Mathematics 5 Worksheet 14 The Horizon
|
|
|
- Adele Harris
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mathematics 5 Worksheet 14 The Horizon For the problems below, we will assume that the Earth is a sphere whose radius is 4,000 miles. Note that there are 5,280 feet in one mile. Problem 1. If a line intersects a circle at precisely one point, P, then the line is perpendicular to the line that contains P and the center of the circle. Draw a picture that describes this relationship. Solution. In the following figure, the center of the circle is the point O, and the line AP is perpendicular to line OP, which passes through the center of the circle and the point P. P O A Problem 2. Draw a sphere and mark two points on the sphere. A plane that intersects the two points on the sphere and the center of the sphere will divide the sphere into two even hemispheres. The intersection of the sphere with this plane is a great circle, a circle whose radius is the radius of the sphere. Convince yourself that this is correct by drawing a picture. Solution. The picture is as follows: 1
2 Problem 3. Suppose that you stand 49 feet above sea level and you look out across the ocean. You see a small dot that sits directly on the horizon. Draw a cross section of the earth that contains the dot, the point at which you stand on the earth, and the center of the earth. This cross section should be a disk whose boundary is a great circle on the surface of the earth. Solution. Again, the picture is below. In addition to the dot representing our position and the small dot on the horizon, we have included some additional lines, which represent our line of sight and segments joining the interesting points to the center of the Earth. These will prove helpful in problem 4, below. 49 ft our position small dot on the horizon 4000 mi α 4000 mi line of sight Problem 4. Suppose that you stand 49 feet above sea level and you look out across the ocean. What is the length of your line of sight? Make sure that you answer give the distance in miles. Solution. We are begin asked to determine the distance to the horizon, i.e. the distance between our position and the small dot on the horizon. The line of sight is tangent to the surface of the Earth, which justifies our assertion in the above figure that the angle between the line of sight and a radius is a right angle. But then we can apply the Pythagorean theorem in order to conclude that distance to horizon = 4000 mi + 49 ft) 2 (4000 mi) mi + 49 ft 1mi = 5280 ft ) 2 (4000 mi) 2 = ) mi 8.6 mi. (use a calculator) Therefore our line of sight is about eight and a half miles. 2
3 Problem 5. In Problem 4, you obtained an exact distance. Find a good estimate that you could use to quickly calculate this distance for relatively small heights. Solution. Let h represent our height above the ground, measured in feet. Then the distance to the horizon is given by the formula distance to horizon = 4000 mi + h ) mi (4000 mi) 2 = ) 5280 h + h mi 8000 = 5280 h + h mi. But if h is small, then h 2 is even smaller, and h 2 / is even smaller still, hence we can ignore this term in our estimate. Thus, we have 8000 distance to horizon 5280 h mi h mi 5 h mi. 4 For example, if we are 49 ft up (as in the previous problems), then the distance to the horizon is about = =8.75 mi. 4 4 This is pretty close to the exact answer, which was approximately 8.6 miles, which indicates that this is likely a good estimate. Problem 6. In Problem 4, you calculated the distance to the horizon. This is not the distance one would have to travel on the earth to get to the horizon. Can you estimate this distance? This is to say, at most how far off is the length of the line of sight from length of the shortest arc that starts at your position and goes to where you see the horizon? Hint: Youll need to draw a picture and think geometrically, remembering a critical fact about triangles. Solution. Let s zoom in on the interesting part of the picture from problem 3: B A C 3
4 In this picture, our position is the point B, the dot on the horizon is the point C, and the point on the ground directly below us is A. The distance along the surface of the Earth is shown as a heavy line joining A and C (this is the arc > AC). In a circle, the length of an arc between two points is greater than the length of the segment between those two points. Thus l( > AC) l(ac), where, via a slight abuse of notation, l(x) denotes the length of some object X. Next, recall that no one side of a triangle can be longer than the sum of the other two sides. Applied to ABC, this means that l(bc) l(ab)+l(ac)= l(ac) l(bc) l(ab). Combining the inequalities, we have l( > AC) l(bc) l(ab), which gives us a lower bound for the length of > AC. That is, we have found something that is smaller than this length, and which we can compute (why? do you remember what l(bc) andl(ab) represent?). Now we want to find an upper bound for l( > AC), with the goal of squeezing this quantity between two things that are very close together. We claim that l(bc) l( > AC). (Do you believe this claim? Can you come up with an argument for whyitmustbetrue?) Butthenl(BC) is exactly the upper bound we require. Combining all of our inequalities, we have l(bc) l( > AC) l(bc) l(ab). But recall that if our height above the ground is h feet, then ell(bc) our distance from the horizon is approximately 5 4 h miles. On the other hand, l(ab) = our height = h ft = h 5280 mi, which is a very small number compared to our distance to the horizon. That is, l(bc) l(ab) (this notation means that l(bc) ismuch larger than l(ab) ). This implies that from which we conclude that l(bc) l(ab) l(bc), l(bc) l( > AC) l(bc) l(ab) l(bc)= l( > AC) l(bc). 4
5 Remember that l(ac) represents how far we would have to walk along the ground to reach a point on the horizon, and that l(bc) represents our straight-line distance to the horizon. Since these two distances are approximately equal to each other, we conclude that if we are at some point above the ground and can see a point on the horizon, the distance we would have to walk on the ground to get to that point is about the same as the straight-line distance along our line of sight. Note, however, that this argument was made using an estimate that relied on h being relatively small it may not hold up for large values of h. 5
DIFFERENTIATION RULES
 3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES If we are pumping air into a balloon, both the volume and the radius of the balloon are increasing and their rates of increase are related to each other. However,
3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES If we are pumping air into a balloon, both the volume and the radius of the balloon are increasing and their rates of increase are related to each other. However,
Distance in the Plane
 Distance in the Plane The absolute value function is defined as { x if x 0; and x = x if x < 0. If the number a is positive or zero, then a = a. If a is negative, then a is the number you d get by erasing
Distance in the Plane The absolute value function is defined as { x if x 0; and x = x if x < 0. If the number a is positive or zero, then a = a. If a is negative, then a is the number you d get by erasing
1 y = Recitation Worksheet 1A. 1. Simplify the following: b. ( ) a. ( x ) Solve for y : 3. Plot these points in the xy plane:
 Math 13 Recitation Worksheet 1A 1 Simplify the following: a ( ) 7 b ( ) 3 4 9 3 5 3 c 15 3 d 3 15 Solve for y : 8 y y 5= 6 3 3 Plot these points in the y plane: A ( 0,0 ) B ( 5,0 ) C ( 0, 4) D ( 3,5) 4
Math 13 Recitation Worksheet 1A 1 Simplify the following: a ( ) 7 b ( ) 3 4 9 3 5 3 c 15 3 d 3 15 Solve for y : 8 y y 5= 6 3 3 Plot these points in the y plane: A ( 0,0 ) B ( 5,0 ) C ( 0, 4) D ( 3,5) 4
Around the corner. Mathematics B-day 2015, Friday November 13, 9:00h-16:00h
 Around the corner Mathematics B-day 2015, Friday November 13, 9:00h-16:00h Exploration 1 (Piano) You have to move a heavy piano through a 1 meter wide corridor with a right-angled corner in it. The figure
Around the corner Mathematics B-day 2015, Friday November 13, 9:00h-16:00h Exploration 1 (Piano) You have to move a heavy piano through a 1 meter wide corridor with a right-angled corner in it. The figure
Answer Explanations for: ACT June 2012, Form 70C
 Answer Explanations for: ACT June 2012, Form 70C Mathematics 1) C) A mean is a regular average and can be found using the following formula: (average of set) = (sum of items in set)/(number of items in
Answer Explanations for: ACT June 2012, Form 70C Mathematics 1) C) A mean is a regular average and can be found using the following formula: (average of set) = (sum of items in set)/(number of items in
Midterm 1 Review. Distance = (x 1 x 0 ) 2 + (y 1 y 0 ) 2.
