The Cell System. The main job of a cell is to make proteins Proteins make up almost all of our body. Proteins do a lot of different things!
|
|
|
- Beryl Hopkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cell System
2 The Cell System The main job of a cell is to make proteins Proteins make up almost all of our body. Proteins do a lot of different things! Structural (build bones, muscles, skin, etc.) Defensive (antibodies, etc. to fight diseases) Enzymatic (control processes such as digestion) Storage (help store things like potassium or iron) Transport (carry things to other cells in the body) And more!
3 The Cell System All organelles have a role to play in the making of proteins. All organelles together make up the cell system. A system is made of parts that work together!
4 Cell Membrane Its job is to let in nutrients that will be used to make proteins. It also lets out waste. INSTRUCTIONS: Draw/label/describe the cell membrane
5 There are 3 steps to the process STEP 1: Before making proteins STEP 2: Making proteins STEP 3: After making proteins
6 Step 1: Before Building Proteins In order to build a protein, we need 3 things: Instructions Energy Materials
7 Nucleus The nucleus holds the DNA, which contain the instructions for making all of the different kinds of proteins
8 Ribosomes The ribosomes build the proteins The blue arrow shows us that the nucleus is sending instructions to the ribosomes, so that they can build the proteins correctly
9 Mitochondria The mitochondria makes the energy that the ribosomes need to build the proteins This blue arrow shows us that the energy is being sent to the ribosomes
10 Cytoplasm (empty space) The cytoplasm is a jelly-like substance that fills the cell. It contains lots of materials (like chemicals) used to make the proteins. This blue arrow shows us that materials are being sent to the ribosomes, to be used to make proteins.
11 INSTRUCTIONS: Draw/label/explain: -nucleus (instructions) -mitochondria (energy) -cytoplasm (materials) -draw the arrows to show that these things are being given to the ribosomes.
12 Step 2: Building the Proteins There are 4 parts: Ribosomes BUILD the proteins Endoplasmic Reticulum MOVES the proteins Golgi Bodies FINISH the proteins Lysosomes GET RID of waste
13 This purple squiggle is a protein that has been built by the ribosome!
14 Lysosomes As the proteins are built, waste is produced. Lysosomes break down the waste material and send it out of the cell. This blue arrow shows us that waste is being sent out of the cell. waste
15 Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Endoplasmic reticulum is like an assembly line. Once the proteins are built, it moves them along. (Rough ER has ribosomes attached. Smooth ER does not..) The blue arrow shows us that a ribosome is moving to the Endoplasmic Reticulum.
16 The ribosome has made a protein! Now that protein will move along the Endoplasmic Reticulum. The ER is how proteins are transported through the cell.
17 This blue arrow shows us that the protein is moving from the ER to the Golgi Body. Golgi Bodies (or Golgi Apparatus) The Golgi Bodies improve the protein and get it ready to be used.
18 INSTRUCTIONS: Draw/label/describe: -ribosomes BUILD proteins -Lysosomes GET RID of waste -ER TRANSPORTS proteins -Golgi bodies FINISH proteins
19 Step 3: After the proteins are built 3 things can happen to the protein. It can be: STORED in a vacuole (for later use) SENT OUT of the cell (for use somewhere else) SENT TO the cytoplasm (for use in the cell)
20 Now, the protein is finished. Where will it go? It can go 3 places.
21 It can move to a vacuole, to be stored until it is needed.
22 It can be sent out of the cell, for use somewhere else.
23 Or, it can be sent to the cytoplasm, to be used by this cell.
24 INSTRUCTIONS: Draw/label/describe: -STORED in a vacuole -SENT OUT of the cell -SENT TO the cytoplasm
25 The Cell System That s it! Be sure you know: The role that each organelle plays in the cell system (how it contributes to making proteins) A step-by-step process for how this happens You should be able to interpret this diagram: both the parts (organelles) and what each arrow represents
Biology. Mrs. Michaelsen. Types of cells. Cells & Cell Organelles. Cell size comparison. The Cell. Doing Life s Work. Hooke first viewed cork 1600 s
 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most
Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most
Cells & Cell Organelles. Doing Life s Work
 Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote Eukaryotes animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria 1-10 microns eukaryotic
Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote Eukaryotes animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria 1-10 microns eukaryotic
The Discovery of Cells
 The Discovery of Cells Microscope observations! General Cell & Organelle Discovery 1600s Observations made by scientists using more powerful microscopes in the 1800s led to the formation of the cell theory.
The Discovery of Cells Microscope observations! General Cell & Organelle Discovery 1600s Observations made by scientists using more powerful microscopes in the 1800s led to the formation of the cell theory.
