction Meiosis results in halving chromosome number, results in genetic variabilty A key step in sexual reproduction Eukaryotic cell Reproduction 1) Review of haploid, diploid, mitosis and meiosis (for relevant reading, see Campbell pp and ) 2) Overview of sexual life cycles 3) Components of the eukaryotic cell 4) Overview of plant tissues Sex or no sex? Advantages and disadvantages First eukaryotes were probably haploid and asexual. Sex gave rise to diploidy polyploidy Many plants (like many animals) can reproduce asexually Alternation of generations Gametophyte and sporophyte and the switch in dominance with advancement to land Drought resistant spores, then seeds (complex multicellular structures in which reproductive structures are surrounded by sterile cells). Seeds have a special covering and stored food Sex? Sex? Sexual reproduction Introduce new genes Diversity in phenotype and genotype Resistance to disease Resistance to environmental change: Adaptation Hard to find a mate Picking the right one Mutations/problems Parental investment? Don t know exactly what you get Asexual reproduction Fast Know exactly what you get Can spread your exact genes Cover an area quickly No need to find a mate No diversity (easily wiped out) Problem (if one exists) is reproduced Need a self recognition mechanism 8
9 Some can do both! Combination of sexual and asexual reproduction can bring the best of both worlds Hermaphrodites: no need to find the right sex! These are organisms that are both sexes at once, or can change from male to female or female to male. Life Cycles Life Cycles and diploidy Zygotic meiosis Isomorphic Alternation of Generations Gametic meiosis heteromorphic Sporic meiosis What is a sexual life cycle? A sexual life cycle (or a sexual part of a life cycle) is one which includes meiosis (which halves ploidy or chromosome number) and fertilization (which doubles it) What is a sexual life cycle? A sexual life cycle (or a sexual part of a life cycle) is one which includes meiosis (which halves ploidy or chromosome number) and fertilization (which doubles it) In contrast with asexual reproduction, which involves only mitosis The three main types of sexual life cycles, differing in the timing of meiosis and fertilization, relative to mitotic growth of multicellular bodies. Zygotic meiosis: zygote divides = 4 haploid cells. Mitosis leads to more haploid cells or a haploid individual. Differentialtion produces gametes. Gametic meiosis: 2N individual produces 1N gametes. These fuse to form a 2N zygote. Mitosis = growth. Sporic Meiosis: sporophyte (2N) individual produces 1N spores via meiosis. Spores undergo mitosis=gametophytes (1N indivviduals). These produce gametes, which fuse to form 2N zygotes =s porophytes A heterokaryotic stage may happen here in fungi. Note that the nuclei in a heterokaryotic cell are usually haploid nuclei. Thus, the code for the dikaryotic condition (one type of heterokaryotic condition) is n+n, rather than 2n. If a cell is not heterokaryotic, it is called mononucleate or monokaryotic. 9
10 Figure 13.6 The three main types of sexual life cycles, differing in the timing of meiosis and fertilization, relative to mitotic growth of multicellular bodies. The life cycle of a fern: note the dominant diploid (sporophyte) generation, and the reduced (but multicellular) gametophyte: heteromorphic alternation of generations (and some algae) Alternation of generations Life cycle of the green alga Ulva Alternation of isomorphic generations Eukaryotic cell 1) Review of haploid, diploid, mitosis and meiosis (for relevant reading, see Campbell pp and ) 2) Overview of sexual life cycles 3) Components of the eukaryotic cell 4) Overview of plant tissues 10
11 Figure 6.9 Anatomy of a single plant cell Figure 6.8 The plasma membrane Note: protoplast = everything inside the cell wall. Plasma membrane The Nucleus and Protein Synthesis Controls passage of materials into and out of cell Many compounds cannot pass directly thorugh the membrane, instead they are transported through specific carrier proteins embedded in the membrane The Endoplasmic Reticulum Endoplasmic Reticulum Smooth ER No ribosomes Involved in lipid synthesis, carbohydrate metabolism, detoxification Rough ER Has ribosomes Involved in protein synthesis Primarily proteins destined for export from the cell 11
12 The Golgi Apparatus Storage, refinement, and shipping of ER products Sacks of digestive enzymes which break down molecules in the cells Digest food, fight invaders, clean house ph of 5 Lysosomes Endomembrane system ER (smooth and rough), Golgi bodies, vesicles, lysosomes Contiguous pathway through cell for the transport of substances Vacuoles: membranous sacs with a variety of functions Vacuoles Sacks which can store enzymes, proteins, water, and cellular byproducts Plants cells often have large Central Vacuole which holds water and other stuff Vacuoles also transport things from one organelle to another within the cell Ribosomes Workbenches for making proteins Small non-membraneous structures consisting of protein and genetic material (RNA) Produced in the nucleus but work outside of it The Mighty Mitochondria Sites of cellular respiration and ATP synthesis 12
13 Plant Cell Most of the living world depends on chloroplasts for its energy! The Chloroplast Two membranes on outside Complex membrane structure on inside Figure 6.27 Microfilaments (actin filaments) are important for cytoplasmic streaming distribution of materials within a cell Central vacuoles Are selective in what passes through tonoplast (membrane enclosing the central vacuole) May be used as disposal or storage sites Can enlarge by gaining water, resulting in cell growth Figure 6.28 Plant cell walls Protects cell, maintains shape, prevents excess water uptake Figure 6.28 Plant cell walls Protects cell, maintains shape, prevents excess water uptake 13