 Midterm 1 Review Comments about the midterm The midterm will consist of five questions and will test on material from the first seven lectures the material given below. No calculus either single variable
Midterm 1 Review Comments about the midterm The midterm will consist of five questions and will test on material from the first seven lectures the material given below. No calculus either single variable
10.1 Tangents to Circles. Geometry Mrs. Spitz Spring 2005
 10.1 Tangents to Circles Geometry Mrs. Spitz Spring 2005 Objectives/Assignment Identify segments and lines related to circles. Use properties of a tangent to a circle. Assignment: Chapter 10 Definitions
10.1 Tangents to Circles Geometry Mrs. Spitz Spring 2005 Objectives/Assignment Identify segments and lines related to circles. Use properties of a tangent to a circle. Assignment: Chapter 10 Definitions
AREA. The Square Inch The Square Foot The Square Yard. 1 foot. 1 foot. The Square Mile The Square Meter The Square Centimeter. 1 meter.
 Tallahassee Community College 48 AREA The area of a figure measures the surface of the figure. The unit of measure for area cannot be a linear unit. To measure area we use square units such as: The Square
Tallahassee Community College 48 AREA The area of a figure measures the surface of the figure. The unit of measure for area cannot be a linear unit. To measure area we use square units such as: The Square
9.7 Extension: Writing and Graphing the Equations
 www.ck12.org Chapter 9. Circles 9.7 Extension: Writing and Graphing the Equations of Circles Learning Objectives Graph a circle. Find the equation of a circle in the coordinate plane. Find the radius and
www.ck12.org Chapter 9. Circles 9.7 Extension: Writing and Graphing the Equations of Circles Learning Objectives Graph a circle. Find the equation of a circle in the coordinate plane. Find the radius and
Trigonometric ratios:
 0 Trigonometric ratios: The six trigonometric ratios of A are: Sine Cosine Tangent sin A = opposite leg hypotenuse adjacent leg cos A = hypotenuse tan A = opposite adjacent leg leg and their inverses:
0 Trigonometric ratios: The six trigonometric ratios of A are: Sine Cosine Tangent sin A = opposite leg hypotenuse adjacent leg cos A = hypotenuse tan A = opposite adjacent leg leg and their inverses:
Unit Circle: The unit circle has radius 1 unit and is centred at the origin on the Cartesian plane. POA
 The Unit Circle Unit Circle: The unit circle has radius 1 unit and is centred at the origin on the Cartesian plane THE EQUATION OF THE UNIT CIRCLE Consider any point P on the unit circle with coordinates
The Unit Circle Unit Circle: The unit circle has radius 1 unit and is centred at the origin on the Cartesian plane THE EQUATION OF THE UNIT CIRCLE Consider any point P on the unit circle with coordinates
Circle geometry investigation: Student worksheet
 Circle geometry investigation: Student worksheet http://topdrawer.aamt.edu.au/geometric-reasoning/good-teaching/exploringcircles/explore-predict-confirm/circle-geometry-investigations About these activities
Circle geometry investigation: Student worksheet http://topdrawer.aamt.edu.au/geometric-reasoning/good-teaching/exploringcircles/explore-predict-confirm/circle-geometry-investigations About these activities
Chapter 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions
 SECTION.1 Linear and Quadratic Functions Chapter Polynomial and Rational Functions Section.1: Linear and Quadratic Functions Linear Functions Quadratic Functions Linear Functions Definition of a Linear
SECTION.1 Linear and Quadratic Functions Chapter Polynomial and Rational Functions Section.1: Linear and Quadratic Functions Linear Functions Quadratic Functions Linear Functions Definition of a Linear
Table of contents. Jakayla Robbins & Beth Kelly (UK) Precalculus Notes Fall / 53
 Table of contents The Cartesian Coordinate System - Pictures of Equations Your Personal Review Graphs of Equations with Two Variables Distance Equations of Circles Midpoints Quantifying the Steepness of
Table of contents The Cartesian Coordinate System - Pictures of Equations Your Personal Review Graphs of Equations with Two Variables Distance Equations of Circles Midpoints Quantifying the Steepness of
The No Calculators Pages
 Trigonometry Summer 2005 Name: The No Calculators Pages Instructions: See front page for general instructions. Finish this page before going to the rest. You may not return to this page once you turn on
Trigonometry Summer 2005 Name: The No Calculators Pages Instructions: See front page for general instructions. Finish this page before going to the rest. You may not return to this page once you turn on
Introduction to Mechanics Unit Conversions Order of Magnitude
 Introduction to Mechanics Unit Conversions Order of Magnitude Lana Sheridan De Anza College Sept 28, 2017 Last time symbols for scaling units scientific notation precision and accuracy dimensional analysis
Introduction to Mechanics Unit Conversions Order of Magnitude Lana Sheridan De Anza College Sept 28, 2017 Last time symbols for scaling units scientific notation precision and accuracy dimensional analysis
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space
 Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space
 Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
Name Date Partners. Lab 2 GAUSS LAW
 L02-1 Name Date Partners Lab 2 GAUSS LAW On all questions, work together as a group. 1. The statement of Gauss Law: (a) in words: The electric flux through a closed surface is equal to the total charge
L02-1 Name Date Partners Lab 2 GAUSS LAW On all questions, work together as a group. 1. The statement of Gauss Law: (a) in words: The electric flux through a closed surface is equal to the total charge
Worksheet #1. A little review.