Parts of the Cell book pgs
 Parts of the Cell book pgs. 12-18 Animal Cell Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Go to Section: Eukaryotic Cell: Organelles & Functions 1. Cell Membrane (Nickname: skin ) Function: A protective layer that covers
Parts of the Cell book pgs. 12-18 Animal Cell Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Go to Section: Eukaryotic Cell: Organelles & Functions 1. Cell Membrane (Nickname: skin ) Function: A protective layer that covers
Cell Organelles Tutorial
 1 Name: Cell Organelles Tutorial TEK 7.12D: Differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast,
1 Name: Cell Organelles Tutorial TEK 7.12D: Differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast,
Biology. Introduction to Cells. Tuesday, February 9, 16
 Biology Introduction to Cells Biology Biology is the study of life. In Biology, we are going to start small (the cell) and end with explaining a larger system (organisms) How small? http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/
Biology Introduction to Cells Biology Biology is the study of life. In Biology, we are going to start small (the cell) and end with explaining a larger system (organisms) How small? http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/
Cell Organelles. Wednesday, October 22, 14
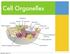 Cell Organelles Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells have a cell membrane It is the layer that surrounds the cell and controls what goes in and out Bacteria (Prokaryotic Cell) Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells
Cell Organelles Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells have a cell membrane It is the layer that surrounds the cell and controls what goes in and out Bacteria (Prokaryotic Cell) Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells
Unit 2: The Structure and function of Organisms. Section 2: Inside Cells
 Unit 2: The Structure and function of Organisms Section 2: 42 Essential Question: Are all cells the same? - Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Organelle Plant Cell Animal Cell Chloroplast
Unit 2: The Structure and function of Organisms Section 2: 42 Essential Question: Are all cells the same? - Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Organelle Plant Cell Animal Cell Chloroplast
Cells and Their Organelles
 Cells and Their Organelles The cell is the basic unit of life. The following is a glossary of animal cell terms. All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane. The cell membrane is semipermeable, allowing
Cells and Their Organelles The cell is the basic unit of life. The following is a glossary of animal cell terms. All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane. The cell membrane is semipermeable, allowing
Cell Structure: What cells are made of. Can you pick out the cells from this picture?
 Cell Structure: What cells are made of Can you pick out the cells from this picture? Review of the cell theory Microscope was developed 1610. Anton van Leeuwenhoek saw living things in pond water. 1677
Cell Structure: What cells are made of Can you pick out the cells from this picture? Review of the cell theory Microscope was developed 1610. Anton van Leeuwenhoek saw living things in pond water. 1677
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells
 Why? Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform
Why? Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform
Cells. basic structure of life
 Cells basic structure of life Cells are the smallest unit of life Cells (the smallest unit of life)- make up all living things, including your own body. Cells can differ in shape and sizes. The different
Cells basic structure of life Cells are the smallest unit of life Cells (the smallest unit of life)- make up all living things, including your own body. Cells can differ in shape and sizes. The different
What in the Cell is Going On?
 What in the Cell is Going On? Robert Hooke naturalist, philosopher, inventor, architect... (July 18, 1635 - March 3, 1703) In 1665 Robert Hooke publishes his book, Micrographia, which contains his drawings
What in the Cell is Going On? Robert Hooke naturalist, philosopher, inventor, architect... (July 18, 1635 - March 3, 1703) In 1665 Robert Hooke publishes his book, Micrographia, which contains his drawings
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells
 Why? Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform
Why? Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform
Name: Date: Hour:
 Name: Date: Hour: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Comprehension Questions 1. At what level of organization does life begin? 2. What surrounds all cells? 3. What is meant by semipermeable? 4. What 2 things make up the cell
Name: Date: Hour: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Comprehension Questions 1. At what level of organization does life begin? 2. What surrounds all cells? 3. What is meant by semipermeable? 4. What 2 things make up the cell
Biology. 7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure 10/29/2013. Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Biology Biology 1of 49 2of 49 Eukaryotic Cell Structures Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists
Biology Biology 1of 49 2of 49 Eukaryotic Cell Structures Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists
A Look At Cells Graphics: Microsoft Clipart
 CELLS, CELLS, CELLS A Look At Cells Graphics: Microsoft Clipart Cells Defined as the basic unit of living things. Cell Theory All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic units of structure
CELLS, CELLS, CELLS A Look At Cells Graphics: Microsoft Clipart Cells Defined as the basic unit of living things. Cell Theory All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic units of structure
Biology. Introduction to Cells. Sunday, November 8, 15
 Biology Introduction to Cells Cell Theory Biology is the study of life. Ideas about cells are built on the cell theory which states: 1. All living things are made of cells and their products. 2. The cell
Biology Introduction to Cells Cell Theory Biology is the study of life. Ideas about cells are built on the cell theory which states: 1. All living things are made of cells and their products. 2. The cell
Cells and Their Organelles
 Mr. Ulrich Regents Biology Name:.. Cells and Their Organelles The cell is the basic unit of life. The following is a glossary of animal cell terms. All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane. The cell
Mr. Ulrich Regents Biology Name:.. Cells and Their Organelles The cell is the basic unit of life. The following is a glossary of animal cell terms. All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane. The cell
protein synthesis cell theory Centrioles specialization. unicellular ribosomes. mitochondria cell interdependence prokaryotes
 All cells must generate proteins. Cells make protein through a process called protein synthesis All living things are made of cells, Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all organisms,
All cells must generate proteins. Cells make protein through a process called protein synthesis All living things are made of cells, Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all organisms,
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
 Cell Dairy Farm 1. Pens and corrals The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a series of interconnecting flattened tunnels which are attached to the outer membrane of the nucleus. The ER is the transport network
Cell Dairy Farm 1. Pens and corrals The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a series of interconnecting flattened tunnels which are attached to the outer membrane of the nucleus. The ER is the transport network
Introduction to Cells- Stations Lab
 Introduction to Cells- Stations Lab Station 1: Microscopes allow scientists to study cells. Microscopes: How do light microscopes differ from electron microscopes? (How does each work? How much can each
Introduction to Cells- Stations Lab Station 1: Microscopes allow scientists to study cells. Microscopes: How do light microscopes differ from electron microscopes? (How does each work? How much can each
The Cell As A City. Each organelle has a job---your cells run like a little city with many jobs to be done.
