Apoptosis: Death Comes for the Cell
|
|
|
- Diane Hoover
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Apoptosis: Death Comes for the Cell Joe W. Ramos From Ingmar Bergman s The Seventh Seal 1
2 2
3 Mutations in proteins that regulate cell proliferation, survival and death can contribute to oncogenesis The Chessboard 3
4 Ways to Die From Okada and Mak, Nat. Rev. Cancer 4:
5 The Morphology of Death 5
6 Apoptosis: Programmed Cell Death A term used to describe the morphological changes associated with programmed cell death. The term was originally used by Wyllie and his colleagues and is from the Greek meaning dropping away as the leaves from a tree. 6
7 Apoptosis l Active cell death l Requires energy and RNA and protein synthesis l Characteristic morphological features l DNA cleaved, chromatin condenses l Cells shrink l Formation of apoptotic body l Cleared by phagocytosis l No inflammation=no tissue damage 7
8 Necrosis l Passive cell death l Cells swell up l Membrane breaks down and cellular contents leak out l Nucleus disintegrates l Cell ghosts l Inflammatory=tissue damage 8
9 The function of Cell death l Multicellular development l involved in deletion of entire structures, l sculpting of tissues, l and regulates the neuron number l The immune response l The body s defense against cancer 9
10 Death and the mouse s paw Dark Green fluorescence indicates apoptotic cells. Fig
11 Apoptosis regulates nerve cell targeting Fig
12 Apoptosis in Lymphocyte development 12
13 How do we recognize Programmed Cell Death? 13
14 The Face of Cell Death: Apoptosis 14
15 Detection of apoptotic cells l l l Microscopy l l Cells have classic features (eg. small darkly stained nuclei) Detection of free 3 ends of DNA by TUNEL assay (terminal deoxytransferase-mediated dutp-biotin nick end labeling) Gel electrophoresis l Detect DNA ladder of 180 bp intervals caused by internucleosomal DNA cleavage Flow cytometry l l Measure externalization of phosphatidylserine (PS) with fluorescently labeled Annexin-V Measure DNA fragmentation with propidium iodide 15 fluorescence
16 Analysis of DNA content with a flow cytometer Recall the fluorescence intensity of the DNA dye (amount of DNA) is measured for each cell. Dead Cells 16
17 Determination of Cell Death by Flow Cytometery Annexin V binds PS on the surface of cells in the early phase of apoptosis 17
18 18
19 Triggers of apoptosis l Programmed cell death in which many more cells are produced than survive (e.g. development of lymphocytes) l Toxic stimuli (viruses, chemicals, ionizing radiation) l Extracellular signals (Fas, p75 NGF-R, TNF) l DNA damage (p53) 19
20 C. elegans has played a key role in our understanding of Apoptosis 1090 total cells 131 die Ced-3=no death Ced-4=no death ced-1 mutant (No engulfment) Ced-9=all die ced-1/ced-3 (No cells die) 20 H.R Horvitz and colleagues responsible for much of this work, 2002 Nobel Prize in Medicine with Sulston and Brenner.
21 C. elegans apoptosis CED-9=Blocks apoptosis CED-4=linker molecule forms activating complex with CED-3 CED-3=Protease that executes cell by chewing up proteins EGL-1=Proapoptotic by blocking CED-9 function 21
22 Three classes of proteins function in the apoptotic pathway-conserved in vertebrates Mammalian Bcl-2 can substitute for Ced-9 in c. elegans 22
23 Death s Methods: A protease cascade These proteases are called caspases Fig
24 Caspases l l l l l Caspases are Cysteine directed proteases that cleave after ASPartate residues Ced-3 is the C. elegans homologue At least 14 family members Synthesized as proenzymes with low levels of caspase activity (~1-2 % of active form) Activated upon after aggregation or cleavage to mature form l l l l Caspases 8 and 9 are initiator caspases Caspases 3 is the effector caspase Caspase activation requires a stimulus They proteolyze cellular proteins to carry out cell death program 24
25 The Caspase Family 25
26 Procaspase activation 26
27 Caspase cascade 27
28 Two Pathways that Initiate Apoptosis l Intrinsic/ Mitochondrial Apoptosis l Regulated by Mitochondria l Cytochrome c release l Extrinsic/ Death Receptor Apoptosis l Activated by ligation of Death Receptors l Fas, TNF alpha l These pathways intersect at the effector caspases 28
29 Activation of the Intrinsic Pathway 29
30 Intrinsic/Mitochondrial Pathway CARD domain 30
31 Mitochondrial permeability PT=Permeability transition, bursts outer membrane 31
32 Intrinsic Pathway: Apaf-1 Induced Apoptosis CARD domains 32
33 Smac/Diablo and IAPs Smac=Second mitochondrial activator of caspases IAP=Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins 33
34 Bcl-2 family members l A very large family with 19 members identified l Bcl-2 (homologous to ced-9) is prototype l All have the BH3 domain (Bcl-2 Homology) l BH-3 is the pro-apoptotic domain exposed on activation l Act as dimers=either hetero or homodimers l Pro-apoptotic dimers (Bax) increase mitochondrial permeability l Anti-apoptotic members (Bcl-2, Bcl-XL) form dimers with pro-apoptotic members to inactivate them 34
35 The Bcl-2 Family BH domains=protein-protein interaction domains 35
36 Intrinsic Apoptosis 36
37 Some trophic factors prevent apoptosis by inducing inactivation of a pro-apoptotic regulator 37 Figure 23-50
38 Two mechanisms for p53 activation of apoptosis 38
39 Extrinsic/Death Receptor Pathway 39
40 Death Receptors and Ligands CD95=Fas 40
41 TNF receptor family Cysteine-Rich Domains (CRD) Death Domains (DD) Bind DDs of other proteins (e.g. FADD) Recruiting them to the plasma membrane. 41
42 Fas-FasL Apoptosis l In response to antigenic stimulation, peripheral T cells expand l The antigen specific T cells generated must be eliminated (except for the memory cells) l Upon repeated antigenic stimulation via the T Cell receptor: T cells upregulate Fas and FasL l Eliminate neighboring T Cells expressing Fas 42
43 Activation of Apoptosis by Fas Ligand 43
44 Fas Induced Apoptosis The Formation of the Death Initiating Signal Complex (DISC) 44
45 Adaptor Proteins contain conserved protein interaction domains = inhibits apoptosis -CARD domain of Apaf-1 binds CARD domain of procaspase-9. -DED domain of FADD binds DED domain of procaspase-8. -DED domains of FLIP can bind to the DED domain of FADD and block procaspase-8 recruitment. 45
46 Fas and the intrinsic pathway:bid /Bax 46
47 Proteolytic targets of effector caspases l l l l Cytoskeletal regulatory proteins l Actin Nuclear Lamins Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) l PARP activity depletes ATP, thus cleavage of PARP may maintain store of ATP to drive apoptosis DNA-fragmentation factor (DFF) 47
48 Removal of apoptotic cell by phagocytosis 48
49 Removal of cell corpses 49
50 Phagocytosis: Necrosis vs. Apoptosis Production of antiinflammatory cytokines and chemokines No up-regulation of costimulatory molecules Production of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines Up-regulation of costimulatory molecules 50