 Worksheet #1. A little review. I. Set up BUT DO NOT EVALUATE definite integrals for each of the following. 1. The area between the curves = 1 and = 3. Solution. The first thing we should ask ourselves
Worksheet #1. A little review. I. Set up BUT DO NOT EVALUATE definite integrals for each of the following. 1. The area between the curves = 1 and = 3. Solution. The first thing we should ask ourselves
Distances in R 3. Last time we figured out the (parametric) equation of a line and the (scalar) equation of a plane:
 Distances in R 3 Last time we figured out the (parametric) equation of a line and the (scalar) equation of a plane: Definition: The equation of a line through point P(x 0, y 0, z 0 ) with directional vector
Distances in R 3 Last time we figured out the (parametric) equation of a line and the (scalar) equation of a plane: Definition: The equation of a line through point P(x 0, y 0, z 0 ) with directional vector
Lesson 6 Plane Geometry Practice Test Answer Explanations
 Lesson 6 Plane Geometry Practice Test Answer Explanations Question 1 One revolution is equal to one circumference: C = r = 6 = 1, which is approximately 37.68 inches. Multiply that by 100 to get 3,768
Lesson 6 Plane Geometry Practice Test Answer Explanations Question 1 One revolution is equal to one circumference: C = r = 6 = 1, which is approximately 37.68 inches. Multiply that by 100 to get 3,768
Name Date Partners. Lab 4 - GAUSS' LAW. On all questions, work together as a group.
 65 Name Date Partners 1. The statement of Gauss' Law: Lab 4 - GAUSS' LAW On all questions, work together as a group. (a) in words: The electric flux through a closed surface is equal to the total charge
65 Name Date Partners 1. The statement of Gauss' Law: Lab 4 - GAUSS' LAW On all questions, work together as a group. (a) in words: The electric flux through a closed surface is equal to the total charge
AP Calculus. Applications of Derivatives. Table of Contents
 AP Calculus 2015 11 03 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Related Rates Linear Motion Linear Approximation & Differentials L'Hopital's Rule Horizontal Tangents 1 Related
AP Calculus 2015 11 03 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Related Rates Linear Motion Linear Approximation & Differentials L'Hopital's Rule Horizontal Tangents 1 Related
Spring 06/MAT 140/Worksheet 1 Name: Show all your work.
 Spring 06/MAT 140/Worksheet 1 Name: Show all your work. 1. (4pts) Write two examples of each kind of number: natural integer rational irrational 2. (12pts) Simplify: ( a) 3 4 2 + 4 2 ) = 3 b) 3 20 7 15
Spring 06/MAT 140/Worksheet 1 Name: Show all your work. 1. (4pts) Write two examples of each kind of number: natural integer rational irrational 2. (12pts) Simplify: ( a) 3 4 2 + 4 2 ) = 3 b) 3 20 7 15
Recognise the Equation of a Circle. Solve Problems about Circles Centred at O. Co-Ordinate Geometry of the Circle - Outcomes
 1 Co-Ordinate Geometry of the Circle - Outcomes Recognise the equation of a circle. Solve problems about circles centred at the origin. Solve problems about circles not centred at the origin. Determine
1 Co-Ordinate Geometry of the Circle - Outcomes Recognise the equation of a circle. Solve problems about circles centred at the origin. Solve problems about circles not centred at the origin. Determine
Assignment 1 and 2: Complete practice worksheet: Simplifying Radicals and check your answers
 Geometry 0-03 Summary Notes Right Triangles and Trigonometry These notes are intended to be a guide and a help as you work through Chapter 8. These are not the only thing you need to read, however. Rely
Geometry 0-03 Summary Notes Right Triangles and Trigonometry These notes are intended to be a guide and a help as you work through Chapter 8. These are not the only thing you need to read, however. Rely
4 The Cartesian Coordinate System- Pictures of Equations
 4 The Cartesian Coordinate System- Pictures of Equations Concepts: The Cartesian Coordinate System Graphs of Equations in Two Variables x-intercepts and y-intercepts Distance in Two Dimensions and the
4 The Cartesian Coordinate System- Pictures of Equations Concepts: The Cartesian Coordinate System Graphs of Equations in Two Variables x-intercepts and y-intercepts Distance in Two Dimensions and the
UNIT 3 CIRCLES AND VOLUME Lesson 1: Introducing Circles Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: performing operations with fractions understanding slope, both algebraically and graphically understanding the relationship of
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: performing operations with fractions understanding slope, both algebraically and graphically understanding the relationship of
NOTES ON VECTORS, PLANES, AND LINES
 NOTES ON VECTORS, PLANES, AND LINES DAVID BEN MCREYNOLDS 1. Vectors I assume that the reader is familiar with the basic notion of a vector. The important feature of the vector is that it has a magnitude
NOTES ON VECTORS, PLANES, AND LINES DAVID BEN MCREYNOLDS 1. Vectors I assume that the reader is familiar with the basic notion of a vector. The important feature of the vector is that it has a magnitude
CHAPTER ONE FUNCTIONS AND GRAPHS. In everyday life, many quantities depend on one or more changing variables eg:
 CHAPTER ONE FUNCTIONS AND GRAPHS 1.0 Introduction to Functions In everyday life, many quantities depend on one or more changing variables eg: (a) plant growth depends on sunlight and rainfall (b) speed
CHAPTER ONE FUNCTIONS AND GRAPHS 1.0 Introduction to Functions In everyday life, many quantities depend on one or more changing variables eg: (a) plant growth depends on sunlight and rainfall (b) speed
Sums of Squares (FNS 195-S) Fall 2014
 Sums of Squares (FNS 195-S) Fall 014 Record of What We Did Drew Armstrong Vectors When we tried to apply Cartesian coordinates in 3 dimensions we ran into some difficulty tryiing to describe lines and
Sums of Squares (FNS 195-S) Fall 014 Record of What We Did Drew Armstrong Vectors When we tried to apply Cartesian coordinates in 3 dimensions we ran into some difficulty tryiing to describe lines and
Error Correcting Codes Prof. Dr. P. Vijay Kumar Department of Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
