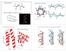
2MHR. Protein structure classification is important because it organizes the protein structure universe that is independent of sequence similarity.
|
|
|
- Clifton Bartholomew Allison
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Protein structure classification is important because it organizes the protein structure universe that is independent of sequence similarity. A global picture of the protein universe will help us to understand the functions of proteins better. Structures are classified usually by their secondary structure content and how they are arranged. Lactate Dehydrogenase SCOP Class: Mixed / Immunoglobulin SCOP Class: Hemoglobin Beta Chain SCOP Class: 2MHR proteins can be modular single chain may be divisible into smaller independent units of tertiary structure called domains domains are the basic unit of structure classification different domains in a protein are also often associated with different functions carried out by the protein. domains are usually the main units for structural classification A polypeptide or part of a polypeptide chain that can independently into a stable tertiary structure... from Introduction to Protein Structure, by Branden & Tooze Compact units within the ing pattern of a single chain that look as if they should have independent stability. from Introduction to Protein Architecture, by Lesk 1
2 Class: derived from secondary structure content Fold: derived from topological connection, orientation, arrangement and number of secondary structures Super: clusters of low sequence similarity but related structures & functions Family: clusers of proteins with sequence similarity > 30% with similar structure & function A hierarchical classification scheme is maintained SCOP Classification root class class Class [C] derived from secondary structure content (automatic) Architecture [A] derived from orientation of 2 o structures (manual) Topology [T] derived from topological connection and # 2 o structures Homologous Super (H) clusters of similar structures & functions In the CATH hierarchy, Class simply describes what type of secondary structure is present. There are only four classes: mainly mainly few secondary structures 90% of structures are trivial to assign at this level. Architecture is hard to define precisely In CATH it is defined broadly as describing general features of protein shape such as arrangements of secondary structure in 3D space It does not define connectivities between secondary structural elements--that s what the topology level does. It does not even explicitly define directionality of secondary structure, e.g. parallel or antiparallel beta-sheets. in CATH, architectures are presently assigned manually, by visual inspection. 2
3 if two proteins have the same topology, it means they have the same number and arrangement of secondary structures, and the connectivities between these elements are the same. this is also sometimes called the of a protein. in CATH, automated structure alignment is used to group proteins according to topology. example: a four-stranded antiparallel beta-sheet can have many different topologies based on the order in which the four beta-strands are connected. up-and-down greek key The lowest two levels in the CATH hierarchy relate to common ancestry some, but not all proteins with the same show evidence of common ancestry the surest way of identifying common ancestry is that two proteins have sequences roughly >30% identical (sequence level) if protein sequences are not that similar, common ancestry may still be inferred on the basis of a combination of structural and functional similarity, and possibly weak sequence similarity (homologous level) SCOP class domain CATH class architecture topology homologous sequence domain CATH more directed toward structural classification, SCOP pays more attention to evolutionary relationships 3
4 in CATH, there is one class to represent mixed alpha-beta in SCOP there are two: : beta structure is largely parallel, made of motifs : alpha and beta structure segregated to different parts of structure they have in common that they are hierarchical and based on abstractions they both include some manual aspects and are curated by experts in the field of protein structure fully automated methods for structure classification/comparison? SCOP Classification root new protein structure class class?? Class membership? Does the query protein belong to a SCOP category? Or does it need a new category to be defined? Binary classification problem: member, non-member Class label assignment? What SCOP category is the query protein assigned to? Multi-class classification problem Let p be a protein structure, proceed bottomup from level to level: Does p belong to a? no yes Does p belong to a? report yes report A consensus classification scheme in which the decisions of a number of individual (component) classifiers are merged together in an intelligent way. Decision Tree Classification is one technique to use as the intelligent way no Does p belong to a? no new yes report 4
5 Using a sequence/structure comparison tool as a classifier Perform a nearest neighbor query: if similarityscore(query, NN) < trained cutoff then not a member of any category else member of class(nn) Comparison tools that we have used: Sequence: PSI-Blast, ER+SUPERFAMILY database Structure:,, Database: SCOP 1.59 Query: SCOP 1.61 SCOP % 66.1% 72.2% 77.6% 78.4% 94.5% 73% Class membership BLAST 92.6% 60.7% 89% 78.5% 89% 82% 89% 85% At least one 98.2% 96% 100% Database: SCOP 1.59 Query: SCOP 1.61 SCOP % 69% 40.5% Class label assignment BLAST 92.3% 12% 0% 91% 81% 80.4% 81.7% 40.5% 88% 46% 92% 54% At least one 97.9% 93.9% 64.9% Universal confidence levels instead of toolspecific scores Perform nearest neighbor queries Database: SCOP 1.59 Query: SCOP 1.61 SCOP 1.59 Partition score space of tools into confidence levels e.g. z-score of 5.4 we are 80% confident that the query protein is a member of an existing. Each component classifier reports a confidence level for the query protein: c = [C 1, C 2, C 3, C 4, C 5 ] What is the best way to combine these probabilistic decisions? A solution: decision trees. < 45% new new < 40% < 55%? else? else +? > 93% > 75% >= 55% existing existing new existing 5
6 The dataset: Database Query new Training v1.59 (20449) v1.61 v1.59 (2241) 248 Evaluation v1.61 (22724) v1.63 v1.59 (2825) 618 Error percentages PSI-Blast Ensemble None new new Family Super Fold Classification level Percentage of misclassified proteins PSI-Blast Ensemble None Russian doll effect: A small structure is contained exactly in a larger structure, but they are classified in different groups in SCOP hierarchy Family Super Fold Classification level Automated classification of a protein structure is feasible. More accurate classifiers can be built by combining less accurate individual classifiers. - VAST - FSSP - PDBsum - The presented classification technique can also be used as an aid to manual classification by providing clues. 6