14 Figure 6.28 Plant cell walls Protects cell, maintains shape, prevents excess water uptake Figure 6.28 Plant cell walls Protects cell, maintains shape, prevents excess water uptake Plasmodesmata: connect adjacent living cells Eukaryotic cell 1) Review of haploid, diploid, mitosis and meiosis (for relevant reading, see Campbell pp and ) 2) Overview of sexual life cycles 3) Components of the eukaryotic cell 4) Overview of plant tissues An introduction to plant tissues Tissue: an integrated group of cells with a common function, structure, or both Three tissue systems of plants Dermal tissue - outer protective covering Epidermis/periderm analogous to skin Cuticle - waxy coating to preserve water Vascular tissue - transport system Xylem: carries water and nutrients from roots to leaves. Support and food storage too. Phloem: transport organic nutrients (sugar), amino acids, lipids, hormones etc. Ground tissue - everything else. Pith (internal to vascular), Cortex Function in storage, photosynthesis, & support 14
15 Figure 35.8 The three tissue systems of a plant Dermal Tissue Epidermis Plant Cell Types Guard Cells Trichomes (appendages). Can be on roots (facilitate absorption), or on hairy leaves - reduce solar radiation in xerophytes). Some secrete salts (in halophiles) These cells provide mechanical protection Many are covered with a cuticle (cutin and wax) to minimize water loss Figure 35.8 The three tissue systems of a plant Ground Tissue pith cortex Epidermis Guard Cells Ground tissue Plant Cell Types Parenchyma: photosynthesis and metabolism (storage and secretion ). Collenchyma: support (flexible) Scelerenchyma: storage, support (firm), protection Parenchyma cells Alive at maturity No secondary walls Site of most plant metabolism Play a role in wound healing and regeneration Collenchyma cells Living at maturity No secondary cell walls or lignin Provide flexible support to growing parts of plant 15
16 Scelerenchyma cells Thick secondary walls, usually with lignin Usually dead at maturity Usually specialized for support and strengthening of parts that have ceased elongating. Sclereids impart hardness to seed coats, shells of nuts (give pears their grit) Fibers are usually long, slender, tapered (hemp and flax fibers) Figure 35.8 The three tissue systems of a plant Vascular Tissue Plant Cell Types Epidermis Guard Cells Ground tissue Parenchyma: photosynthesis and metabolism Collenchyma: support Scelerenchyma: support, storage, protection Vascular tissues Xylem: water and nutrients from roots. Also support and food storage Tracheids, vessel elements Phloem: sugars from leaves Sieve-tube members, companion cells Xylem cells Dead at maturity Tracheids found in all vascular plants Long and thin with tapered ends Lignin for structural support Less specialized than vessel elements ( safer though) Vessel elements found mainly in angiosperms (flowering plants) Generally wider, shorter, and less tapered than tracheids Has perforations for more efficient water flow - but perforations are open systems and can be less safe. 16
17 Phloem Primary and secondary phloem. Primary phloem is often destroyed during elongation of the organ. Principal conducting cells are the sieve elements ( with pores ) Sieve-tube members Alive at maturity, but Lack nucleus, ribosomes, organelles (highly specialized like human red blood cells!) Served by nucleus etc. of adjacent companion cells Connected via plasmodesmata 17
The Science of Plants in Agriculture Pl.Sci 102. Getting to Know Plants
 The Science of Plants in Agriculture Pl.Sci 102 Getting to Know Plants Growth and Development of Plants Growth and Development of Plants Why it s important to have knowledge about plant development. What
The Science of Plants in Agriculture Pl.Sci 102 Getting to Know Plants Growth and Development of Plants Growth and Development of Plants Why it s important to have knowledge about plant development. What
Ginkgo leaf. Ginkgo is dioecious, separate sexes: male and female plants are separate. Monoecious plants have both male and female parts.
 Ginkgo leaf Figure 22-30 Ginkgo tree. Ginkgo is dioecious, separate sexes: male and female plants are separate. Monoecious plants have both male and female parts. The vein pattern is dichotomous: Divided
Ginkgo leaf Figure 22-30 Ginkgo tree. Ginkgo is dioecious, separate sexes: male and female plants are separate. Monoecious plants have both male and female parts. The vein pattern is dichotomous: Divided
Cell Division: the process of copying and dividing entire cells The cell grows, prepares for division, and then divides to form new daughter cells.
 Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle
 Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
THE CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS. Asexual Reproduction: Production of genetically identical offspring from a single parent.
 THE CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction: Production of genetically identical offspring from a single parent. Sexual Reproduction: The fusion of two separate parent cells that produce offspring with
THE CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction: Production of genetically identical offspring from a single parent. Sexual Reproduction: The fusion of two separate parent cells that produce offspring with
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles
 Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Cell cycle, mitosis & meiosis. Chapter 6
 Cell cycle, mitosis & meiosis Chapter 6 Why do cells divide? Asexual reproduction Growth Replacement / repair Cell division: The big picture Two steps Before cells can divide, DNA needs to replicate DNA
Cell cycle, mitosis & meiosis Chapter 6 Why do cells divide? Asexual reproduction Growth Replacement / repair Cell division: The big picture Two steps Before cells can divide, DNA needs to replicate DNA
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION. Chapter 10
 CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
#2 How do organisms grow?