 (Refer Slide Time: 00:15) Error Correcting Codes Prof. Dr. P. Vijay Kumar Department of Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture No. # 03 Mathematical Preliminaries:
(Refer Slide Time: 00:15) Error Correcting Codes Prof. Dr. P. Vijay Kumar Department of Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture No. # 03 Mathematical Preliminaries:
Franklin Math Bowl 2007 Group Problem Solving Test 6 th Grade
 Group Problem Solving Test 6 th Grade 1. Consecutive integers are integers that increase by one. For eample, 6, 7, and 8 are consecutive integers. If the sum of 9 consecutive integers is 9, what is the
Group Problem Solving Test 6 th Grade 1. Consecutive integers are integers that increase by one. For eample, 6, 7, and 8 are consecutive integers. If the sum of 9 consecutive integers is 9, what is the
Jakarta International School 8 th Grade AG1
 Jakarta International School 8 th Grade AG1 Practice Test - Black Points, Lines, and Planes Name: Date: Score: 40 Goal 5: Solve problems using visualization and geometric modeling Section 1: Points, Lines,
Jakarta International School 8 th Grade AG1 Practice Test - Black Points, Lines, and Planes Name: Date: Score: 40 Goal 5: Solve problems using visualization and geometric modeling Section 1: Points, Lines,
Projects in Geometry for High School Students
 Projects in Geometry for High School Students Goal: Our goal in more detail will be expressed on the next page. Our journey will force us to understand plane and three-dimensional geometry. We will take
Projects in Geometry for High School Students Goal: Our goal in more detail will be expressed on the next page. Our journey will force us to understand plane and three-dimensional geometry. We will take
Assuming the Earth is a sphere with radius miles, answer the following questions. Round all answers to the nearest whole number.
 G-MG Satellite Alignments to Content Standards: G-MG.A.3 Task A satellite orbiting the earth uses radar to communicate with two control stations on the earth's surface. The satellite is in a geostationary
G-MG Satellite Alignments to Content Standards: G-MG.A.3 Task A satellite orbiting the earth uses radar to communicate with two control stations on the earth's surface. The satellite is in a geostationary
Gauss Law 1. Name Date Partners GAUSS' LAW. Work together as a group on all questions.
 Gauss Law 1 Name Date Partners 1. The statement of Gauss' Law: (a) in words: GAUSS' LAW Work together as a group on all questions. The electric flux through a closed surface is equal to the total charge
Gauss Law 1 Name Date Partners 1. The statement of Gauss' Law: (a) in words: GAUSS' LAW Work together as a group on all questions. The electric flux through a closed surface is equal to the total charge
Chapter 10. Right Triangles
 Chapter 10 Right Triangles If we looked at enough right triangles and experimented a little, we might eventually begin to notice some relationships developing. For instance, if I were to construct squares
Chapter 10 Right Triangles If we looked at enough right triangles and experimented a little, we might eventually begin to notice some relationships developing. For instance, if I were to construct squares
Section 14.1 Vector Functions and Space Curves
 Section 14.1 Vector Functions and Space Curves Functions whose range does not consists of numbers A bulk of elementary mathematics involves the study of functions - rules that assign to a given input a
Section 14.1 Vector Functions and Space Curves Functions whose range does not consists of numbers A bulk of elementary mathematics involves the study of functions - rules that assign to a given input a
A LEVER PLAYING FIELD 2: NEVER SAY LEVER
 A LEVER PLAYING FIELD 2: NEVER SAY LEVER MATH CIRCLE (BEGINNERS) 05/27/2012 The Law of the Lever, first proved by the Greek mathematician Archimedes, describes the situation in which a scale/balance/lever
A LEVER PLAYING FIELD 2: NEVER SAY LEVER MATH CIRCLE (BEGINNERS) 05/27/2012 The Law of the Lever, first proved by the Greek mathematician Archimedes, describes the situation in which a scale/balance/lever
Math 144 Activity #7 Trigonometric Identities
 144 p 1 Math 144 Activity #7 Trigonometric Identities What is a trigonometric identity? Trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions that are true for every single value
144 p 1 Math 144 Activity #7 Trigonometric Identities What is a trigonometric identity? Trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions that are true for every single value
In other words, we are interested in what is happening to the y values as we get really large x values and as we get really small x values.
 Polynomial functions: End behavior Solutions NAME: In this lab, we are looking at the end behavior of polynomial graphs, i.e. what is happening to the y values at the (left and right) ends of the graph.
Polynomial functions: End behavior Solutions NAME: In this lab, we are looking at the end behavior of polynomial graphs, i.e. what is happening to the y values at the (left and right) ends of the graph.
Solving an equation involves undoing these things. We work backward through this verbal model.
 To solve an equation, undo what was done to the variable. Intermediate algebra Class notes Solving Radical Equations and Problem Solving (section 10.6) Main idea: To solve most linear equations (and some
To solve an equation, undo what was done to the variable. Intermediate algebra Class notes Solving Radical Equations and Problem Solving (section 10.6) Main idea: To solve most linear equations (and some
Integrated Math II. IM2.1.2 Interpret given situations as functions in graphs, formulas, and words.
 Standard 1: Algebra and Functions Students graph linear inequalities in two variables and quadratics. They model data with linear equations. IM2.1.1 Graph a linear inequality in two variables. IM2.1.2
Standard 1: Algebra and Functions Students graph linear inequalities in two variables and quadratics. They model data with linear equations. IM2.1.1 Graph a linear inequality in two variables. IM2.1.2
Volume: The Disk Method. Using the integral to find volume.