7 structural taxonomy reveals that although structures are being solved more rapidly than ever, fewer and fewer of them have new s! Will we get them all soon? 7
CS612 - Algorithms in Bioinformatics
 Fall 2017 Databases and Protein Structure Representation October 2, 2017 Molecular Biology as Information Science > 12, 000 genomes sequenced, mostly bacterial (2013) > 5x10 6 unique sequences available
Fall 2017 Databases and Protein Structure Representation October 2, 2017 Molecular Biology as Information Science > 12, 000 genomes sequenced, mostly bacterial (2013) > 5x10 6 unique sequences available
HMM applications. Applications of HMMs. Gene finding with HMMs. Using the gene finder
 HMM applications Applications of HMMs Gene finding Pairwise alignment (pair HMMs) Characterizing protein families (profile HMMs) Predicting membrane proteins, and membrane protein topology Gene finding
HMM applications Applications of HMMs Gene finding Pairwise alignment (pair HMMs) Characterizing protein families (profile HMMs) Predicting membrane proteins, and membrane protein topology Gene finding
Protein Structure: Data Bases and Classification Ingo Ruczinski
 Protein Structure: Data Bases and Classification Ingo Ruczinski Department of Biostatistics, Johns Hopkins University Reference Bourne and Weissig Structural Bioinformatics Wiley, 2003 More References
Protein Structure: Data Bases and Classification Ingo Ruczinski Department of Biostatistics, Johns Hopkins University Reference Bourne and Weissig Structural Bioinformatics Wiley, 2003 More References
Giri Narasimhan. CAP 5510: Introduction to Bioinformatics. ECS 254; Phone: x3748
 CAP 5510: Introduction to Bioinformatics Giri Narasimhan ECS 254; Phone: x3748 giri@cis.fiu.edu www.cis.fiu.edu/~giri/teach/bioinfs07.html 2/15/07 CAP5510 1 EM Algorithm Goal: Find θ, Z that maximize Pr
CAP 5510: Introduction to Bioinformatics Giri Narasimhan ECS 254; Phone: x3748 giri@cis.fiu.edu www.cis.fiu.edu/~giri/teach/bioinfs07.html 2/15/07 CAP5510 1 EM Algorithm Goal: Find θ, Z that maximize Pr
CMPS 6630: Introduction to Computational Biology and Bioinformatics. Structure Comparison
 CMPS 6630: Introduction to Computational Biology and Bioinformatics Structure Comparison Protein Structure Comparison Motivation Understand sequence and structure variability Understand Domain architecture
CMPS 6630: Introduction to Computational Biology and Bioinformatics Structure Comparison Protein Structure Comparison Motivation Understand sequence and structure variability Understand Domain architecture
Basics of protein structure
 Today: 1. Projects a. Requirements: i. Critical review of one paper ii. At least one computational result b. Noon, Dec. 3 rd written report and oral presentation are due; submit via email to bphys101@fas.harvard.edu
Today: 1. Projects a. Requirements: i. Critical review of one paper ii. At least one computational result b. Noon, Dec. 3 rd written report and oral presentation are due; submit via email to bphys101@fas.harvard.edu
Amino Acid Structures from Klug & Cummings. 10/7/2003 CAP/CGS 5991: Lecture 7 1
 Amino Acid Structures from Klug & Cummings 10/7/2003 CAP/CGS 5991: Lecture 7 1 Amino Acid Structures from Klug & Cummings 10/7/2003 CAP/CGS 5991: Lecture 7 2 Amino Acid Structures from Klug & Cummings
Amino Acid Structures from Klug & Cummings 10/7/2003 CAP/CGS 5991: Lecture 7 1 Amino Acid Structures from Klug & Cummings 10/7/2003 CAP/CGS 5991: Lecture 7 2 Amino Acid Structures from Klug & Cummings
Bioinformatics. Macromolecular structure
 Bioinformatics Macromolecular structure Contents Determination of protein structure Structure databases Secondary structure elements (SSE) Tertiary structure Structure analysis Structure alignment Domain
Bioinformatics Macromolecular structure Contents Determination of protein structure Structure databases Secondary structure elements (SSE) Tertiary structure Structure analysis Structure alignment Domain
Bioinformatics. Proteins II. - Pattern, Profile, & Structure Database Searching. Robert Latek, Ph.D. Bioinformatics, Biocomputing
 Bioinformatics Proteins II. - Pattern, Profile, & Structure Database Searching Robert Latek, Ph.D. Bioinformatics, Biocomputing WIBR Bioinformatics Course, Whitehead Institute, 2002 1 Proteins I.-III.
Bioinformatics Proteins II. - Pattern, Profile, & Structure Database Searching Robert Latek, Ph.D. Bioinformatics, Biocomputing WIBR Bioinformatics Course, Whitehead Institute, 2002 1 Proteins I.-III.
Procheck output. Bond angles (Procheck) Structure verification and validation Bond lengths (Procheck) Introduction to Bioinformatics.
 Structure verification and validation Bond lengths (Procheck) Introduction to Bioinformatics Iosif Vaisman Email: ivaisman@gmu.edu ----------------------------------------------------------------- Bond
Structure verification and validation Bond lengths (Procheck) Introduction to Bioinformatics Iosif Vaisman Email: ivaisman@gmu.edu ----------------------------------------------------------------- Bond
Protein structure alignments
 Protein structure alignments Proteins that fold in the same way, i.e. have the same fold are often homologs. Structure evolves slower than sequence Sequence is less conserved than structure If BLAST gives
Protein structure alignments Proteins that fold in the same way, i.e. have the same fold are often homologs. Structure evolves slower than sequence Sequence is less conserved than structure If BLAST gives
1. Protein Data Bank (PDB) 1. Protein Data Bank (PDB)
 Protein structure databases; visualization; and classifications 1. Introduction to Protein Data Bank (PDB) 2. Free graphic software for 3D structure visualization 3. Hierarchical classification of protein
Protein structure databases; visualization; and classifications 1. Introduction to Protein Data Bank (PDB) 2. Free graphic software for 3D structure visualization 3. Hierarchical classification of protein
Getting To Know Your Protein
 Getting To Know Your Protein Comparative Protein Analysis: Part III. Protein Structure Prediction and Comparison Robert Latek, PhD Sr. Bioinformatics Scientist Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research
Getting To Know Your Protein Comparative Protein Analysis: Part III. Protein Structure Prediction and Comparison Robert Latek, PhD Sr. Bioinformatics Scientist Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research
Heteropolymer. Mostly in regular secondary structure
 Heteropolymer - + + - Mostly in regular secondary structure 1 2 3 4 C >N trace how you go around the helix C >N C2 >N6 C1 >N5 What s the pattern? Ci>Ni+? 5 6 move around not quite 120 "#$%&'!()*(+2!3/'!4#5'!1/,#64!#6!,6!
Heteropolymer - + + - Mostly in regular secondary structure 1 2 3 4 C >N trace how you go around the helix C >N C2 >N6 C1 >N5 What s the pattern? Ci>Ni+? 5 6 move around not quite 120 "#$%&'!()*(+2!3/'!4#5'!1/,#64!#6!,6!
Protein Structure and Function Prediction using Kernel Methods.