 The Cell As A City Each organelle has a job---your cells run like a little city with many jobs to be done. Lets take each organelle and put it s job into a life situation.... Nucleus basically like the
The Cell As A City Each organelle has a job---your cells run like a little city with many jobs to be done. Lets take each organelle and put it s job into a life situation.... Nucleus basically like the
CELL STRUCTURE. What are the basic units of life? What are the structures within a cell and what are they capable of? How and why do cells divide?
 CELL STRUCTURE What are the basic units of life? What are the structures within a cell and what are they capable of? How and why do cells divide? YEAR 8 BODY SYSTEMS Cells alive! Cells are the smallest
CELL STRUCTURE What are the basic units of life? What are the structures within a cell and what are they capable of? How and why do cells divide? YEAR 8 BODY SYSTEMS Cells alive! Cells are the smallest
Unit 3: Cells. Objective: To be able to compare and contrast the differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells.
 Unit 3: Cells Objective: To be able to compare and contrast the differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells. The Cell Theory All living things are composed of cells (unicellular or multicellular).
Unit 3: Cells Objective: To be able to compare and contrast the differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells. The Cell Theory All living things are composed of cells (unicellular or multicellular).
How do we define what it means to be alive?
 How do we define what it means to be alive? Defining Life There is no universal definition of life. To define life in unequivocal terms is still a challenge for scientists. Conventional definition: must
How do we define what it means to be alive? Defining Life There is no universal definition of life. To define life in unequivocal terms is still a challenge for scientists. Conventional definition: must
Structures and Functions of Plant and Animal Cells
 Structures and Functions of Plant and Animal Cells 7.L.1.2 - Compare the structures and functions of plant and animal cells, including major organelles (cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, chloroplasts,
Structures and Functions of Plant and Animal Cells 7.L.1.2 - Compare the structures and functions of plant and animal cells, including major organelles (cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, chloroplasts,
Name Class Date. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank.
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING VOCABULARY 1. Academic Vocabulary Which of the following words is the closest in meaning to the word structure? a. evidence c. duty b. shape d. location Complete each
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING VOCABULARY 1. Academic Vocabulary Which of the following words is the closest in meaning to the word structure? a. evidence c. duty b. shape d. location Complete each
Chapter 7.2. Cell Structure
 Chapter 7.2 Cell Structure Daily Objectives Describe the structure and function of the cell nucleus. Describe the function and structure of membrane bound organelles found within the cell. Describe the
Chapter 7.2 Cell Structure Daily Objectives Describe the structure and function of the cell nucleus. Describe the function and structure of membrane bound organelles found within the cell. Describe the
How do we define what it means to be alive?
 How do we define what it means to be alive? Defining Life-7 Characteristics of Life There is no universal definition of life. To define life in unequivocal terms is still a challenge for scientists. Conventional
How do we define what it means to be alive? Defining Life-7 Characteristics of Life There is no universal definition of life. To define life in unequivocal terms is still a challenge for scientists. Conventional
Directions for Plant Cell 3-Part Cards
 Directions for Plant Cell 3-Part Cards 1. Print out copy of 3 part cards and control cards Laminate for durability. Cut apart description and labels from 3 part cards. 2. As an introductory lesson, students
Directions for Plant Cell 3-Part Cards 1. Print out copy of 3 part cards and control cards Laminate for durability. Cut apart description and labels from 3 part cards. 2. As an introductory lesson, students
3.2 Cell Organelles. KEY CONCEPT Eukaryotic cells share many similarities.
 KEY CONCEPT Eukaryotic cells share many similarities. ! Cells have an internal structure. ! Cells have an internal structure. The cytoskeleton has many functions. ! Cells have an internal structure. The
KEY CONCEPT Eukaryotic cells share many similarities. ! Cells have an internal structure. ! Cells have an internal structure. The cytoskeleton has many functions. ! Cells have an internal structure. The
Eukaryotic Cell Structure. 7.2 Biology Mr. Hines
 Eukaryotic Cell Structure 7.2 Biology Mr. Hines Comparing the cell to a factory In order for a cell to maintain its internal environment (homeostasis), many things must go on. This is similar to a factory.
Eukaryotic Cell Structure 7.2 Biology Mr. Hines Comparing the cell to a factory In order for a cell to maintain its internal environment (homeostasis), many things must go on. This is similar to a factory.