 Volume: The Disk Method Using the integral to find volume. If a region in a plane is revolved about a line, the resulting solid is a solid of revolution and the line is called the axis of revolution. y
Volume: The Disk Method Using the integral to find volume. If a region in a plane is revolved about a line, the resulting solid is a solid of revolution and the line is called the axis of revolution. y
Fall 09/MAT 140/Worksheet 1 Name: Show all your work. 1. (6pts) Simplify and write the answer so all exponents are positive:
 Fall 09/MAT 140/Worksheet 1 Name: Show all your work. 1. (6pts) Simplify and write the answer so all exponents are positive: a) (x 3 y 6 ) 3 x 4 y 5 = b) 4x 2 (3y) 2 (6x 3 y 4 ) 2 = 2. (2pts) Convert to
Fall 09/MAT 140/Worksheet 1 Name: Show all your work. 1. (6pts) Simplify and write the answer so all exponents are positive: a) (x 3 y 6 ) 3 x 4 y 5 = b) 4x 2 (3y) 2 (6x 3 y 4 ) 2 = 2. (2pts) Convert to
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Prep-Year Math Program Math (001) - Term 181 Recitation (1.1)
 Recitation (1.1) Question 1: Find a point on the y-axis that is equidistant from the points (5, 5) and (1, 1) Question 2: Find the distance between the points P(2 x, 7 x) and Q( 2 x, 4 x) where x 0. Question
Recitation (1.1) Question 1: Find a point on the y-axis that is equidistant from the points (5, 5) and (1, 1) Question 2: Find the distance between the points P(2 x, 7 x) and Q( 2 x, 4 x) where x 0. Question
MAC Calculus II Spring Homework #6 Some Solutions.
 MAC 2312-15931-Calculus II Spring 23 Homework #6 Some Solutions. 1. Find the centroid of the region bounded by the curves y = 2x 2 and y = 1 2x 2. Solution. It is obvious, by inspection, that the centroid
MAC 2312-15931-Calculus II Spring 23 Homework #6 Some Solutions. 1. Find the centroid of the region bounded by the curves y = 2x 2 and y = 1 2x 2. Solution. It is obvious, by inspection, that the centroid
Chapter 10 Worksheet 1 Name: Honors Accelerated Geometry Hour:
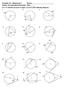 hapter 10 Worksheet 1 Name: Honors ccelerated Geometry Hour: For 1-15, find the measure of angle in each of the following diagrams. 1. 2.. 258 84 140 40 4. 5. 6. 2 y 80 y 72 7. 8. 9. 50 X 40 140 4 y 10.
hapter 10 Worksheet 1 Name: Honors ccelerated Geometry Hour: For 1-15, find the measure of angle in each of the following diagrams. 1. 2.. 258 84 140 40 4. 5. 6. 2 y 80 y 72 7. 8. 9. 50 X 40 140 4 y 10.
Math Precalculus I University of Hawai i at Mānoa Spring
 Math 135 - Precalculus I University of Hawai i at Mānoa Spring - 2014 Created for Math 135, Spring 2008 by Lukasz Grabarek and Michael Joyce Send comments and corrections to lukasz@math.hawaii.edu Contents
Math 135 - Precalculus I University of Hawai i at Mānoa Spring - 2014 Created for Math 135, Spring 2008 by Lukasz Grabarek and Michael Joyce Send comments and corrections to lukasz@math.hawaii.edu Contents
Chapter 7: Practice/review problems The collection of problems listed below contains questions taken from previous MA123 exams.
 Word problems Chapter 7: Practice/review problems The collection of problems listed below contains questions taken from previous MA3 exams. Max-min problems []. A field has the shape of a rectangle with
Word problems Chapter 7: Practice/review problems The collection of problems listed below contains questions taken from previous MA3 exams. Max-min problems []. A field has the shape of a rectangle with
13 Spherical geometry
 13 Spherical geometry Let ABC be a triangle in the Euclidean plane. From now on, we indicate the interior angles A = CAB, B = ABC, C = BCA at the vertices merely by A, B, C. The sides of length a = BC
13 Spherical geometry Let ABC be a triangle in the Euclidean plane. From now on, we indicate the interior angles A = CAB, B = ABC, C = BCA at the vertices merely by A, B, C. The sides of length a = BC
1998 Harvard/MIT Math Tournament GEOMETRY Answer Sheet
 1998 Harvard/MIT Math Tournament GEOMETRY Answer Sheet Name: School: Grade: 1 7 2 8 3 9 4 10a 5 10b 6 10c TOTAL: GEOMETRY Question One. [3 points] Quadrilateral ALEX, pictured below (but not necessarily
1998 Harvard/MIT Math Tournament GEOMETRY Answer Sheet Name: School: Grade: 1 7 2 8 3 9 4 10a 5 10b 6 10c TOTAL: GEOMETRY Question One. [3 points] Quadrilateral ALEX, pictured below (but not necessarily
SOME PROBLEMS YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO DO
 OME PROBLEM YOU HOULD BE ABLE TO DO I ve attempted to make a list of the main calculations you should be ready for on the exam, and included a handful of the more important formulas. There are no examples
OME PROBLEM YOU HOULD BE ABLE TO DO I ve attempted to make a list of the main calculations you should be ready for on the exam, and included a handful of the more important formulas. There are no examples
Math Precalculus I University of Hawai i at Mānoa Spring
 Math 135 - Precalculus I University of Hawai i at Mānoa Spring - 2013 Created for Math 135, Spring 2008 by Lukasz Grabarek and Michael Joyce Send comments and corrections to lukasz@math.hawaii.edu Contents
Math 135 - Precalculus I University of Hawai i at Mānoa Spring - 2013 Created for Math 135, Spring 2008 by Lukasz Grabarek and Michael Joyce Send comments and corrections to lukasz@math.hawaii.edu Contents
ARCS An ARC is any unbroken part of the circumference of a circle. It is named using its ENDPOINTS.