 #2 How do organisms grow? Why doesn t a cell keep growing larger and larger? The larger a cell becomes the more demands the cell places on its DNA. The cell also has trouble moving enough nutrients and
#2 How do organisms grow? Why doesn t a cell keep growing larger and larger? The larger a cell becomes the more demands the cell places on its DNA. The cell also has trouble moving enough nutrients and
Chapter 11 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
 Chapter 11 Meiosis and Sexual S Section 1: S Gamete: Haploid reproductive cell that unites with another haploid reproductive cell to form a zygote. S Zygote: The cell that results from the fusion of gametes
Chapter 11 Meiosis and Sexual S Section 1: S Gamete: Haploid reproductive cell that unites with another haploid reproductive cell to form a zygote. S Zygote: The cell that results from the fusion of gametes
Cells & Cell Organelles. Doing Life s Work
 Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote Eukaryotes animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria 1-10 microns eukaryotic
Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote Eukaryotes animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria 1-10 microns eukaryotic
Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division
 Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The process of meiosis results in: A. the production of four identical cells B. no change in chromosome number from parental cells C. a doubling of
Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The process of meiosis results in: A. the production of four identical cells B. no change in chromosome number from parental cells C. a doubling of
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 11. Reproduction Section 1
 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 11 Reproduction Section 1 Reproduction Key Idea: An individual formed by asexual reproduction is genetically identical to its parent. Asexual Reproduction In asexual
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 11 Reproduction Section 1 Reproduction Key Idea: An individual formed by asexual reproduction is genetically identical to its parent. Asexual Reproduction In asexual
Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis
 Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis 6:1 Chromosomes DNA GENES CHROMATIN/CHROMOSOMES CHROMOSOMES/CHROMATIN are made of units called GENES. GENES are made of a compound called deoxyribonucleic acid or
Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis 6:1 Chromosomes DNA GENES CHROMATIN/CHROMOSOMES CHROMOSOMES/CHROMATIN are made of units called GENES. GENES are made of a compound called deoxyribonucleic acid or
Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division. Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms
 Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms Genes DNA Chromatin fiber Chromosomes Fig. 9.6 Genes, the segments of DNA, are part of chromatin fiber
Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms Genes DNA Chromatin fiber Chromosomes Fig. 9.6 Genes, the segments of DNA, are part of chromatin fiber
Biology. Mrs. Michaelsen. Types of cells. Cells & Cell Organelles. Cell size comparison. The Cell. Doing Life s Work. Hooke first viewed cork 1600 s
 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most
Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most
Microorganisms Answer Key
 Microorganisms Answer Key 1. What is NOT a part of the water cycle? a. condensation b. evaporation c. transpiration d. bacteria 2. Unicellular prokaryotes that may be spherical, rod or spiral shaped. a.
Microorganisms Answer Key 1. What is NOT a part of the water cycle? a. condensation b. evaporation c. transpiration d. bacteria 2. Unicellular prokaryotes that may be spherical, rod or spiral shaped. a.
What is mitosis? -Process in which a cell divides, creating TWO complete Sets of the original cell with the same EXACT genetic Material (DNA)
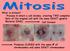 What is mitosis? -Process in which a cell divides, creating TWO complete Sets of the original cell with the same EXACT genetic Material (DNA) Cell Division Produces CLONES with the same # of chromosomes
What is mitosis? -Process in which a cell divides, creating TWO complete Sets of the original cell with the same EXACT genetic Material (DNA) Cell Division Produces CLONES with the same # of chromosomes
For a species to survive, it must REPRODUCE! Ch 13 NOTES Meiosis. Genetics Terminology: Homologous chromosomes
 For a species to survive, it must REPRODUCE! Ch 13 NOTES Meiosis Genetics Terminology: Autosomes Somatic cell Gamete Karyotype Homologous chromosomes Meiosis Sex chromosomes Diploid Haploid Zygote Synapsis
For a species to survive, it must REPRODUCE! Ch 13 NOTES Meiosis Genetics Terminology: Autosomes Somatic cell Gamete Karyotype Homologous chromosomes Meiosis Sex chromosomes Diploid Haploid Zygote Synapsis
Introduction to Cells
 Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 5: Cellular Reproduction
 Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 5: Cellular Reproduction NC Essential Standard: 1.2.2 Analyze how cells grow and reproduce in terms of interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis
Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 5: Cellular Reproduction NC Essential Standard: 1.2.2 Analyze how cells grow and reproduce in terms of interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis
Biology 1 Notebook. Review Answers Pages 17 -?
 Biology 1 Notebook Review Answers Pages 17 -? The History of Cell Studies 1. Robert Hook (1665) used a microscope to examine a thin slice of cork. The little boxes he observed reminded him of the small
Biology 1 Notebook Review Answers Pages 17 -? The History of Cell Studies 1. Robert Hook (1665) used a microscope to examine a thin slice of cork. The little boxes he observed reminded him of the small
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles
 Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Crop Physiology. Plant/Crop Physiology. First
 Plant/Crop Physiology Plant physiology is a sub-discipline of botany concerned with the functioning of plants. Includes the study of all the internal activities of plants those chemical and physical processes
Plant/Crop Physiology Plant physiology is a sub-discipline of botany concerned with the functioning of plants. Includes the study of all the internal activities of plants those chemical and physical processes
MEIOSIS. Making gametes
 MEIOSIS http://waynesword.palomar.edu/lmexer2a.htm Making gametes Remember from Chapter 1: CHARACTERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS ALL LIVING THINGS REPRODUCE Planaria animation: http://www.t3.rim.or.jp/~hylas/planaria/title.htm
MEIOSIS http://waynesword.palomar.edu/lmexer2a.htm Making gametes Remember from Chapter 1: CHARACTERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS ALL LIVING THINGS REPRODUCE Planaria animation: http://www.t3.rim.or.jp/~hylas/planaria/title.htm
Topic 8 Mitosis & Meiosis Ch.12 & 13. The Eukaryotic Genome. The Eukaryotic Genome. The Eukaryotic Genome
 Topic 8 Mitosis & Meiosis Ch.12 & 13 The Eukaryotic Genome pp. 244-245,268-269 Genome All of the genes in a cell. Eukaryotic cells contain their DNA in long linear pieces. In prokaryotic cells, there is
Topic 8 Mitosis & Meiosis Ch.12 & 13 The Eukaryotic Genome pp. 244-245,268-269 Genome All of the genes in a cell. Eukaryotic cells contain their DNA in long linear pieces. In prokaryotic cells, there is
Cell Division: the process of copying and dividing entire cells The cell grows, prepares for division, and then divides to form new daughter cells.
 Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
Cellular Division. copyright cmassengale
 Cellular Division 1 Cell Division All cells are derived from pre- existing cells New cells are produced for growth and to replace damaged or old cells Differs in prokaryotes (bacteria) and eukaryotes (protists,
Cellular Division 1 Cell Division All cells are derived from pre- existing cells New cells are produced for growth and to replace damaged or old cells Differs in prokaryotes (bacteria) and eukaryotes (protists,
Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycle
 Chapter 13. Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycle 1 Cell reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies (clones) same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes asexual
Chapter 13. Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycle 1 Cell reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies (clones) same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes asexual
Reading Assignments. A. Systems of Cell Division. Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division
 Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Death Read Chapter 19 Cell Division Read Chapter 20 pages 659-672 672 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections)
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Death Read Chapter 19 Cell Division Read Chapter 20 pages 659-672 672 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections)
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division
 Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Death Read Chapter 19 Cell Division Read Chapter 20 pages 659-672 672 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections)
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Death Read Chapter 19 Cell Division Read Chapter 20 pages 659-672 672 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections)
Mitosis & Meiosis. PPT Questions. 4. Why must each new cell get a complete copy of the original cell s DNA?
 1. From where do new cells arise? Mitosis & Meiosis PPT Questions 2. Why does the body constantly make new cells? 3. Is cell division the same in all cells? Explain. 4. Why must each new cell get a complete
1. From where do new cells arise? Mitosis & Meiosis PPT Questions 2. Why does the body constantly make new cells? 3. Is cell division the same in all cells? Explain. 4. Why must each new cell get a complete
MEIOSIS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU
 MEIOSIS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes such as animals, plants and fungi The number of sets of chromosomes
MEIOSIS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes such as animals, plants and fungi The number of sets of chromosomes
KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions.
 5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. 5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle Why must cells divide? Growth and Repair -
5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. 5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle Why must cells divide? Growth and Repair -
BOTANY, PLANT PHYSIOLOGY AND PLANT GROWTH
 1 BOTANY, PLANT PHYSIOLOGY AND PLANT GROWTH LESSON 2 PLANT PARTS AND FUNCTIONS CELLS: THE BUILDING BLOCKS OF LIFE 2 The Building Blocks of Life All living things are composed of one or more cells essentially
1 BOTANY, PLANT PHYSIOLOGY AND PLANT GROWTH LESSON 2 PLANT PARTS AND FUNCTIONS CELLS: THE BUILDING BLOCKS OF LIFE 2 The Building Blocks of Life All living things are composed of one or more cells essentially
CELL DIVISION: MEIOSIS
 CELL DIVISION: MEIOSIS How do Organisms Reproduce? Option 1: Asexual Reproduction Can be done by a single organism without the involvement of gametes (sperm or egg) Offspring are clones of the parent,
CELL DIVISION: MEIOSIS How do Organisms Reproduce? Option 1: Asexual Reproduction Can be done by a single organism without the involvement of gametes (sperm or egg) Offspring are clones of the parent,
Introduction to Cells
 Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
2. Cellular and Molecular Biology
 2. Cellular and Molecular Biology 2.1 Cell Structure 2.2 Transport Across Cell Membranes 2.3 Cellular Metabolism 2.4 DNA Replication 2.5 Cell Division 2.6 Biosynthesis 2.1 Cell Structure What is a cell?
2. Cellular and Molecular Biology 2.1 Cell Structure 2.2 Transport Across Cell Membranes 2.3 Cellular Metabolism 2.4 DNA Replication 2.5 Cell Division 2.6 Biosynthesis 2.1 Cell Structure What is a cell?
What in the Cell is Going On?
 What in the Cell is Going On? Robert Hooke naturalist, philosopher, inventor, architect... (July 18, 1635 - March 3, 1703) In 1665 Robert Hooke publishes his book, Micrographia, which contains his drawings
What in the Cell is Going On? Robert Hooke naturalist, philosopher, inventor, architect... (July 18, 1635 - March 3, 1703) In 1665 Robert Hooke publishes his book, Micrographia, which contains his drawings
Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction. What is Cellular Reproduction?
 Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction What is Cellular Reproduction? Answer: The division of a parent cell into two daughter cells Requirements of Each Daughter Cell: 1) Necessary genomic
Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction What is Cellular Reproduction? Answer: The division of a parent cell into two daughter cells Requirements of Each Daughter Cell: 1) Necessary genomic
Sexual reproduction & Meiosis
 Sexual reproduction & Meiosis Sexual Reproduction When two parents contribute DNA to the offspring The offspring are the result of fertilization the unification of two gametes (sperm & egg) Results in
Sexual reproduction & Meiosis Sexual Reproduction When two parents contribute DNA to the offspring The offspring are the result of fertilization the unification of two gametes (sperm & egg) Results in
Sexual and Asexual Reproduction. Cell Reproduction TEST Friday, 11/13
 Sexual and Asexual Reproduction Cell Reproduction TEST Friday, 11/13 How many chromosomes do humans have? What are Chromosomes? How many chromosomes came from your mom? How many chromosomes came from your
Sexual and Asexual Reproduction Cell Reproduction TEST Friday, 11/13 How many chromosomes do humans have? What are Chromosomes? How many chromosomes came from your mom? How many chromosomes came from your
Cellular Reproduction
 Cellular Reproduction Ratio of Surface Area to Volume As the cell grows, its volume increases much more rapidly than the surface area. The cell might have difficulty supplying nutrients and expelling enough
Cellular Reproduction Ratio of Surface Area to Volume As the cell grows, its volume increases much more rapidly than the surface area. The cell might have difficulty supplying nutrients and expelling enough
5.3 Reproduction and Meiosis
 5.3 Reproduction and Meiosis Lesson Objectives Compare and contrast asexual and sexual reproduction. Give an overview of sexual reproduction, and outline the phases of meiosis. Explain why sexual reproduction
5.3 Reproduction and Meiosis Lesson Objectives Compare and contrast asexual and sexual reproduction. Give an overview of sexual reproduction, and outline the phases of meiosis. Explain why sexual reproduction
QQ 10/5/18 Copy the following into notebook:
 Chapter 13- Meiosis QQ 10/5/18 Copy the following into notebook: Similarities: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Differences: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Figure 13.1 Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their
Chapter 13- Meiosis QQ 10/5/18 Copy the following into notebook: Similarities: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Differences: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Figure 13.1 Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their
Anaphase, Telophase. Animal cells divide their cytoplasm by forming? Cleavage furrow. Bacteria, Paramecium, Amoeba, etc. reproduce by...
 The 4 phases of mitosis Animal cells divide their cytoplasm by forming? Bacteria, Paramecium, Amoeba, etc. reproduce by... Cell which after division is identical to the original is called a Prophase, Metaphase,
The 4 phases of mitosis Animal cells divide their cytoplasm by forming? Bacteria, Paramecium, Amoeba, etc. reproduce by... Cell which after division is identical to the original is called a Prophase, Metaphase,
3 The Organization of Living Things
 CHAPTER 1 SECTION Cells: The Basic Units of Life 3 The Organization of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the advantages of
CHAPTER 1 SECTION Cells: The Basic Units of Life 3 The Organization of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the advantages of
Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018
 Class: Date: Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Hooke s discovery of cells was made observing a. living
Class: Date: Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Hooke s discovery of cells was made observing a. living
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell Prokaryotic Cells No nucleus Archaea & Eubacteria One circular chromosome Extremely small Eukaryotic Cells Has a nucleus!!! Membrane-bound organelles Plants, Animals, Fungi, &
Basic Structure of a Cell Prokaryotic Cells No nucleus Archaea & Eubacteria One circular chromosome Extremely small Eukaryotic Cells Has a nucleus!!! Membrane-bound organelles Plants, Animals, Fungi, &
The division of a unicellular organism reproduces an entire organism, increasing the population. Here s one amoeba dividing into 2.
 1. Cell division functions in 3 things : reproduction, growth, and repair The division of a unicellular organism reproduces an entire organism, increasing the population. Here s one amoeba dividing into
1. Cell division functions in 3 things : reproduction, growth, and repair The division of a unicellular organism reproduces an entire organism, increasing the population. Here s one amoeba dividing into
Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division
 Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The process of meiosis results in. A. the production of four identical cells B. no change in chromosome number from parental cells C. a doubling of
Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The process of meiosis results in. A. the production of four identical cells B. no change in chromosome number from parental cells C. a doubling of
Mitosis and Meiosis. 2. The distribution of chromosomes in one type of cell division is shown in the diagram below.
 Name: Date: 1. Jack bought a small turtle. Three months later, the turtle had grown to twice its original size. Which of the following statements best describes why Jack s turtle got bigger? A. Parts of
Name: Date: 1. Jack bought a small turtle. Three months later, the turtle had grown to twice its original size. Which of the following statements best describes why Jack s turtle got bigger? A. Parts of
Discovery of the Cell
 Cell Structure Discovery of the Cell Who discovered cells? 1665 Robert Hooke used a compound microscope to examine a piece of cork (20X magnification) He saw little boxes in the cork and called them cells
Cell Structure Discovery of the Cell Who discovered cells? 1665 Robert Hooke used a compound microscope to examine a piece of cork (20X magnification) He saw little boxes in the cork and called them cells
Roles of Cell Division. Reproduction - Like begets like, more or less. Examples of Cell Numbers. Outline Cell Reproduction
 Outline Cell Reproduction 1. Overview of Cell Reproduction 2. Cell Reproduction in Prokaryotes 3. Cell Reproduction in Eukaryotes 1. Chromosomes 2. Cell Cycle 3. Mitosis and Cytokinesis 4. Sexual Life
Outline Cell Reproduction 1. Overview of Cell Reproduction 2. Cell Reproduction in Prokaryotes 3. Cell Reproduction in Eukaryotes 1. Chromosomes 2. Cell Cycle 3. Mitosis and Cytokinesis 4. Sexual Life
Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction
 Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction Chapter 11: Cellular Reproduction What is Cellular Reproduction? Answer: The division of a parent cell into two daughter cells Requirements of
Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction Chapter 11: Cellular Reproduction What is Cellular Reproduction? Answer: The division of a parent cell into two daughter cells Requirements of
CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location ALL CELLS DNA Common in Animals Uncommon in Plants Lysosome
 CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location is the material that contains the Carry genetic ALL CELLS information that determines material inherited characteristics.
CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location is the material that contains the Carry genetic ALL CELLS information that determines material inherited characteristics.