 Protein Structure and Function Prediction using Kernel Methods. A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Huzefa Rangwala IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE
Protein Structure and Function Prediction using Kernel Methods. A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Huzefa Rangwala IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE
Homology and Information Gathering and Domain Annotation for Proteins
 Homology and Information Gathering and Domain Annotation for Proteins Outline Homology Information Gathering for Proteins Domain Annotation for Proteins Examples and exercises The concept of homology The
Homology and Information Gathering and Domain Annotation for Proteins Outline Homology Information Gathering for Proteins Domain Annotation for Proteins Examples and exercises The concept of homology The
Homology. and. Information Gathering and Domain Annotation for Proteins
 Homology and Information Gathering and Domain Annotation for Proteins Outline WHAT IS HOMOLOGY? HOW TO GATHER KNOWN PROTEIN INFORMATION? HOW TO ANNOTATE PROTEIN DOMAINS? EXAMPLES AND EXERCISES Homology
Homology and Information Gathering and Domain Annotation for Proteins Outline WHAT IS HOMOLOGY? HOW TO GATHER KNOWN PROTEIN INFORMATION? HOW TO ANNOTATE PROTEIN DOMAINS? EXAMPLES AND EXERCISES Homology
Neural Networks for Protein Structure Prediction Brown, JMB CS 466 Saurabh Sinha
 Neural Networks for Protein Structure Prediction Brown, JMB 1999 CS 466 Saurabh Sinha Outline Goal is to predict secondary structure of a protein from its sequence Artificial Neural Network used for this
Neural Networks for Protein Structure Prediction Brown, JMB 1999 CS 466 Saurabh Sinha Outline Goal is to predict secondary structure of a protein from its sequence Artificial Neural Network used for this
CMPS 3110: Bioinformatics. Tertiary Structure Prediction
 CMPS 3110: Bioinformatics Tertiary Structure Prediction Tertiary Structure Prediction Why Should Tertiary Structure Prediction Be Possible? Molecules obey the laws of physics! Conformation space is finite
CMPS 3110: Bioinformatics Tertiary Structure Prediction Tertiary Structure Prediction Why Should Tertiary Structure Prediction Be Possible? Molecules obey the laws of physics! Conformation space is finite
CMPS 6630: Introduction to Computational Biology and Bioinformatics. Tertiary Structure Prediction
 CMPS 6630: Introduction to Computational Biology and Bioinformatics Tertiary Structure Prediction Tertiary Structure Prediction Why Should Tertiary Structure Prediction Be Possible? Molecules obey the
CMPS 6630: Introduction to Computational Biology and Bioinformatics Tertiary Structure Prediction Tertiary Structure Prediction Why Should Tertiary Structure Prediction Be Possible? Molecules obey the
Abstract A lot of work has gone into predicting the secondary (small scale) structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Current research ind
 A Method for Automatically Finding Structural Motifs in Proteins Marc Fasnacht August 2002 CMU-CALD-02-105 School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213 Abstract A lot of work
A Method for Automatically Finding Structural Motifs in Proteins Marc Fasnacht August 2002 CMU-CALD-02-105 School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213 Abstract A lot of work
Data Mining Prof. Pabitra Mitra Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Data Mining Prof. Pabitra Mitra Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 21 K - Nearest Neighbor V In this lecture we discuss; how do we evaluate the
Data Mining Prof. Pabitra Mitra Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 21 K - Nearest Neighbor V In this lecture we discuss; how do we evaluate the
DATE A DAtabase of TIM Barrel Enzymes
 DATE A DAtabase of TIM Barrel Enzymes 2 2.1 Introduction.. 2.2 Objective and salient features of the database 2.2.1 Choice of the dataset.. 2.3 Statistical information on the database.. 2.4 Features....
DATE A DAtabase of TIM Barrel Enzymes 2 2.1 Introduction.. 2.2 Objective and salient features of the database 2.2.1 Choice of the dataset.. 2.3 Statistical information on the database.. 2.4 Features....
Genome Databases The CATH database
 Genome Databases The CATH database Michael Knudsen 1 and Carsten Wiuf 1,2* 1 Bioinformatics Research Centre, Aarhus University, DK-8000 Aarhus C, Denmark 2 Centre for Membrane Pumps in Cells and Disease
Genome Databases The CATH database Michael Knudsen 1 and Carsten Wiuf 1,2* 1 Bioinformatics Research Centre, Aarhus University, DK-8000 Aarhus C, Denmark 2 Centre for Membrane Pumps in Cells and Disease
Bayesian Models and Algorithms for Protein Beta-Sheet Prediction
 0 Bayesian Models and Algorithms for Protein Beta-Sheet Prediction Zafer Aydin, Student Member, IEEE, Yucel Altunbasak, Senior Member, IEEE, and Hakan Erdogan, Member, IEEE Abstract Prediction of the three-dimensional
0 Bayesian Models and Algorithms for Protein Beta-Sheet Prediction Zafer Aydin, Student Member, IEEE, Yucel Altunbasak, Senior Member, IEEE, and Hakan Erdogan, Member, IEEE Abstract Prediction of the three-dimensional
ALL LECTURES IN SB Introduction
 1. Introduction 2. Molecular Architecture I 3. Molecular Architecture II 4. Molecular Simulation I 5. Molecular Simulation II 6. Bioinformatics I 7. Bioinformatics II 8. Prediction I 9. Prediction II ALL
1. Introduction 2. Molecular Architecture I 3. Molecular Architecture II 4. Molecular Simulation I 5. Molecular Simulation II 6. Bioinformatics I 7. Bioinformatics II 8. Prediction I 9. Prediction II ALL
Protein Structure Prediction using String Kernels. Technical Report
 Protein Structure Prediction using String Kernels Technical Report Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Minnesota 4-192 EECS Building 200 Union Street SE Minneapolis, MN 55455-0159
Protein Structure Prediction using String Kernels Technical Report Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Minnesota 4-192 EECS Building 200 Union Street SE Minneapolis, MN 55455-0159
Protein Structure Prediction II Lecturer: Serafim Batzoglou Scribe: Samy Hamdouche
 Protein Structure Prediction II Lecturer: Serafim Batzoglou Scribe: Samy Hamdouche The molecular structure of a protein can be broken down hierarchically. The primary structure of a protein is simply its
Protein Structure Prediction II Lecturer: Serafim Batzoglou Scribe: Samy Hamdouche The molecular structure of a protein can be broken down hierarchically. The primary structure of a protein is simply its
Protein Structure Prediction Using Neural Networks
 Protein Structure Prediction Using Neural Networks Martha Mercaldi Kasia Wilamowska Literature Review December 16, 2003 The Protein Folding Problem Evolution of Neural Networks Neural networks originally
Protein Structure Prediction Using Neural Networks Martha Mercaldi Kasia Wilamowska Literature Review December 16, 2003 The Protein Folding Problem Evolution of Neural Networks Neural networks originally