 ARCS An ARC is any unbroken part of the circumference of a circle. It is named using its ENDPOINTS. A B X Z Y A MINOR arc is LESS than 1/2 way around the circle. A MAJOR arc is MORE than 1/2 way around
ARCS An ARC is any unbroken part of the circumference of a circle. It is named using its ENDPOINTS. A B X Z Y A MINOR arc is LESS than 1/2 way around the circle. A MAJOR arc is MORE than 1/2 way around
5.5 Linearization & Differentials (NO CALCULATOR CALCULUS 30L OUTCOME)
 5.5 Linearization & Differentials (NO CALCULATOR CALCULUS 30L OUTCOME) Calculus I CAN USE LINEAR APPROXIMATION TO ESTIMATE THE VALUE OF A FUNCTION NEAR A POINT OF TANGENCY & FIND THE DIFFERENTIAL OF A
5.5 Linearization & Differentials (NO CALCULATOR CALCULUS 30L OUTCOME) Calculus I CAN USE LINEAR APPROXIMATION TO ESTIMATE THE VALUE OF A FUNCTION NEAR A POINT OF TANGENCY & FIND THE DIFFERENTIAL OF A
Circles Unit Test. Secondary Math II
 Circles Unit Test Secondary Math II 1. Which pair of circles described are congruent to each other? Circle M has a radius of 6 m; Circle N has a diameter of 10 m. Circle J has a circumference of in; Circle
Circles Unit Test Secondary Math II 1. Which pair of circles described are congruent to each other? Circle M has a radius of 6 m; Circle N has a diameter of 10 m. Circle J has a circumference of in; Circle
Lesson 20: The Earth in its Orbit
 291 Lesson 20: The Earth in its Orbit Recall that the Earth s orbit around the un is an ellipse which is almost a perfect circle. The average distance from the un to the Earth is 152,100,000 km (to the
291 Lesson 20: The Earth in its Orbit Recall that the Earth s orbit around the un is an ellipse which is almost a perfect circle. The average distance from the un to the Earth is 152,100,000 km (to the
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2016
 AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2016 You need to do this assignment on your own paper AND YOU MUST SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK TO RECEIVE CREDIT. You can put the answers on this assignment sheet or you can put
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2016 You need to do this assignment on your own paper AND YOU MUST SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK TO RECEIVE CREDIT. You can put the answers on this assignment sheet or you can put
Pre-Calculus Vectors
 Slide 1 / 159 Slide 2 / 159 Pre-Calculus Vectors 2015-03-24 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 159 Table of Contents Intro to Vectors Converting Rectangular and Polar Forms Operations with Vectors Scalar Multiples
Slide 1 / 159 Slide 2 / 159 Pre-Calculus Vectors 2015-03-24 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 159 Table of Contents Intro to Vectors Converting Rectangular and Polar Forms Operations with Vectors Scalar Multiples
PRACTICE TEST 1 Math Level IC
 SOLID VOLUME OTHER REFERENCE DATA Right circular cone L = cl V = volume L = lateral area r = radius c = circumference of base h = height l = slant height Sphere S = 4 r 2 V = volume r = radius S = surface
SOLID VOLUME OTHER REFERENCE DATA Right circular cone L = cl V = volume L = lateral area r = radius c = circumference of base h = height l = slant height Sphere S = 4 r 2 V = volume r = radius S = surface
Worksheet 1.8: Geometry of Vector Derivatives
 Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 1.8: Geometry of Vector Derivatives From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes): Calc I: Computing derivatives of single-variable functions y = f (t).
Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 1.8: Geometry of Vector Derivatives From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes): Calc I: Computing derivatives of single-variable functions y = f (t).
Triangles and Vectors
 Chapter 3 Triangles and Vectors As was stated at the start of Chapter 1, trigonometry had its origins in the study of triangles. In fact, the word trigonometry comes from the Greek words for triangle measurement.
Chapter 3 Triangles and Vectors As was stated at the start of Chapter 1, trigonometry had its origins in the study of triangles. In fact, the word trigonometry comes from the Greek words for triangle measurement.
Integration Made Easy
 Integration Made Easy Sean Carney Department of Mathematics University of Texas at Austin Sean Carney (University of Texas at Austin) Integration Made Easy October 25, 2015 1 / 47 Outline 1 - Length, Geometric
Integration Made Easy Sean Carney Department of Mathematics University of Texas at Austin Sean Carney (University of Texas at Austin) Integration Made Easy October 25, 2015 1 / 47 Outline 1 - Length, Geometric
P1 Chapter 6 :: Circles
 P1 Chapter 6 :: Circles jfrost@tiffin.kingston.sch.uk www.drfrostmaths.com @DrFrostMaths Last modified: 11 th August 2017 Use of DrFrostMaths for practice Register for free at: www.drfrostmaths.com/homework
P1 Chapter 6 :: Circles jfrost@tiffin.kingston.sch.uk www.drfrostmaths.com @DrFrostMaths Last modified: 11 th August 2017 Use of DrFrostMaths for practice Register for free at: www.drfrostmaths.com/homework
Give a geometric description of the set of points in space whose coordinates satisfy the given pair of equations.
 1. Give a geometric description of the set of points in space whose coordinates satisfy the given pair of equations. x + y = 5, z = 4 Choose the correct description. A. The circle with center (0,0, 4)
1. Give a geometric description of the set of points in space whose coordinates satisfy the given pair of equations. x + y = 5, z = 4 Choose the correct description. A. The circle with center (0,0, 4)
Lesson 2B: Thales Theorem
 Lesson 2B: Thales Theorem Learning Targets o I can identify radius, diameter, chords, central circles, inscribed circles and semicircles o I can explain that an ABC is a right triangle, then A, B, and
Lesson 2B: Thales Theorem Learning Targets o I can identify radius, diameter, chords, central circles, inscribed circles and semicircles o I can explain that an ABC is a right triangle, then A, B, and
Vector equations of lines in the plane and 3-space (uses vector addition & scalar multiplication).
 Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 1.6: Lines and Planes From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Plotting points, sketching vectors. Be able to find the component form a vector given
Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 1.6: Lines and Planes From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Plotting points, sketching vectors. Be able to find the component form a vector given
Mu Alpha Theta State 2007 Euclidean Circles
 Mu Alpha Theta State 2007 Euclidean Circles 1. Joe had a bet with Mr. Federer saying that if Federer can solve the following problem in one minute, Joe would be his slave for a whole month. The problem
Mu Alpha Theta State 2007 Euclidean Circles 1. Joe had a bet with Mr. Federer saying that if Federer can solve the following problem in one minute, Joe would be his slave for a whole month. The problem
AP Calculus AB Chapter 4 Packet Implicit Differentiation. 4.5: Implicit Functions
 4.5: Implicit Functions We can employ implicit differentiation when an equation that defines a function is so complicated that we cannot use an explicit rule to find the derivative. EXAMPLE 1: Find dy
4.5: Implicit Functions We can employ implicit differentiation when an equation that defines a function is so complicated that we cannot use an explicit rule to find the derivative. EXAMPLE 1: Find dy
Objectives. Cabri Jr. Tools
 ^Åíáîáíó=NQ Objectives To investigate relationships between angle measurements and sides of a triangle To investigate relationships among the three sides of a triangle Cabri Jr. Tools fåíêççìåíáçå qêá~åöäé=fåéèì~äáíó
^Åíáîáíó=NQ Objectives To investigate relationships between angle measurements and sides of a triangle To investigate relationships among the three sides of a triangle Cabri Jr. Tools fåíêççìåíáçå qêá~åöäé=fåéèì~äáíó
Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry
 Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry Edited by: K V Kumaran Email: kvkumaran@gmail.com Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry 1 Coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane Coordinate geometry of the circle
Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry Edited by: K V Kumaran Email: kvkumaran@gmail.com Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry 1 Coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane Coordinate geometry of the circle
LAMC Beginners Circle November 10, Oleg Gleizer. Warm-up
 LAMC Beginners Circle November 10, 2013 Oleg Gleizer oleg1140@gmail.com Warm-up Problem 1 Can a power of two (a number of the form 2 n ) have all the decimal digits 0, 1,..., 9 the same number of times?