Unit 4: Cells. Biology 309/310. Name: Review Guide
 Unit 4: Cells Review Guide LEARNING TARGETS Place a checkmark next to the learning targets you feel confident on. Then go back and focus on the learning targets that are not checked. Identify the parts
Unit 4: Cells Review Guide LEARNING TARGETS Place a checkmark next to the learning targets you feel confident on. Then go back and focus on the learning targets that are not checked. Identify the parts
7 Characteristics of Life
 7 Characteristics of Life 1. Interdependence 2. Metabolism 3. Homeostasis 4. Cellular Structure and Function 5. Reproduction 6. Heredity 7. Evolution The Cell Theory All living things are composed of one
7 Characteristics of Life 1. Interdependence 2. Metabolism 3. Homeostasis 4. Cellular Structure and Function 5. Reproduction 6. Heredity 7. Evolution The Cell Theory All living things are composed of one
Unit 2: Cells. Students will understand that the organs in an organism are made of cells that have structures & perform specific life functions
 Unit 2: Cells Students will understand that the organs in an organism are made of cells that have structures & perform specific life functions Vocabulary Cell Chloroplast Tissue Cell wall Organ Lysosome
Unit 2: Cells Students will understand that the organs in an organism are made of cells that have structures & perform specific life functions Vocabulary Cell Chloroplast Tissue Cell wall Organ Lysosome
Cell Structure: Organelles. Unit Seventh Grade
 Cell Structure: Organelles Unit 3 --- Seventh Grade Cells are everywhere. Even though most cells cannot be seen with the naked eye, they make up every living thing. Your body contains trillions of cells.
Cell Structure: Organelles Unit 3 --- Seventh Grade Cells are everywhere. Even though most cells cannot be seen with the naked eye, they make up every living thing. Your body contains trillions of cells.
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: A View of the Cell. Use Chapter 8 of your book to complete the chart of eukaryotic cell components.
 NAME: PERIOD: DATE: A View of the Cell Use Chapter 8 of your book to complete the chart of eukaryotic cell components. Cell Part Cell Wall Centriole Chloroplast Cilia Cytoplasm Cytoskeleton Endoplasmic
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: A View of the Cell Use Chapter 8 of your book to complete the chart of eukaryotic cell components. Cell Part Cell Wall Centriole Chloroplast Cilia Cytoplasm Cytoskeleton Endoplasmic
Cell Alive Homeostasis Plants Animals Fungi Bacteria. Loose DNA DNA Nucleus Membrane-Bound Organelles Humans
 UNIT 3: The Cell DAYSHEET 45: Introduction to Cellular Organelles Name: Biology I Date: Bellringer: Place the words below into the correct space on the Venn Diagram: Cell Alive Homeostasis Plants Animals
UNIT 3: The Cell DAYSHEET 45: Introduction to Cellular Organelles Name: Biology I Date: Bellringer: Place the words below into the correct space on the Venn Diagram: Cell Alive Homeostasis Plants Animals
Function and Illustration. Nucleus. Nucleolus. Cell membrane. Cell wall. Capsule. Mitochondrion
 Intro to Organelles Name: Block: Organelles are small structures inside cells. They are often covered in membranes. Each organelle has a job to do in the cell. Their name means little organ. Just like
Intro to Organelles Name: Block: Organelles are small structures inside cells. They are often covered in membranes. Each organelle has a job to do in the cell. Their name means little organ. Just like
CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
 7-1 Life Is Cellular CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall The Discovery of the Cell 1665: Robert Hooke used an early compound microscope to look at a thin slice of cork. Cork looked
7-1 Life Is Cellular CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall The Discovery of the Cell 1665: Robert Hooke used an early compound microscope to look at a thin slice of cork. Cork looked
Just Print Science. Pack
 Just Print Science Pack Plant and Animal Cells Jennifer Findley Note to Teacher This resource includes several resources for teaching and reviewing plant and animal cells. The resource includes a one-page
Just Print Science Pack Plant and Animal Cells Jennifer Findley Note to Teacher This resource includes several resources for teaching and reviewing plant and animal cells. The resource includes a one-page
prokaryotic eukaryotic
 Cell Basics Two Basic Cell Types All cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic Prokaryotic Cells a.k.a. Bacteria Prokaryotes, which includes all bacteria. They are the simplest cellular organisms. They
Cell Basics Two Basic Cell Types All cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic Prokaryotic Cells a.k.a. Bacteria Prokaryotes, which includes all bacteria. They are the simplest cellular organisms. They
Cell Structure and Function. Chapter 4
 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Chapter 4: Cell Structure Section 1: The History of Cell Biology Section 2: Introduction to Cells Section 3: Cell Organelles and Features Section 4: Unique Features
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Chapter 4: Cell Structure Section 1: The History of Cell Biology Section 2: Introduction to Cells Section 3: Cell Organelles and Features Section 4: Unique Features
Biology Cell Organelle Webquest. Name Period Date
 Biology Cell Organelle Webquest Name Period Date This webquest has TWO parts to it. You need to go to www.rodensclassroom.com and click on the "BIOLOGY" link. Once there click on the Unit 3-Cell Organelles
Biology Cell Organelle Webquest Name Period Date This webquest has TWO parts to it. You need to go to www.rodensclassroom.com and click on the "BIOLOGY" link. Once there click on the Unit 3-Cell Organelles
Turns sunlight, water & carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) into sugar & oxygen through photosynthesis
 CELL PART/ ORGANELLE FUNCTION (what it does) PICTURE Plant, Animal, or Both Cell Membrane controls what goes in & out of the cell protects the cell Nucleus directs all the cell s activities contains cell
CELL PART/ ORGANELLE FUNCTION (what it does) PICTURE Plant, Animal, or Both Cell Membrane controls what goes in & out of the cell protects the cell Nucleus directs all the cell s activities contains cell
Eukaryotic Cells: The Inside Story. Day 1
 Eukaryotic Cells: The Inside Story Day 1 Objective 1. I will describe each part of a eukaryotic. 2. I will explain the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell. 3. I will describe the difference between
Eukaryotic Cells: The Inside Story Day 1 Objective 1. I will describe each part of a eukaryotic. 2. I will explain the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell. 3. I will describe the difference between
Cell City Introduction!