SCOP. all-β class. all-α class, 3 different folds. T4 endonuclease V. 4-helical cytokines. Globin-like
 SCOP all-β class 4-helical cytokines T4 endonuclease V all-α class, 3 different folds Globin-like TIM-barrel fold α/β class Profilin-like fold α+β class http://scop.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/scop CATH Class, Architecture,
SCOP all-β class 4-helical cytokines T4 endonuclease V all-α class, 3 different folds Globin-like TIM-barrel fold α/β class Profilin-like fold α+β class http://scop.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/scop CATH Class, Architecture,
Integrating multi-attribute similarity networks for robust representation of the protein space
 BIOINFORMATICS ORIGINAL PAPER Vol. 22 no. 13 2006, pages 1585 1592 doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btl130 Structural bioinformatics Integrating multi-attribute similarity networks for robust representation
BIOINFORMATICS ORIGINAL PAPER Vol. 22 no. 13 2006, pages 1585 1592 doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btl130 Structural bioinformatics Integrating multi-attribute similarity networks for robust representation
STRUCTURAL BIOINFORMATICS I. Fall 2015
 STRUCTURAL BIOINFORMATICS I Fall 2015 Info Course Number - Classification: Biology 5411 Class Schedule: Monday 5:30-7:50 PM, SERC Room 456 (4 th floor) Instructors: Vincenzo Carnevale - SERC, Room 704C;
STRUCTURAL BIOINFORMATICS I Fall 2015 Info Course Number - Classification: Biology 5411 Class Schedule: Monday 5:30-7:50 PM, SERC Room 456 (4 th floor) Instructors: Vincenzo Carnevale - SERC, Room 704C;
Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling. Chapter 4 Part I
 Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling Chapter 4 Part I 1 Information on Proteins Each modeling study depends on the quality of the known experimental data. Basis of the model Search in the literature
Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling Chapter 4 Part I 1 Information on Proteins Each modeling study depends on the quality of the known experimental data. Basis of the model Search in the literature
Outline. Levels of Protein Structure. Primary (1 ) Structure. Lecture 6:Protein Architecture II: Secondary Structure or From peptides to proteins
 Lecture 6:Protein Architecture II: Secondary Structure or From peptides to proteins Margaret Daugherty Fall 2004 Outline Four levels of structure are used to describe proteins; Alpha helices and beta sheets
Lecture 6:Protein Architecture II: Secondary Structure or From peptides to proteins Margaret Daugherty Fall 2004 Outline Four levels of structure are used to describe proteins; Alpha helices and beta sheets
Statistical Machine Learning Methods for Bioinformatics IV. Neural Network & Deep Learning Applications in Bioinformatics
 Statistical Machine Learning Methods for Bioinformatics IV. Neural Network & Deep Learning Applications in Bioinformatics Jianlin Cheng, PhD Department of Computer Science University of Missouri, Columbia
Statistical Machine Learning Methods for Bioinformatics IV. Neural Network & Deep Learning Applications in Bioinformatics Jianlin Cheng, PhD Department of Computer Science University of Missouri, Columbia
CAP 5510: Introduction to Bioinformatics CGS 5166: Bioinformatics Tools. Giri Narasimhan
 CAP 5510: Introduction to Bioinformatics CGS 5166: Bioinformatics Tools Giri Narasimhan ECS 254; Phone: x3748 giri@cis.fiu.edu www.cis.fiu.edu/~giri/teach/bioinff18.html Proteins and Protein Structure
CAP 5510: Introduction to Bioinformatics CGS 5166: Bioinformatics Tools Giri Narasimhan ECS 254; Phone: x3748 giri@cis.fiu.edu www.cis.fiu.edu/~giri/teach/bioinff18.html Proteins and Protein Structure
Week 10: Homology Modelling (II) - HHpred
 Week 10: Homology Modelling (II) - HHpred Course: Tools for Structural Biology Fabian Glaser BKU - Technion 1 2 Identify and align related structures by sequence methods is not an easy task All comparative
Week 10: Homology Modelling (II) - HHpred Course: Tools for Structural Biology Fabian Glaser BKU - Technion 1 2 Identify and align related structures by sequence methods is not an easy task All comparative
Presentation Outline. Prediction of Protein Secondary Structure using Neural Networks at Better than 70% Accuracy
 Prediction of Protein Secondary Structure using Neural Networks at Better than 70% Accuracy Burkhard Rost and Chris Sander By Kalyan C. Gopavarapu 1 Presentation Outline Major Terminology Problem Method
Prediction of Protein Secondary Structure using Neural Networks at Better than 70% Accuracy Burkhard Rost and Chris Sander By Kalyan C. Gopavarapu 1 Presentation Outline Major Terminology Problem Method
The CATH Database provides insights into protein structure/function relationships
 1999 Oxford University Press Nucleic Acids Research, 1999, Vol. 27, No. 1 275 279 The CATH Database provides insights into protein structure/function relationships C. A. Orengo, F. M. G. Pearl, J. E. Bray,
1999 Oxford University Press Nucleic Acids Research, 1999, Vol. 27, No. 1 275 279 The CATH Database provides insights into protein structure/function relationships C. A. Orengo, F. M. G. Pearl, J. E. Bray,
Outline. Levels of Protein Structure. Primary (1 ) Structure. Lecture 6:Protein Architecture II: Secondary Structure or From peptides to proteins
 Lecture 6:Protein Architecture II: Secondary Structure or From peptides to proteins Margaret Daugherty Fall 2003 Outline Four levels of structure are used to describe proteins; Alpha helices and beta sheets
Lecture 6:Protein Architecture II: Secondary Structure or From peptides to proteins Margaret Daugherty Fall 2003 Outline Four levels of structure are used to describe proteins; Alpha helices and beta sheets
Jessica Wehner. Summer Fellow Bioengineering and Bioinformatics Summer Institute University of Pittsburgh 29 May 2008
 Journal Club Jessica Wehner Summer Fellow Bioengineering and Bioinformatics Summer Institute University of Pittsburgh 29 May 2008 Comparison of Probabilistic Combination Methods for Protein Secondary Structure
Journal Club Jessica Wehner Summer Fellow Bioengineering and Bioinformatics Summer Institute University of Pittsburgh 29 May 2008 Comparison of Probabilistic Combination Methods for Protein Secondary Structure
Protein Structure. Hierarchy of Protein Structure. Tertiary structure. independently stable structural unit. includes disulfide bonds
 Protein Structure Hierarchy of Protein Structure 2 3 Structural element Primary structure Secondary structure Super-secondary structure Domain Tertiary structure Quaternary structure Description amino
Protein Structure Hierarchy of Protein Structure 2 3 Structural element Primary structure Secondary structure Super-secondary structure Domain Tertiary structure Quaternary structure Description amino
D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X 1
 11/7/05 Protein Structure: Classification, Databases, Visualization Announcements BCB 544 Projects - Important Dates: Nov 2 Wed noon - Project proposals due to David/Drena Nov 4 Fri PM - Approvals/responses