CELL REPRODUCTION NOTES
 CELL REPRODUCTION NOTES CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION The adult human body produces roughly cells every day. WHY DO CELLS REPRODUCE? So that the organism can and As multicellular organisms grow larger, its
CELL REPRODUCTION NOTES CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION The adult human body produces roughly cells every day. WHY DO CELLS REPRODUCE? So that the organism can and As multicellular organisms grow larger, its
Sexual Reproduction ( Cell Division ) - Chromosome # s
 Sexual Reproduction ( Cell Division ) - Chromosome # s somatic cells: all the cells in the body except for specialized sex cells each somatic cell has a specific # of chromosomes - ( humans have 46, 23
Sexual Reproduction ( Cell Division ) - Chromosome # s somatic cells: all the cells in the body except for specialized sex cells each somatic cell has a specific # of chromosomes - ( humans have 46, 23
Meiosis and Life Cycles - 1
 Meiosis and Life Cycles - 1 We have just finished looking at the process of mitosis, a process that produces cells genetically identical to the original cell. Mitosis ensures that each cell of an organism
Meiosis and Life Cycles - 1 We have just finished looking at the process of mitosis, a process that produces cells genetically identical to the original cell. Mitosis ensures that each cell of an organism
Name Chapter 10: Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis Mrs. Laux Take home test #7 DUE: MONDAY, NOVEMBER 16, 2009 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A bacterial chromosome consists of: A. a linear DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. B. a circular DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. C. a circular DNA
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A bacterial chromosome consists of: A. a linear DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. B. a circular DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. C. a circular DNA
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12
 The Cell Cycle Chapter 12 Why are cells small? As cells get bigger they don t work as well WHY? Difficulties Larger Cells Have: More demands on its DNA Less efficient in moving nutrients/waste across its
The Cell Cycle Chapter 12 Why are cells small? As cells get bigger they don t work as well WHY? Difficulties Larger Cells Have: More demands on its DNA Less efficient in moving nutrients/waste across its
Cell Reproduction Mitosis & Meiosis
 Cell Reproduction Mitosis & Meiosis Outcomes 1. Describe mitosis in detail (460-465) interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis (the cell cycle) explain the importance of maintaining chromosome number through
Cell Reproduction Mitosis & Meiosis Outcomes 1. Describe mitosis in detail (460-465) interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis (the cell cycle) explain the importance of maintaining chromosome number through
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division
 Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Read Chapter 19 pages 651-663 663 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections these are in Chapter
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Read Chapter 19 pages 651-663 663 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections these are in Chapter
Mitosis & Meiosis Practice Test
 Name: DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST Class: ALL ID: A Mitosis & Meiosis Practice Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make
Name: DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST Class: ALL ID: A Mitosis & Meiosis Practice Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make
Benchmark Clarification for SC.912.L.16.17
 Benchmark Clarification for SC.912.L.16.17 Students will: Differentiate the process of meiosis and meiosis Describe the role of mitosis in asexual reproduction, and/or the role of meiosis in sexual reproduction,
Benchmark Clarification for SC.912.L.16.17 Students will: Differentiate the process of meiosis and meiosis Describe the role of mitosis in asexual reproduction, and/or the role of meiosis in sexual reproduction,
Chapter 6: Cell Growth and Reproduction Lesson 6.3: Meiosis and Reproduction
 Chapter 6: Cell Growth and Reproduction Lesson 6.3: Meiosis and Reproduction One parent or two? That is the main difference between sexual and asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction just means combining
Chapter 6: Cell Growth and Reproduction Lesson 6.3: Meiosis and Reproduction One parent or two? That is the main difference between sexual and asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction just means combining
Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis
 Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis Omnis cellula e cellula Cell Div. In Eukaryotic cells Chromosome structure Biparental inheritance and diploidy Mitosis: Karyokinesis and cytokinesis 5 stages: PPMAT Regulating
Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis Omnis cellula e cellula Cell Div. In Eukaryotic cells Chromosome structure Biparental inheritance and diploidy Mitosis: Karyokinesis and cytokinesis 5 stages: PPMAT Regulating
Cell Division: the process of copying and dividing entire cells The cell grows, prepares for division, and then divides to form new daughter cells.
 Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
MGC New Life Christian Academy
 A. Meiosis Main Idea: Meiosis produces haploid gametes. Key Concept: Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces offspring that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent. Sexual
A. Meiosis Main Idea: Meiosis produces haploid gametes. Key Concept: Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces offspring that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent. Sexual
Cell Growth and Division
 Cell Growth and Division Why do cells divide* Life and reproduction require cell division You require constant cell reproduction to live Mitosis: development (a) mitotic cell division (b) mitotic cell
Cell Growth and Division Why do cells divide* Life and reproduction require cell division You require constant cell reproduction to live Mitosis: development (a) mitotic cell division (b) mitotic cell
Meiosis. Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and meiosis II
 Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
Bio 105: Cell Division
 Cell Division Bio 105: Cell Division Starts with DNA Replication Laboratory 8 DNA Replication When does DNA replicate? Just prior to cell division Multicellular Organisms Grow Replace old cells Unicellular
Cell Division Bio 105: Cell Division Starts with DNA Replication Laboratory 8 DNA Replication When does DNA replicate? Just prior to cell division Multicellular Organisms Grow Replace old cells Unicellular
Honors Biology Midterm Exam Study Guide--January 2019