 Cell City Introduction! Floating around in the cytoplasm are small structures called organelles. Like the organs in your own body, each one carries out a specific function necessary for the cell to survive.
Cell City Introduction! Floating around in the cytoplasm are small structures called organelles. Like the organs in your own body, each one carries out a specific function necessary for the cell to survive.
The Cell. The basic unit of all living things
 The Cell The basic unit of all living things 1 Robert Hooke was the first to name the cell (1665) 2 The Cell Theory The cell is the unit of Structure of all living things. The cell is the unit of Function
The Cell The basic unit of all living things 1 Robert Hooke was the first to name the cell (1665) 2 The Cell Theory The cell is the unit of Structure of all living things. The cell is the unit of Function
3.2. Eukaryotic Cells and Cell Organelles. Teacher Notes and Answers. section
 section 3.2 Eukaryotic Cells and Cell Organelles Teacher Notes and Answers SECTION 2 Instant Replay 1. Answers will vary. An example answer is a shapeless bag. 2. store and protect the DNA 3. mitochondria
section 3.2 Eukaryotic Cells and Cell Organelles Teacher Notes and Answers SECTION 2 Instant Replay 1. Answers will vary. An example answer is a shapeless bag. 2. store and protect the DNA 3. mitochondria
The diagram below represents levels of organization within a cell of a multicellular organism.
 STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
Eukaryotic Cell Structure: Organelles in Animal & Plant Cells Why are organelles important and how are plants and animals different?
 Why? Eukaryotic Cell Structure: Organelles in Animal & Plant Cells Why are organelles important and how are plants and animals different? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things.
Why? Eukaryotic Cell Structure: Organelles in Animal & Plant Cells Why are organelles important and how are plants and animals different? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things.
Chapter 7 Learning Targets Cell Structure & Function
 Name: Chapter 7 Learning Targets Cell Structure & Function a. Define the word cell: 1. I know the history of the cell: b. Who discovered the cell? What did he observe? 2. I can list the three parts of
Name: Chapter 7 Learning Targets Cell Structure & Function a. Define the word cell: 1. I know the history of the cell: b. Who discovered the cell? What did he observe? 2. I can list the three parts of
Introduction to Cells. Intro to Cells. Scientists who contributed to cell theory. Cell Theory. There are 2 types of cells: All Cells:
 Intro to Cells Key Concept: Cells are the basic unit of life. Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: 1 Animal Cell
Intro to Cells Key Concept: Cells are the basic unit of life. Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: 1 Animal Cell
7.L.1.2 Plant and Animal Cells. Plant and Animal Cells
 7.L.1.2 Plant and Animal Cells Plant and Animal Cells Clarifying Objective: 7.L.1.2 Compare the structures and functions of plant and animal cells; include major organelles (cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus,
7.L.1.2 Plant and Animal Cells Plant and Animal Cells Clarifying Objective: 7.L.1.2 Compare the structures and functions of plant and animal cells; include major organelles (cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus,
Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor, Pharmacology
 Cytology Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor, Pharmacology Email: da.hassan@psau.edu.sa Cells All living things are made up of cells Basic building blocks of life It is the smallest functional and
Cytology Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor, Pharmacology Email: da.hassan@psau.edu.sa Cells All living things are made up of cells Basic building blocks of life It is the smallest functional and
Cells. Part 1: Characteristics of Living Things
 Cells Part 1: Characteristics of Living Things Introduction Living or Non-living? How do you know? What characteristics does it have that makes you think that way? Living? What makes something living?
Cells Part 1: Characteristics of Living Things Introduction Living or Non-living? How do you know? What characteristics does it have that makes you think that way? Living? What makes something living?
COMMON CORE Lessons & Activities
 T E AC H I T SA M PL E COMMON CORE Lessons & Activities DAY! O T Common Core Lessons & Activities: Cell Structure By Carole Marsh Published by Gallopade International, Inc. Carole Marsh/Gallopade Printed
T E AC H I T SA M PL E COMMON CORE Lessons & Activities DAY! O T Common Core Lessons & Activities: Cell Structure By Carole Marsh Published by Gallopade International, Inc. Carole Marsh/Gallopade Printed
UNIT 3 CP BIOLOGY: Cell Structure
 UNIT 3 CP BIOLOGY: Cell Structure Page CP: CHAPTER 3, Sections 1-3; HN: CHAPTER 7, Sections 1-2 Standard B-2: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of cells and their
UNIT 3 CP BIOLOGY: Cell Structure Page CP: CHAPTER 3, Sections 1-3; HN: CHAPTER 7, Sections 1-2 Standard B-2: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of cells and their
Name Class Date. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank.