11/7/05 Protein Structure: Classification, Databases, Visualization Announcements BCB 544 Projects - Important Dates: Nov 2 Wed noon - Project proposals due to David/Drena Nov 4 Fri PM - Approvals/responses
Bioinformatics. Dept. of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics
 Bioinformatics Dept. of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics 3 Bioinformatics - play with sequences & structures Dept. of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics 4 ORGANIZATION OF LIFE ROLE OF BIOINFORMATICS
Bioinformatics Dept. of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics 3 Bioinformatics - play with sequences & structures Dept. of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics 4 ORGANIZATION OF LIFE ROLE OF BIOINFORMATICS
Protein tertiary structure prediction with new machine learning approaches
 Protein tertiary structure prediction with new machine learning approaches Rui Kuang Department of Computer Science Columbia University Supervisor: Jason Weston(NEC) and Christina Leslie(Columbia) NEC
Protein tertiary structure prediction with new machine learning approaches Rui Kuang Department of Computer Science Columbia University Supervisor: Jason Weston(NEC) and Christina Leslie(Columbia) NEC
Number sequence representation of protein structures based on the second derivative of a folded tetrahedron sequence
 Number sequence representation of protein structures based on the second derivative of a folded tetrahedron sequence Naoto Morikawa (nmorika@genocript.com) October 7, 2006. Abstract A protein is a sequence
Number sequence representation of protein structures based on the second derivative of a folded tetrahedron sequence Naoto Morikawa (nmorika@genocript.com) October 7, 2006. Abstract A protein is a sequence
SINGLE-SEQUENCE PROTEIN SECONDARY STRUCTURE PREDICTION BY NEAREST-NEIGHBOR CLASSIFICATION OF PROTEIN WORDS
 SINGLE-SEQUENCE PROTEIN SECONDARY STRUCTURE PREDICTION BY NEAREST-NEIGHBOR CLASSIFICATION OF PROTEIN WORDS Item type Authors Publisher Rights text; Electronic Thesis PORFIRIO, DAVID JONATHAN The University
SINGLE-SEQUENCE PROTEIN SECONDARY STRUCTURE PREDICTION BY NEAREST-NEIGHBOR CLASSIFICATION OF PROTEIN WORDS Item type Authors Publisher Rights text; Electronic Thesis PORFIRIO, DAVID JONATHAN The University
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary information S3 (box) Methods Methods Genome weighting The currently available collection of archaeal and bacterial genomes has a highly biased distribution of isolates across taxa. For example,
Supplementary information S3 (box) Methods Methods Genome weighting The currently available collection of archaeal and bacterial genomes has a highly biased distribution of isolates across taxa. For example,
Biological Networks: Comparison, Conservation, and Evolution via Relative Description Length By: Tamir Tuller & Benny Chor
 Biological Networks:,, and via Relative Description Length By: Tamir Tuller & Benny Chor Presented by: Noga Grebla Content of the presentation Presenting the goals of the research Reviewing basic terms
Biological Networks:,, and via Relative Description Length By: Tamir Tuller & Benny Chor Presented by: Noga Grebla Content of the presentation Presenting the goals of the research Reviewing basic terms
Protein structure analysis. Risto Laakso 10th January 2005
 Protein structure analysis Risto Laakso risto.laakso@hut.fi 10th January 2005 1 1 Summary Various methods of protein structure analysis were examined. Two proteins, 1HLB (Sea cucumber hemoglobin) and 1HLM
Protein structure analysis Risto Laakso risto.laakso@hut.fi 10th January 2005 1 1 Summary Various methods of protein structure analysis were examined. Two proteins, 1HLB (Sea cucumber hemoglobin) and 1HLM
Identification of Representative Protein Sequence and Secondary Structure Prediction Using SVM Approach
 Identification of Representative Protein Sequence and Secondary Structure Prediction Using SVM Approach Prof. Dr. M. A. Mottalib, Md. Rahat Hossain Department of Computer Science and Information Technology
Identification of Representative Protein Sequence and Secondary Structure Prediction Using SVM Approach Prof. Dr. M. A. Mottalib, Md. Rahat Hossain Department of Computer Science and Information Technology
Multiple structure alignment with mstali
 Multiple structure alignment with mstali Shealy and Valafar Shealy and Valafar BMC Bioinformatics 2012, 13:105 Shealy and Valafar BMC Bioinformatics 2012, 13:105 SOFTWARE Open Access Multiple structure
Multiple structure alignment with mstali Shealy and Valafar Shealy and Valafar BMC Bioinformatics 2012, 13:105 Shealy and Valafar BMC Bioinformatics 2012, 13:105 SOFTWARE Open Access Multiple structure
CSCE555 Bioinformatics. Protein Function Annotation
 CSCE555 Bioinformatics Protein Function Annotation Why we need to do function annotation? Fig from: Network-based prediction of protein function. Molecular Systems Biology 3:88. 2007 What s function? The
CSCE555 Bioinformatics Protein Function Annotation Why we need to do function annotation? Fig from: Network-based prediction of protein function. Molecular Systems Biology 3:88. 2007 What s function? The
INDEXING METHODS FOR PROTEIN TERTIARY AND PREDICTED STRUCTURES
 INDEXING METHODS FOR PROTEIN TERTIARY AND PREDICTED STRUCTURES By Feng Gao A Thesis Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for
INDEXING METHODS FOR PROTEIN TERTIARY AND PREDICTED STRUCTURES By Feng Gao A Thesis Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for
A General Model for Amino Acid Interaction Networks
 Author manuscript, published in "N/P" A General Model for Amino Acid Interaction Networks Omar GACI and Stefan BALEV hal-43269, version - Nov 29 Abstract In this paper we introduce the notion of protein
Author manuscript, published in "N/P" A General Model for Amino Acid Interaction Networks Omar GACI and Stefan BALEV hal-43269, version - Nov 29 Abstract In this paper we introduce the notion of protein
Modern Information Retrieval
 Modern Information Retrieval Chapter 8 Text Classification Introduction A Characterization of Text Classification Unsupervised Algorithms Supervised Algorithms Feature Selection or Dimensionality Reduction
Modern Information Retrieval Chapter 8 Text Classification Introduction A Characterization of Text Classification Unsupervised Algorithms Supervised Algorithms Feature Selection or Dimensionality Reduction
Protein Structure & Motifs
 & Motifs Biochemistry 201 Molecular Biology January 12, 2000 Doug Brutlag Introduction Proteins are more flexible than nucleic acids in structure because of both the larger number of types of residues
& Motifs Biochemistry 201 Molecular Biology January 12, 2000 Doug Brutlag Introduction Proteins are more flexible than nucleic acids in structure because of both the larger number of types of residues
Support Vector Machine. Industrial AI Lab.