51 Phagocytosis tags and receptors 51
52 Two roads to activate apoptosis Extrinsic Intrinsic Cell-extrinsic pathway Pro-apoptotic ligand DR5 Chemotherapy Radiotherapy DR4 DNA damage FLIP Procaspase 8, 10 FADD p53 PUMA, NOXA BID BAX, BAK Mitochondria BCL2, BCLX L, MCL1 Cell-intrinsic pathway Caspase 8, 10 Cytochrome c Caspase 9 APAF1 Caspase 3, 6, 7 IAP Apoptosis SMAC/DIABLO p53 DNA damage 52
53 TNFα Can also activate Necroptosis 53
54 Necroptosis: RIP3 Dependent programed necrosis 54
55 Autophagy Autophagy, literally means self-eating. Two major functions: o to eliminate damaged or superfluous proteins and organelles, commonly referred to as the protein and organelle quality control function of autophagy. o to degrade and recycle intracellular components to sustain sustain metabolism and homeostasis in the absence of external nutrients, commonly referred to as the catabolic function of autophagy. 55
56 The Autophagic Process 56
57 Autophagy under the microscope Autophagic Vesicles LC3-II punctae 57
58 Signals Controlling Autophagy Genotoxic and oncogenic stresses result in nuclear p53 stabilization and activation, which stimulates autophagy through activation of AMPK AMPK phosphorylates and activates the GAP complex TSC1/TSC2, leading to inactivation of mtorc1 and autophagy induction. Rheb is a GTPase AMPK->mTORC1 PI3K-> AKT activates autophagy blocks autophagy Current Opinion in Cell Biology 2010, 22:
59 Autophagy in Cancer Autophagy Can promote tumor formation or block it depending on context. Clin Cancer Res; 21(3):
60 Questions? 60
Apoptosis: Death comes for the Cell. Apoptosis: Programmed Cell Death. Apoptosis. Necrosis
 poptosis: eath comes for the Cell Mutations in proteins that regulate cell proliferation, survival and death can contribute to oncogenesis Joe W. Ramos jramos@crch.hawaii.edu From Ingmar Bergman s The
poptosis: eath comes for the Cell Mutations in proteins that regulate cell proliferation, survival and death can contribute to oncogenesis Joe W. Ramos jramos@crch.hawaii.edu From Ingmar Bergman s The
Cell Death & Trophic Factors II. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cell Death & Trophic Factors II Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Remember? Neurotrophins are cell survival factors that neurons get from their target cells! There is a
Cell Death & Trophic Factors II Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Remember? Neurotrophins are cell survival factors that neurons get from their target cells! There is a
Cell Survival Curves (Chap. 3)
 Cell Survival Curves (Chap. 3) Example of pedigress of EMT6 mouse cells Clone The in vitro cell survival curve Cell Survival Assay Dye exclusion assay: membrane integrity MTT assay: respiratory activity
Cell Survival Curves (Chap. 3) Example of pedigress of EMT6 mouse cells Clone The in vitro cell survival curve Cell Survival Assay Dye exclusion assay: membrane integrity MTT assay: respiratory activity
Apoptosis EXTRA REQUIREMETS
 Apoptosis Introduction (SLIDE 1) Organisms develop from a single cell, and in doing so an anatomy has to be created. This process not only involves the creation of new cells, but also the removal of cells
Apoptosis Introduction (SLIDE 1) Organisms develop from a single cell, and in doing so an anatomy has to be created. This process not only involves the creation of new cells, but also the removal of cells
Programmed Cell Death
 Programmed Cell Death Dewajani Purnomosari Department of Histology and Cell Biology Faculty of Medicine Universitas Gadjah Mada d.purnomosari@ugm.ac.id What is apoptosis? a normal component of the development
Programmed Cell Death Dewajani Purnomosari Department of Histology and Cell Biology Faculty of Medicine Universitas Gadjah Mada d.purnomosari@ugm.ac.id What is apoptosis? a normal component of the development
A. Incorrect! The Cell Cycle contains 4 distinct phases: (1) G 1, (2) S Phase, (3) G 2 and (4) M Phase.
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 21: Cell Cycle and Cell Death Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the cell cycle is correct? Question #1 (A) The Cell Cycle contains 3
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 21: Cell Cycle and Cell Death Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the cell cycle is correct? Question #1 (A) The Cell Cycle contains 3
Massive loss of neurons in embryos occurs during normal development (!)
 Types of Cell Death Apoptosis (Programmed Cell Death) : Cell-Autonomous Stereotypic Rapid Clean (dead cells eaten) Necrosis : Not Self-Initiated Not Stereotypic Can Be Slow Messy (injury can spread) Apoptosis
Types of Cell Death Apoptosis (Programmed Cell Death) : Cell-Autonomous Stereotypic Rapid Clean (dead cells eaten) Necrosis : Not Self-Initiated Not Stereotypic Can Be Slow Messy (injury can spread) Apoptosis
Mechanisms of Cell Death
 Mechanisms of Cell Death Etiology of cell death Major Factors Accidental Genetic Necrosis Apoptosis Necrosis: The sum of the morphologic changes that follow cell death in a living tissue or organ Apoptosis:
Mechanisms of Cell Death Etiology of cell death Major Factors Accidental Genetic Necrosis Apoptosis Necrosis: The sum of the morphologic changes that follow cell death in a living tissue or organ Apoptosis:
Bio 3411, Fall 2006, Lecture 19-Cell Death.
 Types of Cell Death Questions : Apoptosis (Programmed Cell Death) : Cell-Autonomous Stereotypic Rapid Clean (dead cells eaten) Necrosis : Not Self-Initiated Not Stereotypic Can Be Slow Messy (injury can
Types of Cell Death Questions : Apoptosis (Programmed Cell Death) : Cell-Autonomous Stereotypic Rapid Clean (dead cells eaten) Necrosis : Not Self-Initiated Not Stereotypic Can Be Slow Messy (injury can
Apoptosis in Mammalian Cells
 Apoptosis in Mammalian Cells 7.16 2-10-05 Apoptosis is an important factor in many human diseases Cancer malignant cells evade death by suppressing apoptosis (too little apoptosis) Stroke damaged neurons
Apoptosis in Mammalian Cells 7.16 2-10-05 Apoptosis is an important factor in many human diseases Cancer malignant cells evade death by suppressing apoptosis (too little apoptosis) Stroke damaged neurons
Mechanisms. Cell Death. Carol M. Troy, MD PhD August 24, 2009 PHENOMENOLOGY OF CELL DEATH I. DEVELOPMENT 8/20/2009
 Mechanisms of Cell Death Carol M. Troy, MD PhD August 24, 2009 PHENOMENOLOGY OF CELL DEATH I. DEVELOPMENT A. MORPHOGENESIS: SCULPTING/SHAPING STRUCTURES CREATION OF CAVITIES AND TUBES FUSION OF TISSUE
Mechanisms of Cell Death Carol M. Troy, MD PhD August 24, 2009 PHENOMENOLOGY OF CELL DEATH I. DEVELOPMENT A. MORPHOGENESIS: SCULPTING/SHAPING STRUCTURES CREATION OF CAVITIES AND TUBES FUSION OF TISSUE
Death signaling. Color PDF file of handouts can be found at Wu lab web-page:
 Death signaling Hao Wu References 1. Wang, X. The expanding role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev 15, 2922-2933. (2001). 2. Fesik, S. W. Insights into programmed cell death through structural biology.