LAMC Beginners Circle November 10, 2013 Oleg Gleizer oleg1140@gmail.com Warm-up Problem 1 Can a power of two (a number of the form 2 n ) have all the decimal digits 0, 1,..., 9 the same number of times?
For the intersections: cos x = 0 or sin x = 1 2
 Chapter 6 Set-up examples The purpose of this document is to demonstrate the work that will be required if you are asked to set-up integrals on an exam and/or quiz.. Areas () Set up, do not evaluate, any
Chapter 6 Set-up examples The purpose of this document is to demonstrate the work that will be required if you are asked to set-up integrals on an exam and/or quiz.. Areas () Set up, do not evaluate, any
4. Solve for x: 5. Use the FOIL pattern to multiply (4x 2)(x + 3). 6. Simplify using exponent rules: (6x 3 )(2x) 3
 SUMMER REVIEW FOR STUDENTS COMPLETING ALGEBRA I WEEK 1 1. Write the slope-intercept form of an equation of a. Write a definition of slope. 7 line with a slope of, and a y-intercept of 3. 11 3. You want
SUMMER REVIEW FOR STUDENTS COMPLETING ALGEBRA I WEEK 1 1. Write the slope-intercept form of an equation of a. Write a definition of slope. 7 line with a slope of, and a y-intercept of 3. 11 3. You want
ACCESS TO SCIENCE, ENGINEERING AND AGRICULTURE: MATHEMATICS 1 MATH00030 SEMESTER / Lines and Their Equations
 ACCESS TO SCIENCE, ENGINEERING AND AGRICULTURE: MATHEMATICS 1 MATH00030 SEMESTER 1 017/018 DR. ANTHONY BROWN. Lines and Their Equations.1. Slope of a Line and its y-intercept. In Euclidean geometry (where
ACCESS TO SCIENCE, ENGINEERING AND AGRICULTURE: MATHEMATICS 1 MATH00030 SEMESTER 1 017/018 DR. ANTHONY BROWN. Lines and Their Equations.1. Slope of a Line and its y-intercept. In Euclidean geometry (where
Unit 1. GSE Analytic Geometry EOC Review Name: Units 1 3. Date: Pd:
 GSE Analytic Geometry EOC Review Name: Units 1 Date: Pd: Unit 1 1 1. Figure A B C D F is a dilation of figure ABCDF by a scale factor of. The dilation is centered at ( 4, 1). 2 Which statement is true?
GSE Analytic Geometry EOC Review Name: Units 1 Date: Pd: Unit 1 1 1. Figure A B C D F is a dilation of figure ABCDF by a scale factor of. The dilation is centered at ( 4, 1). 2 Which statement is true?
Geometry: Hutschenreuter Semester II. Select the best answer for each question. Show expected work. MAKE A SUPPORTING SKETCH!
 Geometry: Hutschenreuter Semester II Review B Name Period Date Select the best answer for each question. Show expected work. MAKE A SUPPORTING SKETCH! 1. A parallelogram has a diagonal of 41 cm and side
Geometry: Hutschenreuter Semester II Review B Name Period Date Select the best answer for each question. Show expected work. MAKE A SUPPORTING SKETCH! 1. A parallelogram has a diagonal of 41 cm and side
Solutions to Math 51 First Exam October 13, 2015
 Solutions to Math First Exam October 3, 2. (8 points) (a) Find an equation for the plane in R 3 that contains both the x-axis and the point (,, 2). The equation should be of the form ax + by + cz = d.
Solutions to Math First Exam October 3, 2. (8 points) (a) Find an equation for the plane in R 3 that contains both the x-axis and the point (,, 2). The equation should be of the form ax + by + cz = d.
Circles. Parts of a Circle: Vocabulary. Arc : Part of a circle defined by a chord or two radii. It is a part of the whole circumference.
 Page 1 Circles Parts of a Circle: Vocabulary Arc : Part of a circle defined by a chord or two radii. It is a part of the whole circumference. Area of a disc : The measure of the surface of a disc. Think
Page 1 Circles Parts of a Circle: Vocabulary Arc : Part of a circle defined by a chord or two radii. It is a part of the whole circumference. Area of a disc : The measure of the surface of a disc. Think
221 MATH REFRESHER session 3 SAT2015_P06.indd 221 4/23/14 11:39 AM
 Math Refresher Session 3 1 Area, Perimeter, and Volume Problems Area, Perimeter, and Volume 301. Formula Problems. Here, you are given certain data about one or more geometric figures, and you are asked
Math Refresher Session 3 1 Area, Perimeter, and Volume Problems Area, Perimeter, and Volume 301. Formula Problems. Here, you are given certain data about one or more geometric figures, and you are asked
with dt. with 2. If x = u, find an equation relating du dt
 MATH 2250 Royal Section 3.10: Related Rates EXPANDED VERSION In this section, we consider two (or more) dependent variables that depend on a third variable (the independent variable). Usually, the independent
MATH 2250 Royal Section 3.10: Related Rates EXPANDED VERSION In this section, we consider two (or more) dependent variables that depend on a third variable (the independent variable). Usually, the independent
FORCE TABLE INTRODUCTION
 FORCE TABLE INTRODUCTION All measurable quantities can be classified as either a scalar 1 or a vector 2. A scalar has only magnitude while a vector has both magnitude and direction. Examples of scalar
FORCE TABLE INTRODUCTION All measurable quantities can be classified as either a scalar 1 or a vector 2. A scalar has only magnitude while a vector has both magnitude and direction. Examples of scalar
Exercises for Unit V (Introduction to non Euclidean geometry)
 Exercises for Unit V (Introduction to non Euclidean geometry) V.1 : Facts from spherical geometry Ryan : pp. 84 123 [ Note : Hints for the first two exercises are given in math133f07update08.pdf. ] 1.