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. cell organ cell membrane prokaryote organelles eukaryote cell wall
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. cell organ cell membrane prokaryote organelles eukaryote cell wall
The Cell Theory. Prokaryotic (Pre) ( Nucleus) Cells 10/28/2013. Types of Cells. All living things have cells. Always single- celled lacks organelles
 Types of Cells Cells 1. I can explain the cell theory The Cell Theory 1. All living things are composed of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function. 3. Cells are produced
Types of Cells Cells 1. I can explain the cell theory The Cell Theory 1. All living things are composed of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function. 3. Cells are produced
WHAT S ON THE INSIDE An Introduction to Plant and Animal Cells
 W 531 WHAT S ON THE INSIDE An Introduction to Plant and Animal Cells Tonya Bain, UT Extension Agent, Crockett County Jennifer Richards, Curriculum Specialist, Tennessee 4-H Youth Development Tennessee
W 531 WHAT S ON THE INSIDE An Introduction to Plant and Animal Cells Tonya Bain, UT Extension Agent, Crockett County Jennifer Richards, Curriculum Specialist, Tennessee 4-H Youth Development Tennessee
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 chapter 7 Test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Who was one of the first people to identify and see cork cells? a. Anton van
chapter 7 Test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Who was one of the first people to identify and see cork cells? a. Anton van
THE CELL THEORY (R+R+R+E+G+N+T+S) 3).
 CELL BIOLOGY All living things are made up of small individual units called cells. Cells are the smallest functioning living unit. Cells can not normally be seen with the naked eye. To usually observe
CELL BIOLOGY All living things are made up of small individual units called cells. Cells are the smallest functioning living unit. Cells can not normally be seen with the naked eye. To usually observe
Science Interactive Notebook ZcienceClass.com
 Science Interactive Notebook ZcienceClass.com Mr. Zamarripa If found return to room 206 Week of 09/12/2016 65A Warm-Up Tuesday A student walks 2 km in 30 minutes. What is the student s average speed in
Science Interactive Notebook ZcienceClass.com Mr. Zamarripa If found return to room 206 Week of 09/12/2016 65A Warm-Up Tuesday A student walks 2 km in 30 minutes. What is the student s average speed in
Mitochondria. Nickname: Batteries. bean shaped. Structure: Function: provides energy for the cell (powerhouse of the cell)
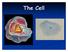 The Cell #1 Mitochondria Mitochondria Nickname: Batteries Structure: bean shaped Function: provides energy for the cell (powerhouse of the cell) Mitochondria #2 Nucleus Nucleus Nickname: Structure: Function:
The Cell #1 Mitochondria Mitochondria Nickname: Batteries Structure: bean shaped Function: provides energy for the cell (powerhouse of the cell) Mitochondria #2 Nucleus Nucleus Nickname: Structure: Function:
STUDENT PACKET #1 Student Exploration: Cell Structure
 STUDENT PACKET #1 Student Exploration: Cell Structure Big Idea 14: Organization and Development of Living Organisms SC.6.L.14.1 Describe and identify patterns in the hierarchical organization of organisms
STUDENT PACKET #1 Student Exploration: Cell Structure Big Idea 14: Organization and Development of Living Organisms SC.6.L.14.1 Describe and identify patterns in the hierarchical organization of organisms
7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
 1 of 49 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic
1 of 49 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic
and their organelles
 and their organelles Discovery Video: Cells REVIEW!!!! The Cell Theory 1. Every living organism is made of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function. It is the smallest
and their organelles Discovery Video: Cells REVIEW!!!! The Cell Theory 1. Every living organism is made of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function. It is the smallest
Introduction 1) List the 3 types of cells you will be comparing in today s lesson. a. b. c.
 Name: Date: Period: Cell Structure Internet Lesson Directions: Answer the following question by visiting the web site below. http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cell_structure/cell_structure.htm
Name: Date: Period: Cell Structure Internet Lesson Directions: Answer the following question by visiting the web site below. http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cell_structure/cell_structure.htm
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below which represents a typical green plant cell and on your knowledge of biology.
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below which represents a typical green plant cell and on your knowledge of biology. 5. Which letter corresponds to that of the endoplasmic reticulum?
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below which represents a typical green plant cell and on your knowledge of biology. 5. Which letter corresponds to that of the endoplasmic reticulum?
A D A E J (L) J(s) K L
 I A E A D G C B C F G E F H B J (L) H K L J(s) Animal Cells Less Support Needed Large, multicellular organisms made of animal cells often have support systems such as bones or exoskeletons Plant and Animal
I A E A D G C B C F G E F H B J (L) H K L J(s) Animal Cells Less Support Needed Large, multicellular organisms made of animal cells often have support systems such as bones or exoskeletons Plant and Animal
Chapter 4 Cells: The Basic Units of Life The Big Idea All organisms are composed of one or more cells.
 Chapter 4 Cells: The Basic Units of Life The Big Idea All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Section 1 The Characteristics of Cells Key Concept Cells function similarly in all living organisms.
Chapter 4 Cells: The Basic Units of Life The Big Idea All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Section 1 The Characteristics of Cells Key Concept Cells function similarly in all living organisms.