Death signaling Hao Wu References 1. Wang, X. The expanding role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev 15, 2922-2933. (2001). 2. Fesik, S. W. Insights into programmed cell death through structural biology.
The Caspase System: a potential role in muscle proteolysis and meat quality? Tim Parr
 The Caspase System: a potential role in muscle proteolysis and meat quality? Tim Parr Caroline Kemp, Ron Bardsley,, Peter Buttery Division of Nutritional Sciences, School of Biosciences, University of
The Caspase System: a potential role in muscle proteolysis and meat quality? Tim Parr Caroline Kemp, Ron Bardsley,, Peter Buttery Division of Nutritional Sciences, School of Biosciences, University of
Mechanisms of Cell Death
 Mechanisms of Cell Death CELL DEATH AND FORMATION OF THE SEMICIRCULAR CANALS Carol M. Troy, MD PhD August 24, 2009 FROM: Fekete et al., Development 124: 2451 (1997) PHENOMENOLOGY OF CELL DEATH I. DEVELOPMENT
Mechanisms of Cell Death CELL DEATH AND FORMATION OF THE SEMICIRCULAR CANALS Carol M. Troy, MD PhD August 24, 2009 FROM: Fekete et al., Development 124: 2451 (1997) PHENOMENOLOGY OF CELL DEATH I. DEVELOPMENT
Mechanisms of Cell Death
 Mechanisms of Cell Death Etiology of cell death Major Factors Accidental Genetic Necrosis Apoptosis Necrosis: The sum of the morphologic changes that follow cell death in a living tissue or organ Apoptosis:
Mechanisms of Cell Death Etiology of cell death Major Factors Accidental Genetic Necrosis Apoptosis Necrosis: The sum of the morphologic changes that follow cell death in a living tissue or organ Apoptosis:
Apoptosis and Carcinogenesis
 Death Becomes Us: Apoptosis and Carcinogenesis by Michele M. Cox Department of Biology, University of the Virgin Islands Part I What Is Cancer? Hi, Derek. Studying for your Cell and Molec final? asked
Death Becomes Us: Apoptosis and Carcinogenesis by Michele M. Cox Department of Biology, University of the Virgin Islands Part I What Is Cancer? Hi, Derek. Studying for your Cell and Molec final? asked
Chemical aspects of the cell. Compounds that induce cell proliferation, differentiation and death
 Chemical aspects of the cell Compounds that induce cell proliferation, differentiation and death Cell proliferation The cell cycle Chapter 17 Molecular Biology of the Cell 2 Cell cycle Chapter 17 Molecular
Chemical aspects of the cell Compounds that induce cell proliferation, differentiation and death Cell proliferation The cell cycle Chapter 17 Molecular Biology of the Cell 2 Cell cycle Chapter 17 Molecular
Chang 1. Characterization of the Drosophila Ortholog of the Mammalian Anti-apoptotic Protein Aven
 Chang 1 Characterization of the Drosophila Ortholog of the Mammalian Anti-apoptotic Protein Aven Joy Chang Georgetown University Senior Digital Thesis May 1, 2006 Chang 2 Table of Contents BACKGROUND 4
Chang 1 Characterization of the Drosophila Ortholog of the Mammalian Anti-apoptotic Protein Aven Joy Chang Georgetown University Senior Digital Thesis May 1, 2006 Chang 2 Table of Contents BACKGROUND 4
Death Ligand- Death Receptor. Annexin V. Fas PI MKK7 PIP3. pro-caspase-3. Granzyme B. Caspase Activation. Bid. Bcl-2 Caspase-3 Caspase-12
 International Corporation life. science. discovery. { Apoptosis Apoptosis Kits International Corporation Apoptosis Signal Cascade and Detection Kits Annexin V Kits MEBCYTO Apoptosis Kit Annexin V Apoptosis
International Corporation life. science. discovery. { Apoptosis Apoptosis Kits International Corporation Apoptosis Signal Cascade and Detection Kits Annexin V Kits MEBCYTO Apoptosis Kit Annexin V Apoptosis
cellular division cell division cell cycle cell cycle kinases chapter 18-19
 cellular division chapter 18-19 cell division when? growth replacement of older cells production of specialized cells asexual reproduction sexual reproduction production of gametes prokaryotic binary fission
cellular division chapter 18-19 cell division when? growth replacement of older cells production of specialized cells asexual reproduction sexual reproduction production of gametes prokaryotic binary fission
 http://cwp.embo.org/w09-13/index.html Roads to Ruin is s o t p o ap healthy cell autophagic cell death ne cr os is Thanks to Seamus Martin! Evolution of apoptosis signalling cascades Inhibitor Adopted
http://cwp.embo.org/w09-13/index.html Roads to Ruin is s o t p o ap healthy cell autophagic cell death ne cr os is Thanks to Seamus Martin! Evolution of apoptosis signalling cascades Inhibitor Adopted
Apoptosis & Autophagy
 SPETSAI SUMMER SCHOOL 2010 Host Microbe Interactions Cellular Response to Infection: Apoptosis & Autophagy Christoph Dehio There are many ways to die Apoptosis: Historical perspective Process of programmed
SPETSAI SUMMER SCHOOL 2010 Host Microbe Interactions Cellular Response to Infection: Apoptosis & Autophagy Christoph Dehio There are many ways to die Apoptosis: Historical perspective Process of programmed
cellular division cell division cell cycle cell cycle kinases chapter 18-19
 cellular division chapter 18-19 cell division when? growth replacement of older cells production of specialized cells asexual reproduction sexual reproduction production of gametes prokaryotic binary fission
cellular division chapter 18-19 cell division when? growth replacement of older cells production of specialized cells asexual reproduction sexual reproduction production of gametes prokaryotic binary fission
Major Factors. Accidental Genetic. Necrosis Apoptosis
 Mechanisms of Cell Death Etiology of cell death Major Factors Accidental Genetic Necrosis Apoptosis Necrosis: The sum of the morphologic changes that follow cell death in a living tissue or organ A t Apoptosis:
Mechanisms of Cell Death Etiology of cell death Major Factors Accidental Genetic Necrosis Apoptosis Necrosis: The sum of the morphologic changes that follow cell death in a living tissue or organ A t Apoptosis:
Bio-Plex Pro RBM Apoptosis Assays
 Acute Phase Apoptosis Cancer Cardiovascular Disease Cytokines Chemokines, Growth Factors Diabetes Gene Expression Genotyping Immunoglobulin Isotyping MicroRNA Expression Bio-Plex Pro RBM Apoptosis Assays
Acute Phase Apoptosis Cancer Cardiovascular Disease Cytokines Chemokines, Growth Factors Diabetes Gene Expression Genotyping Immunoglobulin Isotyping MicroRNA Expression Bio-Plex Pro RBM Apoptosis Assays
Monte Carlo study elucidates the type 1/type 2 choice in apoptotic death signaling in normal and cancer cells
 Cells 2013, 2, 1-x manuscripts; doi:10.3390/cells20x000x OPEN ACCESS cells ISSN 2073-4409 www.mdpi.com/journal/cells Article Monte Carlo study elucidates the type 1/type 2 choice in apoptotic death signaling
Cells 2013, 2, 1-x manuscripts; doi:10.3390/cells20x000x OPEN ACCESS cells ISSN 2073-4409 www.mdpi.com/journal/cells Article Monte Carlo study elucidates the type 1/type 2 choice in apoptotic death signaling