 Support Vector Machine Industrial AI Lab. Classification (Linear) Autonomously figure out which category (or class) an unknown item should be categorized into Number of categories / classes Binary: 2 different
Support Vector Machine Industrial AI Lab. Classification (Linear) Autonomously figure out which category (or class) an unknown item should be categorized into Number of categories / classes Binary: 2 different
Lecture 10 (10/4/17) Lecture 10 (10/4/17)
 Lecture 10 (10/4/17) Reading: Ch4; 125, 138-141, 141-142 Problems: Ch4 (text); 7, 9, 11 Ch4 (study guide); 1, 2 NEXT Reading: Ch4; 125, 132-136 (structure determination) Ch4; 12-130 (Collagen) Problems:
Lecture 10 (10/4/17) Reading: Ch4; 125, 138-141, 141-142 Problems: Ch4 (text); 7, 9, 11 Ch4 (study guide); 1, 2 NEXT Reading: Ch4; 125, 132-136 (structure determination) Ch4; 12-130 (Collagen) Problems:
SUPERVISED LEARNING: INTRODUCTION TO CLASSIFICATION
 SUPERVISED LEARNING: INTRODUCTION TO CLASSIFICATION 1 Outline Basic terminology Features Training and validation Model selection Error and loss measures Statistical comparison Evaluation measures 2 Terminology
SUPERVISED LEARNING: INTRODUCTION TO CLASSIFICATION 1 Outline Basic terminology Features Training and validation Model selection Error and loss measures Statistical comparison Evaluation measures 2 Terminology
Advanced Certificate in Principles in Protein Structure. You will be given a start time with your exam instructions
 BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London) Advanced Certificate in Principles in Protein Structure MSc Structural Molecular Biology Date: Thursday, 1st September 2011 Time: 3 hours You will be given a start
BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London) Advanced Certificate in Principles in Protein Structure MSc Structural Molecular Biology Date: Thursday, 1st September 2011 Time: 3 hours You will be given a start
Protein Structure Prediction and Display
 Protein Structure Prediction and Display Goal Take primary structure (sequence) and, using rules derived from known structures, predict the secondary structure that is most likely to be adopted by each
Protein Structure Prediction and Display Goal Take primary structure (sequence) and, using rules derived from known structures, predict the secondary structure that is most likely to be adopted by each
2 Dean C. Adams and Gavin J. P. Naylor the best three-dimensional ordination of the structure space is found through an eigen-decomposition (correspon
 A Comparison of Methods for Assessing the Structural Similarity of Proteins Dean C. Adams and Gavin J. P. Naylor? Dept. Zoology and Genetics, Iowa State University, Ames, IA 50011, U.S.A. 1 Introduction
A Comparison of Methods for Assessing the Structural Similarity of Proteins Dean C. Adams and Gavin J. P. Naylor? Dept. Zoology and Genetics, Iowa State University, Ames, IA 50011, U.S.A. 1 Introduction
Conditional Graphical Models
 PhD Thesis Proposal Conditional Graphical Models for Protein Structure Prediction Yan Liu Language Technologies Institute University Thesis Committee Jaime Carbonell (Chair) John Lafferty Eric P. Xing
PhD Thesis Proposal Conditional Graphical Models for Protein Structure Prediction Yan Liu Language Technologies Institute University Thesis Committee Jaime Carbonell (Chair) John Lafferty Eric P. Xing
EBI web resources II: Ensembl and InterPro. Yanbin Yin Spring 2013
 EBI web resources II: Ensembl and InterPro Yanbin Yin Spring 2013 1 Outline Intro to genome annotation Protein family/domain databases InterPro, Pfam, Superfamily etc. Genome browser Ensembl Hands on Practice
EBI web resources II: Ensembl and InterPro Yanbin Yin Spring 2013 1 Outline Intro to genome annotation Protein family/domain databases InterPro, Pfam, Superfamily etc. Genome browser Ensembl Hands on Practice
Large-Scale Genomic Surveys
 Bioinformatics Subtopics Fold Recognition Secondary Structure Prediction Docking & Drug Design Protein Geometry Protein Flexibility Homology Modeling Sequence Alignment Structure Classification Gene Prediction
Bioinformatics Subtopics Fold Recognition Secondary Structure Prediction Docking & Drug Design Protein Geometry Protein Flexibility Homology Modeling Sequence Alignment Structure Classification Gene Prediction
Chapter 2 Structures. 2.1 Introduction Storing Protein Structures The PDB File Format
 Chapter 2 Structures 2.1 Introduction The three-dimensional (3D) structure of a protein contains a lot of information on its function, and can be used for devising ways of modifying it (propose mutants,
Chapter 2 Structures 2.1 Introduction The three-dimensional (3D) structure of a protein contains a lot of information on its function, and can be used for devising ways of modifying it (propose mutants,
YAPS: Yet Another Protein Similarity
 2009 International Conference of Soft Computing and Pattern Recognition YAPS: Yet Another Protein Similarity Tomáš Novosád, Václav Snášel Department of Computer Science VŠB - Technical University of Ostrava
2009 International Conference of Soft Computing and Pattern Recognition YAPS: Yet Another Protein Similarity Tomáš Novosád, Václav Snášel Department of Computer Science VŠB - Technical University of Ostrava
Protein Secondary Structure Prediction
 part of Bioinformatik von RNA- und Proteinstrukturen Computational EvoDevo University Leipzig Leipzig, SS 2011 the goal is the prediction of the secondary structure conformation which is local each amino
part of Bioinformatik von RNA- und Proteinstrukturen Computational EvoDevo University Leipzig Leipzig, SS 2011 the goal is the prediction of the secondary structure conformation which is local each amino
ECE 592 Topics in Data Science
 ECE 592 Topics in Data Science Final Fall 2017 December 11, 2017 Please remember to justify your answers carefully, and to staple your test sheet and answers together before submitting. Name: Student ID:
ECE 592 Topics in Data Science Final Fall 2017 December 11, 2017 Please remember to justify your answers carefully, and to staple your test sheet and answers together before submitting. Name: Student ID:
Physiochemical Properties of Residues
 Physiochemical Properties of Residues Various Sources C N Cα R Slide 1 Conformational Propensities Conformational Propensity is the frequency in which a residue adopts a given conformation (in a polypeptide)
Physiochemical Properties of Residues Various Sources C N Cα R Slide 1 Conformational Propensities Conformational Propensity is the frequency in which a residue adopts a given conformation (in a polypeptide)
Protein Structures. Sequences of amino acid residues 20 different amino acids. Quaternary. Primary. Tertiary. Secondary. 10/8/2002 Lecture 12 1
 Protein Structures Sequences of amino acid residues 20 different amino acids Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary 10/8/2002 Lecture 12 1 Angles φ and ψ in the polypeptide chain 10/8/2002 Lecture 12 2