LIFE SCIENCE CHAPTER 3 FLASHCARDS
 LIFE SCIENCE CHAPTER 3 FLASHCARDS Human beings are A. machines. B. organisms. C. systems. D. protists. One benefit of being a large organism is that you have A. larger cells. B. simpler functions. C. fewer
LIFE SCIENCE CHAPTER 3 FLASHCARDS Human beings are A. machines. B. organisms. C. systems. D. protists. One benefit of being a large organism is that you have A. larger cells. B. simpler functions. C. fewer
BASIC BIOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES
 BASIC BIOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES A1 A1. Basic Biological Principles 1. Describe the characteristics of life shared by all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms 2. Compare cellular structures and their function
BASIC BIOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES A1 A1. Basic Biological Principles 1. Describe the characteristics of life shared by all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms 2. Compare cellular structures and their function
CELL THEORY & CELL STRUCUTRE M R S. G R E E N
 CELL THEORY & CELL STRUCUTRE M R S. G R E E N BELL WORK What are plant cells made up of? What are animal cells made up of? PRE-TEST I will be handing out the pre-test. My expectations are: Once the test
CELL THEORY & CELL STRUCUTRE M R S. G R E E N BELL WORK What are plant cells made up of? What are animal cells made up of? PRE-TEST I will be handing out the pre-test. My expectations are: Once the test
Introduction to Cells
 Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
Honors Biology summer assignment. Review the notes and study them. There will be a test on this information the 1 st week of class
 Honors Biology summer assignment Review the notes and study them. There will be a test on this information the 1 st week of class Biomolecules Molecules that make up living things. There are 4 molecules
Honors Biology summer assignment Review the notes and study them. There will be a test on this information the 1 st week of class Biomolecules Molecules that make up living things. There are 4 molecules
Pre-lab homework Lab 4: The Cell
 Pre-lab homework Lab 4: The Cell Lab Section: Name: After reading over the lab and chapter 5 in your textbook, answer these questions to be turned in at the beginning of the lab! 1. Define organelle 2.
Pre-lab homework Lab 4: The Cell Lab Section: Name: After reading over the lab and chapter 5 in your textbook, answer these questions to be turned in at the beginning of the lab! 1. Define organelle 2.
Organelle Description Function Animal, Plant or Both
 Biology Name: Date: Period: Organelle Description Function Animal, Plant or CELL WALL Rigid, tough, made of cellulose Protects and supports the cell Plant CELL MEMBRANE Thin, covering, protects cells Protects
Biology Name: Date: Period: Organelle Description Function Animal, Plant or CELL WALL Rigid, tough, made of cellulose Protects and supports the cell Plant CELL MEMBRANE Thin, covering, protects cells Protects
The Basic Unit of Life Copyright Amy Brown Science Stuff
 Cell Structure and Function The Basic Unit of Life Copyright Amy Brown Science Stuff The Discovery of the Cell Robert Hooke looked at thin slices of cork (plant cells) under the microscope. Named it a
Cell Structure and Function The Basic Unit of Life Copyright Amy Brown Science Stuff The Discovery of the Cell Robert Hooke looked at thin slices of cork (plant cells) under the microscope. Named it a
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell What jobs do cells have to do for an organism to live Gas exchange CO 2 & O 2 Eat (take in & digest food) Make energy ATP Build
Cell Structure and Function Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell What jobs do cells have to do for an organism to live Gas exchange CO 2 & O 2 Eat (take in & digest food) Make energy ATP Build
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Class: Date: Ch 7 Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Researchers use fluorescent labels and light microscopy to a. follow
Class: Date: Ch 7 Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Researchers use fluorescent labels and light microscopy to a. follow
8/25/ Opening Questions: Are all living things made of cells? What are at least five things you know about cells?
 Chapter 3 The Cell: Module Hyperlinks 3.1 Cells are the fundamental units of life 3.2 Plant vs. animal cells 3.3 Membranes: structure 3.4 Membranes: function 3.5 The nucleus 3.6 Organelles in protein production
Chapter 3 The Cell: Module Hyperlinks 3.1 Cells are the fundamental units of life 3.2 Plant vs. animal cells 3.3 Membranes: structure 3.4 Membranes: function 3.5 The nucleus 3.6 Organelles in protein production
BIO.A.1 Basic Biological Principles
 BIO.A.1 Basic Biological Principles Bio.A.1.1 - Explain the characteristics common to all organisms Bio.A.1.2 Describe relationships between the structure & function at biological levels of organization
BIO.A.1 Basic Biological Principles Bio.A.1.1 - Explain the characteristics common to all organisms Bio.A.1.2 Describe relationships between the structure & function at biological levels of organization
Division Ave. High School AP Biology
 Tour of the Cell 1 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Why organelles? Specialized structures u specialized functions cilia
Tour of the Cell 1 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Why organelles? Specialized structures u specialized functions cilia
Topic 3: Cells Ch. 6. Microscopes pp Microscopes. Microscopes. Microscopes. Microscopes
 Topic 3: Cells Ch. 6 -All life is composed of cells and all cells have a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA. pp.105-107 - The development of the microscope was the key to understanding that all living
Topic 3: Cells Ch. 6 -All life is composed of cells and all cells have a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA. pp.105-107 - The development of the microscope was the key to understanding that all living