Apoptosis and Cancer. Carol M. Troy, MD, PhD October 26, 2016
 Apoptosis and Cancer Carol M. Troy, MD, PhD October 26, 2016 PHENOMENOLOGY OF CELL DEATH -1 I. DEVELOPMENT A. MORPHOGENESIS: SCULPTING/SHAPING STRUCTURES FUSION OF TISSUE MASSES (PALATE/NEURAL TUBE) CREATION
Apoptosis and Cancer Carol M. Troy, MD, PhD October 26, 2016 PHENOMENOLOGY OF CELL DEATH -1 I. DEVELOPMENT A. MORPHOGENESIS: SCULPTING/SHAPING STRUCTURES FUSION OF TISSUE MASSES (PALATE/NEURAL TUBE) CREATION
IAPs. Structure of BIR2 Zn finger domain from XIAP
 IAPs The only known endogenous caspase inhibitors are members of a second family of proteins identified by apoptosis research, the IAP (inhibitor of apoptosis proteins) family. IAPs were originally described
IAPs The only known endogenous caspase inhibitors are members of a second family of proteins identified by apoptosis research, the IAP (inhibitor of apoptosis proteins) family. IAPs were originally described
Proteases for Cell Suicide: Functions and Regulation of Caspases
 MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS, Dec. 2000, p. 821 846 Vol. 64, No. 4 1092-2172/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Proteases for Cell Suicide:
MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS, Dec. 2000, p. 821 846 Vol. 64, No. 4 1092-2172/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Proteases for Cell Suicide:
TNFα 18hr. Control. CHX 18hr. TNFα+ CHX 18hr. TNFα: 18 18hr (KDa) PARP. Cleaved. Cleaved. Cleaved. Caspase3. Pellino3 shrna. Control shrna.
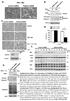 Survival ( %) a. TNFα 18hr b. Control sirna Pellino3 sirna TNFα: 18 18hr c. Control shrna Pellino3 shrna Caspase3 Actin Control d. Control shrna Pellino3 shrna *** 100 80 60 CHX 18hr 40 TNFα+ CHX 18hr
Survival ( %) a. TNFα 18hr b. Control sirna Pellino3 sirna TNFα: 18 18hr c. Control shrna Pellino3 shrna Caspase3 Actin Control d. Control shrna Pellino3 shrna *** 100 80 60 CHX 18hr 40 TNFα+ CHX 18hr
Validation of Petri Net Apoptosis Models Using P-Invariant Analysis
 2009 IEEE International Conference on Control and Automation Christchurch, New Zealand, December 9-11, 2009 WeMT5.1 Validation of Petri Net Apoptosis Models Using P-Invariant Analysis Ian Wee Jin Low,
2009 IEEE International Conference on Control and Automation Christchurch, New Zealand, December 9-11, 2009 WeMT5.1 Validation of Petri Net Apoptosis Models Using P-Invariant Analysis Ian Wee Jin Low,
Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 5 4/27/15
 Name: Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 5 4/27/15 Answer each of the following short answer questions in the space provided, giving explanations when asked to do so. Circle the correct answer or answers
Name: Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 5 4/27/15 Answer each of the following short answer questions in the space provided, giving explanations when asked to do so. Circle the correct answer or answers
Signal Transduction. Dr. Chaidir, Apt
 Signal Transduction Dr. Chaidir, Apt Background Complex unicellular organisms existed on Earth for approximately 2.5 billion years before the first multicellular organisms appeared.this long period for
Signal Transduction Dr. Chaidir, Apt Background Complex unicellular organisms existed on Earth for approximately 2.5 billion years before the first multicellular organisms appeared.this long period for
AP Biology Gene Regulation and Development Review
 AP Biology Gene Regulation and Development Review 1. What does the regulatory gene code for? 2. Is the repressor by default active/inactive? 3. What changes the repressor activity? 4. What does repressor
AP Biology Gene Regulation and Development Review 1. What does the regulatory gene code for? 2. Is the repressor by default active/inactive? 3. What changes the repressor activity? 4. What does repressor
12/5/2014. The cell cycle and cell death. The cell cycle: cells duplicate their contents and divide
 The cell cycle and cell death The cell cycle: cells duplicate their contents and divide 1 The cell cycle may be divided into 4 phases Eucaryotic cell division: Mitosis (nuclear division) Cytokinesis (cell
The cell cycle and cell death The cell cycle: cells duplicate their contents and divide 1 The cell cycle may be divided into 4 phases Eucaryotic cell division: Mitosis (nuclear division) Cytokinesis (cell
 Cell-cell communication in development Review of cell signaling, paracrine and endocrine factors, cell death pathways, juxtacrine signaling, differentiated state, the extracellular matrix, integrins, epithelial-mesenchymal
Cell-cell communication in development Review of cell signaling, paracrine and endocrine factors, cell death pathways, juxtacrine signaling, differentiated state, the extracellular matrix, integrins, epithelial-mesenchymal
Study Guide 11 & 12 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Study Guide 11 & 12 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The receptors for a group of signaling molecules known as growth factors are
Study Guide 11 & 12 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The receptors for a group of signaling molecules known as growth factors are
Regulation and signaling. Overview. Control of gene expression. Cells need to regulate the amounts of different proteins they express, depending on
 Regulation and signaling Overview Cells need to regulate the amounts of different proteins they express, depending on cell development (skin vs liver cell) cell stage environmental conditions (food, temperature,
Regulation and signaling Overview Cells need to regulate the amounts of different proteins they express, depending on cell development (skin vs liver cell) cell stage environmental conditions (food, temperature,
Analysis of retinoblastoma protein function in the regulation of apoptosis
 Analysis of retinoblastoma protein function in the regulation of apoptosis Analyse der Funktion des Retinoblastoma-Proteins in der Apoptose-Regulation Dissertation zur Erlangung des akademischen Grades
Analysis of retinoblastoma protein function in the regulation of apoptosis Analyse der Funktion des Retinoblastoma-Proteins in der Apoptose-Regulation Dissertation zur Erlangung des akademischen Grades
APOPTOSIS REGULATOR BCL-2
 Papers on Anthropology Apoptosis regulator XXII, 2013, BCL-2 pp. 63 67 P. Hussar, M. Žuravskaja, M. Kärner APOPTOSIS REGULATOR BCL-2 Piret Hussar 1, Maria Žuravskaja 2, Martin Kärner 2 1 Institute of Anatomy,
Papers on Anthropology Apoptosis regulator XXII, 2013, BCL-2 pp. 63 67 P. Hussar, M. Žuravskaja, M. Kärner APOPTOSIS REGULATOR BCL-2 Piret Hussar 1, Maria Žuravskaja 2, Martin Kärner 2 1 Institute of Anatomy,