Protein Structures Sequences of amino acid residues 20 different amino acids Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary 10/8/2002 Lecture 12 1 Angles φ and ψ in the polypeptide chain 10/8/2002 Lecture 12 2
09/06/25. Computergestützte Strukturbiologie (Strukturelle Bioinformatik) Non-uniform distribution of folds. Scheme of protein structure predicition
 Sequence identity Structural similarity Computergestützte Strukturbiologie (Strukturelle Bioinformatik) Fold recognition Sommersemester 2009 Peter Güntert Structural similarity X Sequence identity Non-uniform
Sequence identity Structural similarity Computergestützte Strukturbiologie (Strukturelle Bioinformatik) Fold recognition Sommersemester 2009 Peter Güntert Structural similarity X Sequence identity Non-uniform
Supersecondary Structures (structural motifs)
 Supersecondary Structures (structural motifs) Various Sources Slide 1 Supersecondary Structures (Motifs) Supersecondary Structures (Motifs): : Combinations of secondary structures in specific geometric
Supersecondary Structures (structural motifs) Various Sources Slide 1 Supersecondary Structures (Motifs) Supersecondary Structures (Motifs): : Combinations of secondary structures in specific geometric
Protein Structure Basics
 Protein Structure Basics Presented by Alison Fraser, Christine Lee, Pradhuman Jhala, Corban Rivera Importance of Proteins Muscle structure depends on protein-protein interactions Transport across membranes
Protein Structure Basics Presented by Alison Fraser, Christine Lee, Pradhuman Jhala, Corban Rivera Importance of Proteins Muscle structure depends on protein-protein interactions Transport across membranes
Introduction to" Protein Structure
 Introduction to" Protein Structure Function, evolution & experimental methods Thomas Blicher, Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Learning Objectives Outline the basic levels of protein structure.
Introduction to" Protein Structure Function, evolution & experimental methods Thomas Blicher, Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Learning Objectives Outline the basic levels of protein structure.
Reconstructing Amino Acid Interaction Networks by an Ant Colony Approach
 Author manuscript, published in "Journal of Computational Intelligence in Bioinformatics 2, 2 (2009) 131-146" Reconstructing Amino Acid Interaction Networks by an Ant Colony Approach Omar GACI and Stefan
Author manuscript, published in "Journal of Computational Intelligence in Bioinformatics 2, 2 (2009) 131-146" Reconstructing Amino Acid Interaction Networks by an Ant Colony Approach Omar GACI and Stefan
Modern Information Retrieval
 Modern Information Retrieval Chapter 8 Text Classification Introduction A Characterization of Text Classification Unsupervised Algorithms Supervised Algorithms Feature Selection or Dimensionality Reduction
Modern Information Retrieval Chapter 8 Text Classification Introduction A Characterization of Text Classification Unsupervised Algorithms Supervised Algorithms Feature Selection or Dimensionality Reduction
Motif Prediction in Amino Acid Interaction Networks
 Motif Prediction in Amino Acid Interaction Networks Omar GACI and Stefan BALEV Abstract In this paper we represent a protein as a graph where the vertices are amino acids and the edges are interactions
Motif Prediction in Amino Acid Interaction Networks Omar GACI and Stefan BALEV Abstract In this paper we represent a protein as a graph where the vertices are amino acids and the edges are interactions
Efficient Protein Tertiary Structure Retrievals and Classifications Using Content Based Comparison Algorithms
 Efficient Protein Tertiary Structure Retrievals and Classifications Using Content Based Comparison Algorithms A Dissertation presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School University of Missouri-Columbia
Efficient Protein Tertiary Structure Retrievals and Classifications Using Content Based Comparison Algorithms A Dissertation presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School University of Missouri-Columbia
Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques. (3 rd ed.) Chapter 8. Chapter 8. Classification: Basic Concepts
 Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques (3 rd ed.) Chapter 8 1 Chapter 8. Classification: Basic Concepts Classification: Basic Concepts Decision Tree Induction Bayes Classification Methods Rule-Based Classification
Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques (3 rd ed.) Chapter 8 1 Chapter 8. Classification: Basic Concepts Classification: Basic Concepts Decision Tree Induction Bayes Classification Methods Rule-Based Classification
Support Vector Machine. Industrial AI Lab. Prof. Seungchul Lee
 Support Vector Machine Industrial AI Lab. Prof. Seungchul Lee Classification (Linear) Autonomously figure out which category (or class) an unknown item should be categorized into Number of categories /
Support Vector Machine Industrial AI Lab. Prof. Seungchul Lee Classification (Linear) Autonomously figure out which category (or class) an unknown item should be categorized into Number of categories /
Style-aware Mid-level Representation for Discovering Visual Connections in Space and Time
 Style-aware Mid-level Representation for Discovering Visual Connections in Space and Time Experiment presentation for CS3710:Visual Recognition Presenter: Zitao Liu University of Pittsburgh ztliu@cs.pitt.edu
Style-aware Mid-level Representation for Discovering Visual Connections in Space and Time Experiment presentation for CS3710:Visual Recognition Presenter: Zitao Liu University of Pittsburgh ztliu@cs.pitt.edu
Bio nformatics. Lecture 23. Saad Mneimneh
 Bio nformatics Lecture 23 Protein folding The goal is to determine the three-dimensional structure of a protein based on its amino acid sequence Assumption: amino acid sequence completely and uniquely
Bio nformatics Lecture 23 Protein folding The goal is to determine the three-dimensional structure of a protein based on its amino acid sequence Assumption: amino acid sequence completely and uniquely
Improving Protein Function Prediction using the Hierarchical Structure of the Gene Ontology
 Improving Protein Function Prediction using the Hierarchical Structure of the Gene Ontology Roman Eisner, Brett Poulin, Duane Szafron, Paul Lu, Russ Greiner Department of Computing Science University of
Improving Protein Function Prediction using the Hierarchical Structure of the Gene Ontology Roman Eisner, Brett Poulin, Duane Szafron, Paul Lu, Russ Greiner Department of Computing Science University of
Algorithm-Independent Learning Issues
 Algorithm-Independent Learning Issues Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr CS 551, Spring 2007 c 2007, Selim Aksoy Introduction We have seen many learning
Algorithm-Independent Learning Issues Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr CS 551, Spring 2007 c 2007, Selim Aksoy Introduction We have seen many learning
Biophysics 101: Genomics & Computational Biology. Section 8: Protein Structure S T R U C T U R E P R O C E S S. Outline.