Exercises for Unit V (Introduction to non Euclidean geometry) V.1 : Facts from spherical geometry Ryan : pp. 84 123 [ Note : Hints for the first two exercises are given in math133f07update08.pdf. ] 1.
Mathematics Trigonometry: Unit Circle
 a place of mind F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagog Mathematics Trigonometr: Unit Circle Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported b UBC Teaching and
a place of mind F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagog Mathematics Trigonometr: Unit Circle Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported b UBC Teaching and
Edexcel New GCE A Level Maths workbook Circle.
 Edexcel New GCE A Level Maths workbook Circle. Edited by: K V Kumaran kumarmaths.weebly.com 1 Finding the Midpoint of a Line To work out the midpoint of line we need to find the halfway point Midpoint
Edexcel New GCE A Level Maths workbook Circle. Edited by: K V Kumaran kumarmaths.weebly.com 1 Finding the Midpoint of a Line To work out the midpoint of line we need to find the halfway point Midpoint
Section 6-5 : Stokes' Theorem
 ection 6-5 : tokes' Theorem In this section we are going to take a look at a theorem that is a higher dimensional version of Green s Theorem. In Green s Theorem we related a line integral to a double integral
ection 6-5 : tokes' Theorem In this section we are going to take a look at a theorem that is a higher dimensional version of Green s Theorem. In Green s Theorem we related a line integral to a double integral
WW Prob Lib1 Math course-section, semester year
 Young-Seon Lee WW Prob Lib Math course-section, semester year WeBWorK assignment due /4/03 at :00 PM..( pt) Give the rational number whose decimal form is: 0 7333333 Answer:.( pt) Solve the following inequality:
Young-Seon Lee WW Prob Lib Math course-section, semester year WeBWorK assignment due /4/03 at :00 PM..( pt) Give the rational number whose decimal form is: 0 7333333 Answer:.( pt) Solve the following inequality:
LAMC Intermediate I & II March 1, Oleg Gleizer. A natural unit of measuring angles, a radian
 LAMC Intermediate I & II March 1, 2015 Oleg Gleizer prof1140g@math.ucla.edu A natural unit of measuring angles, a radian Consider an angle and a circle such that the vertex of the angle is the center of
LAMC Intermediate I & II March 1, 2015 Oleg Gleizer prof1140g@math.ucla.edu A natural unit of measuring angles, a radian Consider an angle and a circle such that the vertex of the angle is the center of
2017 SUMMER REVIEW FOR STUDENTS ENTERING GEOMETRY
 2017 SUMMER REVIEW FOR STUDENTS ENTERING GEOMETRY The following are topics that you will use in Geometry and should be retained throughout the summer. Please use this practice to review the topics you
2017 SUMMER REVIEW FOR STUDENTS ENTERING GEOMETRY The following are topics that you will use in Geometry and should be retained throughout the summer. Please use this practice to review the topics you
16 circles. what goes around...
 16 circles. what goes around... 2 lesson 16 this is the first of two lessons dealing with circles. this lesson gives some basic definitions and some elementary theorems, the most important of which is
16 circles. what goes around... 2 lesson 16 this is the first of two lessons dealing with circles. this lesson gives some basic definitions and some elementary theorems, the most important of which is
Complex numbers, the exponential function, and factorization over C
 Complex numbers, the exponential function, and factorization over C 1 Complex Numbers Recall that for every non-zero real number x, its square x 2 = x x is always positive. Consequently, R does not contain
Complex numbers, the exponential function, and factorization over C 1 Complex Numbers Recall that for every non-zero real number x, its square x 2 = x x is always positive. Consequently, R does not contain
CHAPTER 6 VECTOR CALCULUS. We ve spent a lot of time so far just looking at all the different ways you can graph
 CHAPTER 6 VECTOR CALCULUS We ve spent a lot of time so far just looking at all the different ways you can graph things and describe things in three dimensions, and it certainly seems like there is a lot
CHAPTER 6 VECTOR CALCULUS We ve spent a lot of time so far just looking at all the different ways you can graph things and describe things in three dimensions, and it certainly seems like there is a lot
CHAPTER 1 NUMBER SYSTEMS. 1.1 Introduction
 N UMBER S YSTEMS NUMBER SYSTEMS CHAPTER. Introduction In your earlier classes, you have learnt about the number line and how to represent various types of numbers on it (see Fig..). Fig.. : The number
N UMBER S YSTEMS NUMBER SYSTEMS CHAPTER. Introduction In your earlier classes, you have learnt about the number line and how to represent various types of numbers on it (see Fig..). Fig.. : The number
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2017
 P Physics 1 Summer ssignment 2017 The attached pages contain a brief review, hints, and example problems. It is hoped that based on your previous math knowledge and some review, this assignment will be
P Physics 1 Summer ssignment 2017 The attached pages contain a brief review, hints, and example problems. It is hoped that based on your previous math knowledge and some review, this assignment will be
Number Sets 1,0,1,2,3,... } 3. Rational Numbers ( Q) 1. Natural Numbers ( N) A number is a rational number if. it can be written as where a and
 Number Sets 1. Natural Numbers ( N) N { 0,1,,,... } This set is often referred to as the counting numbers that include zero.. Integers ( Z) Z {...,,, 1,0,1,,,... }. Rational Numbers ( Q) A number is a
Number Sets 1. Natural Numbers ( N) N { 0,1,,,... } This set is often referred to as the counting numbers that include zero.. Integers ( Z) Z {...,,, 1,0,1,,,... }. Rational Numbers ( Q) A number is a
Essential Question How can you find a trigonometric function of an acute angle θ? opp. hyp. opp. adj. sec θ = hyp. adj.
 . Right Triangle Trigonometry Essential Question How can you find a trigonometric function of an acute angle? Consider one of the acute angles of a right triangle. Ratios of a right triangle s side lengths
. Right Triangle Trigonometry Essential Question How can you find a trigonometric function of an acute angle? Consider one of the acute angles of a right triangle. Ratios of a right triangle s side lengths
STEP Support Programme. Mechanics STEP Questions
 STEP Support Programme Mechanics STEP Questions This is a selection of mainly STEP I questions with a couple of STEP II questions at the end. STEP I and STEP II papers follow the same specification, the
STEP Support Programme Mechanics STEP Questions This is a selection of mainly STEP I questions with a couple of STEP II questions at the end. STEP I and STEP II papers follow the same specification, the