Reception The target cell s detection of a signal coming from outside the cell May Occur by: Direct connect Through signal molecules
 Why Do Cells Communicate? Regulation Cells need to control cellular processes In multicellular organism, cells signaling pathways coordinate the activities within individual cells that support the function
Why Do Cells Communicate? Regulation Cells need to control cellular processes In multicellular organism, cells signaling pathways coordinate the activities within individual cells that support the function
Biology Teach Yourself Series Topic 2: Cells
 Biology Teach Yourself Series Topic 2: Cells A: Level 14, 474 Flinders Street Melbourne VIC 3000 T: 1300 134 518 W: tssm.com.au E: info@tssm.com.au TSSM 2013 Page 1 of 14 Contents Cells... 3 Prokaryotic
Biology Teach Yourself Series Topic 2: Cells A: Level 14, 474 Flinders Street Melbourne VIC 3000 T: 1300 134 518 W: tssm.com.au E: info@tssm.com.au TSSM 2013 Page 1 of 14 Contents Cells... 3 Prokaryotic
Cell Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development June 25, 2008 Cell Cell Communication Concepts Cells in developing organisms develop in the context of their environment, including
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication in Development June 25, 2008 Cell Cell Communication Concepts Cells in developing organisms develop in the context of their environment, including
A MATHEMATICAL MODEL FOR DYNAMIC SIMULATION OF APOPTOSIS PATHWAYS
 A MATHEMATICAL MODEL FOR DYNAMIC SIMULATION OF APOPTOSIS PATHWAYS Paolo Massari Department of Information Engineering Bioengineering University of Padova April 2014 Advisor: Gianna Maria Toolo Coadvisor:
A MATHEMATICAL MODEL FOR DYNAMIC SIMULATION OF APOPTOSIS PATHWAYS Paolo Massari Department of Information Engineering Bioengineering University of Padova April 2014 Advisor: Gianna Maria Toolo Coadvisor:
Apoptosis Detection Using the BD Accuri C6 Flow Cytometer
 Apoptosis Detection Using the BD Accuri C6 Flow Cytometer Stacey Roys, Marketing Applications Specialist, BD Biosciences Cyndy Lane, Senior Product Manager, BD Biosciences 23-14519-00 Outline What is apoptosis?
Apoptosis Detection Using the BD Accuri C6 Flow Cytometer Stacey Roys, Marketing Applications Specialist, BD Biosciences Cyndy Lane, Senior Product Manager, BD Biosciences 23-14519-00 Outline What is apoptosis?
CHAPTER 3. Cell Structure and Genetic Control. Chapter 3 Outline
 CHAPTER 3 Cell Structure and Genetic Control Chapter 3 Outline Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm and Its Organelles Cell Nucleus and Gene Expression Protein Synthesis and Secretion DNA Synthesis and Cell Division
CHAPTER 3 Cell Structure and Genetic Control Chapter 3 Outline Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm and Its Organelles Cell Nucleus and Gene Expression Protein Synthesis and Secretion DNA Synthesis and Cell Division
16 The Cell Cycle. Chapter Outline The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression The Events of M Phase Meiosis and Fertilization
 The Cell Cycle 16 The Cell Cycle Chapter Outline The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression The Events of M Phase Meiosis and Fertilization Introduction Self-reproduction is perhaps
The Cell Cycle 16 The Cell Cycle Chapter Outline The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression The Events of M Phase Meiosis and Fertilization Introduction Self-reproduction is perhaps
Journal Club & MSc Seminar
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Journal Club & MSc Seminar The relationship between apoptosis and microorganisms Superviser: Dr. Presented by: Mehri Sadeghi MSc Medical Microbiology What is it? Why is it important?
IN THE NAME OF GOD Journal Club & MSc Seminar The relationship between apoptosis and microorganisms Superviser: Dr. Presented by: Mehri Sadeghi MSc Medical Microbiology What is it? Why is it important?
Proteome-wide High Throughput Cell Based Assay for Apoptotic Genes
 John Kenten, Doug Woods, Pankaj Oberoi, Laura Schaefer, Jonathan Reeves, Hans A. Biebuyck and Jacob N. Wohlstadter 9238 Gaither Road, Gaithersburg, MD 2877. Phone: 24.631.2522 Fax: 24.632.2219. Website:
John Kenten, Doug Woods, Pankaj Oberoi, Laura Schaefer, Jonathan Reeves, Hans A. Biebuyck and Jacob N. Wohlstadter 9238 Gaither Road, Gaithersburg, MD 2877. Phone: 24.631.2522 Fax: 24.632.2219. Website:
Apoptosis regulators and their role in tumorigenesis
 Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1551 (2001) F1^F37 www.bba-direct.com Review Apoptosis regulators and their role in tumorigenesis Martin Zo«rnig a; *, Anne-Odile Hueber b, Wiebke Baum a, Gerard Evan c b
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1551 (2001) F1^F37 www.bba-direct.com Review Apoptosis regulators and their role in tumorigenesis Martin Zo«rnig a; *, Anne-Odile Hueber b, Wiebke Baum a, Gerard Evan c b
Modelling intrinsic apoptosis
 Modelling intrinsic apoptosis In this part of the course we will model the steps that take place inside a cell when intrinsic apoptosis is triggered. The templates and instructions for preparing the models
Modelling intrinsic apoptosis In this part of the course we will model the steps that take place inside a cell when intrinsic apoptosis is triggered. The templates and instructions for preparing the models
Growth factors and cell death. Urmas Arumäe Institute of Biotechnology
 Growth factors and cell death Urmas Arumäe Institute of Biotechnology 24.03.2011 Growth factors stimulate cell survival (among other activities). Or conversely: absence of the growth factors causes cell
Growth factors and cell death Urmas Arumäe Institute of Biotechnology 24.03.2011 Growth factors stimulate cell survival (among other activities). Or conversely: absence of the growth factors causes cell
Examination paper for Bi3016 Molecular Cell Biology
 Department of Biology Examination paper for Bi3016 Molecular Cell Biology Academic contact during examination: Per Winge Phone: 99369359 Examination date: 20 th December 2017 Examination time (from-to):
Department of Biology Examination paper for Bi3016 Molecular Cell Biology Academic contact during examination: Per Winge Phone: 99369359 Examination date: 20 th December 2017 Examination time (from-to):
A Multi-scale Extensive Petri Net Model of Bacterialmacrophage
 A Multi-scale Extensive Petri Net Model of Bacterialmacrophage Interaction Rafael V. Carvalho Imaging & BioInformatics, Leiden Institute of Advanced Computer Science Introduction - Mycobacterial infection
A Multi-scale Extensive Petri Net Model of Bacterialmacrophage Interaction Rafael V. Carvalho Imaging & BioInformatics, Leiden Institute of Advanced Computer Science Introduction - Mycobacterial infection
Game and Players: Mitochondrial Apoptosis and the Therapeutic Potential of Ursodeoxycholic Acid
 Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 9: 123 139. Online journal at www.cimb.org Game and Players: Mitochondrial Apoptosis and the Therapeutic Potential of Ursodeoxycholic Acid Susana Solá 1, Márcia M. Aranha 1, Clifford
Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 9: 123 139. Online journal at www.cimb.org Game and Players: Mitochondrial Apoptosis and the Therapeutic Potential of Ursodeoxycholic Acid Susana Solá 1, Márcia M. Aranha 1, Clifford
CC2.04_t.txt The Caspase System and Muscle Degradation Tim Parr
 The Caspase System and Muscle Degradation Tim Parr [1]Our last speaker of the day is Dr. Tim Parr. Dr. Parr graduated in 1987 from the University of Southampton with a degree in physiology, biochemistry,
The Caspase System and Muscle Degradation Tim Parr [1]Our last speaker of the day is Dr. Tim Parr. Dr. Parr graduated in 1987 from the University of Southampton with a degree in physiology, biochemistry,
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences V1(2)2010 PETRI NET IMPLEMENTATION OF CELL SIGNALING FOR CELL DEATH
 SHRUTI JAIN *1, PRADEEP K. NAIK 2, SUNIL V. BHOOSHAN 1 1, 3 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Jaypee University of Information Technology, Solan-173215, India 2 Department of Biotechnology
SHRUTI JAIN *1, PRADEEP K. NAIK 2, SUNIL V. BHOOSHAN 1 1, 3 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Jaypee University of Information Technology, Solan-173215, India 2 Department of Biotechnology
Lecture 10: Cyclins, cyclin kinases and cell division
 Chem*3560 Lecture 10: Cyclins, cyclin kinases and cell division The eukaryotic cell cycle Actively growing mammalian cells divide roughly every 24 hours, and follow a precise sequence of events know as
Chem*3560 Lecture 10: Cyclins, cyclin kinases and cell division The eukaryotic cell cycle Actively growing mammalian cells divide roughly every 24 hours, and follow a precise sequence of events know as
Cytochrome c, cytochrome b 5 and electron transfer
 Cytochrome c, cytochrome b 5 and electron transfer Covalent bonds Cytochrome c is a major player in membrane associated electron transport systems in bacteria and mitochondria. Cytochrome c has two axial
Cytochrome c, cytochrome b 5 and electron transfer Covalent bonds Cytochrome c is a major player in membrane associated electron transport systems in bacteria and mitochondria. Cytochrome c has two axial
Drosophila Apoptosis and the Regulation of the Caspase Cascade
 Drosophila Apoptosis and the Regulation of the Caspase Cascade Kate Stafford March 18, 2005 Abstract The caspase cascade in Drosophila is controlled primarily by DIAP1 (Drosophila inhibitor of apoptosis),
Drosophila Apoptosis and the Regulation of the Caspase Cascade Kate Stafford March 18, 2005 Abstract The caspase cascade in Drosophila is controlled primarily by DIAP1 (Drosophila inhibitor of apoptosis),
BIOH111. o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook
BIOH111 o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook
Cell-Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development October 2, 2007 Cell-Cell Communication - Topics Induction and competence Paracrine factors inducer molecules Signal transduction
Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development October 2, 2007 Cell-Cell Communication - Topics Induction and competence Paracrine factors inducer molecules Signal transduction
Activation of a receptor. Assembly of the complex
 Activation of a receptor ligand inactive, monomeric active, dimeric When activated by growth factor binding, the growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylates the neighboring receptor. Assembly
Activation of a receptor ligand inactive, monomeric active, dimeric When activated by growth factor binding, the growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylates the neighboring receptor. Assembly
Role of mitochondria transmembrane potential in lymphocyte
 Original Article Fac Med Baghdad 2009; Vol. 51, No. 1 Received Mar.2008 Accepted May 2008 Role of mitochondria transmembrane potential in lymphocyte apoptosis * PhD Summary: Background: Mitochondria play
Original Article Fac Med Baghdad 2009; Vol. 51, No. 1 Received Mar.2008 Accepted May 2008 Role of mitochondria transmembrane potential in lymphocyte apoptosis * PhD Summary: Background: Mitochondria play
S1 Gene ontology (GO) analysis of the network alignment results
 1 Supplementary Material for Effective comparative analysis of protein-protein interaction networks by measuring the steady-state network flow using a Markov model Hyundoo Jeong 1, Xiaoning Qian 1 and
1 Supplementary Material for Effective comparative analysis of protein-protein interaction networks by measuring the steady-state network flow using a Markov model Hyundoo Jeong 1, Xiaoning Qian 1 and
Delivery. Delivery Processes. Delivery Processes: Distribution. Ultimate Toxicant
 Delivery Ultimate Toxicant The chemical species that reacts with the endogenous target. Toxicity depends on the concentration (dose) of the ultimate toxicant at the target site Delivery Processes Absorption
Delivery Ultimate Toxicant The chemical species that reacts with the endogenous target. Toxicity depends on the concentration (dose) of the ultimate toxicant at the target site Delivery Processes Absorption
Cell-Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development June 23, 2009 Concepts Cell-Cell Communication Cells develop in the context of their environment, including: - their immediate
Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development June 23, 2009 Concepts Cell-Cell Communication Cells develop in the context of their environment, including: - their immediate
Proteomics Analysis of Protein-Producing Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells. during Apoptosis in Prolonged Cultivation
 Proteomics Analysis of Protein-Producing Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells during Apoptosis in Prolonged Cultivation by Yi-Yun Wei A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfilment of the thesis
Proteomics Analysis of Protein-Producing Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells during Apoptosis in Prolonged Cultivation by Yi-Yun Wei A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfilment of the thesis
Multiple Choice Review- Eukaryotic Gene Expression
 Multiple Choice Review- Eukaryotic Gene Expression 1. Which of the following is the Central Dogma of cell biology? a. DNA Nucleic Acid Protein Amino Acid b. Prokaryote Bacteria - Eukaryote c. Atom Molecule
Multiple Choice Review- Eukaryotic Gene Expression 1. Which of the following is the Central Dogma of cell biology? a. DNA Nucleic Acid Protein Amino Acid b. Prokaryote Bacteria - Eukaryote c. Atom Molecule
RNA Synthesis and Processing