 Objective Response Reflection 3 = I totally know this! :) 2 = I remember this somewhat 1 = I don't remember this at all Explain the difference between independent and dependent variables. Explain what
Objective Response Reflection 3 = I totally know this! :) 2 = I remember this somewhat 1 = I don't remember this at all Explain the difference between independent and dependent variables. Explain what
2:1 Chromosomes DNA Genes Chromatin Chromosomes CHROMATIN: nuclear material in non-dividing cell, composed of DNA/protein in thin uncoiled strands
 Human Heredity Chapter 2 Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis 2:1 Chromosomes DNA Genes Chromatin Chromosomes CHROMATIN: nuclear material in non-dividing cell, composed of DNA/protein in thin uncoiled strands
Human Heredity Chapter 2 Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis 2:1 Chromosomes DNA Genes Chromatin Chromosomes CHROMATIN: nuclear material in non-dividing cell, composed of DNA/protein in thin uncoiled strands
Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division
 LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division The larger the cell, the more trouble the cell has moving nutrients and waste across the cell membrane. LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH 1. DNA/information
LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division The larger the cell, the more trouble the cell has moving nutrients and waste across the cell membrane. LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH 1. DNA/information
Cell division / Asexual reproduction
 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produces cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes same genetic information Asexual
Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produces cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes same genetic information Asexual
Ladies and Gentlemen.. The King of Rock and Roll
 Ladies and Gentlemen.. The King of Rock and Roll Learning Objectives: The student is able to construct an explanation, using visual representations or narratives, as to how DNA in chromosomes is transmitted
Ladies and Gentlemen.. The King of Rock and Roll Learning Objectives: The student is able to construct an explanation, using visual representations or narratives, as to how DNA in chromosomes is transmitted
Ch. 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles
 Introduction Ch. 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles 2004-05 Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. -Offspring resemble their parents more than they do less closely
Introduction Ch. 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles 2004-05 Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. -Offspring resemble their parents more than they do less closely
Chapter 6: Mendel and Meiosis Meiosis Gamete Production Lecture Guide
 Chromosomes and Meiosis Specialized cells in the body Chromosomes 2 types: Chapter 6: Mendel and Meiosis Meiosis Gamete Production Lecture Guide (body cells) Makes up your DNA in your body cells passed
Chromosomes and Meiosis Specialized cells in the body Chromosomes 2 types: Chapter 6: Mendel and Meiosis Meiosis Gamete Production Lecture Guide (body cells) Makes up your DNA in your body cells passed
2. The development of revolutionized the of life.
 Science 10 Unit 7 Worksheet Chapter 15, Part 1. 1. Briefly describe the three main parts of cell theory: 2. The development of revolutionized the of life. 3. Individual cells need to take in to build and
Science 10 Unit 7 Worksheet Chapter 15, Part 1. 1. Briefly describe the three main parts of cell theory: 2. The development of revolutionized the of life. 3. Individual cells need to take in to build and
Sexual Reproduction. The two parent cells needed for sexual reproduction are called gametes. They are formed during a process known as meiosis.
 Sexual Reproduction Recall that asexual reproduction involves only one parent cell. This parent cell divides to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent. Sexual reproduction,
Sexual Reproduction Recall that asexual reproduction involves only one parent cell. This parent cell divides to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent. Sexual reproduction,
Chapter 5: Mitosis is the Basis of Asexual Reproduction
 Chapter 5: Mitosis is the Basis of Asexual Reproduction Section 5.1: The Cell Cycle and Mitosis Living things must be able to reproduce. For unicellular organisms, cell reproduction is necessary to maintain
Chapter 5: Mitosis is the Basis of Asexual Reproduction Section 5.1: The Cell Cycle and Mitosis Living things must be able to reproduce. For unicellular organisms, cell reproduction is necessary to maintain
Cell Structure: What cells are made of. Can you pick out the cells from this picture?
 Cell Structure: What cells are made of Can you pick out the cells from this picture? Review of the cell theory Microscope was developed 1610. Anton van Leeuwenhoek saw living things in pond water. 1677
Cell Structure: What cells are made of Can you pick out the cells from this picture? Review of the cell theory Microscope was developed 1610. Anton van Leeuwenhoek saw living things in pond water. 1677
CHAPTER 29 PLANT DIVERSITY I: HOW PLANTS COLONIZED LAND. Section A: An Overview of Land Plant Evolution
 CHAPTER 29 PLANT DIVERSITY I: HOW PLANTS COLONIZED LAND Section A: An Overview of Land Plant Evolution 1. Evolutionary adaptations to terrestrial living characterize the four main groups of land plants
CHAPTER 29 PLANT DIVERSITY I: HOW PLANTS COLONIZED LAND Section A: An Overview of Land Plant Evolution 1. Evolutionary adaptations to terrestrial living characterize the four main groups of land plants
REVISION: CELL DIVISION 20 MARCH 2013
 REVISION: CELL DIVISION 20 MARCH 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we revise: The Cell Theory and the parts of plant and animal cells The process of mitosis The structure and function of different
REVISION: CELL DIVISION 20 MARCH 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we revise: The Cell Theory and the parts of plant and animal cells The process of mitosis The structure and function of different
Cell Reproduction Review
 Name Date Period Cell Reproduction Review Explain what is occurring in each part of the cell cycle --- G 0, G1, S, G2, and M. 1 CELL DIVISION Label all parts of each cell in the cell cycle and explain
Name Date Period Cell Reproduction Review Explain what is occurring in each part of the cell cycle --- G 0, G1, S, G2, and M. 1 CELL DIVISION Label all parts of each cell in the cell cycle and explain
Biology. Chapter 10 Cell Reproduction. I. Chromosomes
 Biology Chapter 10 Cell Reproduction I. Chromosomes Long thin molecules that store genetic information. A. Chromosome Structure 1. Rod shaped structure composed of DNA and protein. 2. DNA is wrapped around
Biology Chapter 10 Cell Reproduction I. Chromosomes Long thin molecules that store genetic information. A. Chromosome Structure 1. Rod shaped structure composed of DNA and protein. 2. DNA is wrapped around
Why mitosis?
 Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotes. Prokaryotes (i.e., archaea and bacteria) divide via binary fission. Mitosis is the process by which the somatic cells of all multicellular organisms multiply. Somatic
Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotes. Prokaryotes (i.e., archaea and bacteria) divide via binary fission. Mitosis is the process by which the somatic cells of all multicellular organisms multiply. Somatic
Cell Is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life and are often called
 The Cell Cell Is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life and are often called the "building blocks of life". The study of
The Cell Cell Is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life and are often called the "building blocks of life". The study of
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 5: Chromosomes and Inheritance
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 5: Chromosomes and Inheritance Chromosomes and Inheritance Learning Outcomes 5.1 Differentiate between sexual and asexual reproduction in terms of the genetic variation of the offspring.
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 5: Chromosomes and Inheritance Chromosomes and Inheritance Learning Outcomes 5.1 Differentiate between sexual and asexual reproduction in terms of the genetic variation of the offspring.
Outline for today s lecture (Ch. 13)
 Outline for today s lecture (Ch. 13) Sexual and asexual life cycles Meiosis Origins of Genetic Variation Independent assortment Crossing over ( recombination ) Heredity Transmission of traits between generations
Outline for today s lecture (Ch. 13) Sexual and asexual life cycles Meiosis Origins of Genetic Variation Independent assortment Crossing over ( recombination ) Heredity Transmission of traits between generations
The Cellular Basis of Inheritance
 CHAPTER 9 The Cellular Basis of Inheritance Summary of Key Concepts Concept 9.1 All cells come from cells. (pp. 180 181) Cell reproduction is an important process. Three functions of cell reproduction
CHAPTER 9 The Cellular Basis of Inheritance Summary of Key Concepts Concept 9.1 All cells come from cells. (pp. 180 181) Cell reproduction is an important process. Three functions of cell reproduction
MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS STUDY GUIDE CREATED BY : Alistaire Rauch (Mr. Galego s Class) Definition of Mitosis and Meiosis (Basic):
 MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS STUDY GUIDE CREATED BY : Alistaire Rauch (Mr. Galego s Class) Definition of Mitosis and Meiosis (Basic): Mitosis and Meiosis are basically cycles of cells but they are different in
MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS STUDY GUIDE CREATED BY : Alistaire Rauch (Mr. Galego s Class) Definition of Mitosis and Meiosis (Basic): Mitosis and Meiosis are basically cycles of cells but they are different in
Chapter 8 Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida
 Chapter 8 The Continuity of Life: How Cells Reproduce Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 8.1 Why Do Cells Divide? Cells reproduce by cell division.
Chapter 8 The Continuity of Life: How Cells Reproduce Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 8.1 Why Do Cells Divide? Cells reproduce by cell division.
Notes Chapter 4 Cell Reproduction. That cell divided and becomes two, two become, four become eight, and so on.
 Notes Chapter 4 Cell Reproduction 4.1 Cell Division and Mitosis Many organisms start as. That cell divided and becomes two, two become, four become eight, and so on. Many-celled organisms, including you,
Notes Chapter 4 Cell Reproduction 4.1 Cell Division and Mitosis Many organisms start as. That cell divided and becomes two, two become, four become eight, and so on. Many-celled organisms, including you,
Cells. The basic units of a living system or organism
 Cells The basic units of a living system or organism Cell Theory developed by 3 German scientists: Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolf Virchow These scientists discoveries led to the cell theory
Cells The basic units of a living system or organism Cell Theory developed by 3 German scientists: Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolf Virchow These scientists discoveries led to the cell theory
ACCELERATE ITS BIOCHEMICAL PROCESSES WHICH WERE SLOWED DOWN BY MITOSIS. THE LENGTH OF THE G1 PHASE CREATES THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN FAST DIVIDING
 CHAPTER 1: OVERVIEW OF THE CELL CYCLE THE THREE STAGES OF INTERPHASE: INTERPHASE BEFORE A CELL CAN ENTER CELL DIVISION, IT NEEDS TO PREPARE ITSELF BY REPLICATING ITS GENETIC INFORMATION AND ALL OF THE
CHAPTER 1: OVERVIEW OF THE CELL CYCLE THE THREE STAGES OF INTERPHASE: INTERPHASE BEFORE A CELL CAN ENTER CELL DIVISION, IT NEEDS TO PREPARE ITSELF BY REPLICATING ITS GENETIC INFORMATION AND ALL OF THE
Fertilization of sperm and egg produces offspring
 In sexual reproduction Fertilization of sperm and egg produces offspring In asexual reproduction Offspring are produced by a single parent, without the participation of sperm and egg CONNECTIONS BETWEEN
In sexual reproduction Fertilization of sperm and egg produces offspring In asexual reproduction Offspring are produced by a single parent, without the participation of sperm and egg CONNECTIONS BETWEEN
Notes Chapter 4 Cell Reproduction. That cell divided and becomes two, two become four, four become eight, and so on.
 4.1 Cell Division and Mitosis Many organisms start as one cell. Notes Chapter 4 Cell Reproduction That cell divided and becomes two, two become four, four become eight, and so on. Many-celled organisms,
4.1 Cell Division and Mitosis Many organisms start as one cell. Notes Chapter 4 Cell Reproduction That cell divided and becomes two, two become four, four become eight, and so on. Many-celled organisms,
Meiosis. What is meiosis? How is it different from mitosis? Stages Genetic Variation
 Meiosis What is meiosis? How is it different from mitosis? Stages Genetic Variation Reproduction Asexual reproduction resulting from mitosis (or a similar process) that involves only one parent; the offspring
Meiosis What is meiosis? How is it different from mitosis? Stages Genetic Variation Reproduction Asexual reproduction resulting from mitosis (or a similar process) that involves only one parent; the offspring