 Biophysics 101: Genomics & Computational Biology Section 8: Protein Structure Faisal Reza Nov. 11 th, 2003 B101.pdb from PS5 shown at left with: animated ball and stick model, colored CPK H-bonds on, colored
Biophysics 101: Genomics & Computational Biology Section 8: Protein Structure Faisal Reza Nov. 11 th, 2003 B101.pdb from PS5 shown at left with: animated ball and stick model, colored CPK H-bonds on, colored
Protein folding. α-helix. Lecture 21. An α-helix is a simple helix having on average 10 residues (3 turns of the helix)
 Computat onal Biology Lecture 21 Protein folding The goal is to determine the three-dimensional structure of a protein based on its amino acid sequence Assumption: amino acid sequence completely and uniquely
Computat onal Biology Lecture 21 Protein folding The goal is to determine the three-dimensional structure of a protein based on its amino acid sequence Assumption: amino acid sequence completely and uniquely
Some Problems from Enzyme Families
 Some Problems from Enzyme Families Greg Butler Department of Computer Science Concordia University, Montreal www.cs.concordia.ca/~faculty/gregb gregb@cs.concordia.ca Abstract I will discuss some problems
Some Problems from Enzyme Families Greg Butler Department of Computer Science Concordia University, Montreal www.cs.concordia.ca/~faculty/gregb gregb@cs.concordia.ca Abstract I will discuss some problems
Carson Andorf 1,3, Adrian Silvescu 1,3, Drena Dobbs 2,3,4, Vasant Honavar 1,3,4. University, Ames, Iowa, 50010, USA. Ames, Iowa, 50010, USA
 Learning Classifiers for Assigning Protein Sequences to Gene Ontology Functional Families: Combining of Function Annotation Using Sequence Homology With that Based on Amino Acid k-gram Composition Yields
Learning Classifiers for Assigning Protein Sequences to Gene Ontology Functional Families: Combining of Function Annotation Using Sequence Homology With that Based on Amino Acid k-gram Composition Yields
EBI web resources II: Ensembl and InterPro
 EBI web resources II: Ensembl and InterPro Yanbin Yin http://www.ebi.ac.uk/training/online/course/ 1 Homework 3 Go to http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/training.htmland finish the second online training course
EBI web resources II: Ensembl and InterPro Yanbin Yin http://www.ebi.ac.uk/training/online/course/ 1 Homework 3 Go to http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/training.htmland finish the second online training course
Holdout and Cross-Validation Methods Overfitting Avoidance
 Holdout and Cross-Validation Methods Overfitting Avoidance Decision Trees Reduce error pruning Cost-complexity pruning Neural Networks Early stopping Adjusting Regularizers via Cross-Validation Nearest
Holdout and Cross-Validation Methods Overfitting Avoidance Decision Trees Reduce error pruning Cost-complexity pruning Neural Networks Early stopping Adjusting Regularizers via Cross-Validation Nearest
08/21/2017 BLAST. Multiple Sequence Alignments: Clustal Omega
 BLAST Multiple Sequence Alignments: Clustal Omega What does basic BLAST do (e.g. what is input sequence and how does BLAST look for matches?) Susan Parrish McDaniel College Multiple Sequence Alignments
BLAST Multiple Sequence Alignments: Clustal Omega What does basic BLAST do (e.g. what is input sequence and how does BLAST look for matches?) Susan Parrish McDaniel College Multiple Sequence Alignments
Final Exam, Machine Learning, Spring 2009
 Name: Andrew ID: Final Exam, 10701 Machine Learning, Spring 2009 - The exam is open-book, open-notes, no electronics other than calculators. - The maximum possible score on this exam is 100. You have 3
Name: Andrew ID: Final Exam, 10701 Machine Learning, Spring 2009 - The exam is open-book, open-notes, no electronics other than calculators. - The maximum possible score on this exam is 100. You have 3
Clustering. CSL465/603 - Fall 2016 Narayanan C Krishnan
 Clustering CSL465/603 - Fall 2016 Narayanan C Krishnan ckn@iitrpr.ac.in Supervised vs Unsupervised Learning Supervised learning Given x ", y " "%& ', learn a function f: X Y Categorical output classification
Clustering CSL465/603 - Fall 2016 Narayanan C Krishnan ckn@iitrpr.ac.in Supervised vs Unsupervised Learning Supervised learning Given x ", y " "%& ', learn a function f: X Y Categorical output classification
Machine Learning
 Machine Learning 10-601 Tom M. Mitchell Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University October 11, 2012 Today: Computational Learning Theory Probably Approximately Coorrect (PAC) learning theorem
Machine Learning 10-601 Tom M. Mitchell Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University October 11, 2012 Today: Computational Learning Theory Probably Approximately Coorrect (PAC) learning theorem
Grundlagen der Bioinformatik Summer semester Lecturer: Prof. Daniel Huson
 Grundlagen der Bioinformatik, SS 10, D. Huson, April 12, 2010 1 1 Introduction Grundlagen der Bioinformatik Summer semester 2010 Lecturer: Prof. Daniel Huson Office hours: Thursdays 17-18h (Sand 14, C310a)
Grundlagen der Bioinformatik, SS 10, D. Huson, April 12, 2010 1 1 Introduction Grundlagen der Bioinformatik Summer semester 2010 Lecturer: Prof. Daniel Huson Office hours: Thursdays 17-18h (Sand 14, C310a)
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS Enhanced Recognition of Transmembrane Protein Domains with Prediction-based Structural Profiles Baoqiang Cao, Aleksey Porollo, Rafal Adamczak, Mark Jarrell and Jaroslaw Meller Contact:
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS Enhanced Recognition of Transmembrane Protein Domains with Prediction-based Structural Profiles Baoqiang Cao, Aleksey Porollo, Rafal Adamczak, Mark Jarrell and Jaroslaw Meller Contact:
Large-Scale Genomic Surveys
 Bioinformatics Subtopics Fold Recognition Secondary Structure Prediction Docking & Drug Design Protein Geometry Structural Informatics Homology Modeling Sequence Alignment Structure Classification Gene
Bioinformatics Subtopics Fold Recognition Secondary Structure Prediction Docking & Drug Design Protein Geometry Structural Informatics Homology Modeling Sequence Alignment Structure Classification Gene
Molecular Modeling Lecture 7. Homology modeling insertions/deletions manual realignment
 Molecular Modeling 2018-- Lecture 7 Homology modeling insertions/deletions manual realignment Homology modeling also called comparative modeling Sequences that have similar sequence have similar structure.
Molecular Modeling 2018-- Lecture 7 Homology modeling insertions/deletions manual realignment Homology modeling also called comparative modeling Sequences that have similar sequence have similar structure.