 RNA Synthesis and Processing Introduction Regulation of gene expression allows cells to adapt to environmental changes and is responsible for the distinct activities of the differentiated cell types that
RNA Synthesis and Processing Introduction Regulation of gene expression allows cells to adapt to environmental changes and is responsible for the distinct activities of the differentiated cell types that
Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. Tuesday, December 27, 16
 Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. Enduring understanding 3.B: Expression of genetic information involves cellular and molecular
Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. Enduring understanding 3.B: Expression of genetic information involves cellular and molecular
Modeling heterogeneous responsiveness of intrinsic apoptosis pathway
 Ooi and Ma BMC Systems Biology 213, 7:65 http://www.biomedcentral.com/1752-59/7/65 RESEARCH ARTICLE OpenAccess Modeling heterogeneous responsiveness of intrinsic apoptosis pathway Hsu Kiang Ooi and Lan
Ooi and Ma BMC Systems Biology 213, 7:65 http://www.biomedcentral.com/1752-59/7/65 RESEARCH ARTICLE OpenAccess Modeling heterogeneous responsiveness of intrinsic apoptosis pathway Hsu Kiang Ooi and Lan
Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg Lapets ASSAY and Drug Development Technologies 2004, 2:
 1 3/1/2005 A Quantitative Cell-Based High-Content Screening Assay for the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Specific Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg
1 3/1/2005 A Quantitative Cell-Based High-Content Screening Assay for the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Specific Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg
CELL CYCLE AND GROWTH REGULATION
 CELL CYCLE AND GROWTH REGULATION The cell cycle is the set of stages through which a cell progresses from one division to the next. Interphase is the period between mitotic cell divisions; divided into
CELL CYCLE AND GROWTH REGULATION The cell cycle is the set of stages through which a cell progresses from one division to the next. Interphase is the period between mitotic cell divisions; divided into
CELL CYCLE AND DIFFERENTIATION
 CELL CYCLE AND DIFFERENTIATION Dewajani Purnomosari Department of Histology and Cell Biology Faculty of Medicine Universitas Gadjah Mada d.purnomosari@ugm.ac.id WHAT IS CELL CYCLE? 09/12/14 d.purnomosari@ugm.ac.id
CELL CYCLE AND DIFFERENTIATION Dewajani Purnomosari Department of Histology and Cell Biology Faculty of Medicine Universitas Gadjah Mada d.purnomosari@ugm.ac.id WHAT IS CELL CYCLE? 09/12/14 d.purnomosari@ugm.ac.id
16 CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION
 16 CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION Chapter Outline 16.1 REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION IN PROKARYOTES The operon is the unit of transcription in prokaryotes The lac operon for lactose metabolism is transcribed
16 CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION Chapter Outline 16.1 REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION IN PROKARYOTES The operon is the unit of transcription in prokaryotes The lac operon for lactose metabolism is transcribed
5- Semaphorin-Plexin-Neuropilin
 5- Semaphorin-Plexin-Neuropilin 1 SEMAPHORINS-PLEXINS-NEUROPILINS ligands receptors co-receptors semaphorins and their receptors are known signals for: -axon guidance -cell migration -morphogenesis -immune
5- Semaphorin-Plexin-Neuropilin 1 SEMAPHORINS-PLEXINS-NEUROPILINS ligands receptors co-receptors semaphorins and their receptors are known signals for: -axon guidance -cell migration -morphogenesis -immune
13-3. Synthesis-Secretory pathway: Sort lumenal proteins, Secrete proteins, Sort membrane proteins
 13-3. Synthesis-Secretory pathway: Sort lumenal proteins, Secrete proteins, Sort membrane proteins Molecular sorting: specific budding, vesicular transport, fusion 1. Why is this important? A. Form and
13-3. Synthesis-Secretory pathway: Sort lumenal proteins, Secrete proteins, Sort membrane proteins Molecular sorting: specific budding, vesicular transport, fusion 1. Why is this important? A. Form and
Human Biology. THEORY Conceptual Scheme
 Human Biology Introduction: Definition of BIOLOGY Scientific method: 1. observation 2. hypothesis 3. experimentation 4. conclusion Terms: variables, controls, theory, law, data, repeatable Assumptions:
Human Biology Introduction: Definition of BIOLOGY Scientific method: 1. observation 2. hypothesis 3. experimentation 4. conclusion Terms: variables, controls, theory, law, data, repeatable Assumptions:
Divergence from a Dedicated Cellular Suicide Mechanism: Exploring the Evolution of Cell Death. Review. Junying Yuan 1, * 1 Department of Cell Biology
 Molecular Cell 23, 1 12, July 7, 2006 ª2006 Elsevier Inc. DOI 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.06.008 Divergence from a Dedicated Cellular Suicide Mechanism: Exploring the Evolution of Cell Death Review Junying Yuan
Molecular Cell 23, 1 12, July 7, 2006 ª2006 Elsevier Inc. DOI 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.06.008 Divergence from a Dedicated Cellular Suicide Mechanism: Exploring the Evolution of Cell Death Review Junying Yuan
ADAM FAMILY. ephrin A INTERAZIONE. Eph ADESIONE? PROTEOLISI ENDOCITOSI B A RISULTATO REPULSIONE. reverse. forward
 ADAM FAMILY - a family of membrane-anchored metalloproteases that are known as A Disintegrin And Metalloprotease proteins and are key components in protein ectodomain shedding Eph A INTERAZIONE B ephrin
ADAM FAMILY - a family of membrane-anchored metalloproteases that are known as A Disintegrin And Metalloprotease proteins and are key components in protein ectodomain shedding Eph A INTERAZIONE B ephrin
COMPUTER SIMULATION OF DIFFERENTIAL KINETICS OF MAPK ACTIVATION UPON EGF RECEPTOR OVEREXPRESSION
 COMPUTER SIMULATION OF DIFFERENTIAL KINETICS OF MAPK ACTIVATION UPON EGF RECEPTOR OVEREXPRESSION I. Aksan 1, M. Sen 2, M. K. Araz 3, and M. L. Kurnaz 3 1 School of Biological Sciences, University of Manchester,
COMPUTER SIMULATION OF DIFFERENTIAL KINETICS OF MAPK ACTIVATION UPON EGF RECEPTOR OVEREXPRESSION I. Aksan 1, M. Sen 2, M. K. Araz 3, and M. L. Kurnaz 3 1 School of Biological Sciences, University of Manchester,
Life of the Cell. Learning Objectives
 Life of the Cell Society on a micro-scale 1 Learning Objectives 1. What are the characteristics that distinguish prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Which type of cell is believed to be older (more primitive)?
Life of the Cell Society on a micro-scale 1 Learning Objectives 1. What are the characteristics that distinguish prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Which type of cell is believed to be older (more primitive)?