Basic Cell Organelle
 Basic Cell Organelle 5 th grade, Science Standards/Framework (Common Core, NAEYC, Mid-level.): LS.2.5.3 Describe the similarities of basic cell functions in all organisms. Vocabulary Cell (Plasma) Membrane
Basic Cell Organelle 5 th grade, Science Standards/Framework (Common Core, NAEYC, Mid-level.): LS.2.5.3 Describe the similarities of basic cell functions in all organisms. Vocabulary Cell (Plasma) Membrane
Cells were in by, who under a microscope He saw He called them Several worked to the which states:
 Cells were in by, who under a microscope He saw He called them Several worked to the which states: Cells Because, the before scientists could study them Cells are very tiny structures called Plant cells
Cells were in by, who under a microscope He saw He called them Several worked to the which states: Cells Because, the before scientists could study them Cells are very tiny structures called Plant cells
 http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html 4A: Students will compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Robert Hooke (1665) Used a compound microscope to look at thin slices of cork (oak
http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html 4A: Students will compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Robert Hooke (1665) Used a compound microscope to look at thin slices of cork (oak
Organelles & Cells Student Edition. A. chromosome B. gene C. mitochondrion D. vacuole
 Name: Date: 1. Which structure is outside the nucleus of a cell and contains DNA? A. chromosome B. gene C. mitochondrion D. vacuole 2. A potato core was placed in a beaker of water as shown in the figure
Name: Date: 1. Which structure is outside the nucleus of a cell and contains DNA? A. chromosome B. gene C. mitochondrion D. vacuole 2. A potato core was placed in a beaker of water as shown in the figure
Setting our Cytes Ahead!! Part 2
 Setting our Cytes Ahead!! Part 2 Remember!! CELLS are the smallest unit of LIFE! They control how organisms are made and function! So far, we have covered.. Structures for Assembly and We already mentioned
Setting our Cytes Ahead!! Part 2 Remember!! CELLS are the smallest unit of LIFE! They control how organisms are made and function! So far, we have covered.. Structures for Assembly and We already mentioned
Biology Test Review Science 8
 Biology Test Review Science 8 Introduction to Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems 304-7 Explain structural and functional relationships between and among cells, tissues, organs and systems in the human
Biology Test Review Science 8 Introduction to Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems 304-7 Explain structural and functional relationships between and among cells, tissues, organs and systems in the human
Discovery of the Cell
 Cells Chapter 4 Discovery of the Cell 1665 Robert Hooke used a microscope to examine a piece of cork. He saw little boxes in the cork and called them cells. 1673 Anton van Leeuwenhoek was the first person
Cells Chapter 4 Discovery of the Cell 1665 Robert Hooke used a microscope to examine a piece of cork. He saw little boxes in the cork and called them cells. 1673 Anton van Leeuwenhoek was the first person
Cell Types. Prokaryotes
 Cell Types Prokaryotes before nucleus no membrane-bound nucleus only organelle present is the ribosome all other reactions occur in the cytoplasm not very efficient Ex.: bacteria 1 Cell Types Eukaryotes
Cell Types Prokaryotes before nucleus no membrane-bound nucleus only organelle present is the ribosome all other reactions occur in the cytoplasm not very efficient Ex.: bacteria 1 Cell Types Eukaryotes
Name Hour. Section 7-1 Life Is Cellular (pages )
 Name Hour Section 7-1 Life Is Cellular (pages 169-173) Introduction (page 169) 1. What is the structure that makes up every living thing? The Discovery of the Cell (pages 169-170) 2. What was Anton van
Name Hour Section 7-1 Life Is Cellular (pages 169-173) Introduction (page 169) 1. What is the structure that makes up every living thing? The Discovery of the Cell (pages 169-170) 2. What was Anton van
7-1 Life Is Cellular. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 7-1 Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell What is the cell theory? The Discovery of the Cell The cell theory states: All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure
7-1 Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell What is the cell theory? The Discovery of the Cell The cell theory states: All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure
Cell Organelles. a review of structure and function
 Cell Organelles a review of structure and function TEKS and Student Expectations (SE s) B.4 Science concepts. The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things with specialized
Cell Organelles a review of structure and function TEKS and Student Expectations (SE s) B.4 Science concepts. The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things with specialized
T HE C ELL C H A P T E R 1 P G. 4-23
 T HE C ELL C H A P T E R 1 P G. 4-23 A CELL IS THE SMALLEST LIVING UNIT KNOWN. IT IS OFTEN CALLED THE BUILDING BLOCK OF THE BODY, AND IS THE BASIC STRUCTURAL AND FUNCTIONAL UNIT OF AN ORGANISM. CELL THEORY
T HE C ELL C H A P T E R 1 P G. 4-23 A CELL IS THE SMALLEST LIVING UNIT KNOWN. IT IS OFTEN CALLED THE BUILDING BLOCK OF THE BODY, AND IS THE BASIC STRUCTURAL AND FUNCTIONAL UNIT OF AN ORGANISM. CELL THEORY
Chapter: Life's Structure and Classification
 Table of Contents Chapter: Life's Structure and Classification Section 1: Living Things 1- What is an organism? Any living thing is called an organism. Organisms vary in size: 1)one-celled or unicellular
Table of Contents Chapter: Life's Structure and Classification Section 1: Living Things 1- What is an organism? Any living thing is called an organism. Organisms vary in size: 1)one-celled or unicellular