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS
 LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS a.a. amino acid AIF apoptosis-inducing factor AM acetoxymethyl ester AMP adenosine monophosphate APAF-1 apoptotic protease-activating factor-1 ASK1 apoptotic signaling kinase 1 ATG5
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS a.a. amino acid AIF apoptosis-inducing factor AM acetoxymethyl ester AMP adenosine monophosphate APAF-1 apoptotic protease-activating factor-1 ASK1 apoptotic signaling kinase 1 ATG5
Modeling a Snap-Action, Variable-Delay Switch Controlling Extrinsic Cell Death
 Modeling a Snap-Action, Variable-Delay Switch Controlling Extrinsic Cell Death John G. Albeck 1[, John M. Burke 1,2[, Sabrina L. Spencer 1,3, Douglas A. Lauffenburger 2,3, Peter K. Sorger 1,2* PLoS BIOLOGY
Modeling a Snap-Action, Variable-Delay Switch Controlling Extrinsic Cell Death John G. Albeck 1[, John M. Burke 1,2[, Sabrina L. Spencer 1,3, Douglas A. Lauffenburger 2,3, Peter K. Sorger 1,2* PLoS BIOLOGY
Class Work 31. Describe the function of the Golgi apparatus? 32. How do proteins travel from the E.R. to the Golgi apparatus? 33. After proteins are m
 Eukaryotes Class Work 1. What does the word eukaryote mean? 2. What is the one major difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes? 3. List the different kingdoms of the eukaryote domain in the order in
Eukaryotes Class Work 1. What does the word eukaryote mean? 2. What is the one major difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes? 3. List the different kingdoms of the eukaryote domain in the order in
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta
 Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1843 (2014) 2100 2113 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Biochimica et Biophysica Acta journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/bbamcr Review Regulating cell death
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1843 (2014) 2100 2113 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Biochimica et Biophysica Acta journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/bbamcr Review Regulating cell death
Tour of the Cell 2. AP Biology
 Tour of the Cell 2 2007-2008 Cells gotta work to live! What jobs do cells have to do? make proteins proteins control every cell function make energy for daily life for growth make more cells growth repair
Tour of the Cell 2 2007-2008 Cells gotta work to live! What jobs do cells have to do? make proteins proteins control every cell function make energy for daily life for growth make more cells growth repair
ATP. Division Ave. High School AP Biology. Tour of the Cell 2. Cells gotta work to live! Making Energy. What jobs do cells have to do?
 Tour of the Cell 2 Cells gotta work to live! What jobs do cells have to do? u make proteins proteins control every cell function u make energy for daily life for growth u make more cells growth repair
Tour of the Cell 2 Cells gotta work to live! What jobs do cells have to do? u make proteins proteins control every cell function u make energy for daily life for growth u make more cells growth repair
Study Guide A. Answer Key. Cell Growth and Division. SECTION 1. THE CELL CYCLE 1. a; d; b; c 2. gaps 3. c and d 4. c 5. b and d 6.
 Cell Growth and Division Answer Key SECTION 1. THE CELL CYCLE 1. a; d; b; c 2. gaps 3. c and d 4. c 5. b and d 6. G 1 7. G 0 8. c 9. faster; too large 10. volume 11. a and b 12. repeating pattern or repetition
Cell Growth and Division Answer Key SECTION 1. THE CELL CYCLE 1. a; d; b; c 2. gaps 3. c and d 4. c 5. b and d 6. G 1 7. G 0 8. c 9. faster; too large 10. volume 11. a and b 12. repeating pattern or repetition
MITOCHONDRIAL BIOGENESIS AND REDOX REGULATION
 MITOCHONDRIAL BIOGENESIS AND REDOX Claude A. Piantadosi, MD Professor of Medicine and Pathology Duke University Medical Center Durham, N.C. USA Objectives Provide an overview of the physiological and pathological
MITOCHONDRIAL BIOGENESIS AND REDOX Claude A. Piantadosi, MD Professor of Medicine and Pathology Duke University Medical Center Durham, N.C. USA Objectives Provide an overview of the physiological and pathological
Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018
 Class: Date: Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Hooke s discovery of cells was made observing a. living
Class: Date: Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Hooke s discovery of cells was made observing a. living
Cell Division and Reproduction
 Cell Division and Reproduction What do you think this picture shows? If you guessed that it s a picture of two cells, you are right. In fact, the picture shows human cancer cells, and they are nearing
Cell Division and Reproduction What do you think this picture shows? If you guessed that it s a picture of two cells, you are right. In fact, the picture shows human cancer cells, and they are nearing
Answer Key. Cell Growth and Division
 Cell Growth and Division Answer Key SECTION 1. THE CELL CYCLE Cell Cycle: (1) Gap1 (G 1): cells grow, carry out normal functions, and copy their organelles. (2) Synthesis (S): cells replicate DNA. (3)
Cell Growth and Division Answer Key SECTION 1. THE CELL CYCLE Cell Cycle: (1) Gap1 (G 1): cells grow, carry out normal functions, and copy their organelles. (2) Synthesis (S): cells replicate DNA. (3)
Unraveling Apoptosis Signalling using Linear Control Methods: Linking the Loop Gain to Reverting the Decision to Undergo Apoptosis
 Preprints of the 9th International Symposium on Advanced Control of Chemical Processes The International Federation of Automatic Control TuPoster.3 Unraveling Apoptosis Signalling using Linear Control
Preprints of the 9th International Symposium on Advanced Control of Chemical Processes The International Federation of Automatic Control TuPoster.3 Unraveling Apoptosis Signalling using Linear Control
Principles of Cellular Biology
 Principles of Cellular Biology آشنایی با مبانی اولیه سلول Biologists are interested in objects ranging in size from small molecules to the tallest trees: Cell Basic building blocks of life Understanding
Principles of Cellular Biology آشنایی با مبانی اولیه سلول Biologists are interested in objects ranging in size from small molecules to the tallest trees: Cell Basic building blocks of life Understanding
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division
 Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Read Chapter 19 pages 651-663 663 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections these are in Chapter
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Read Chapter 19 pages 651-663 663 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections these are in Chapter
Supplementary Figure 1. AnnexinV FITC and Sytox orange staining in wild type, Nlrp3 /, ASC / and casp1/11 / TEC treated with TNF /CHX.
 Supplementary Figure 1. AnnexinV FITC and Sytox orange staining in wild type, Nlrp3 /, ASC / and casp1/11 / TEC treated with TNF /CHX. Phase contrast and widefield fluorescence microscopy (20x magnification).
Supplementary Figure 1. AnnexinV FITC and Sytox orange staining in wild type, Nlrp3 /, ASC / and casp1/11 / TEC treated with TNF /CHX. Phase contrast and widefield fluorescence microscopy (20x magnification).
Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry
 Name Period Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were
Name Period Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were
Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Department of Biology, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States of America
 Both the Caspase CSP-1 and a Caspase-Independent Pathway Promote Programmed Cell Death in Parallel to the Canonical Pathway for Apoptosis in Caenorhabditis elegans Daniel P. Denning, Victoria Hatch, H.
Both the Caspase CSP-1 and a Caspase-Independent Pathway Promote Programmed Cell Death in Parallel to the Canonical Pathway for Apoptosis in Caenorhabditis elegans Daniel P. Denning, Victoria Hatch, H.
